
Microsoft’s November 2024 Patch Tuesday: 89 Vulnerabilities Addressed, Two Active Zero-Day Exploits
Microsoft has released its latest security updates with November 2024 Patch Tuesday, addressing a broad range of security vulnerabilities across its products. This month’s release includes fixes for 89 CVEs, covering various threat categories, with Remote Code Execution (RCE) and Privilege Escalation flaws taking the lead. Notably, these updates include two actively exploited zero-day vulnerabilities.
Among the vulnerabilities patched this month:
- 51 Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerabilities pose risks where attackers could execute commands or inject malicious code on vulnerable systems.
- 28 Elevation of Privilege (EoP) vulnerabilities provide attackers opportunities to gain unauthorized access to higher privilege levels.
- Additional vulnerabilities include Denial of Service (4), Spoofing (3), Security Feature Bypass (2), and Information Disclosure (1).
With multiple high-impact vulnerabilities addressed, including critical flaws and actively exploited zero-days, this month’s update necessitates immediate attention to protect systems from potential exploitation.
Actively Exploited Zero-Days in November 2024 Patch Tuesday: CVE-2024-49039 and CVE-2024-43451
In November 2024’s Patch Tuesday, Microsoft addresses two zero-day vulnerabilities currently being exploited in the wild:
CVE-2024-49039 – Windows Task Scheduler Elevation of Privilege (CVSS 8.8)
This vulnerability, exploited as a zero-day, allows an authenticated attacker to elevate privileges by running a specially crafted application on a target system.
By exploiting this flaw, attackers can move from a low-privilege AppContainer to a Medium Integrity Level, enabling access to restricted RPC functions typically reserved for higher-privilege accounts.
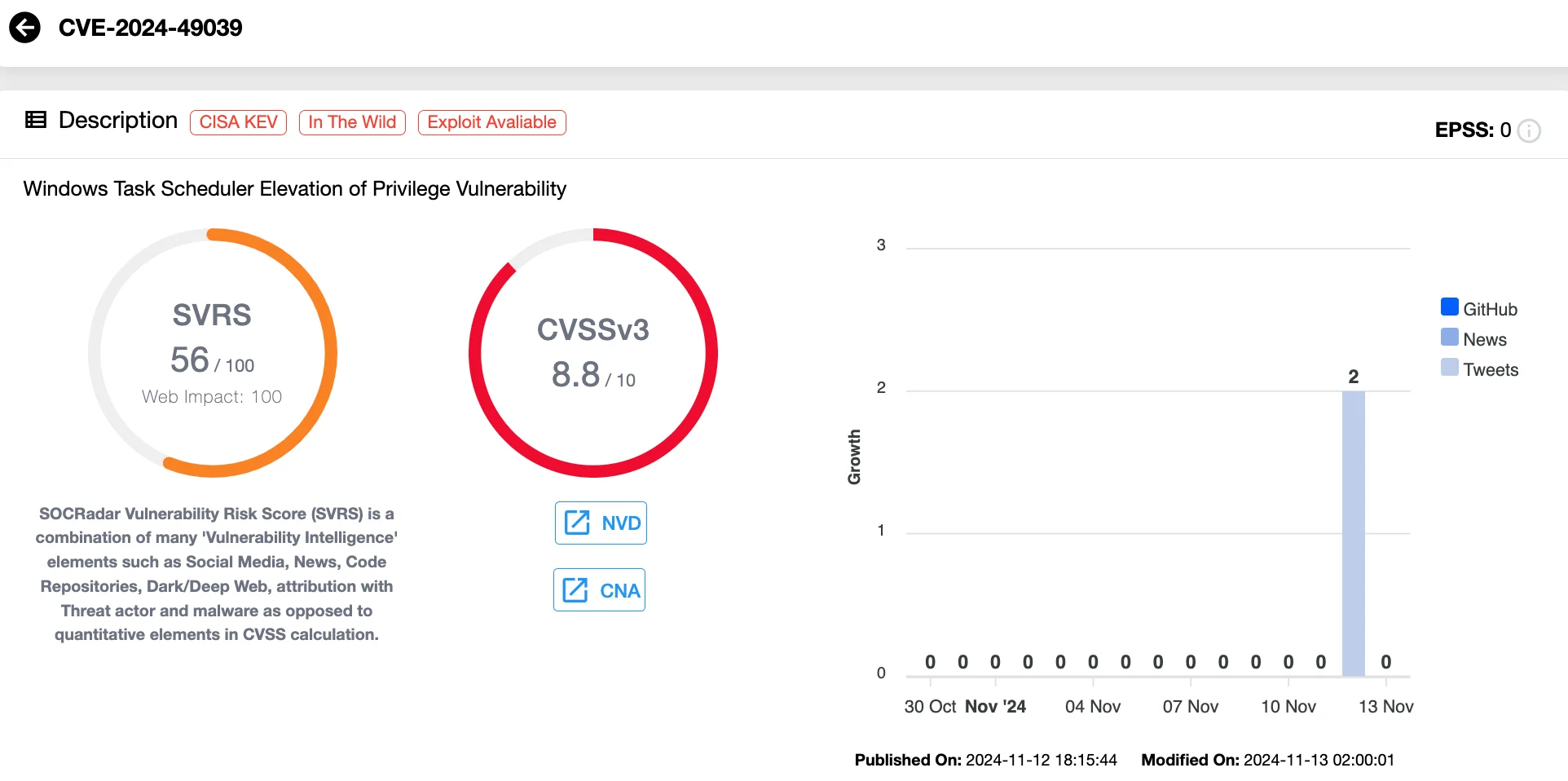
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-49039 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
The attack vector does not require user interaction, further heightening its risk, especially in enterprise environments where attackers could misuse elevated privileges for unauthorized actions.
Currently, details of exploitation are not available for CVE-2024-49039.
