
May 2025 Patch Tuesday: 78 Flaws, 5 Exploited, & Critical SAP Fixes
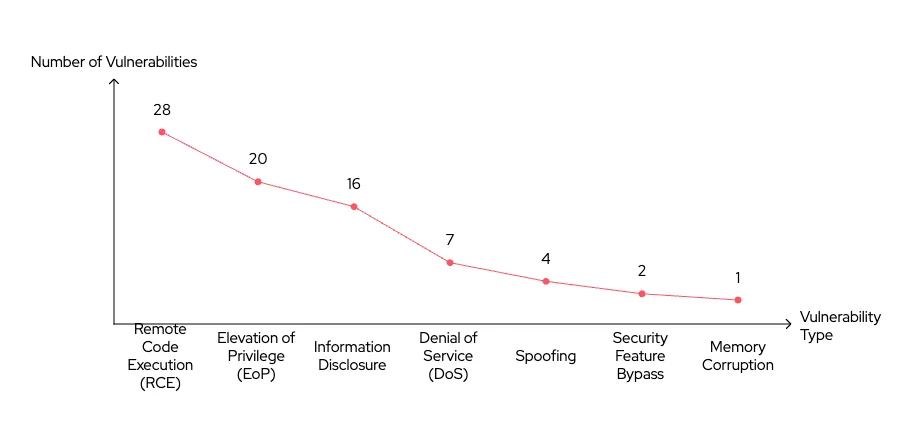
Microsoft has released its May 2025 Patch Tuesday updates, addressing a total of 78 vulnerabilities across its software. Among these are:
- 28 Remote Code Execution (RCE) Vulnerabilities
- 20 Elevation of Privilege (EoP) Vulnerabilities
- 16 Information Disclosure Vulnerability
- 7 Denial of Service (DoS) Vulnerability
- 4 Spoofing Vulnerabilities
- 2 Security Feature Bypass Vulnerabilities
- 1 Memory Corruption Vulnerability
Notably, five zero-days have been confirmed as exploited in the wild, prompting urgent attention. Microsoft also flagged 11 vulnerabilities as critical, with some affecting cloud services like Azure and business platforms such as Office.
May 2025 Patch Tuesday vulnerabilities overview
In parallel, SAP administrators are advised to review newly released updates that patch an exploited flaw in SAP NetWeaver. The discovery confirms attackers have been chaining multiple vulnerabilities in real-world intrusions, including an unauthenticated file upload zero-day.
The following sections provide an overview of the latest Patch Tuesday updates by Microsoft, outlining the most severe flaws, and vulnerabilities more likely to be weaponized – followed by a roundup of the SAP Security Patch Day highlights.
Which Zero-Day Vulnerabilities Were Addressed in May 2025 Patch Tuesday?
Microsoft’s May 2025 Patch Tuesday includes five zero-day vulnerabilities confirmed as actively exploited and two others that were publicly disclosed before patches were made available. Some exploited flaws involve privilege escalation via Windows kernel components, while others allow Remote Code Execution (RCE) and account spoofing.
Organizations should prioritize these patches immediately, as CISA has already added all five exploited vulnerabilities to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog with a patch deadline of June 3, 2025.
5 Zero-Day Vulnerabilities Exploited
Five of the vulnerabilities patched this month have already been leveraged by attackers in active campaigns. These vulnerabilities pose a significant risk and should be patched immediately.
- CVE-2025-30400 (CVSS 7.8) is a use-after-free bug in the Windows Desktop Window Manager (DWM) Core Library. An authenticated attacker can exploit this issue to elevate privileges to SYSTEM level, potentially taking control of critical system resources.
