
Securing the Chain: How Threat Intelligence Strengthens Third-Party Risk Management
Businesses increasingly face new cybersecurity incidents that are disruptive, costly, and can significantly damage their reputations. Large enterprises, at the center of vast digital ecosystems, encounter a particularly complex challenge (Third-Party Risk Management): Managing the cyber risks associated with their information being shared with third parties and beyond. These businesses transmit data to service providers and subcontractors to enhance service delivery and reduce costs. During this process, data ownership changes multiple times, and documents—often containing sensitive information about businesses and customers—circulate throughout the ecosystem. Therefore, it is critical to understand the measures third parties take to safeguard this information and to ensure its protection further along the value chain.
The aforementioned risks, now known as third-party data breaches, can lead to severe reputational damage for your organization. They are exacerbated by the potential harm to personal and sensitive data compromised by threat actors. Across various sectors, from education to healthcare and finance to administration, it is crucial to implement security measures to manage the data protection risks you face. This article aims to enhance understanding of the scope and significance of these third-party risks, which are beyond your direct control, and to highlight necessary improvements in Cyber Threat Intelligence across the links of the chain.
What are Third-Party Organizations?
An organization’s scope of third parties encompasses the range of relationships with external entities that provide goods, services, or support to its operations, objectives, or customers. The number of third parties may vary based on the organization’s nature, size, and complexity. Key third parties include suppliers and vendors, contract manufacturers and distributors, affiliates and joint venture partners, R&D organizations and consultants, sales channels and agents.
These represent common types of third parties in an organization’s network. Third parties can significantly influence an organization’s performance, risk profile, and reputation, both quantitatively and qualitatively. For instance, a data breach at a Managed Service Provider (MSP) overseeing the organization’s security operations could represent a worst-case scenario. Consequently, it is essential for an organization to monitor and manage third-party relationships effectivelyrather than simply delegating the responsibility.
What Are the Third-Party Cyber Risks for Organizations?
As business processes become more complex, companies increasingly rely on third parties to enhance their capabilities in providing critical services, such as cloud storage, data management, and security. It is often more efficient and cost-effective to outsource these tasks to external entities, which might otherwise require significant labor and in-house resources.
However, using third-party services also introduces significant risks, some of which may be unforeseen. Depending on their scope, third parties can expose organizations to various risks, including strategic, operational, reputational, regulatory and compliance, financial, and cybersecurity. For instance, a software vulnerability might create an entry point for intrusion, a service disruption can harm a company’s reputation and operations, and a data breach may lead to regulatory issues. Even poorly managed disengagement from a vendor can be hazardous, resulting in loss of access to systems implemented by the third-party, loss of data oversight, or complete data loss. Among these, cybersecurity risks have become the most prominent in enterprise risk programs in recent years.
