
Dark Web Profile: Black Basta Ransomware
By SOCRadar Research
[Update] May 13, 2024: Read the subheading “CISA’s Advisory for Black Basta”
[Update] January 3, 2024: Read the subheading “Turning the Tables on Black Basta”
One of the perpetrators of the ransomware attacks, which increased by 59% in the last year, is the Russian-speaking origin ransomware group, Black Basta. They emerged in April 2022 and became notorious for breaching nearly a hundred organizations by October 2022.
Although the LockBit group is the most active ransomware group in the gap opened after Conti’s dissolution, the Black Basta is in second place, taking on 9% of ransomware attacks. On Dark Web, it has not been seen so far that they are advertising or looking for affiliates, but the group members, which reached large attack volumes in this brief time, are well-organized and experienced threat actors.
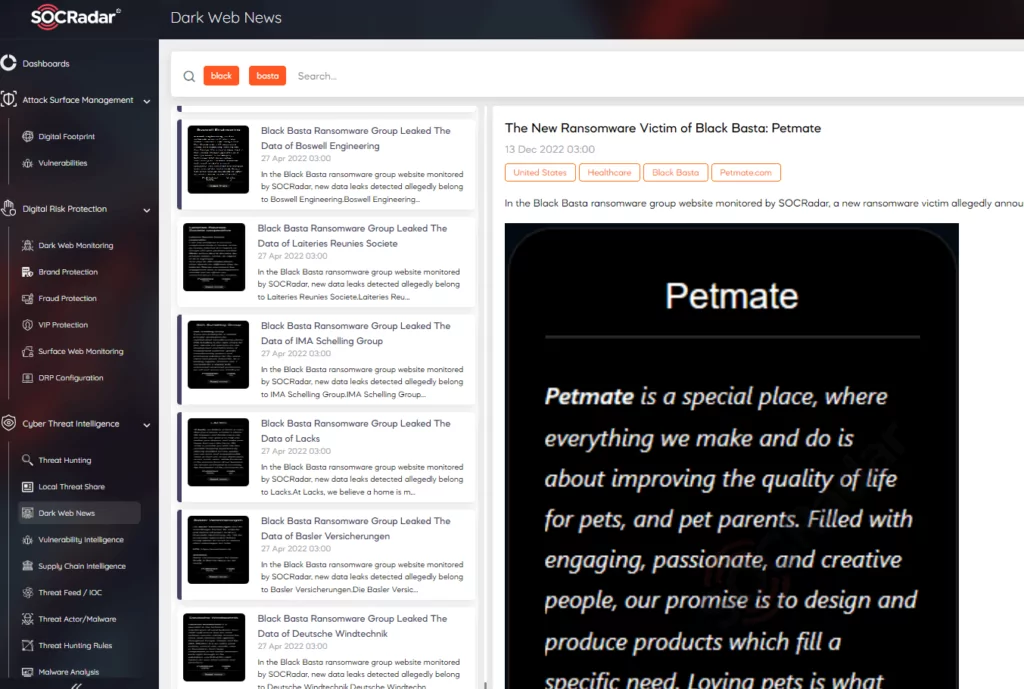
Who is Black Basta?
According to some researchers, Black Basta is a ransomware group that works with the RaaS (ransomware as a service) model. Still, SOCRadar Dark Web Team reports that no such advertisements on hacker forums or black markets have been found so far. However, they may still be using the RaaS model with the affiliates and partners they trust.