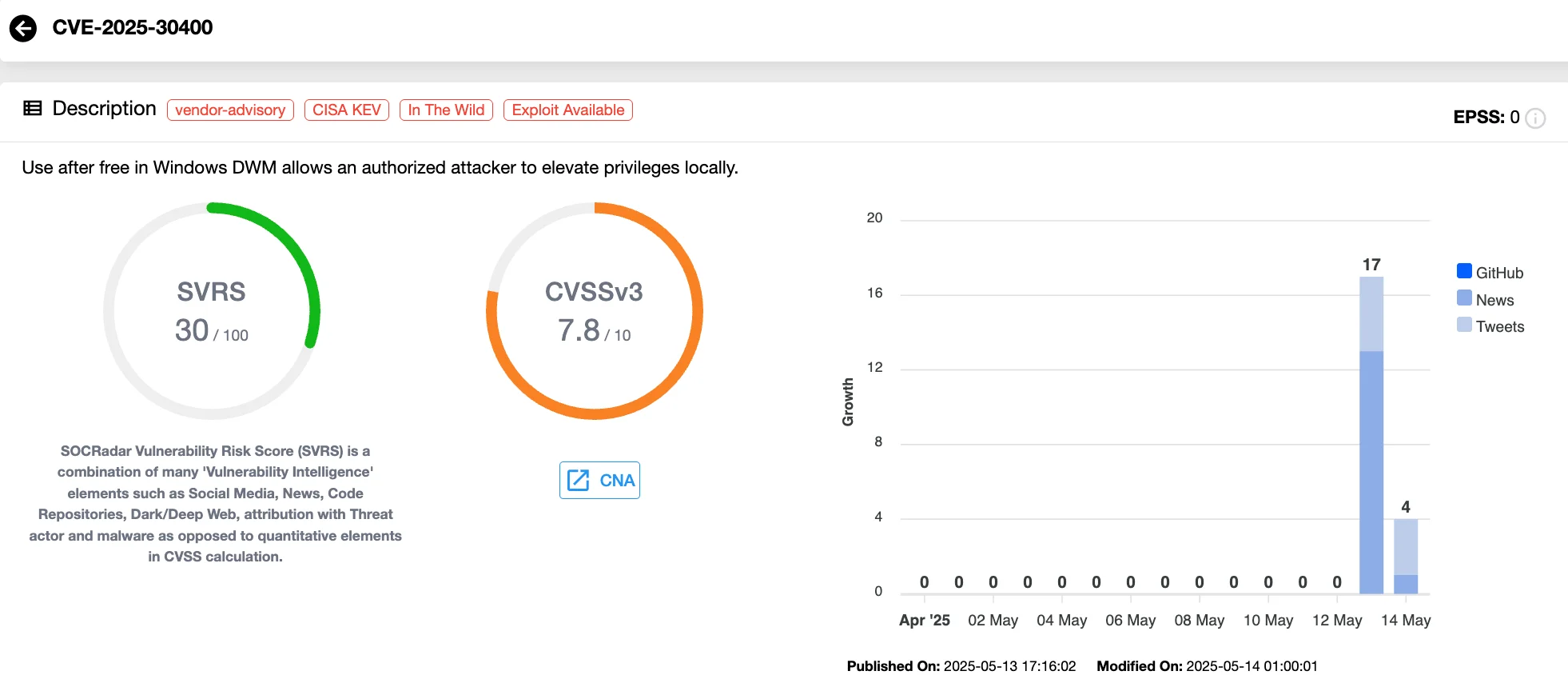
Vulnerability card of CVE-2025-30400 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
- CVE-2025-32701 (CVSS 7.8) affects the Common Log File System (CLFS) driver, which supports transactional logging across many Windows services. The flaw is another use-after-free vulnerability that enables local attackers to gain elevated privileges.
- CVE-2025-32706 (CVSS 7.8) is also found in the CLFS driver but results from improper input validation. If exploited by an authenticated user, this vulnerability can allow SYSTEM-level access.
- CVE-2025-32709 (CVSS 7.8) involves a use-after-free flaw in the Ancillary Function Driver for WinSock. This driver is helpful in handling networking operations, and successful exploitation lets a local user escalate privileges within the operating system, gaining SYSTEM privileges.
- CVE-2025-30397 (CVSS 7.5) targets the Windows scripting engine. This memory corruption issue enables RCE if a user is tricked into clicking a malicious link, making it particularly dangerous for browser-based or email-delivered attacks.
2 Other Zero-Day Flaws Were Publicly Disclosed
While not yet exploited in the wild, two zero-day vulnerabilities patched this month were publicly disclosed before fixes became available. Public disclosure often accelerates threat actor interest, as Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit code or technical details may already exist.
- CVE-2025-32702 (CVSS 7.8) is a command injection vulnerability in Visual Studio. It allows unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary code locally due to poor input sanitization.
- CVE-2025-26685 (CVSS 6.5) is a spoofing vulnerability in Microsoft Defender for Identity that allows unauthenticated attackers on the same local network to impersonate other accounts. The issue stems from improper authentication handling.