CVE-2024-43451 – NTLM Hash Disclosure Spoofing (CVSS 6.5)
Also exploited in the wild, and publicly disclosed prior to patches, this spoofing vulnerability can lead to the unauthorized disclosure of a user’s NTLMv2 hash, enabling attackers to authenticate as the compromised user and access restricted data, leading to total loss of confidentiality.
Triggered by minimal user interaction—such as selecting or right-clicking a malicious file—this vulnerability poses a significant risk.
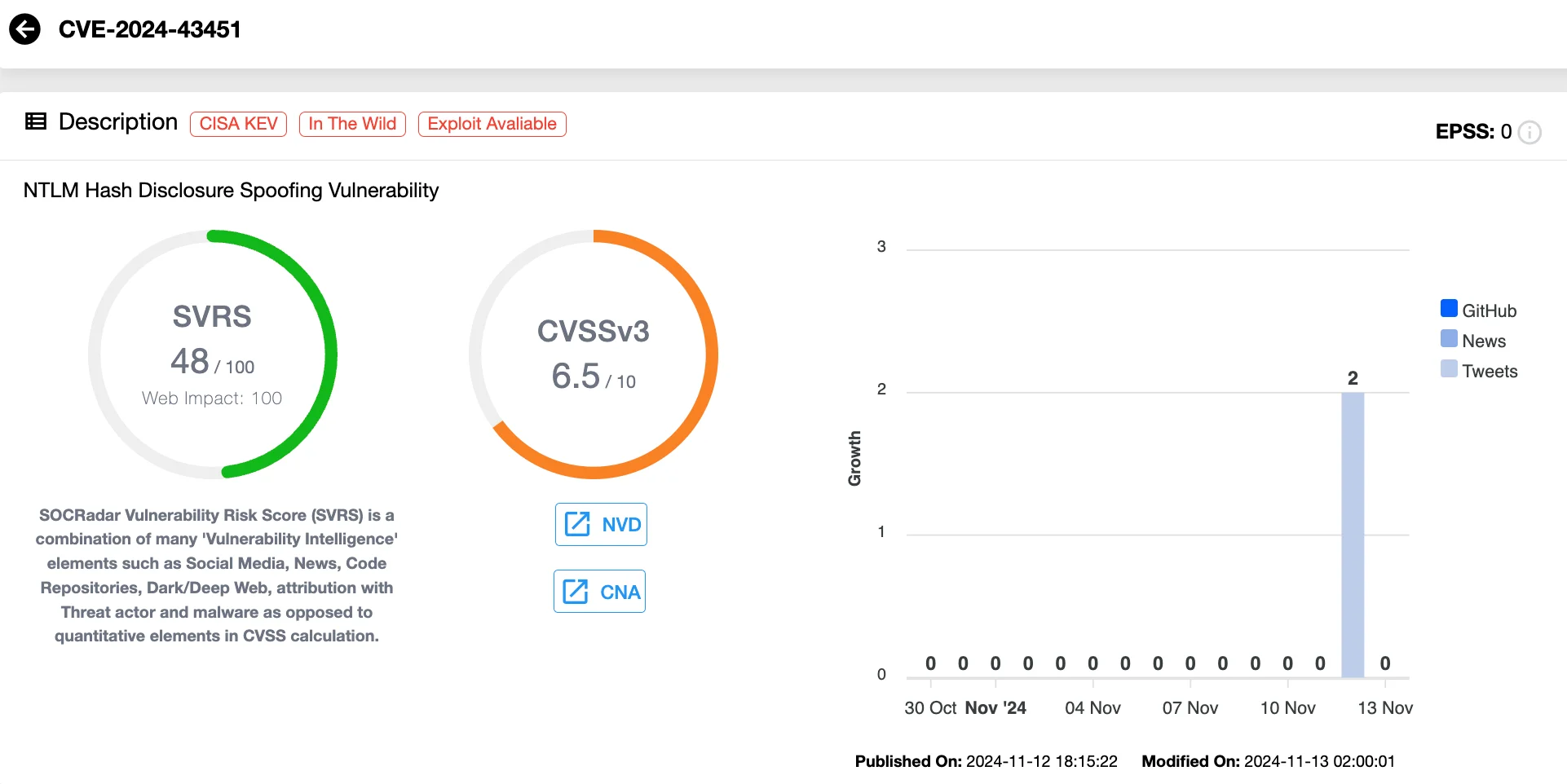
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-43451 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
Microsoft recommends users installing Security Only updates to also apply Internet Explorer Cumulative Updates to fully mitigate risks related to this flaw, given the MSHTML platform’s ongoing role in certain applications despite the retirement of Internet Explorer 11.
To stay protected against actively exploited vulnerabilities like CVE-2024-49039 and CVE-2024-43451, SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence equips you with in-depth, actionable insights.
