
Understanding Identity and Access Management (IAM)
In a world where digital tools, cloud services, and remote work have become the norm, managing who has access to sensitive data and systems will determine an organization’s security success. Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a security framework designed to ensure the right people have the right access at the right time.
Organizations today face growing cybersecurity threats and operational challenges, making IAM solutions a necessity. With the rise in phishing attacks, social engineering schemes, and account takeover incidents aiming for unauthorized access, a well-implemented IAM system secures your digital assets while also simplifying access control and increasing user productivity, serving as a critical defense mechanism.
This article explores Identity and Access Management (IAM) in detail, including its key components, benefits, and best practices. By understanding IAM, you can strengthen your organization’s security posture and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.

“Identity and Access Management” illustrated by DALL-E
What is Identity and Access Management?
At its core, Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a set of policies, processes, and technologies that help organizations manage user identities and control access to digital resources. It ensures that employees, partners, customers, or even devices have appropriate access while keeping unauthorized users out.
IAM serves two primary purposes: security and efficiency. By verifying user identities and setting access permissions, IAM prevents unauthorized access, reduces data breach risks and identity attacks, and automates access-related tasks.
How IAM Works
IAM relies on three core principles:
- Identification: Determining who a user is using unique credentials (e.g., username or ID).
- Authentication: Verifying the user’s identity through passwords, Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), or biometrics.
- Authorization: Granting or limiting access to resources based on predefined roles or policies.
Whether managing employee logins, granting customer access to specific applications, or securing third-party integrations, IAM ensures that access to resources is controlled, monitored, and secure.
Key Components of IAM
An effective Identity and Access Management (IAM) system consists of several core components, each working together to ensure secure and seamless access to resources. Here are the key components that form the backbone of any IAM solution:
- User Provisioning and Deprovisioning
User provisioning involves creating and managing user accounts, assigning roles, and granting access rights to systems and applications. Deprovisioning ensures that access is revoked when users leave the organization or no longer require specific permissions. This process helps reduce the risk of unauthorized access and insider threats, which are often exploited in social engineering and phishing attacks. - Authentication
Authentication verifies a user’s identity before granting access. This is achieved through credentials like passwords, biometrics, or Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). MFA adds an additional layer of security by requiring multiple verification methods, such as a password combined with a one-time code sent to a mobile device. This extra layer helps mitigate the risk of account takeover (ATO) attacks. - Authorization
Authorization determines what resources a user can access and what actions they can perform. It is often role-based, where permissions are granted based on job roles, ensuring users have the least privilege access necessary to perform their tasks. Authorization policies are critical for minimizing risks while maintaining operational efficiency. - Directory Services
Directory services act as a central repository for user identities and access information. Systems like Active Directory (AD) or cloud-based directories store user credentials, group memberships, and access policies. These services enable IAM solutions to authenticate and authorize users efficiently across various systems. - Password Management
Password management involves enforcing policies for creating, storing, and resetting passwords. IAM systems ensure strong password practices, such as complexity requirements, regular updates, and self-service password resets. This minimizes the risk of password-related breaches while reducing IT support workloads. - Access Governance
Access governance focuses on monitoring and auditing user access to ensure compliance with organizational policies and regulations. It provides visibility into who has access to what, identifies unnecessary privileges, and ensures that access rights align with security standards.
How These Components Work Together
In a fully integrated IAM system, these components interact seamlessly to secure access:
- User provisioning creates accounts with appropriate roles.
- Authentication validates user identities upon login.
- Authorization ensures they can access only the resources they are allowed.
- Directory services manage identity data, while password management enforces secure login practices.
- Access governance continuously monitors and audits these processes to ensure compliance.
Together, these components enable organizations to manage user identities efficiently, secure access to resources, and maintain a strong cybersecurity posture.
Protect Your Organization’s Sensitive Data from Dark Web Threats
Your organization’s sensitive data could already be put up for sale on the Dark Web, exposing you to significant risks. It’s essential to stay ahead of these threats by actively monitoring and mitigating potential security issues before they escalate.
SOCRadar’s Dark Web Monitoring module allows you to track leaked credentials and confidential information across multiple Dark Web marketplaces. Our tool scans various forums and alerts you to unauthorized data exposure, helping prevent unauthorized access to your systems.