Cyber Threat Intelligence module, Vulnerability Intelligence (SOCRadar XTI)
To reduce exposure to vulnerability threats, your security team can leverage SOCRadar’s Cyber Threat Intelligence module. Its Vulnerability Intelligence feature delivers real-time context and prioritization support, helping teams defend against critical flaws by tracking exploitation trends and patch urgency before attackers act.
Critical Microsoft Vulnerabilities in May 2025 Patch Tuesday
Microsoft flagged 11 vulnerabilities as critical in this month’s rollout, based on max severity and the potential for remote code execution, privilege escalation, spoofing, and data exposure. Several of these impact widely used enterprise services, including Azure, Microsoft Office, and Remote Desktop Client. Their critical ratings highlight the risk of widespread exploitation if left unpatched.
Here are the vulnerabilities Microsoft labeled as critical:
- CVE-2025-29813 (CVSS 10.0): Elevation of Privilege in Azure DevOps Server
- CVE-2025-29827 (CVSS 9.9): Elevation of Privilege in Azure Automation
- CVE-2025-29972 (CVSS 9.9): Spoofing in Azure Storage Resource Provider
- CVE-2025-47733 (CVSS 9.1): Information Disclosure in Microsoft Power Apps
- CVE-2025-29967 (CVSS 8.8): Remote Code Execution in Remote Desktop Client
- CVE-2025-29966 (CVSS 8.8): Remote Code Execution in Remote Desktop Client
- CVE-2025-47732 (CVSS 8.7): Remote Code Execution in Microsoft Dataverse
- CVE-2025-30377 (CVSS 8.4): Remote Code Execution in Microsoft Office
- CVE-2025-30386 (CVSS 8.4): Remote Code Execution in Microsoft Office
- CVE-2025-33072 (CVSS 8.1): Information Disclosure in msagsfeedback.azurewebsites.net
- CVE-2025-29833 (CVSS 7.1): Remote Code Execution in Microsoft Virtual Machine Bus (VMBus)
Among these, CVE-2025-29813 stands out with a perfect CVSS score of 10.0. It affects Azure DevOps Server and can allow an attacker to gain elevated privileges – a critical concern for development pipelines.
Similarly, CVE-2025-29972 and CVE-2025-29827 pose serious risks to Azure environments, potentially allowing attackers to spoof users or escalate access in cloud automation processes.
The Office and Remote Desktop Client RCEs also represent high-value targets, especially in enterprise deployments.
Patch These Microsoft Vulnerabilities Before They’re Targeted
While not currently being used in attacks, multiple vulnerabilities fixed in this month’s update carry characteristics that make them more attractive for exploitation. These include lack of mitigations, high-value target surfaces, and exposure in enterprise environments. Security teams should monitor these closely and apply patches without delay.
- CVE-2025-30386 (CVSS 8.4) – Microsoft Office RCE
- CVE-2025-24063 (CVSS 7.8) – Windows Kernel Streaming Service Driver Elevation of Privilege
- CVE-2025-29976 (CVSS 7.8) – Microsoft Office SharePoint Server Elevation of Privilege
- CVE-2025-30382 (CVSS 7.8) – Microsoft Office SharePoint Server RCE
- CVE-2025-30385 (CVSS 7.8) – Windows Common Log File System Driver Elevation of Privilege
- CVE-2025-30388 (CVSS 7.8) – Windows Graphics Component RCE
- CVE-2025-29971 (CVSS 7.5) – Web Threat Defense (WTD.sys) DoS Vulnerability
- CVE-2025-29841 (CVSS 7.0) – Universal Print Management Service Elevation of Privilege
While each of these flaws targets different parts of the Microsoft ecosystem, most are capable of enabling privilege escalation or unauthorized access when exploited. As threat actors increasingly scan for newly patched bugs, delaying remediation may invite avoidable risk.
Strengthen Your Defenses with Patch Management and ASM
With multiple zero-days already exploited and several critical vulnerabilities affecting widely used Microsoft services, organizations must act fast. Prioritize patch deployment, assess your external exposure, and ensure continuous visibility into emerging threats.
SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) module offers comprehensive insight into your digital footprint, helping your team identify vulnerable assets, monitor for exposure, and respond before attackers can exploit newly disclosed flaws. From automated alerts to real-time vulnerability tracking, ASM enables a more proactive defense posture.
To further support rapid patching efforts and compliance mandates, SOCRadar also features CISA KEV Check – a capability that highlights whether your organization is exposed to vulnerabilities listed in the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog.