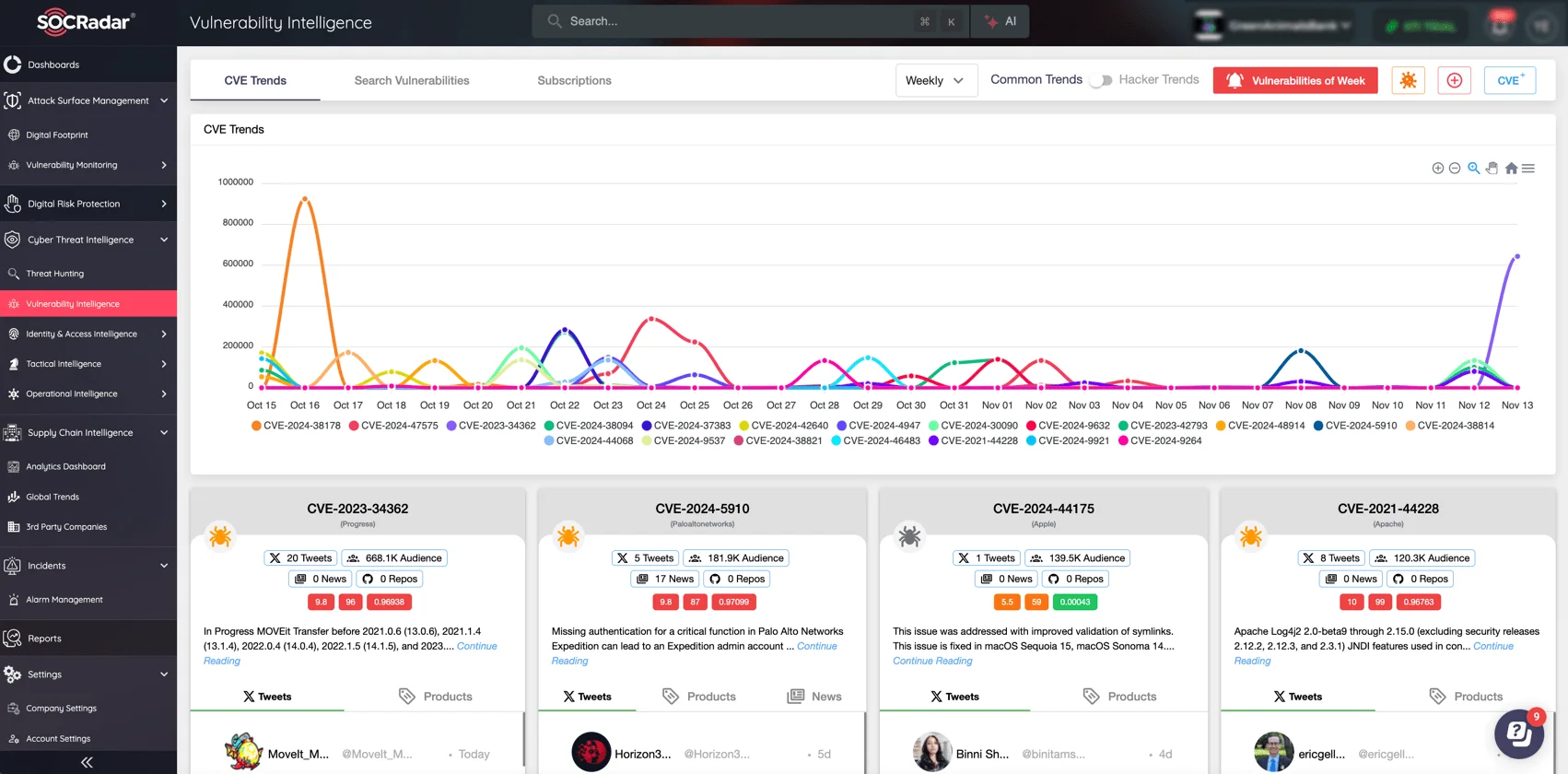
SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence – Newest CVEs and updates
By monitoring exploitation trends, hacker activity, and vulnerability lifecycle, SOCRadar’s platform allows your team to identify high-risk vulnerabilities as they emerge, understand their potential impact, and prioritize patches accordingly. With real-time alerts and continuous analysis of hacker trends, Vulnerability Intelligence ensures your organization can take proactive steps to mitigate risks before they escalate.
Publicly Disclosed Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
Microsoft’s November Patch Tuesday also addresses two other zero-day vulnerabilities that were publicly disclosed before patches became available. Although active exploitation has not yet been reported, these vulnerabilities pose significant risks if left unpatched.
CVE-2024-49019 – Active Directory Certificate Services Elevation of Privilege (CVSS 7.8)
This vulnerability in Active Directory Certificate Services allows attackers to escalate privileges to domain administrator if certain AD certificate configurations are used. Specifically, certificates created with version 1 templates, where the subject name source is set to “Supplied in the request” and broader enrollment permissions are enabled, may be vulnerable.
