
Malvertising Campaign Targets Windows Administrators Using PuTTy and WinSCP

An AI illustration of the malvertising campaign using PuTTy and WinSCP
In the ever-evolving landscape of digital security, cyber threats are continually adapting and becoming more sophisticated. Among these threats, malvertising has emerged as a particularly devious form of attack. Malvertising involves embedding malicious software within online advertisements, targeting unsuspecting users as they browse the internet.
Windows administrators, who rely heavily on secure communication and file transfer protocols, are increasingly being targeted by malvertising attacks. Tools like PuTTY and WinSCP, which are essential for secure SSH connections and file transfers, have become prime targets. The popularity of these tools makes them attractive to cybercriminals seeking to exploit any vulnerabilities.
How Do Malvertising Attacks Work?
Malvertising attacks are a complex form of cybercrime that exploit online advertising networks to spread malware. Here’s an overview of how these attacks typically unfold:
- Infiltrating Ad Networks:Cybercriminals gain access to legitimate ad networks either by posing as genuine advertisers or by directly compromising the ad network’s infrastructure. This allows them to insert malicious advertisements into the network.
- Creating Deceptive Ads: Once inside the ad network, attackers design ads that look legitimate and enticing. These ads can be static banners, pop-ups, or even video ads, all crafted to lure users into clicking on them.
- Distributing Malware: The malicious ads contain hidden code that either redirects users to infected websites or directly downloads malware onto their devices. This malware can exploit vulnerabilities in web browsers, plugins, and operating systems to gain unauthorized access.
- Targeting Vulnerabilities: The malware delivered through malvertising often targets specific software vulnerabilities, especially in widely used applications like PuTTY and WinSCP. This increases the likelihood of successful infections while reducing the chances of detection.
Case Study: Recent Malvertising Campaign Distributing Malicious PuTTy and WinSCP Installers
A recent malvertising campaign targeting PuTTY and WinSCP users highlights the evolving threat landscape faced by Windows administrators. In this real-world attack, cybercriminals used deceptive tactics to lure victims into downloading trojanized installers from fake download sites.
For more details, see the Malvertising Campaign via PuTTy and WinSCP on SOCRadar Platform’s Campaigns page
In the campaign, the attackers employ fake websites mimicking legitimate software download pages, using typosquatting domains to make them appear genuine. Users searching for PuTTY or WinSCP download pages are directed to these malicious sites via online search result ads.
A cloned WinSCP website.
However, these fake sites include trojanized installers. Upon downloading and extracting the .ZIP files posing as legitimate downloads from these mimic sites, a user can become compromised. These trojanized installers contain malicious payloads that, once executed, deploy ransomware and extract sensitive data from the affected systems. This could result in significant data loss and operational disruptions.