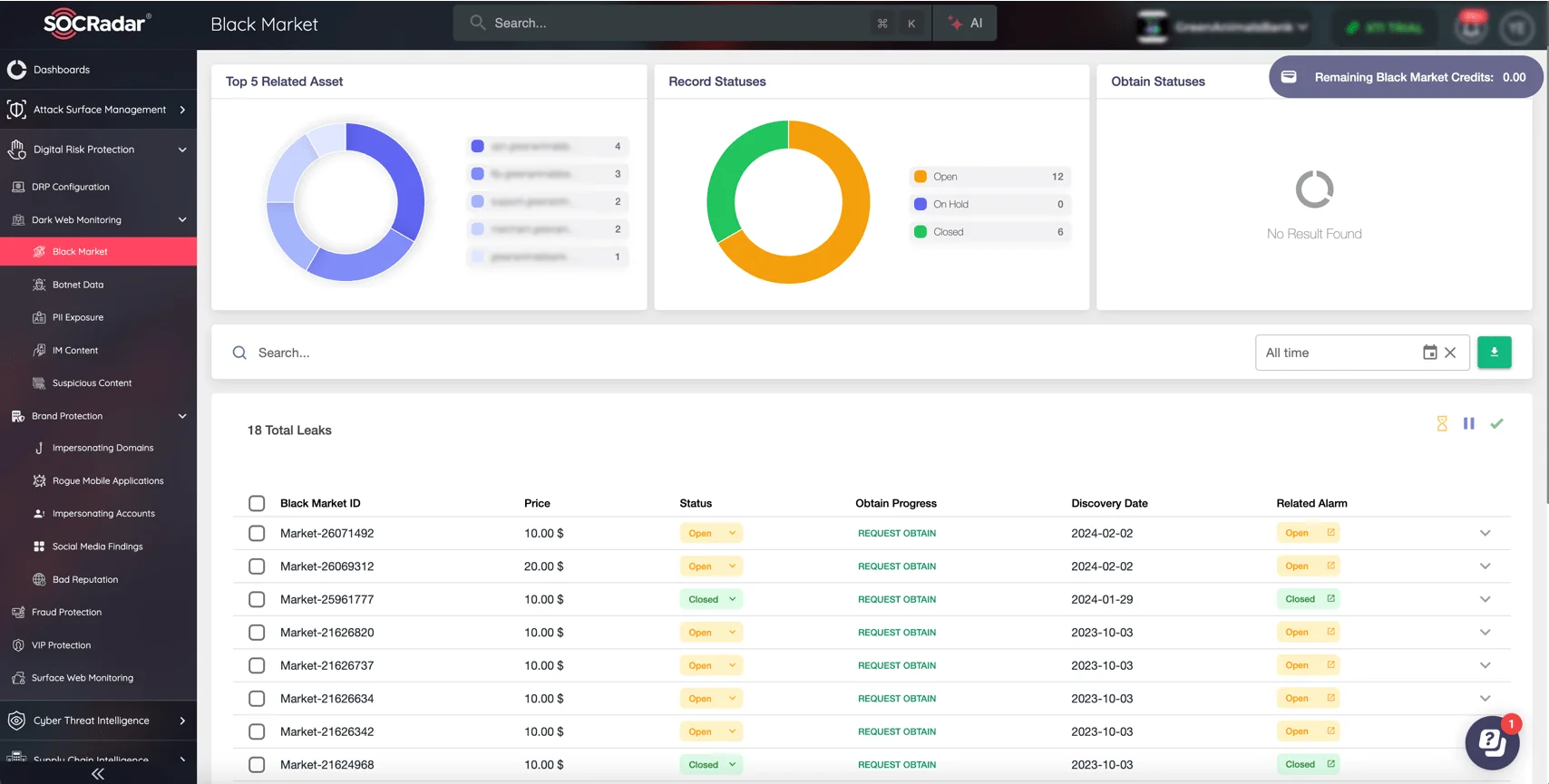
Monitor your company’s exposure via SOCRadar’s Dark Web Monitoring
Additionally, SOCRadar’s Dark Web News module keeps you updated about the latest trends and discussions in Deep Web and Dark Web forums, including hacker activities on platforms like Telegram. This feature helps organizations monitor emerging threats and take proactive steps to address risks before they become serious security concerns.
