
The “Evil” of Everything – Part II: Evilginx and EvilQR Rises AitM

In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity threats, it is imperative to maintain vigilance and adaptability. As we delve deeper into the realm of Adversary-in-the-Middle (AiTM) attacks, the second installment of this research series seeks to unravel the intricacies of two notorious tools, Evilginx and EvilQR.
In Part I, we comprehensively explored the evil capabilities of EvilProxy, shedding light on its advanced methodologies and the challenges it poses to organizations and individuals alike. Building upon that foundation, Part II examines Evilginx and EvilQR, two prominent actors in the AiTM arsenal.
Evilginx, known for its deceptive prowess in phishing campaigns, and EvilQR, a potent weapon in QR code-based attacks, exemplify the relentless innovation of cyber adversaries. These tools epitomize the adaptability and sophistication of contemporary cyber threats, underscoring the necessity for robust cybersecurity strategies.
This segment of our research aims to provide an in-depth analysis of Evilginx and EvilQR, elucidating their mechanisms, attack vectors, and potential consequences. By enhancing our understanding of these malicious tools, we equip ourselves to better combat AiTM attacks and fortify our defenses against an ever-evolving digital threat landscape.
Navigating the Evolving Threatscape with EvilGinx
Introducing cutting-edge tools in the dynamic cybersecurity arena often presents novel challenges that demand proactive analysis and awareness. One such tool, EvilGinx, has recently undergone an upgrade, ushering in a new wave of potential risks that warrant close attention and scrutiny. As the SOCRadar Threat Research team delved into the intricacies of this latest version, we unearthed a plethora of vulnerabilities that could have far-reaching consequences across the digital landscape.
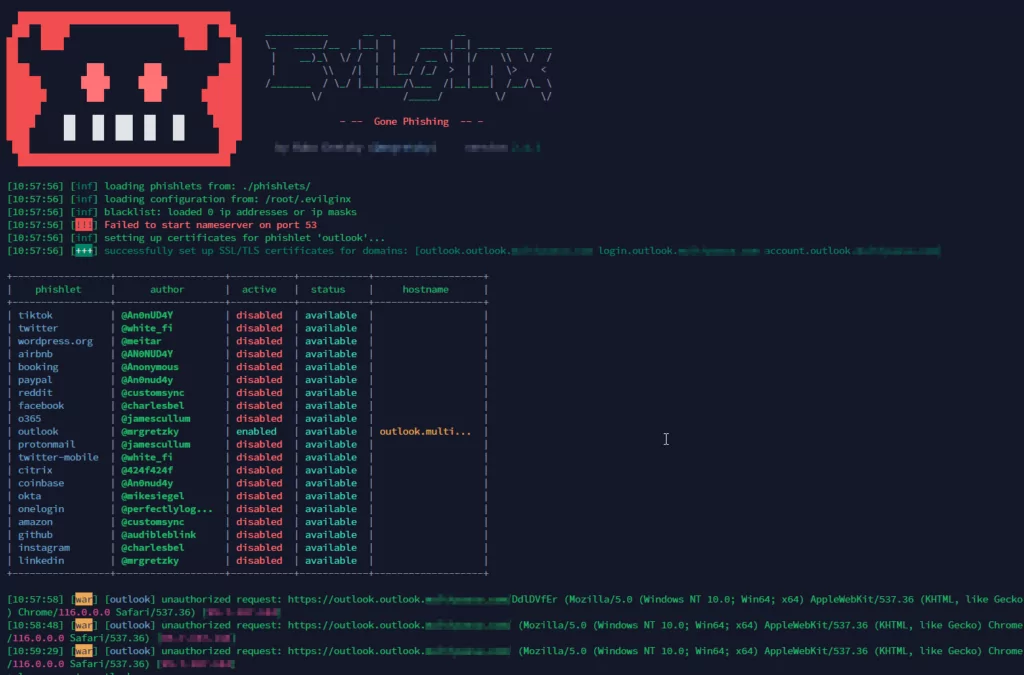
Our comprehensive examination underscored the disconcerting ease with which threat actors could deploy scripts like EvilGinx at minimal expense. Forums dedicated to cybercrime were found to host a marketplace for advanced iterations of such tools, catering to a growing demand for enhanced capabilities. Developer advertisements further reinforced the availability of refined tools, creating an alarming scenario where malicious actors could access powerful weapons with minimal technical hurdles.