The following is a diagram of the attack flow, showing how attackers compromise systems:
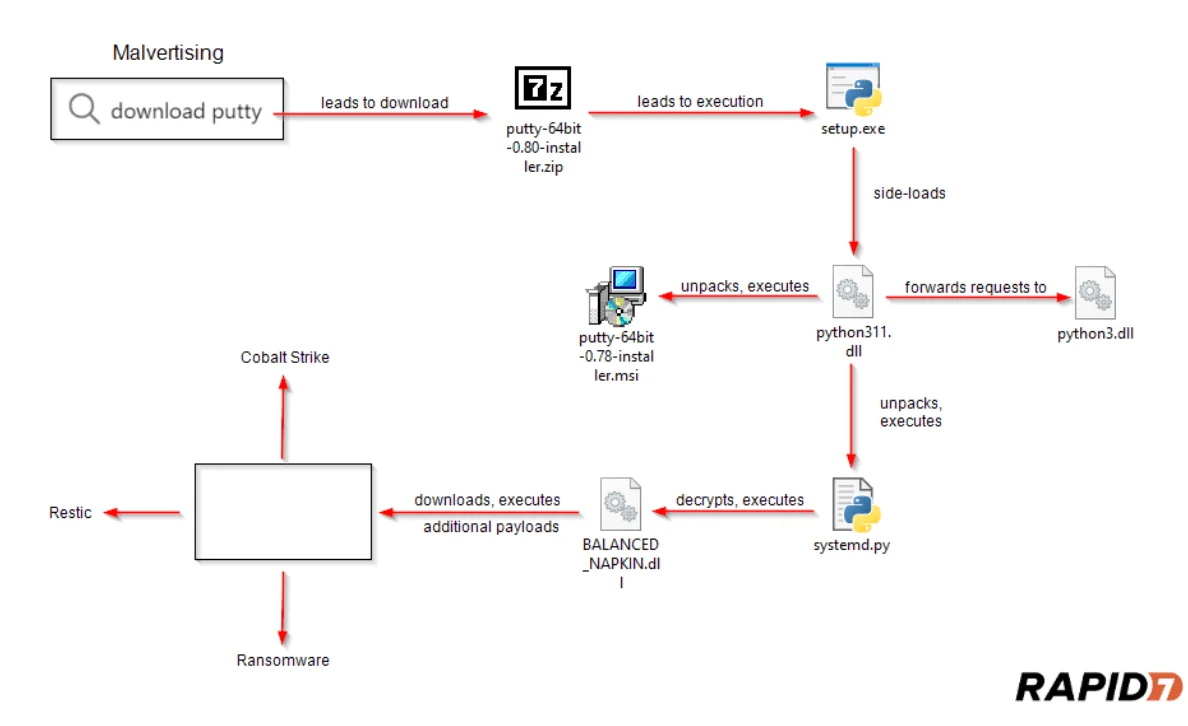
The attack flow (Rapid7)
This case study underscores the importance of increased awareness and robust security measures to combat sophisticated malvertising attacks targeting PuTTY and WinSCP users.
Risks for PuTTY and WinSCP Users
PuTTY and WinSCP are invaluable tools for Windows administrators, but they are not immune to malvertising attacks. Here are the key risks that threaten users of these tools:
- Specific Vulnerabilities: Due to their widespread use, PuTTY and WinSCP are attractive targets for cybercriminals. Attackers exploit vulnerabilities in these tools to distribute malware through malicious ads.
- Ransomware: Malicious ads can lead users to fake download sites that offer trojanized versions of PuTTY or WinSCP installers. These installers can deploy ransomware, encrypting files and demanding a ransom.
- Trojans and Spyware: Ads may contain hidden malicious code that downloads trojans or spyware onto the victim’s computer, stealing sensitive information like login credentials or financial data.
Protecting Against Malvertising Attacks
To safeguard PuTTY and WinSCP users from malvertising attacks, several key measures can be taken:
- Use Comprehensive Security Software: Ensure that robust antivirus and antimalware programs are installed on your system to detect and block malicious ads.
- Keep Software Updated: Regularly update PuTTY, WinSCP, and other software to protect against known vulnerabilities. Updates often include security patches that address potential weaknesses.
- Exercise Caution with Ads: Be vigilant when encountering online ads while using PuTTY or WinSCP. Avoid clicking on suspicious or unfamiliar advertisements and visit the official websites for any necessary downloads or updates.
- Enable Ad Blockers: Use ad-blocking extensions or plugins in your web browser to filter out potentially harmful advertisements.
- Practice Safe Browsing Habits: Adopt safe browsing habits by avoiding untrusted websites, especially those known for hosting malicious ads or distributing pirated software.
- Role of Ad Blockers: Ad blockers are crucial for protecting against malvertising attacks. By blocking ads from untrusted sources, ad blockers reduce the risk of encountering malicious advertisements. Implementing ad blockers is an essential part of a comprehensive security strategy.
Conclusion
PuTTY and WinSCP are essential tools for Windows administrators, providing secure communication and file transfer capabilities. However, it is crucial to recognize that these tools are not immune to malvertising attacks. To protect against these threats, comprehensive security measures, including the use of ad blockers, regular software updates, and cautious interaction with online advertisements, must be implemented.
By staying informed about the risks of malvertising and adopting proactive security practices, Windows administrators can continue to leverage the capabilities of PuTTY and WinSCP while minimizing their exposure to malicious threats.
For more detailed information on recent campaigns and advanced mitigation strategies, visit the Campaigns page on SOCRadar LABS.