Attack Surface Management (ASM) module, Company Vulnerabilities (SOCRadar XTI)
For the complete list of vulnerabilities and technical details from this month’s release, visit Microsoft’s official May 2025 Patch Tuesday notes.
SAP May 2025 Patch Day: NetWeaver Exploits and Visual Composer Fixes (CVE-2025-42999 & CVE-2025-31324)
Following our overview of Microsoft’s security updates, let’s take a look at SAP’s May advisories, which also reveal serious vulnerabilities.
As part of its May 2025 Security Patch Day, SAP released 16 new security notes and two updates to earlier advisories. Among them is a patch for another vulnerability linked to active exploitation involving SAP NetWeaver systems, discovered as part of an ongoing investigation into a previous zero-day attack.
Tracked as CVE-2025-42999 (CVSS 9.1), this newly addressed issue involves insecure deserialization in the Visual Composer component and was uncovered during an investigation into earlier zero-day activity involving CVE-2025-31324, a missing authentication issue addressed in April.
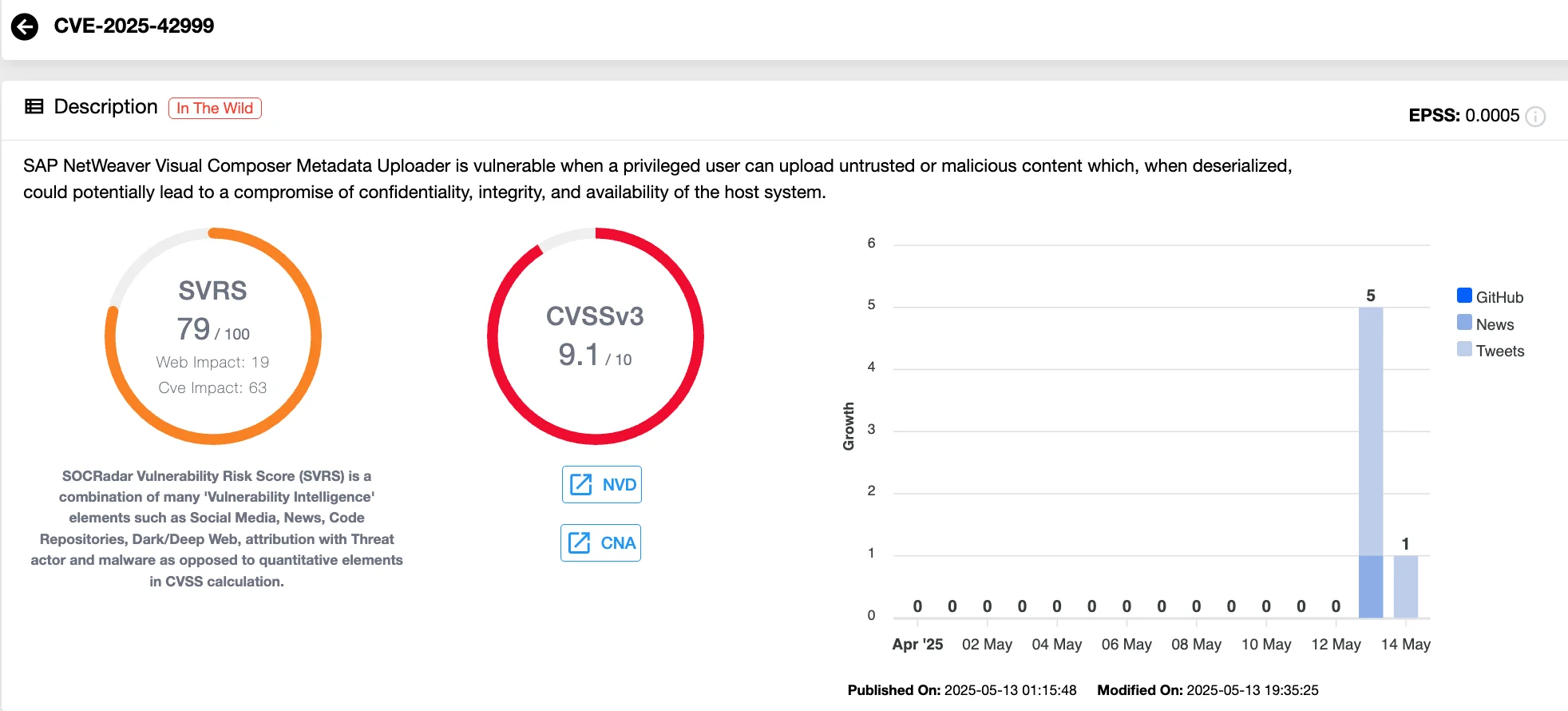
Vulnerability card of CVE-2025-42999 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
Threat actors have reportedly exploited these vulnerabilities to deploy web shells and tools like Brute Ratel, even against fully patched systems. Some cases have been linked to a threat group known as Chaya_004, with thousands of NetWeaver instances observed exposed online.
