Major Cyber Attacks in Review: September 2022
Threat actors did not sit idle throughout September. They messed with citizens of various governments, giant companies like Uber, and even the gaming industry. Considering SOCRadar analysts’ September findings, it seems that it has become necessary for all organizations, big or small, to deal with the issue of cyber security with a more proactive approach.
Here are the top cyber incidents of September 2022.
Akamai Stopped DDoS That Set a New Record

On September 12, Akamai stopped a distributed denial-of-service attack that set a new record.
According to Akamai, the threat actor responsible for the DDoS attack they stopped in July was still in operation and decided to abuse the same victim with increased network traffic. Compared to the previous attack, the number of source IPs rose from 512 to 1813, and the traffic peaked at 704.8 Mpps per minute.
The threat actor’s motivation is still unknown.
$162 Million Was Stolen from Wintermute

Hackers stole $162 million from the DeFi section of Wintermute’s platform. Crypto experts think the hacker exploited a bug in Profanity, an Ethereum vanity address generator, to create a compromised Wintermute wallet.
After the incidents, Profanity’s author archived the project to stop its abusive use.
Read more about it in our blog.
Uber Breach Affected Most of Its IT System: Vulnerability Reports are Stolen
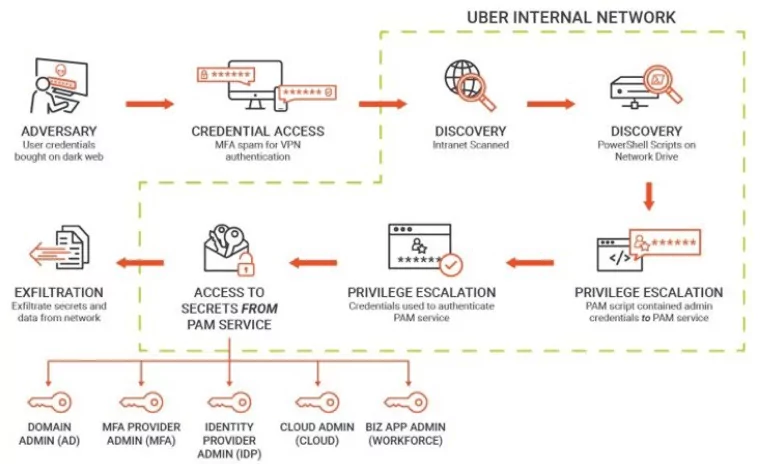
Uber confirmed that one of its high-security internal systems was the victim of a data breach by a hacker who claims to now have access to the company’s critical data. The hacker sent screenshots of the company’s email dashboard, Windows domain, Slack server, and IT systems. They also appeared to gain access to the Google-hosted cloud infrastructure and Uber’s Amazon Web Services interface, and they utilized both to send out breach notices.
GTA 6 Source Code Stolen

Rockstar Games’ Slack and Confluence servers were hacked, causing a network breach. GTA 5 and 6 source code and assets and GTA 6 testing videos were claimed to be stolen. “teapotuberhacker,” who was involved in Uber’s network breach, leaked the stolen data on GTAForums. Threat actor tried to extort Rockstar Games and allegedly put some game data on sale for more than $10,000.
Data Breach on Swachh City Platform Exposes 16 Million User Records
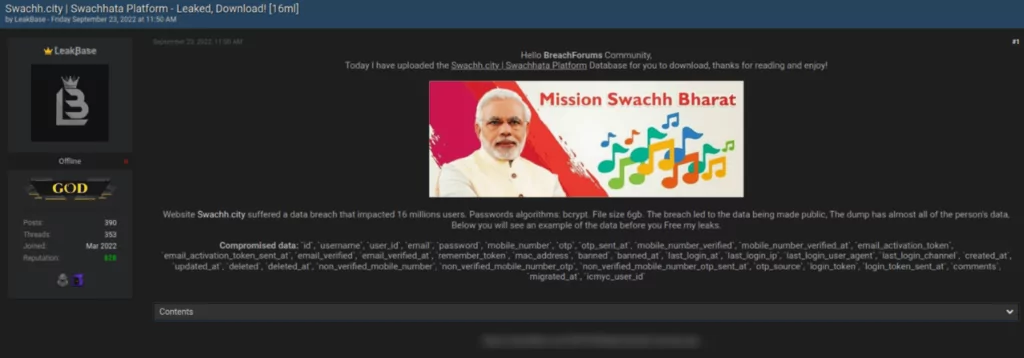
Threat actor LeakBase is said to have released a database of personal data that reportedly pertains to 16 million users of Swachh City, an Indian complaint redressal platform.
Usernames, email addresses, password hashes, mobile numbers, one-time passwords, last-login times, and IP addresses are some of the information that has been exposed.
According to Cyble, the database contains 15,835,111 distinct cell numbers and 101,718 unique email addresses, placing users at risk for identity theft, phishing, smishing, and social engineering.
Hard-coded AWS Credentials Discovered in Over 1,800 Apps