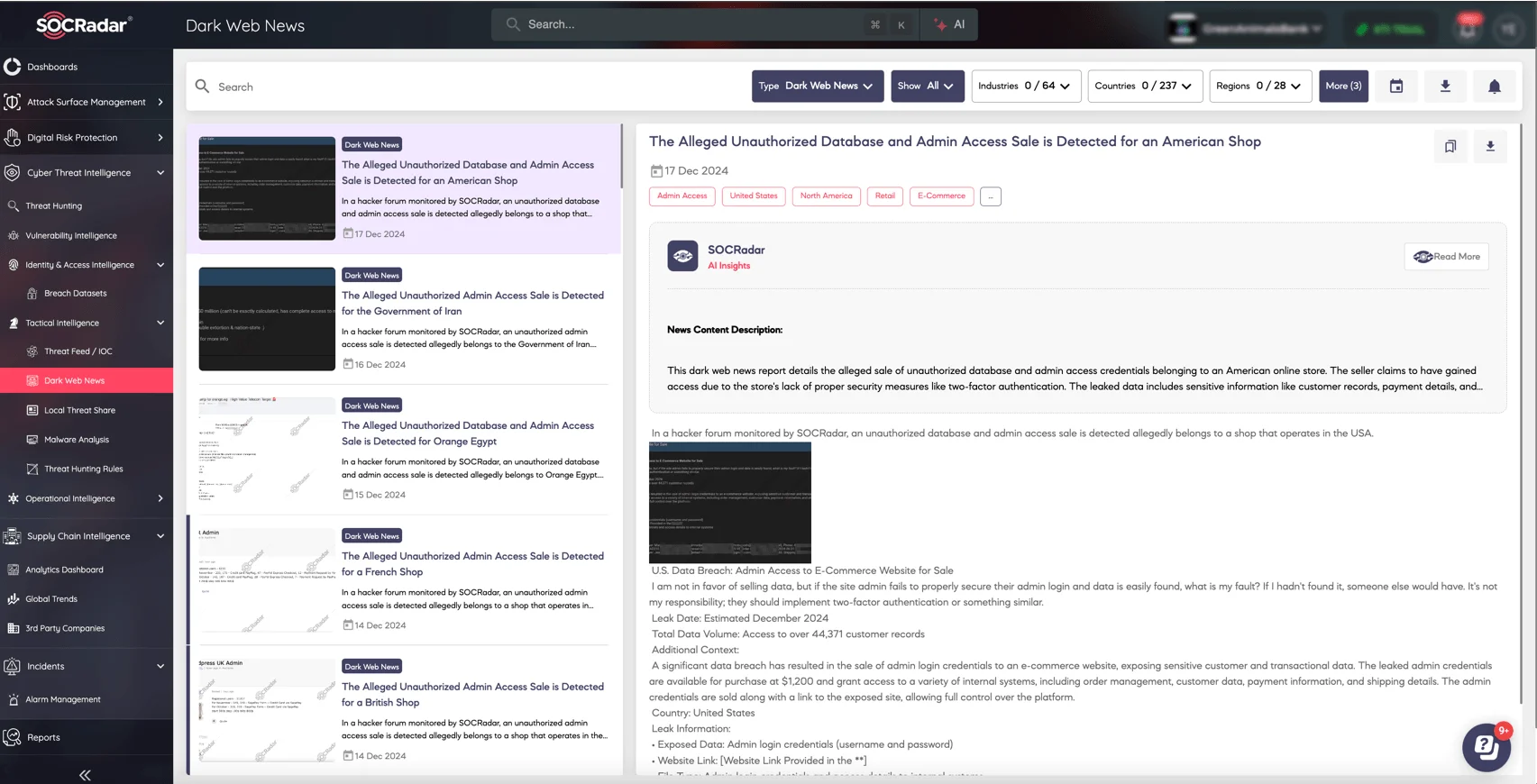
Recent access sale threats, viewed on SOCRadar Dark Web News
Benefits of Implementing IAM Solutions
Implementing an Identity and Access Management (IAM) solution offers significant benefits by enhancing security, streamlining user management, and ensuring compliance.