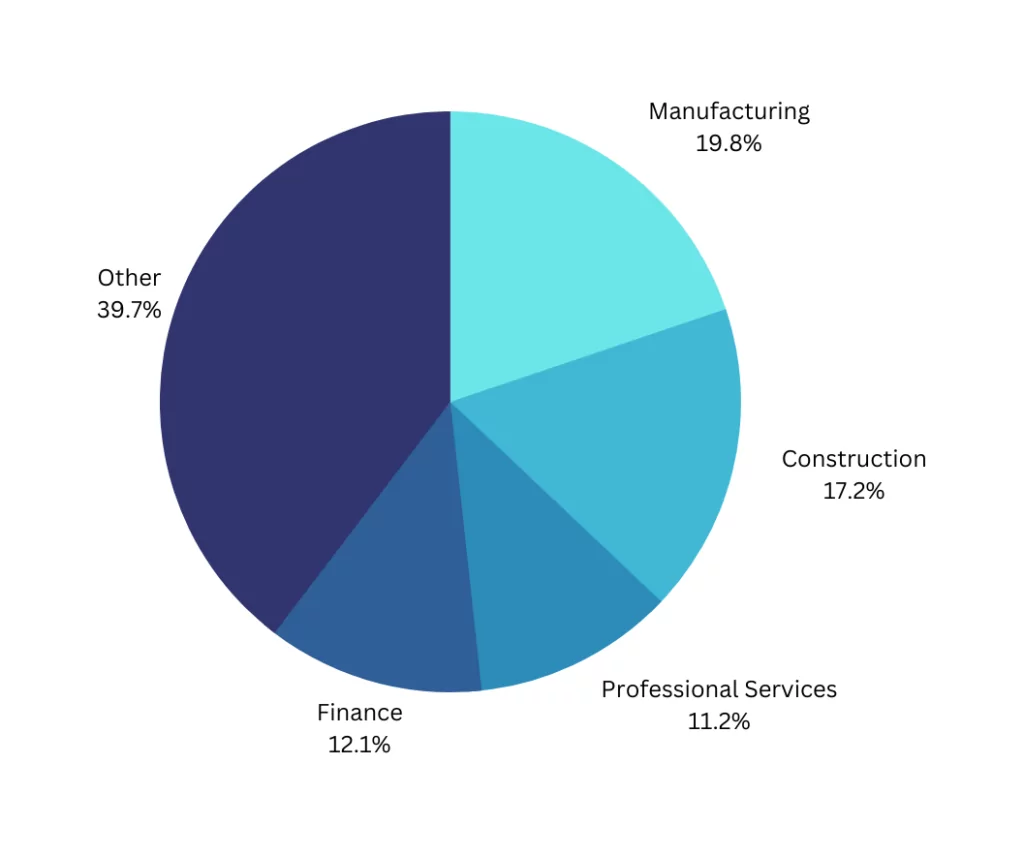
As observed by researchers, they generally use the double-extortion method, which we often encounter in ransomware incidents, and the ransom fee they demand exceeds millions of dollars sometimes. Most of the group’s targets so far have been western countries, and the country with the most cases is the United States. The industries they target are varied. Although the sector they targeted the most is manufacturing, they had many different victims, from appeal and fashion to Healthcare, such as American Dental Association, Deutsche Windtechnik, and Knauf.

Are There Any Relations with Other Groups?
Security researchers state that Black Basta develops and maintains their ransomware kits and tools themselves or collaborates with close threat actors they trust, which also speculates that the group is an offshoot of Conti or has some members of the group.
According to another research, the group was also observed to be linked to the FIN7(Carbanak). This ransomware group had been engaged in criminal activities for several years before the Black Basta. Security researchers examined the toolkits and found one or more developed by the FIN7 threat group. Moreover, the IP addresses, attack techniques, and EDR evasion techniques used by Black Basta also intersect with the FIN7 group, which may indicate that the two groups are closely related or that some threat actors are in both groups.