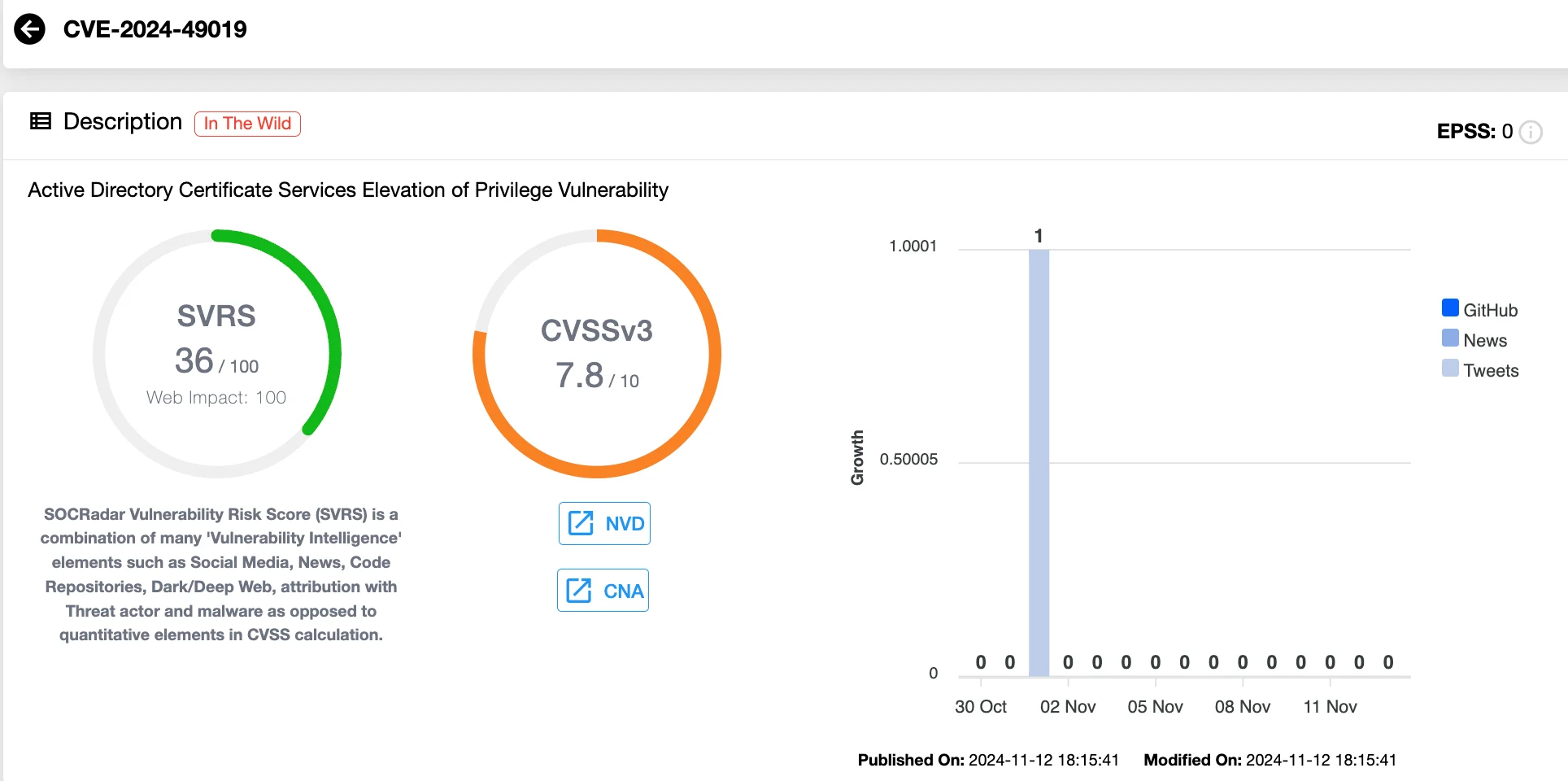
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-49019 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
To mitigate this risk, Microsoft advises limiting Enroll permissions and removing unused certificate templates. For more hardening guidance, refer to its initial research blog and Microsoft’s documentation on securing PKI.