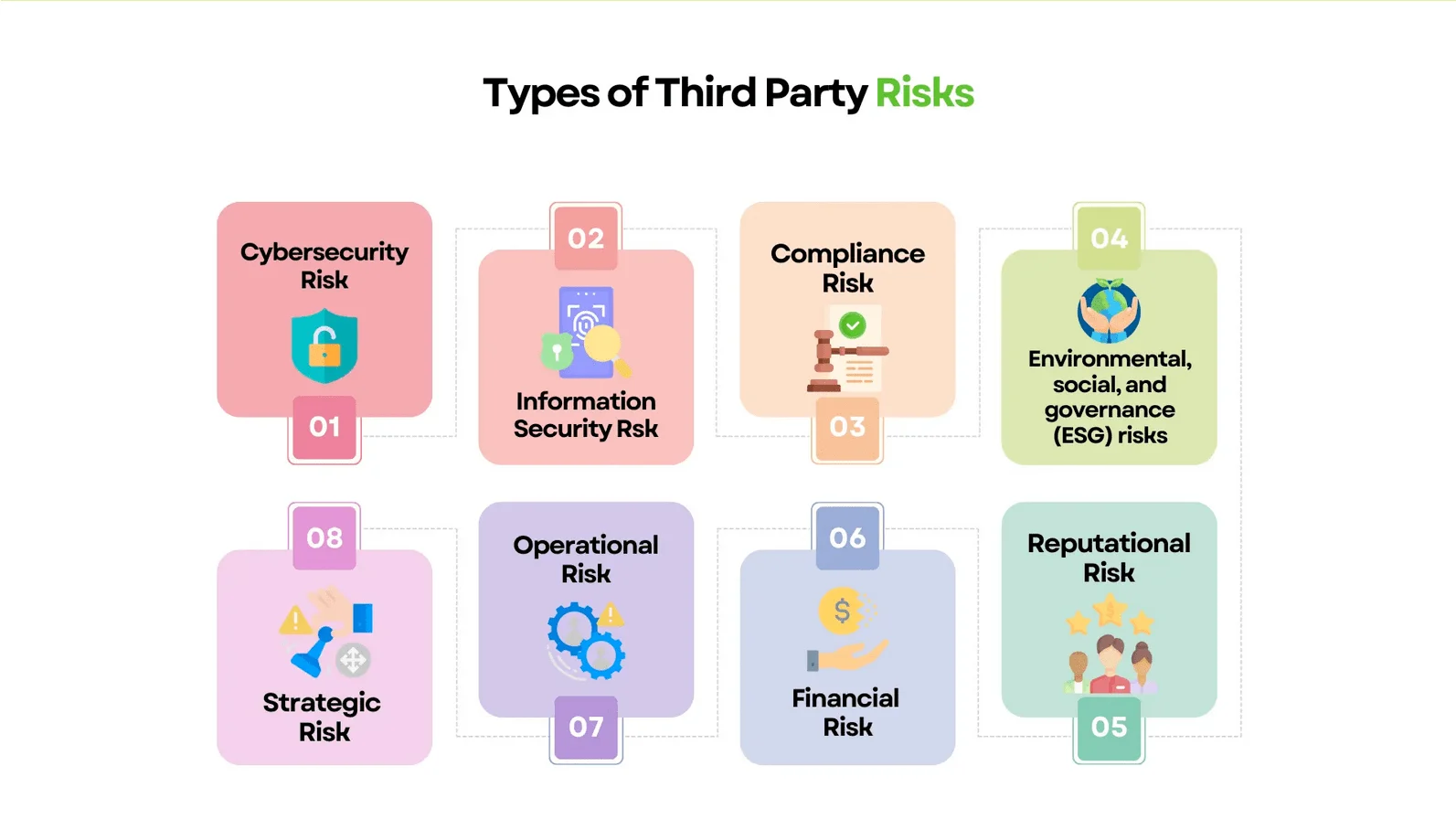
Third-Party Risk Types (Source: SignalX)
Cybersecurity risk refers to the danger of unauthorized access, theft, or damage to your organization’s or a third-party vendor’s data, systems, or networks. For example, if a third-party vendor providing software solutions or tools for storing or processing your sensitive data has inadequate security controls or suffers a data breach or ransomware attack, this could compromise your data security and privacy.
To manage and mitigate these risks, it’s essential to conduct regular third-party risk assessments, implement role-based access controls, enforce risk-based multi-factor authentication (MFA), develop use cases in the security operations center to detect suspicious activities, create incident response guides for third-party supply-chain attack scenarios, mandate security training and certifications, include service-level agreements and escalation protocols in third-party contracts, adopt a third-party risk management framework, and utilize contemporary approaches like threat intelligence to align cybersecurity with your organization’s needs.