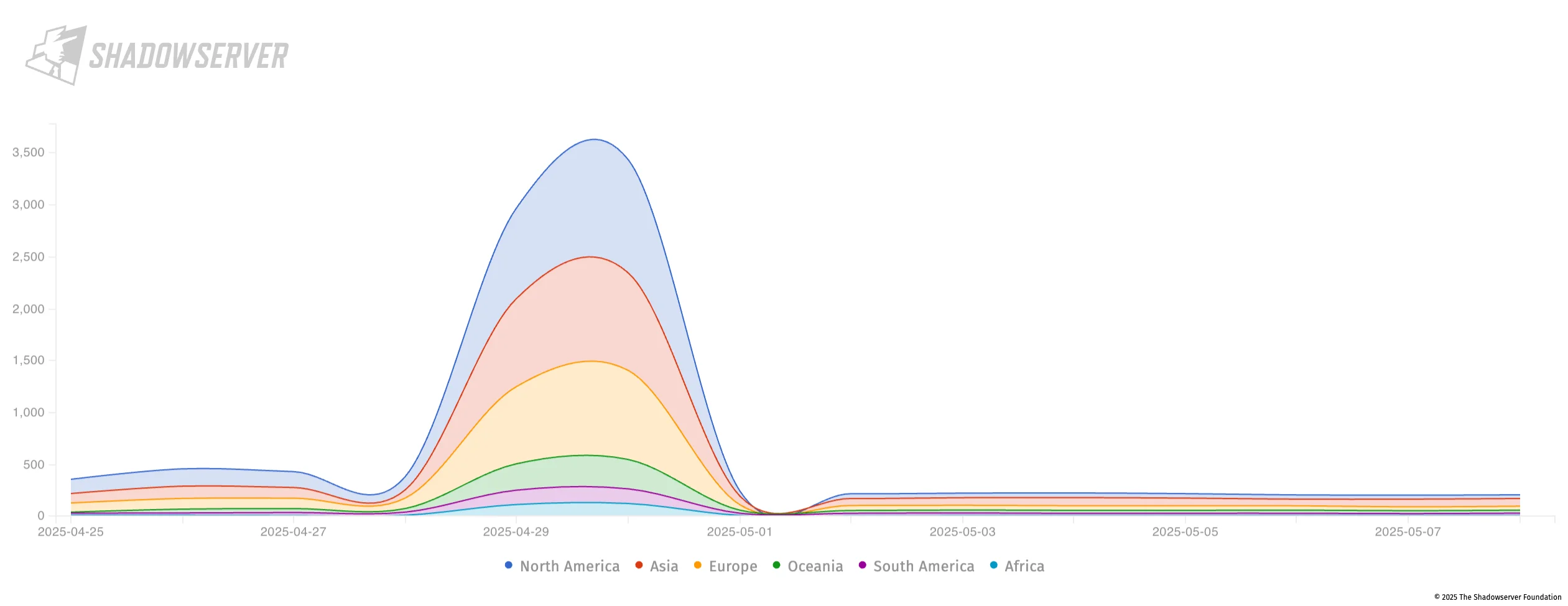
CVE-2025-31324 exposure timeline (Shadowserver)
The campaign reportedly began as early as January 2025, with attackers exploiting both CVE-2025-31324 and CVE-2025-42999 in attacks.
In response to the activity, CISA has added CVE-2025-31324 to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog and mandated federal agencies to apply patches by May 20, 2025.
SAP admins are strongly urged to apply patches associated with Security Notes 3594142 and 3604119, both rated critical with CVSS scores of 10.0 and 9.1, respectively. These notes address flaws that could allow Remote Code Execution (RCE) without authentication under certain role conditions in Visual Composer.
As a precaution, SAP also recommends disabling the Visual Composer service if possible, restricting access to metadata upload functions, and actively monitoring systems for suspicious activity.
For full details, visit SAP’s May 2025 Security Notes page.




