During our investigative endeavors, tests were conducted to assess the compatibility of EvilGinx and the Phishlets templates. The results revealed the seamless convergence of the two, allowing attackers to execute intricate phishing campaigns seamlessly. We observed that legitimate services could be redirected to a distinct part with utmost precision when utilizing a reverse proxy hidden behind a domain. This elaborate mechanism demonstrated the tool’s potential to effortlessly deceive end users, making them susceptible to compromise.
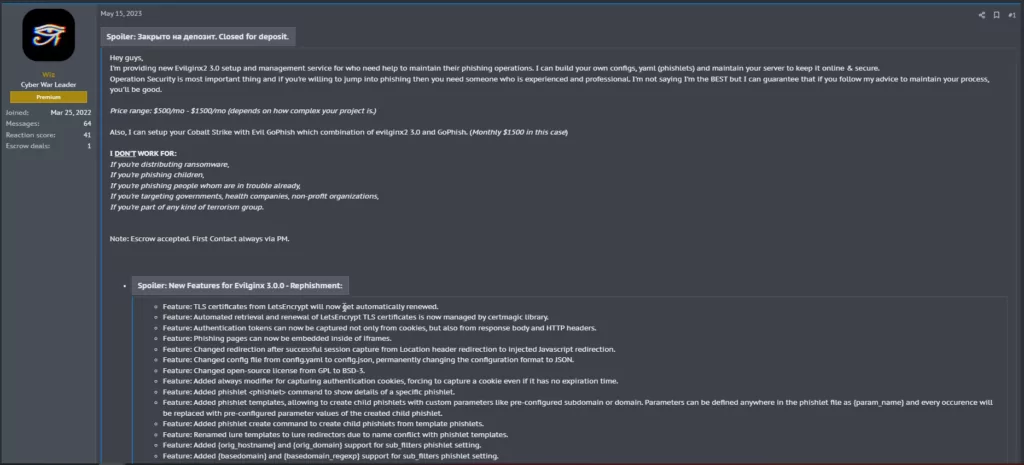
The criticality of this threat is further exacerbated by the fact that the extended functionalities of EvilGinx, often operating behind legitimate domains, could easily infiltrate unsuspecting users’ digital activities. As cyber adversaries refine their techniques, the risks associated with such tools escalate significantly, emphasizing the urgency of comprehensive protective measures.
Organizations and individuals are urged to remain vigilant and well-informed in response to this emerging threat landscape. The SOCRadar Extended Threat Intelligence solution is a reliable bulwark against these evolving risks. By partnering with SOCRadar, entities can ensure real-time awareness of potential threats, enabling proactive mitigation strategies that fortify digital defenses and safeguard sensitive information.
In this era of unprecedented technological innovation, we must be proactive guardians of our digital realm. Through continuous vigilance, informed decision-making, and strategic partnerships, we can navigate the complex terrain of cybersecurity with resilience and confidence.
A Deeper Dive into EvilGinx: Unveiling Vulnerabilities through Rigorous Examination
With the recent unveiling of EvilGinx’s 3.2 version, the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity leaves us in anticipation of future technologies. As we contemplate the implications of this new iteration, it becomes apparent that the rapid pace of technological advancement continues to shape the realm of digital threats.
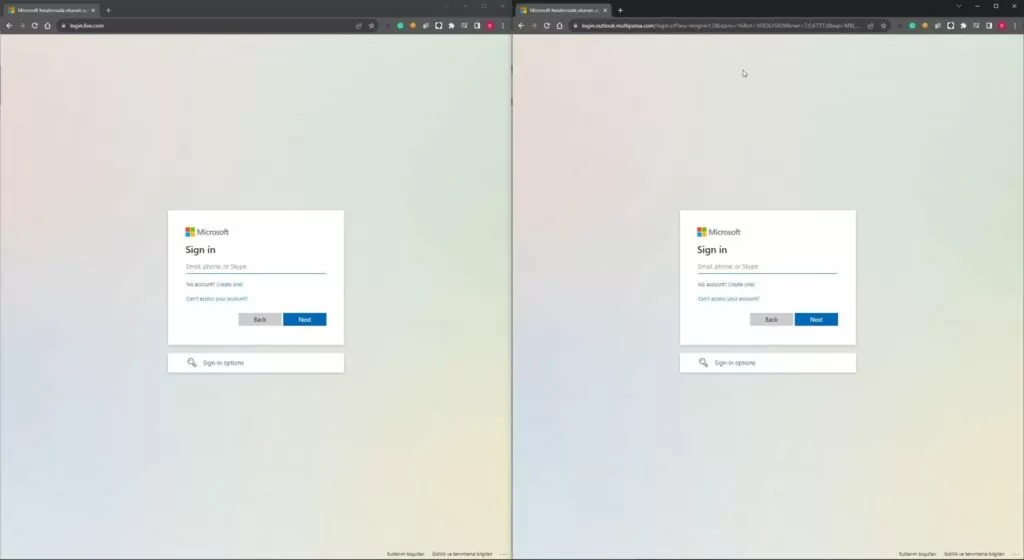
To comprehensively assess the capabilities and potential risks associated with EvilGinx’s technology, our team embarked on an intensive exploration. Beginning with establishing an Amazon Ubuntu server, we created a controlled environment to delve into the inner workings of EvilGinx. A test domain was meticulously set up, and subdomain DNS requests were systematically directed to the Amazon server, enabling us to meticulously configure the setup.