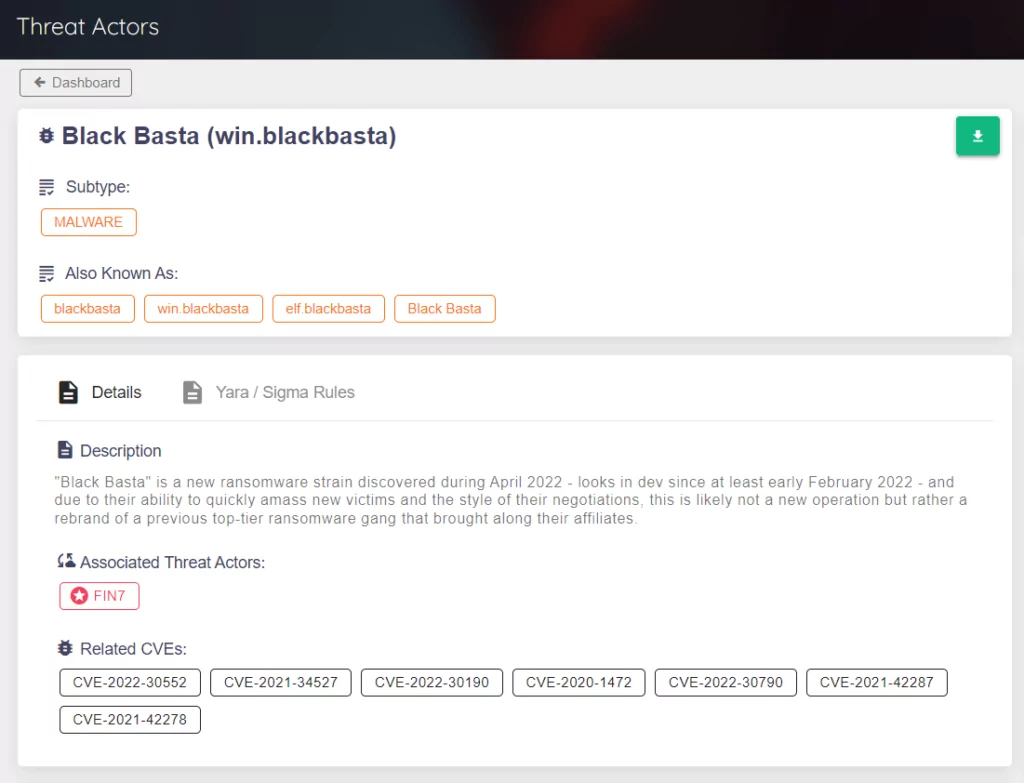
FIN7
The FIN7, also known as the Carbanak or Navigator group, made its name by stealing $1+ billion from more than 100 companies in 2014. They first appeared with credit card skimmer software targeting victims’ point-of-sale systems. They were already one of the most skillful threat groups, but later down the track, they increased their notoriety by adding ransomware to their arsenal.
Black Basta Infection Chain
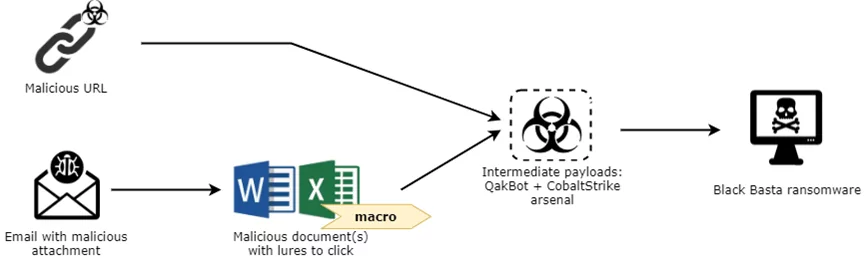
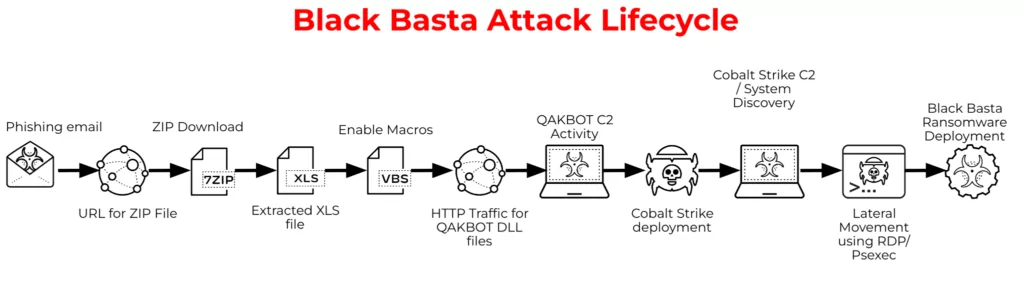
Ransomware must be delivered before its execution, and there are various initial vectors that threat group members can transmit to the victim’s machine using advanced social engineering techniques. These are primarily phishing-style attacks. When the malware -macro-based MS Office documents- sent in such attacks is executed, various macros start the HTTP Traffic for, QakBot, and Cobalt Strike activities begin for system discovery.