SOCRadar LABS, Campaigns page
MITRE ATT&CK TTPs of the PuTTy and WinSCP Malvertising Campaign
| Tactic | Technique | Procedure |
|---|---|---|
| Resource Development | T1583.008: Acquire Infrastructure: Malvertising | The threat actor uses ads to promote malware delivery via popular search engines. |
| Initial Access | T1189: Drive-by Compromise | The user clicks on a malicious ad populated from a typical search engine query for a software utility and is ultimately redirected to a page hosting malware. |
| Execution | T1106: Native API | The malware dynamically resolves and executes functions from ntdll.dll at runtime. |
| Execution | T1204.002: User Execution: Malicious File | The user downloads and executes setup.exe (renamed pythonw.exe), which side-loads and executes the malicious DLL python311.dll. |
| Execution | T1059.006: Command and Scripting Interpreter: Python | The malware executes a python script to load and execute a Sliver beacon. |
| Persistence | T1543.003: Create or Modify System Process: Windows Service | The threat actor creates a service to execute a C2 beacon. The threat actor loads a vulnerable driver to facilitate disabling antivirus software and other defenses present. |
| Persistence | T1053.005: Scheduled Task/Job: Scheduled Task | The threat actor creates a scheduled task to execute a C2 beacon. |
| Defense Evasion | T1140: Deobfuscate/Decode Files or Information | The malware uses various string manipulation and obfuscation techniques. |
| Defense Evasion | T1222.001: File and Directory Permissions Modification: Windows File and Directory Permissions Modification | The malware calls chmod to change file permissions prior to execution. |
| Defense Evasion | T1574.001: Hijack Execution Flow: DLL Search Order Hijacking | The malware contained in python311.dll is loaded by a renamed copy of pythonw.exe from the same directory. |
| Defense Evasion | T1574.002: Hijack Execution Flow: DLL Side-Loading | The malware contained in python311.dll is loaded by a renamed copy of pythonw.exe and proxies requests to a renamed copy of the legitimate DLL. |
| Defense Evasion | T1027.002: Obfuscated Files or Information: Software Packing | The final payload executed by the malware is unpacked through several layers of compression, encryption, and file formats. |
| Defense Evasion | T1027.013: Obfuscated Files or Information: Encrypted/Encoded File | The malware also stores other file dependencies with several layers of obfuscation |
| Defense Evasion | T1055.001: Process Injection: Dynamic-link Library Injection | The malware loads a Sliver beacon DLL via python script. |
| Lateral Movement | T1570: Lateral Tool Transfer | The threat actor uses SMB via Cobalt Strike to pivot post compromise |
| Exfiltration | T1567.002: Exfiltration Over Web Service: Exfiltration to Cloud Storage | The threat actor attempts to exfiltrate data to a backup using Restic. |
| Impact | T1486: Data Encrypted for Impact | The threat actor attempts the deployment of ransomware after exfiltrating data. |
Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) Related to the PuTTy and WinSCP Malvertising Campaign
Network-Based Indicators:
| Domain/IPv4 Address | Notes |
|---|---|
| wnscp[.]net | Typo-squatted domain, found via DNSTwist |
| puttyy[.]org | Typo-squatted domain, found via DNSTwist |
| puutty[.]org | Typo-squatted domain, found via DNSTwist |
| putyy[.]org | Typo-squatted domain, found via DNSTwist |
| vvinscp[.]net | Typo-squatted domain |
| winnscp[.]net | Typo-squatted domain |
| puttty[.]org | Typo-squatted domain |
| areauni[.]com | Malicious zip archive host, likely compromised domain |
| mkt[.]geostrategy-ec[.]com | Malicious zip archive host, likely compromised domain |
| fkm-system[.]com | Malicious zip archive host, likely compromised domain |
| 185.82.219[.]92 | C2 address |
| 91.92.242[.]183 | C2 address |
| 91.92.244[.]41 | C2 address |
| 91.92.249[.]106 | C2 address |
| 91.92.249[.]155 | C2 address |
| 91.92.252[.]238 | C2 address |