The installation of EvilGinx onto the server facilitated the initiation of our comprehensive testing procedure. For this purpose, an Outlook template was employed, meticulously chosen for its relevance and familiarity. This template was seamlessly integrated into our configured setup, allowing us to simulate real-world scenarios and gauge the tool’s efficacy.
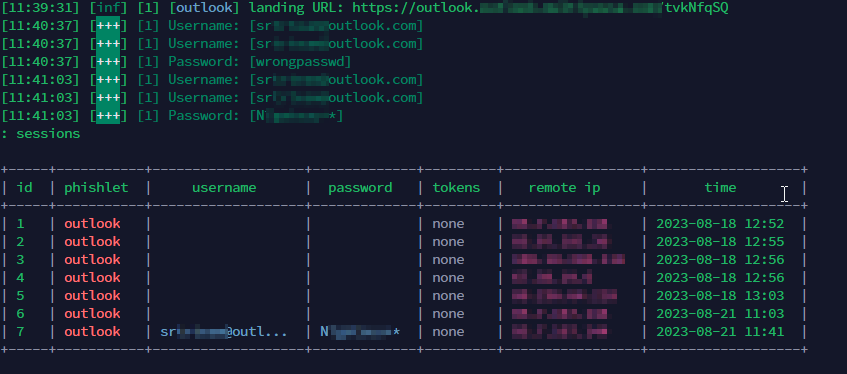
Also, It has been observed that some forum sites are posting job advertisements for an Evilginx developer. Our investigation aimed not only to comprehend the functionalities of EvilGinx but also to uncover potential vulnerabilities that threat actors could exploit. By closely emulating the tactics employed by cybercriminals, we were able to gauge the severity of the risks posed by the tool’s capabilities. These examinations and SOCRadar product capabilities will provide invaluable insights into the multifaceted nature of the threat landscape that cybersecurity professionals and organizations must navigate.
As the digital realm becomes more intertwined with our daily lives, initiatives like SOCRadar Extended Threat Intelligence are crucial pillars of defense. By staying vigilant and informed, organizations and individuals can proactively defend against emerging threats, ensuring the safety and integrity of their digital interactions. Through a steadfast commitment to understanding, vigilance, and innovation, we remain resilient in an ever-changing cybersecurity landscape.
Although Phishlets templates were included in the 2x version of the open source application Evilginx, they were not included in the 3x versions. Recently, it seems that some people are voluntarily sharing ready-made templates for the 3x versions.