CVE-2024-49040 – Microsoft Exchange Server Spoofing Vulnerability (CVSS 7.5)
This vulnerability in Microsoft Exchange Server’s handling of the P2 FROM header could allow attackers to perform spoofing attacks. Exploiting flaws in the header verification process, attackers can make email clients, such as Microsoft Outlook, display a forged sender address.
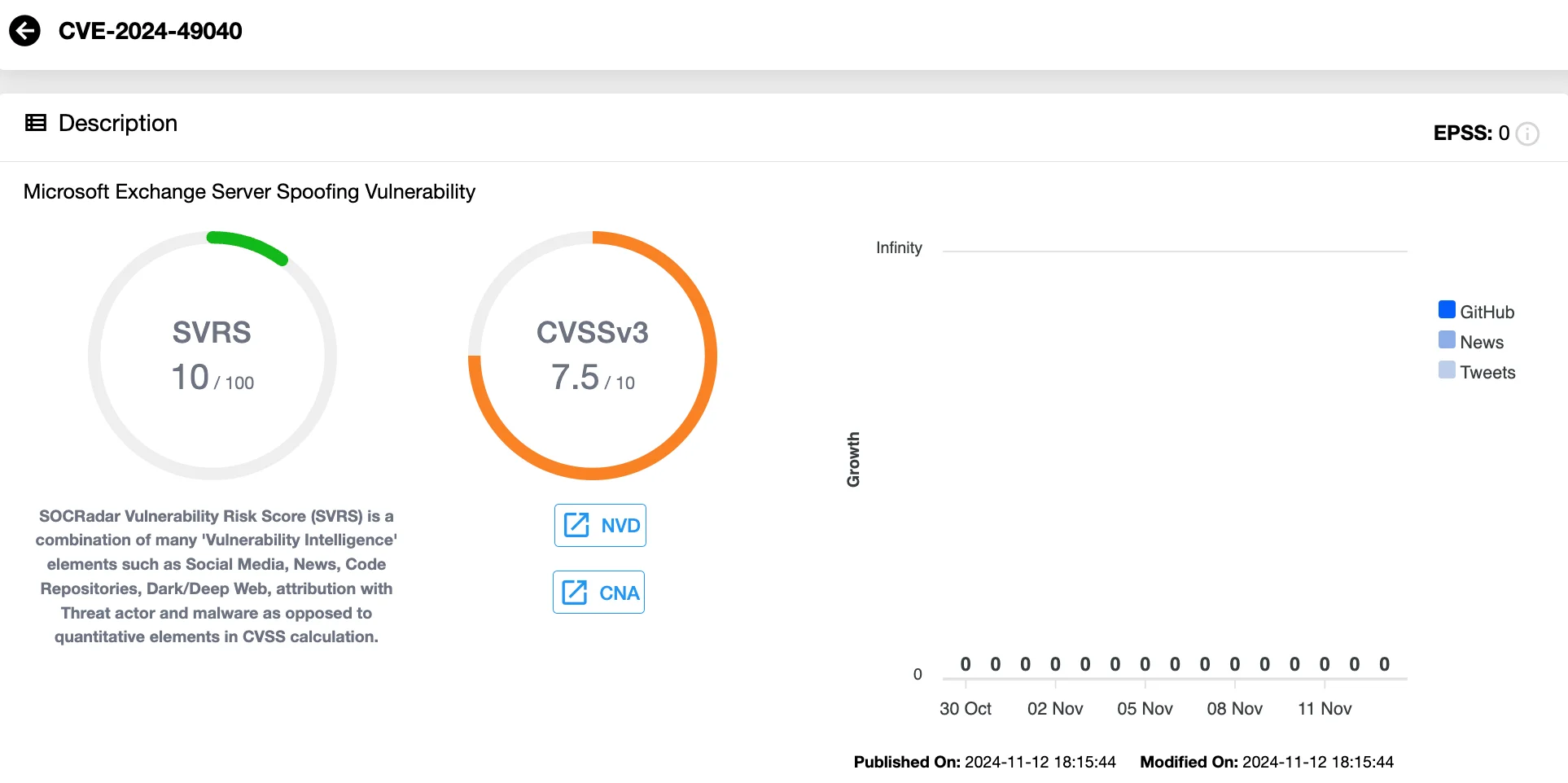
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-49040 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
Starting with the November 2024 Security Update, Exchange Server now includes detection mechanisms to flag emails containing suspicious P2 FROM headers. For further details, see Microsoft’s advisory and the technical deep dive where this vulnerability was explained.