1,859 apps were found to have hard-coded Amazon Web Services (AWS) credentials. It is a serious security concern, according to researchers. Most apps were developed for iOS, while only 37 were for Android. The problem is typically caused by a component that is used by many developers, like a third-party library or SDK.
Although the issue of exposing credentials is not new, the research highlights a potential supply chain risk.
You can read possible cases concerning AWS here.
350,000 Projects Affected by Unfixed Python Flaw
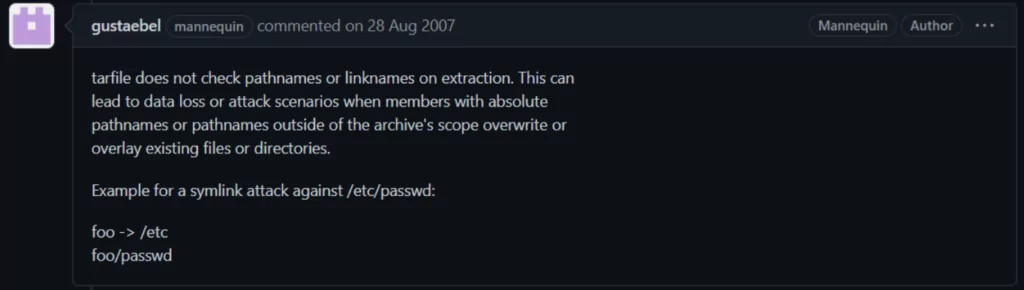
Python’s tarfile module has been carrying an unfixed flaw for 15 years. The flaw tracked as CVE-2007-4559 allowed reading and writing tar archives due to directory traversal. 350,000 open-source projects are using the module. The patching process for all projects is still ongoing.
1.7M Indian and Foreigners’ Covid Antigen Test Results Leaked
The Covid antigen test results of Indians and foreigners who went to or from India in the previous two years are currently available on an Elasticsearch server owned by an Indian healthcare software vendor.
According to Anurag’s investigation, the leaked records are the results of Covid antigen tests, and the breach has affected over 1.7 million people. These findings include both personal and traveler medical records.
SSU in Ukraine Uncovered a Cyber Gang Stolen 30M Accounts

The Security Service of Ukraine’s (SSU) cyber division has eliminated a group of hackers responsible for the data theft of nearly 30 million people. According to the SSU, the gang sold the stolen accounts on the dark web and made approximately UAH 14 million from the sale.
LockBit Ransomware Version 3.0 Has Been Made Public

According to rumors, the developers of the LockBit ransomware (version 3.0) leaked it online. The 3.0 builder (also known as LockBit Black), disclosed on Twitter, is thought to have been done by two people (or the same individual).
The security community is highly concerned about the current breach since more threat actors are anticipated to use the builder to create their own ransomware.
A Hacking Gang Released 10 Gigabytes of Military Emails and Information

Nearly 10 terabytes of emails and other documents from military and police organizations in Chile, Mexico, El Salvador, Colombia, and Peru were made public by a hacker group primarily focused on Central American targets.
The data dump is the most recent offering from the group, which has been working since March 2022 to compromise law enforcement, several regulatory bodies in Latin America, mining and oil companies, and other businesses.
Indian Citizens Lose $529M to Chinese-linked Cybercriminals

Chinese scammers allegedly stole $529 million from Indian citizens by exploiting instant lending apps, employment offers, and fake cryptocurrency trading schemes.
The scammers advertised their fraud by bulk TXT messages, which the authorities were able to trace to the Middle Kingdom. Some operators were reportedly based in Nepal and were guided by Chinese threat actors. Cryptocurrency apps and fake websites have been created to entice investors.