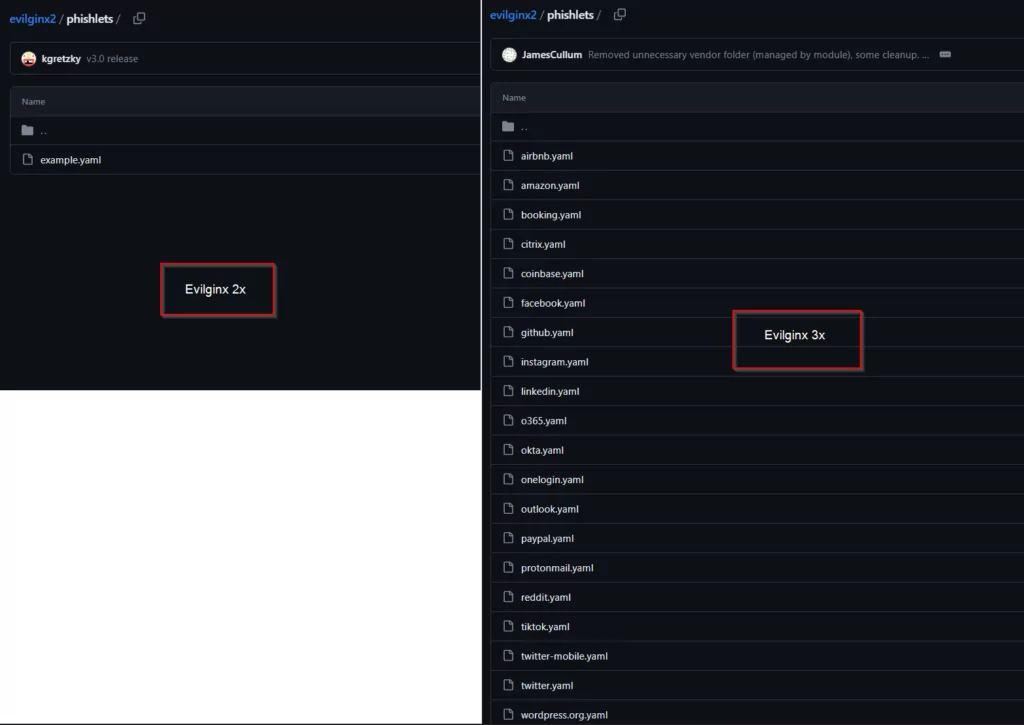
Below are the Phishlets templates shared on GitHub for the Evilginx 3x version. This highlights the increasingly wide range of easy-to-implement cyber threats.
The Rising Threat of EvilQR: Exploiting QR Codes for Unauthorized Access
In contemporary cybersecurity challenges, the emergence of the EvilQR technology has triggered significant concern. This innovative technique, favored by threat actors recently, has introduced a new dimension to the arsenal of cyberattacks. EvilQR, owing to its unique characteristics, has garnered attention for its capacity to exploit legitimate QR codes, ultimately facilitating unauthorized access to sensitive information.

Of paramount concern is EvilQR’s capability to intercept and harvest the cookie information transmitted to the browser when a QR code linked to a legitimate website is scanned. This functionality empowers malicious actors to bypass conventional security measures and directly access a user’s online session. The implications of this capability are substantial, as it enables attackers to assume the user’s identity and potentially compromise confidential data.
Instances of QR code attacks have become increasingly prevalent, serving as a grim reminder of the evolving threat landscape. QR codes embedded within seemingly innocuous emails from well-known services have transformed into potent cyberattack vectors. As individuals become more accustomed to scanning QR codes from trusted sources, the line between legitimate and malicious codes blurs, making it a prime avenue for exploitation by threat actors.
As the cybersecurity community grapples with the ramifications of EvilQR’s emergence, proactive awareness, education, and countermeasures are pivotal in mitigating its potential impact. This research seeks to unravel the intricacies of EvilQR attacks, providing invaluable insights into its methodologies and potential counterstrategies, thus fortifying our collective defenses against this evolving and insidious threat.
Evil QR: A Comprehensive Overview of its Working Structure
Evil QR is a sophisticated Proof-of-Concept tool designed to showcase the practical implications of dynamic QR swap phishing attacks. Rooted in the principles of QRLJacking, this tool offers a novel approach to remote account takeovers by leveraging sign-in QR code phishing techniques.
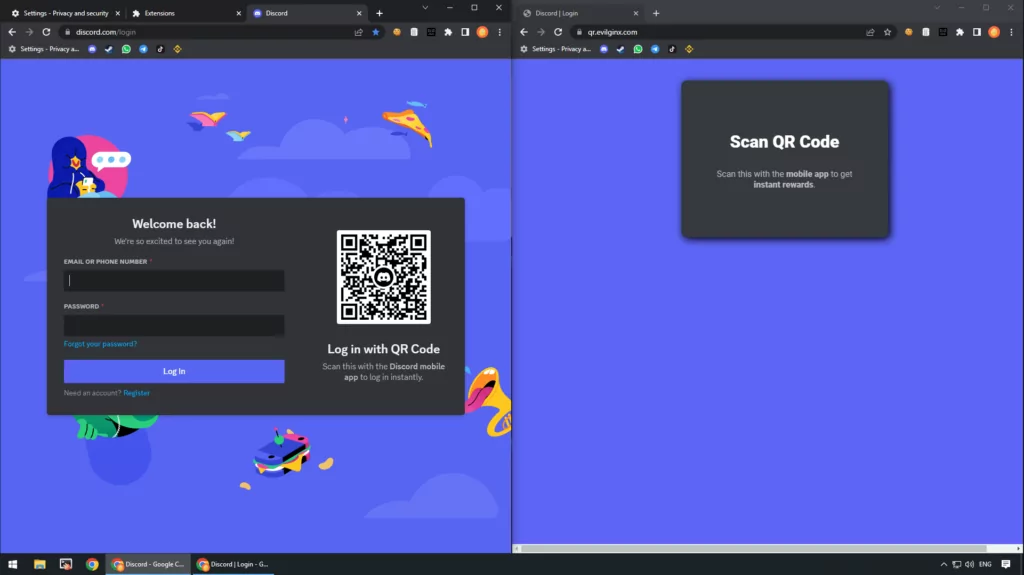
This is the primary interface used by the attacker. Its main function is to extract the sign-in QR code from the target platform. The extension is designed to be compatible with popular web browsers, such as Chrome, ensuring a broad range of potential targets.