IAM improves security by restricting access to authorized users, utilizing features like Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), continuous monitoring, and least-privilege access. It simplifies user management by automating provisioning, deprovisioning, and role management, reducing errors and saving time. IAM also boosts productivity with Single Sign-On (SSO), eliminating the need for multiple passwords.
Additionally, it lowers operational costs by reducing IT support burdens and improving security to minimize breach-related expenses. IAM helps organizations comply with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA by enforcing access controls and generating audit-ready reports.
Together, these benefits make IAM an essential tool for protecting digital resources, improving operations, and achieving compliance.
Best Practices for Effective IAM
Implementing an Identity and Access Management (IAM) system is only the first step toward securing an organization’s resources. To ensure its effectiveness, organizations must adopt best practices for managing and maintaining IAM systems. Here are key practices to follow:

How to implement Identity and Access Management, best practices
- Regularly Review User Access Rights, Automate Provisioning/Deprovisioning
Over time, users may accumulate unnecessary or outdated permissions, increasing the risk of unauthorized access. Regularly reviewing and auditing user access ensures that permissions align with current roles and responsibilities. It is best to establish a routine process for reviewing access rights, particularly after role changes, terminations, or department transfers.
On another note, automating the process of granting and revoking access can ensure users have the right permissions at the right time. It also reduces errors and ensures that inactive accounts are deactivated promptly. You may also integrate IAM with HR systems to streamline onboarding and offboarding processes.
- Enforce Strong Password Policies and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Passwords remain a common entry point for cyberattacks. Enforcing strong password policies can reduce the risk of breaches caused by weak or reused credentials.
Also, be reminded that relying solely on passwords is no longer sufficient. Implementing MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide additional verification factors, such as a one-time code or biometric authentication.
- Provide User Training and Awareness
IAM systems are only as effective as the people using them. Educating employees about access management policies, phishing risks, and secure password practices helps reduce human error and insider threats.
Conduct regular training sessions and workshops within your company to keep employees informed about IAM-related security measures. This training is especially important as phishing attacks and social engineering schemes are increasingly targeting organizations. One particularly dangerous tactic is Business Email Compromise (BEC), where attackers impersonate company executives or colleagues to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data or financial systems. These impersonations often lead to credential theft or the compromise of company assets.
- Audit and Monitor IAM Logs
Continuous monitoring of IAM logs helps identify suspicious activity, such as failed login attempts, unauthorized access, or unusual user behavior. Use automated tools to monitor IAM logs and set up alerts for anomalies that could indicate a security threat.
- Implement the Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP)
Limit user permissions to the minimum level required to perform their job. This reduces the risk of misuse and prevents attackers from accessing critical systems if a user account is compromised.
Failing to adhere to these best practices can lead to significant security vulnerabilities, such as unauthorized access, data breaches, and compliance violations. Inadequate IAM management increases the risk of insider threats, phishing attacks (such as BEC), and account takeovers, which can result in operational disruptions, reputational damage, and financial losses. By following these practices, organizations can mitigate risks and ensure that their IAM systems effectively protect sensitive resources.
Protect Against Employee Credential Compromise and Unauthorized Access with SOCRadar XTI
Organizations are continuously challenged by the need to protect against unauthorized access. SOCRadar’s Identity & Access Intelligence module provides a strong solution to detect and mitigate credential compromise risks.