Supply chain attacks, which target organizations by compromising legitimate software to distribute malware, often exploit vulnerabilities in third-party vendors. To prevent service providers from becoming a vulnerable and insecure link in your digital supply chain, which can weaken your security posture, the SOCRadar Supply Chain Intelligence module can be instrumental. This module alerts you about companies that have been targets of cyberattacks, retrospectively extracting actionable intelligence. It collects and analyzes dark web data on cyber incidents and data breaches related to major software vendors, providing reports enriched with threat intelligence.
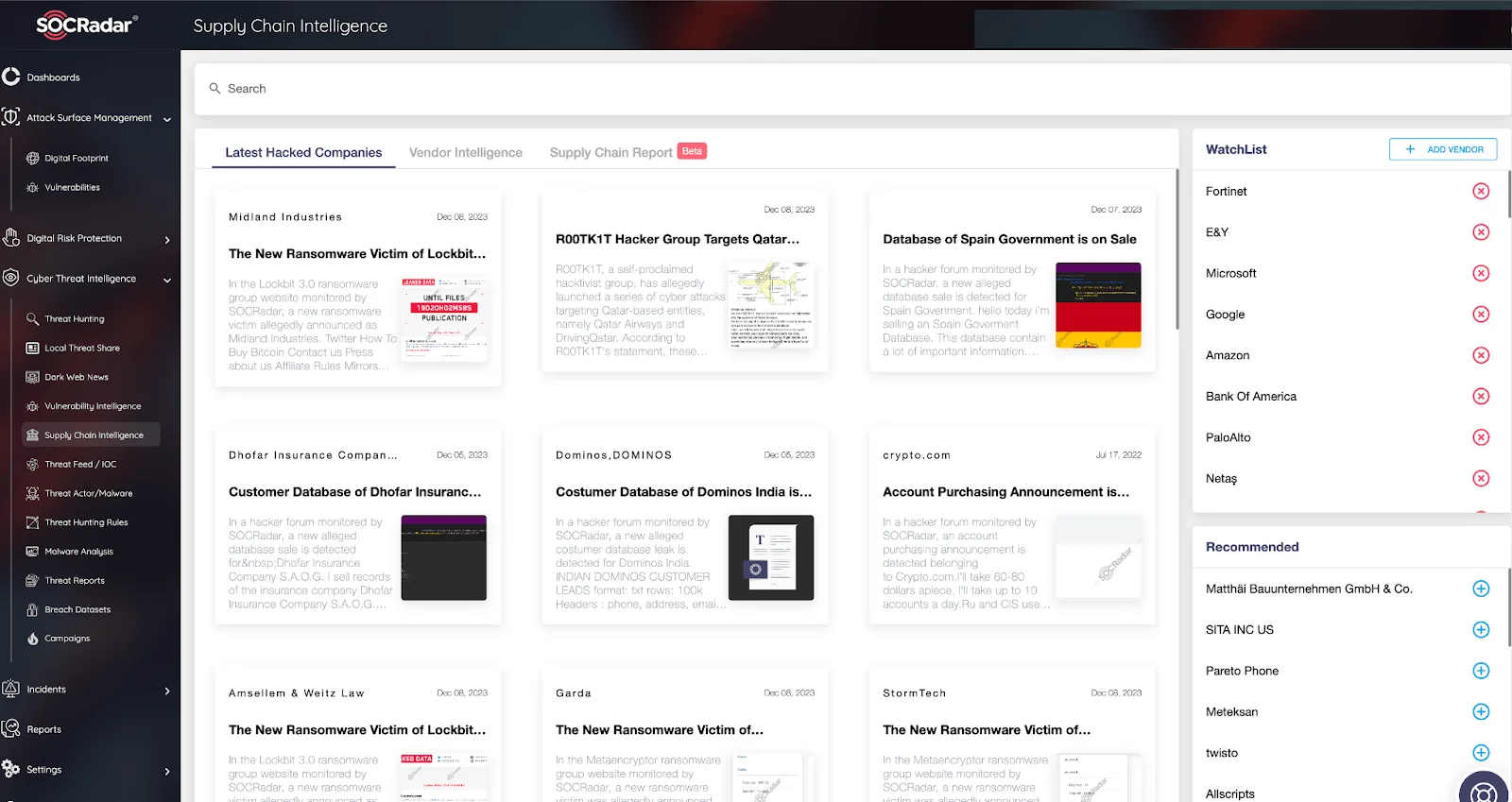
SOCRadar Supply Chain Intelligence Module
Prominent Data Breaches Targeting Third Parties
Data breaches are among the most significant emerging cyber threats in recent years. Unfortunately, organizations of all sizes struggle to prevent data breaches. Cybercriminals continually find innovative ways to steal private or sensitive information, which they often monetize on forums and channels in the dark web. A notable example is the 2023 MOVEit incident by the Cl0p ransomware group, also known as TA505. Zero-day vulnerabilities pose a significant threat to many companies, mainly when found in widely used software and involving third parties. As of December 2023, the MOVEit data breach affected 2,592 victim organizations from over 30 countries, including 2,271 from the United States, impacting more than 80 million individuals.