This component retrieves the extracted sign-in QR codes and subsequently displays them on the phishing pages hosted by the attacker. The server application plays a pivotal role in ensuring the seamless execution of the phishing attack.
Upon activation, the browser extension scans the web page for sign-in QR codes. Once identified, these codes are extracted and sent to the server application. The server, in turn, displays these QR codes on the phishing pages. Unsuspecting users, believing these to be legitimate sign-in codes, may scan them, inadvertently granting the attacker access to their accounts.
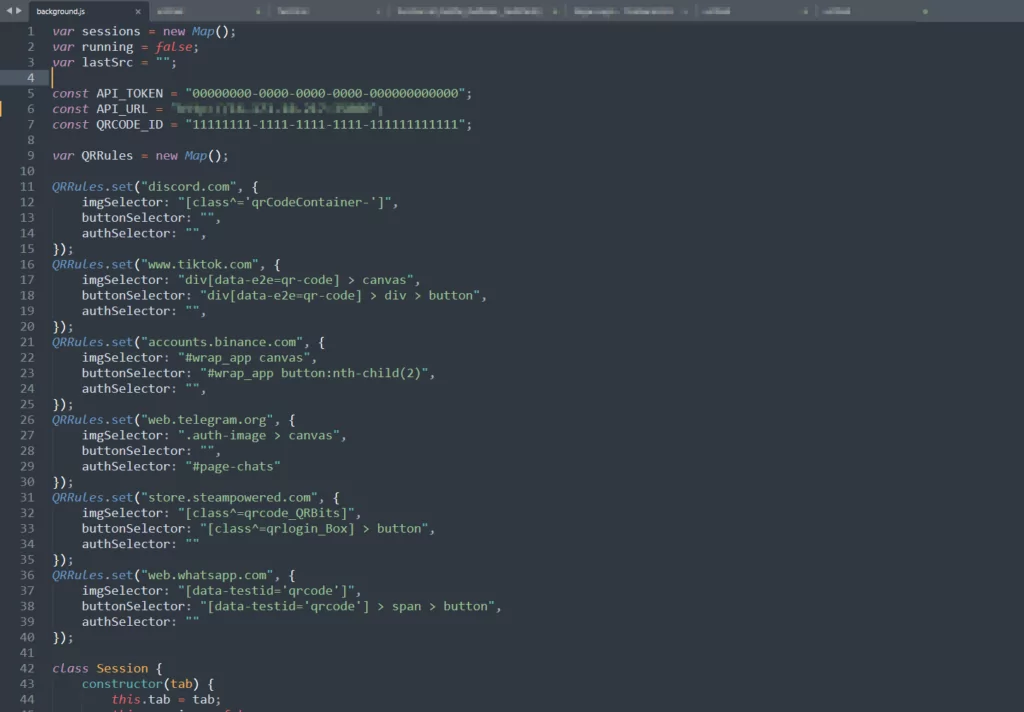
Specific parameters within EvilQR are hardcoded into the extension and server source code for optimal functionality. These parameters include API tokens for authentication, QR code IDs for binding the extracted code with the displayed one, and server details such as IP addresses and ports. Before deployment, modifying these parameters to custom values is imperative to ensure the tool’s effectiveness and security.
Evil QR underscores the evolving nature of phishing attacks and the importance of user awareness. Demonstrating the feasibility of QR code-based phishing highlights the need for robust security measures and user education to counter such threats.
In conclusion, Evil QR is a testament to the innovative ways cybercriminals can exploit seemingly secure technologies. As with all security tools, its purpose is to educate and inform, allowing for the development of countermeasures and strategies to protect against such attacks.



