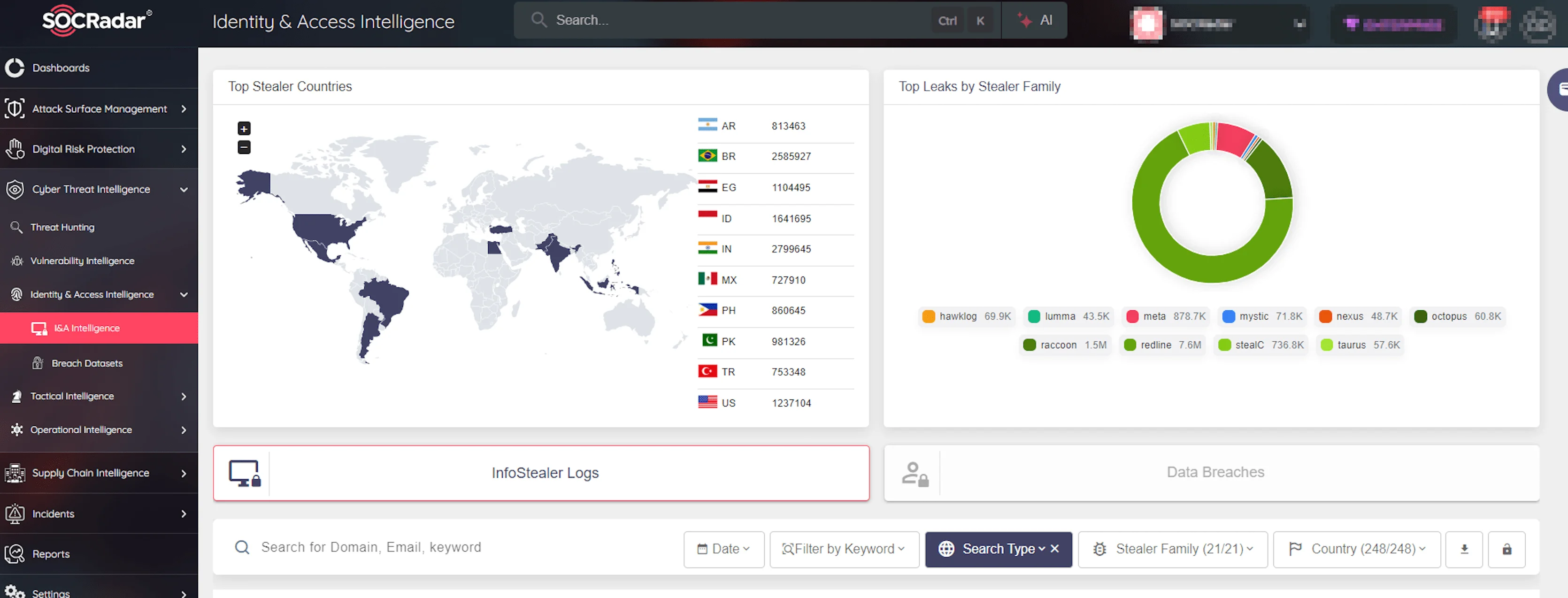
SOCRadar’s Identity and Access Intelligence module page
With this module, you can:
- Identify Compromised Credentials: Track compromised credentials across various sources, including data leaks and the Dark Web.
- Monitor Risky Access Patterns: Analyze login attempts and user behavior to flag suspicious activity.
- Gain Deep Insights: Understand how, when, and where credentials were exposed with detailed access information, helping to detect early signs of potential breaches.
- Access Stealer Logs: Analyze extensive stealer log data to identify exposed credentials and stop attackers before they can infiltrate your network.
Beyond the Identity & Access Intelligence module, SOCRadar also offers:
- Threat Hunting: Leverage SOCRadar’s extensive breach datasets and stealer logs to search for exposed credentials across millions of records. This proactive approach allows you to identify risks and take action before they escalate.