AT&T
On July 6, 2023, a new alleged database leak concerning AT&T was detected on a hacker forum monitored by SOCRadar. The post claims that in January 2023, a 4.9 GB database containing 129,539 contact details of AT&T employees was put up for sale after one of its contractors suffered a cyberattack. The leaked database, which includes sample data, contains account/billing fees, account notes, account numbers, and emails. AT&T (The American Telephone and Telegraph Company) is the world’s fourth-largest telecommunications company by revenue and the largest wireless operator in the United States. As of 2023, it ranked 13th in the Fortune 500, with revenues of $120.7 billion.

AT&T (The American Telephone and Telegraph Company) Database Leak
Materna group

Black Basta Ransomware victim: The Materna Group
On June 20, 2023, the Black Basta ransomware group claimed on their website, monitored by SOCRadar, that the Materna Group was a new victim of their ransomware attack. Founded in 1980 in Germany, the Materna Group reported a group turnover of €554 million in 2022 and includes several subsidiaries and a holding company. Operating in 40 locations worldwide, Materna offers IT and digitalization project services through its subsidiaries.
T-Mobile
On July 22, 2023, another alleged database leak for T-Mobile was reported on a hacker forum monitored by SOCRadar. This database, shared as sample data, is purportedly from a data breach that occurred in April 2023, exposing sales data/analytics. The database for sale reportedly contains T-Mobile support calls, customer and employee credentials, partial SSNs, email addresses, and other customer data.
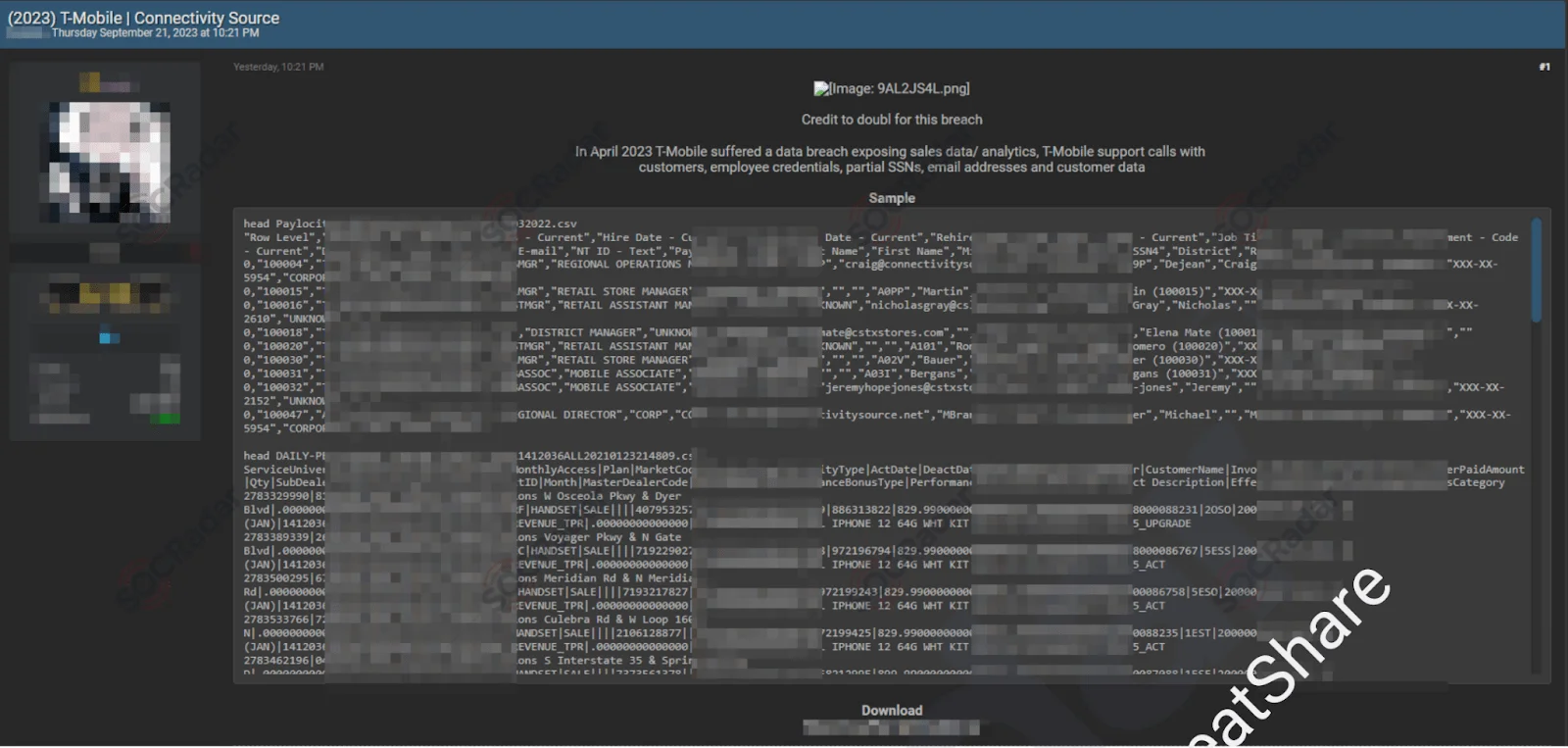
T-Mobile Database Leak