It is also known that the group purchases leaked credentials for initial access.
After completing the discovery phase, they send droppers for Black Basta, and the dropper checks some rules and decides whether to deploy the ransomware. If the dropper encounters one of these rules, it terminates itself without deploying the ransomware. When evasion and lateral movement tactics are successful, ransomware is sent to the system in an obfuscated way to avoid being caught by scanners.
When ransomware runs, it encrypts files with ChaCha20 stream cipher, and for each file, it encrypts with a randomly generated key. The key is then passed to RSA encryption with a hard-coded public key to retrieve 512 bytes of the encrypted ChaCha20 key, then it gets added to the end of the encrypted file.
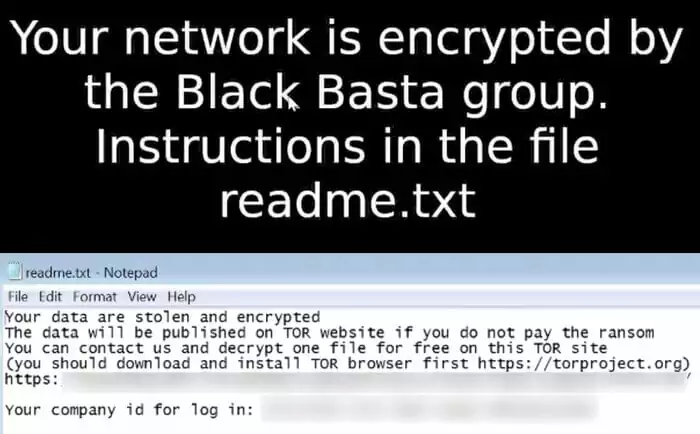
After this point, the file extensions change to “.basta,” the desktop darkens, and a “txt” file is left for the victim to explain how to pay the ransom.
Latest Attacks
Black Basta performs comprehensive analyses and acts selective when choosing its victims. They work carefully by taking various controls and precautions before the encryption phase, and they try to make their attacks successful by blending technical and soft skills.
They also actively continue their malicious activities, with their biggest recent attack affecting Canadian food retail company Sobey in November 2022. Their attack tally constantly expands, and they had more than ten victims last November alone; they continue their activities and haven’t slowed down.
As the volume of cyber threats like ransomware and the damage they cause increases, organizations should strengthen their defenses against ransomware attacks to avoid falling victim to threat actors.
Turning the Tables on Black Basta
A development in the ransomware landscape has emerged with the creation of Black Basta Buster, a decryption tool by SRLabs. This tool addresses a specific vulnerability in the Black Basta ransomware, enabling some victims to recover their encrypted files. As we analyzed, active since April 2022, Black Basta has been linked to many devastating attacks; therefore, this development will surely hinder their ability.
The decryptor, available on GitHub, is adequate for files encrypted by specific versions of the ransomware until late December 2023. This breakthrough offers significant relief for victims affected by these earlier versions of Black Basta ransomware.
CISA’s Advisory for Black Basta
Recently, the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) released a joint Cybersecurity Advisory (CSA) with the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), and Multi-State Information Sharing and Analysis Center (MS-ISAC), shedding light on the Black Basta ransomware variant.
Black Basta has garnered attention for encrypting and stealing data from critical infrastructure sectors, affecting at least 12 out of 16 sectors, including the Healthcare and Public Health (HPH) Sector. Notably, healthcare organizations are particularly attractive targets due to their size, technological dependence, and access to sensitive information.
Key insights from the advisory include:
- Black Basta is categorized as a ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) variant and was first identified in April 2022. Its impact has been felt across North America, Europe, and Australia, affecting over 500 organizations globally as of May 2024.