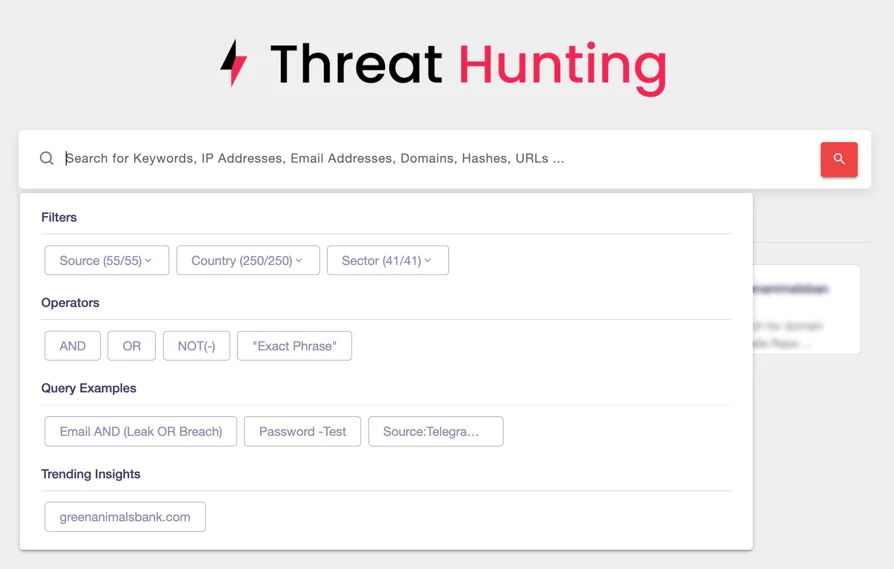
Threat Hunting search page on SOCRadar XTI platform
- Email Threat Analyzer: This tool detects and blocks phishing attempts aimed at your employees, safeguarding your organization from credential theft. It is available for free trial on SOCRadar LABS, alongside other SOC tools.
Free Email Threat Analyzer tool (SOCRadar LABS’ SOC Tools)
With SOCRadar’s extensive toolset, you can easily take the steps to protect your organization and employees against phishing, credential compromise, and unauthorized access.
Future Trends in IAM
As cybersecurity challenges evolve, so do the technologies and approaches that shape Identity and Access Management (IAM). Organizations are adopting advanced solutions to address modern threats, improve user experiences, and adapt to decentralized work environments.
Here are the key trends shaping the future of IAM:
- Biometric Authentication: Passwords are often vulnerable to theft and misuse, making biometrics a secure and user-friendly alternative. Biometric authentication uses unique physical or behavioral traits, such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or voice patterns, to verify identities.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is revolutionizing IAM with intelligent automation, anomaly detection, and adaptive access control. Machine learning algorithms analyze user behavior to detect suspicious activities in real time and automatically adjust access permissions when necessary. For instance, AI-powered systems can flag unusual login patterns and prompt additional verification to prevent unauthorized access.
- Decentralized Identity Solutions: Decentralized identity moves away from traditional, centralized identity providers by giving users control over their credentials. Using blockchain or distributed ledger technologies, users can securely manage and share their identities without relying on a single authority. For example, verifiable digital credentials stored in decentralized wallets reduce the risks tied to large, centralized identity databases while providing users with greater privacy and control.
- Zero Trust Architecture: Zero Trust is a security model that assumes no user or device can be trusted by default, even within the corporate network. IAM plays a critical role by continuously verifying identities and assessing risk in real time before granting access. For example, access to sensitive data or systems is only allowed after rigorous authentication and authorization, ensuring that users receive the minimum permissions needed.
- Passwordless Authentication: The shift toward passwordless authentication methods – such as biometrics, security keys, and one-time tokens – eliminates the risks associated with traditional passwords. This approach improves security and simplifies the user experience. For instance, smartphone-based authentications or physical security keys allow users to log in securely without needing to manage complex passwords.
- IoT Integration: As IoT devices grow, IAM solutions are expanding to manage and secure device identities and access rights across networks. Organizations must extend their IAM capabilities to manage IoT access in industrial and corporate environments, ensuring every device is tracked and controlled to prevent unauthorized activity.
By embracing these innovations, like biometrics, AI, and Zero Trust, your organization can ensure its IAM systems are prepared to handle emerging cybersecurity threats and modern workplace challenges.
Conclusion
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is an essential framework for securing access to systems, data, and applications while improving operational efficiency. From verifying identities to granting appropriate access, IAM solutions play a key role in protecting organizations against unauthorized activity and regulatory non-compliance.
By understanding IAM’s components, benefits, and best practices, organizations can better manage access, reduce security risks, and streamline operations. As IAM continues to evolve with trends like biometric authentication, AI-driven controls, and Zero Trust, its role in protecting businesses will only become more critical.
Investing in a well-implemented IAM system ensures your organization remains resilient, secure, and prepared for the challenges of today’s digital landscape.



