T-Mobile has experienced multiple data breaches since 2018, including two in 2023. In early January 2023, T-Mobile discovered a breach where a malicious actor had accessed their systems the previous November, stealing personal information from over 37 million customers, including names, emails, and birthdays. These data breaches have caused significant damage to T-Mobile, not only financially but also in terms of customer trust, due to repeated breaches of personal information.
How Does Threat Intelligence Help to Mitigate Third-Party Risks?
In the wake of the 2023 MOVEit incident, it has become increasingly clear that organizations must enhance the protection of their vendor and third-party ecosystems. A recent study by SecurityScorecard and the Cyentia Institute, analyzing data from over 230,000 companies, found that 98% of organizations conduct business with at least one-third of the parties that have experienced a data breach. The report also revealed that the average firm has relationships with 11 direct third-party and hundreds of indirect fourth and nth-party entities. Consequently, up-to-date approaches like Cyber Threat Intelligence are essential to safeguard companies from the growing susceptibility to cyberattacks due to expanding attack surfaces.
Managing digital attack surfaces through Attack Surface Management (ASM) services is crucial. These services help discover digital assets, identify potential vulnerabilities, assess and mitigate cybersecurity risks. They are vital as they offer a unified view of cyber assets, providing complete visibility of your expanding attack surface. The SOCRadar ASM module starts by searching for public shadow IT assets to uncover potential vulnerabilities exploitable by threat actors.