- Initial access techniques primarily involve spearphishing, with reports of exploitation of vulnerabilities like the ConnectWise vulnerability CVE-2024-1709 and abuse of valid credentials.
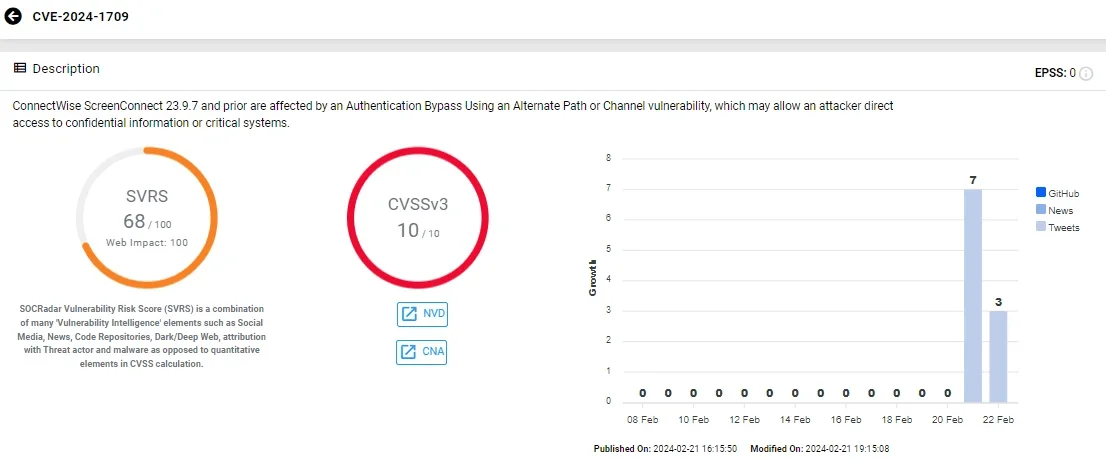
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-1709 (SOCRadar)
- The ransomware employs a double-extortion model, encrypting systems and exfiltrating data. Victims are given a unique code and directed to contact the ransomware group through a .onion URL accessible via the Tor browser.
- Black Basta affiliates utilize various tools for lateral movement, privilege escalation, and data exfiltration, including PowerShell, BITSAdmin, PsExec, and RClone.
To mitigate the risks posed by Black Basta and similar ransomware attacks, the authoring organizations recommend implementing the following measures:
- Patch Vulnerabilities: Regularly update and patch systems, applications, and devices to address known vulnerabilities. Specifically, address vulnerabilities like the ConnectWise CVE-2024-1709 and other known exploits.
- Email Security: Enhance email security protocols to detect and prevent spear phishing attempts, a common initial access technique for Black Basta affiliates.
- Endpoint Protection: Deploy and maintain robust endpoint protection solutions, including antivirus and Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) tools, to detect and mitigate ransomware activity.
- Network Segmentation: Implement network segmentation to contain the spread of ransomware and limit lateral movement within the network.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Maintain regular backups of critical data and ensure backups are stored securely offline. Test backup restoration procedures regularly to verify their effectiveness.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and regularly update an incident response plan that includes procedures for responding to ransomware incidents. Conduct tabletop exercises to ensure readiness.
- Threat Intelligence: Stay informed about emerging ransomware threats and IOCs through threat intelligence sources like CISA, FBI, and industry partners. Use this information to enhance cybersecurity defenses.
- Organizations, especially those in critical infrastructure sectors like healthcare, are encouraged to apply these mitigations promptly to reduce the risk of compromise from Black Basta and other ransomware threats. In case of a ransomware incident, promptly report the incident to your local FBI field office or CISA for assistance.
For more detailed technical information, including MITRE ATT&CK techniques, indicators of compromise (IOCs), and tools used by Black Basta affiliates, refer to the official PDF report from CISA.





