| 91.92.255[.]71 | C2 address |
| 91.92.255[.]77 | C2 address |
| 94.156.65[.]115 | C2 address |
| 94.156.65[.]98 | C2 address |
| 94.156.67[.]185 | C2 address |
| 94.156.67[.]188 | C2 address |
| 94.156.67[.]83 | C2 address |
| 94.158.244[.]32 | C2 address |
Host-Based Indicators:
| File | SHA256 | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| DellAPC.exe | 8b1946e3e88cff3bee6b8a2ef761513fb82a1c81f97a27f959c08d08e4c75324 | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| DellCTSW2.exe | N/A | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| DellCTSWin.exe | 2ee435033d0e2027598fc6b35d8d6cbca32380eb4c059ba0806b9cfb1b4275cc | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| DellPPem.exe | 4b618892c9a397b2b831917264aaf0511ac1b7e4d5e56f177217902daab74a36 | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| DellPRT.exe | 725aa783a0cd17df603fbe6b11b5a41c9fbfd6fc9e4f2e468c328999e5716faa | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| KeePassDR.exe | c9042a7ed34847fee538c213300374c70c76436ee506273b35282c86a11d9e6a | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| NVDisplay.Contain64.exe | 35161a508dfaf8e04bb6de6bc793a3840a05f2c04bbbbf8c2237abebe8e670aa | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| NVDisplay.Container64.exe | 8bc39017b1ea59386f74d7c7822063b3b00315dd317f55ddc6634bde897c45c1 | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| NVDisplay.exe | bbdf350c6ae2438bf14fc6dc82bb54030abf9da0c948c485e297330e08850575 | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| OktaServiceAgent.exe | 28e5ee69447cea77eee2942c04009735a199771ba64f6bce4965d674515d7322 | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| OktaServiceAgent.exe | f36e9dec2e7c574c07f3c01bbbb2e8a6294e85863f4d6552cccb71d9b73688ad | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| PDMVault.exe | 242b2c948181f8c2543163c961775393220d128ecb38a82fa62b80893f209cab | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| PDMVault.exe | 9be715df88024582eeabdb0a621477e04e2cf5f57895fa6420334609138463b9 | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| PDMVaultConf.exe | 8b0d04f65a6a5a3c8fb111e72a1a176b7415903664bc37f0a9015b85d3fc0aa7 | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| PDMVaultL.exe | 169ef0e828c3cd35128b0e8d8ca91fbf54120d9a2facf9eb8b57ea88542bc427 | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| PDMVaultLP.exe | N/A | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| PDMVaultSec.exe | 61214a7b14d6ffb4d27e53e507374aabcbea21b4dc574936b39bec951220e7ea | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| PDMVaultSecs.exe | 51af3d778b5a408b725fcf11d762b0f141a9c1404a8097675668f64e10d44d64 | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| PDMVaultTest.exe | 96ea33a5f305015fdd84bea48a9e266c0516379ae33321a1db16bc6fabad5679 | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| ServerController.exe | 02330e168d4478a4cd2006dd3a856979f125fd30f5ed24ee70a41e03e4c0d2f8 | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| SgrmBroker.exe | 8834ec9b0778a08750156632b8e74b9b31134675a95332d1d38f982510c79acb | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| VMImportHost.exe | c8a982e2be4324800f69141b5be814701bcc4167b39b3e47ed8908623a13eb10 | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| VMImportHost2.exe | 47ec3a1ece8b30e66afd6bb510835bb072bbccc8ea19a557c59ccdf46fe83032 | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| VMImportHost3.exe | 9bd3c7eff51c5746c21cef536971cc65d25e3646533631344728e8061a0624cb | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| VMSAdmin.exe | f89720497b810afc9666f212e8f03787d72598573b41bc943cd59ce1c620a861 | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| VMSAdminUtil.exe | ca05485a1ec408e2f429e2e377cc5af2bee37587a2eb91dc86e8e48211ffc49e | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| VMSAdminUtilityUp.exe | 972ca168f7a8cddd77157e7163b196d1267fe2b338b93dabacc4a681e3d46b57 | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| VMSBackupConfig.exe | 1576f71ac41c4fc93c8717338fbc2ba48374894345c33bdf831b16d0d06df23d | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| VMSBackupUpdate.exe | a5dfc9c326b1303cc1323c286ecd9751684fb1cd509527e2f959fb79e5a792c2 | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| dp_agent.exe | 13B2E749EB1E45CE999427A12BB78CBEBC87C415685315C77CDFB7F64CB9AAB0 | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| local.exe | bd4abc70de30e036a188fc9df7b499a19a0b49d5baefc99844dfdec6e70faf75 | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| lr_agent.exe | d95f6dec32b4ebed2c45ecc05215e76bf2f520f86ad6b5c5da1326083ba72e89 | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| ntfrss.exe | f36089675a652d7447f45c604e062c2a58771ec54778f6e06b2332d1f60b1999 | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| op_agent.exe | 17e0005fd046e524c1681304493f0c51695ba3f24362a61b58bd2968aa1bd01a | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| pp.txt | N/A | Notable naming scheme |
| pr_agent.exe | d27f9c0d761e5e1de1a741569e743d6747734d3cdaf964a9e8ca01ce662fac90 | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| python311.dll | CD7D59105B0D0B947923DD9ED371B9CFC2C2AA98F29B2AFBDCD3392AD26BDE94 | Malicious DLL sideloaded by setup.exe. Compiled 2024-03-05. Original name: python311_WinSCP.dll. |
| python311.dll | 02D8E4E5F74D38C8E1C9AD893E0CEC1CC19AA08A43ECC87AC043FA825382A583 | Malicious DLL sideloaded by setup.exe. Compiled 2024-04-03. Original name: python311_WinSCP.dll. |
| python311.dll | 500574522DBCDE5E6C89803C3DCA7F857F73E0868FD7F8D2F437F3CC31CE9E8D | Malicious DLL sideloaded by setup.exe. Compiled 2024-04-10. Original name: python311_Putty.dll. |
| -redacted-.exe | a1cb8761dd8e624d6872960e1443c85664e9fbf24d3e208c3584df49bbdb2d9c | Ransomware, named after the impacted domain. |
| readme.txt | N/A | Ransom note |
| resticORIG.exe | 33f6acd3dfeda1aadf0227271937c1e5479c2dba24b4dca5f3deccc83e6a2f04 | Exfil tool dropped by the threat actor |
| rr__agent.exe | d94ed93042d240e4eaac8b1b397abe60c6c50a5ff11e62180a85be8aa0b0cc4a | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| truesight.sys | bfc2ef3b404294fe2fa05a8b71c7f786b58519175b7202a69fe30f45e607ff1c | AV/EDR killer, used to facilitate the execution of ransomware. |
| veeam.backups.shell.exe | 7d53122d6b7cff81e1c5fcdb3523ccef1dbd46c93020a0de65bc475760faff7d | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| vmtools.exe | ED501E49B9418FCFAF56A2EFF7ADCF85A648BDEE2C42BB09DB8C11F024667BFA | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| vmtoolsda.exe | 12AFBEC79948007E87FDF9E311736160797F245857A45C040966E8E029CA97B3 | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| vmtoolsdr.exe | 989A8E6A01AA20E298B1FFAE83B50CEF3E08F6B64A8F022288DC8D5729301674 | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| vmtoolsds.exe | 0AA248300A9F6C498F5305AE3CB871E9EC78AE62E6D51C05C4D6DD069622F442 | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| vmtoolsdt.exe | DF0213E4B784A7E7E3B4C799862DB6EA60E34D8E22EB5E72A980A8C2E9B36177 | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| DellPP.exe | 51D898DE0C300CAE7A57C806D652809D19BEB3E52422A7D8E4CB1539A1E2485D | Dropped by the threat actor post compromise |
| DellPP2.exe | 8827B6FA639AFE037BB2C3F092CCB12D49B642CE5CEC496706651EBCB23D5B9E | Dropped by threat actor post compromise |
| data.aes | F18367D88F19C555F19E3A40B17DE66D4A6F761684A5EF4CDD3D9931A6655490 | Encrypted Sliver beacon |
| data.aes | C33975AA4AB4CDF015422608962BD04C893F27BD270CF3F30958981541CDFEAD | |
| Encrypted Sliver beacon | ||
| data.aes | 868CD4974E1F3AC7EF843DA8040536CB04F96A2C5779265A69DF58E87DC03029 | Encrypted Sliver beacon |
| systemd.py | 69583C4A9BF96E0EDAFCF1AC4362C51D6FF71BBA0F568625AE65A1E378F15C65 | Sliver beacon loader |
| systemd.py | 03D18441C04F12270AAB3E55F68284DCD84721D1E56B32F8D8B732A52A654D2D | Sliver beacon loader |
| systemd.py | CF82366E319B6736A7EE94CCA827790E9FDEDFACE98601F0499ABEE61F613D5D | Sliver beacon loader |

