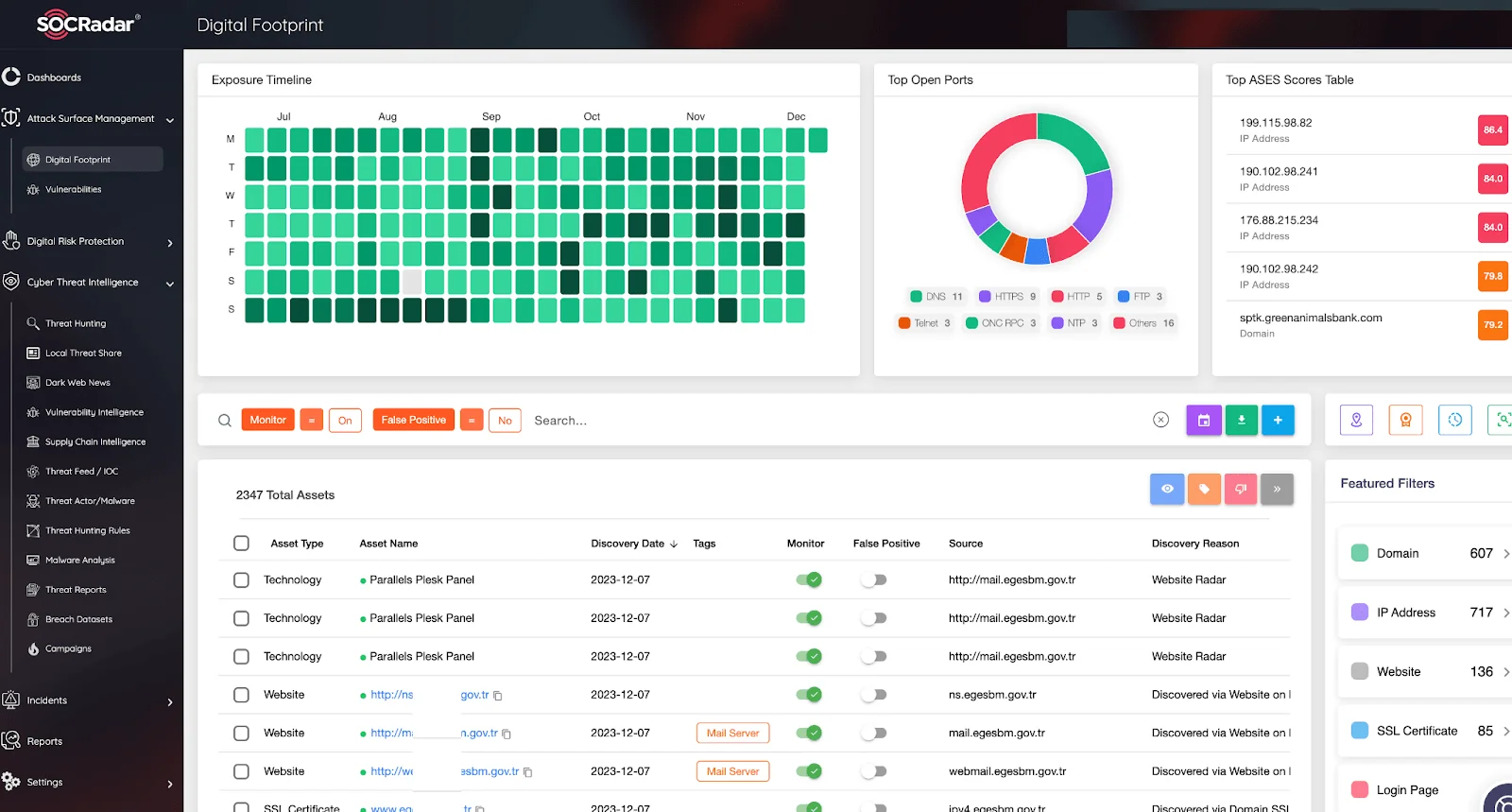
SOCRadar Attack Surface Management Module
The role of Cyber Threat Intelligence in mitigating third-party risks is multifaceted and crucial for the security and integrity of an organization’s operations. Key benefits include:
- Identifying Emerging Threats: Threat intelligence helps identify new and emerging cybersecurity threats that could impact third-party partners. For example, organizations can proactively take steps to protect against a growing ransomware attack in the industry in which they or their third-party service providers operate.