Critical Vulnerabilities That Demand Immediate Attention
Microsoft’s November 2024 Patch Tuesday addresses multiple vulnerabilities marked as critical, which could threaten enterprise and cloud environments if left unpatched.
- CVE-2024-43498 (CVSS 9.8) – .NET and Visual Studio Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
- CVE-2024-43639 (CVSS 9.8) – Windows Kerberos Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
- CVE-2024-43625 (CVSS 8.1) – Microsoft Windows VMSwitch Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
- CVE-2024-49056 (CVSS 7.3) – Airlift.microsoft.com Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
Additionally, although marked as ‘Important’ in max severity, the highest-rated vulnerability in this update is CVE-2024-43602. It holds a CVSS score of 9.9 due to its critical impact on Azure CycleCloud.
This Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability allows attackers with minimal permissions to craft requests that grant them root-level access. In certain cases, attackers could even compromise administrative credentials, enabling them to execute code across clusters and fully control affected cloud environments.
Which Vulnerabilities Are Highly Exploitable?
Microsoft’s November Patch Tuesday update highlights several vulnerabilities that pose immediate security threats due to their high exploitability. These include the two publicly disclosed zero-day vulnerabilities, CVE-2024-49039 and CVE-2024-43451, as well as multiple elevation of privilege flaws that could be exploited to compromise system integrity or disrupt services:
- CVE-2024-43623 (CVSS 7.8) – Windows NT OS Kernel Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
- CVE-2024-43629 (CVSS 7.8) – Windows DWM Core Library Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
- CVE-2024-43630 (CVSS 7.8) – Windows Kernel Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
- CVE-2024-43636 (CVSS 7.8) – Win32k Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
- CVE-2024-43642 (CVSS 7.5) – Windows SMB Denial of Service Vulnerability
- CVE-2024-49033 (CVSS 7.5) – Microsoft Word Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability
These vulnerabilities demand rapid attention due to their potential for privilege escalation and disruption. Swift remediation is recommended to prevent exploitation, particularly in environments where attackers could gain unauthorized access or disrupt business-critical services.
For more detailed information, refer to Microsoft’s November 2024 Patch Tuesday Release Notes.
How SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) Can Help You Stay Secure
SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) module offers essential tools to help organizations maintain security by providing continuous visibility into their exposed assets. With the expanding landscape of digital threats, ASM helps identify unpatched systems and vulnerable assets across networks, enabling you to manage and minimize your organization’s attack surface effectively.
ASM not only flags at-risk assets but also helps prioritize patching efforts by assessing the exploitability of specific vulnerabilities, ensuring that critical patches are addressed first.
SOCRadar’s ASM module, Company Vulnerabilities
By proactively monitoring for security gaps, the module helps detect potential breach points before attackers can exploit them, reducing the likelihood of unauthorized access and data breaches.


