- Improving Risk Assessment:Actionable threat intelligence allows for informed and accurate risk assessments, including those of third-party vendors. Detailed threat intelligence helps organizations assess the security posture of their vendors and pinpoint potential vulnerabilities.
The SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence module, for instance, provides insights into vulnerabilities currently exploited by threat actors, accelerating risk assessment and information validation processes.
SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence Module
If your organization conducts an annual security assessment on third parties, external threat intelligence can fill in the gaps between these assessments so you don’t miss potentially critical threats as they emerge.
- Enhancing Decision-Making: Comprehensive threat intelligence equips decision-makers with the information needed to make informed choices regarding collaborations with third-party providers, particularly concerning security requirements and compliance standards. Strategic threat intelligence supplies security executives with critical data for board-level decision-making.
- Enabling Proactive Security Measures: Threat intelligence allows organizations to proactively implement measures to mitigate threats before they escalate into attacks. For example, timely identification of user information circulating on dark web markets can help identify weak links potentially involving third parties.
- Facilitating Alignment with Regulations and Compliance: Understanding the threat landscape ensures third-party vendors’ compliance with relevant industry regulations and standards, which is crucial for avoiding financial penalties and maintaining customer trust. If subject to regulations like HIPAA or GDPR, ensuring third-party compliance is essential. Integrating threat intelligence into cybersecurity strategies helps identify third-party risks leading to non-compliance, allowing for appropriate mitigation steps.
- Improving Vendor Management Processes: Threat intelligence can be integrated into vendor management processes and used as a core part of evaluating, selecting and monitoring third-party providers for security considerations.
Threat intelligence can be used to build a picture of the risks a potential vendor brings to your environment. For example, during the selection phase of a third-party vendor or supplier relationship, intelligence on previous data breaches, security incidents, compliance issues, sanctions, etc. can provide strategic information for vendor selection decisions. A vendor with a low security score may not match your organization’s risk tolerance.
- Supporting Business Continuity Planning and Full Visibility: Threat intelligence helps identify risks that could disrupt business operations, enabling organizations to develop more effective business continuity and disaster recovery plans that consider the potential impact of third-party security risks.
It is important to continuously monitor the level of cybersecurity from the time you start receiving services from a supplier until the time you divorce. By doing so, you can ensure that you can identify potential risks or issues as soon as they arise and take action to mitigate them before they become major persistent problems. Just when you think everything is going well, threat intelligence can give you a closer view of threats and risks and enable you to take timely action with full security visibility. This means always having a clear view of your vendor’s risk posture and benefiting from automation and real-time monitoring.
Conclusion
As organizations increasingly rely on third parties like vendors, suppliers, contractors, and partners, cybercriminals exploit these relationships to access the organizations themselves. Deepening technical relationships with third-party service providers is part of the digital transformation of businesses and supply chains. Assessing risks and maintaining an accurate security posture picture with these partners is increasingly important in this evolving service network.
While traditional third-party risk management programs have relied on surveys and high-level monitoring and planning, experts now recommend using threat intelligence to validate security controls and assess security postures.
Traditional methods often fail to identify and act against third-party risks. With the rise of supply chain attacks and expanding attack surfaces, Cyber Threat Intelligence has become a critical component of every organization’s cybersecurity strategy. Third-party risk intelligence is increasingly vital to keep pace with changing regulatory requirements and the evolving threat landscape.



































