
What is Technical Cyber Threat Intelligence and How to Use It
As cyber threats become more sophisticated, many organizations pay more attention to their security programs. Organizations of all sizes build security teams to deploy network solutions and address threats.
A key component to the success of these initiatives is access to up-to-date cyber threat intelligence. This blog describes the significance of technical threat intelligence for organizations.
Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI)
Before deep-diving into the definition of terms, we should describe what Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) is. CTI is a form of threat intelligence that can better understand the threats it currently deals with or will deal with in the future.
What are the Types of Cyber Threat Intelligence?
Threat intelligence falls into 4 categories within the framework of applicable information: Strategic, Tactical, Operational, and Technical. For these four types of intelligence, data collection, analysis, and consumption of intelligence differ. SOCRadar generates intelligence at different levels with the information it collects and ensures the best use of data.
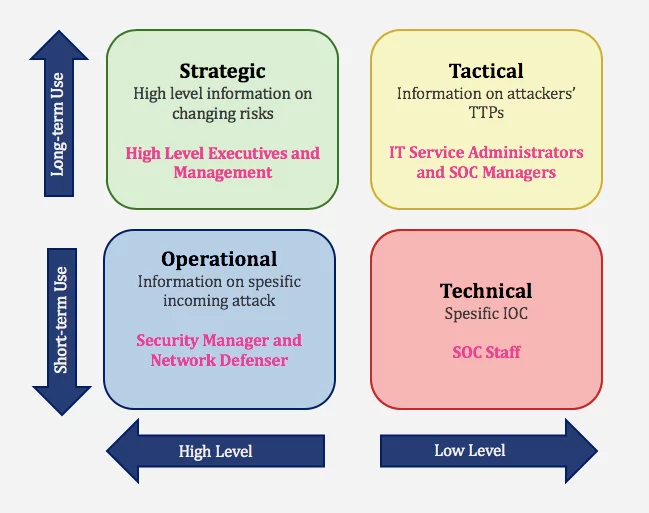
- Strategic Cyber Intelligence: The audience does not need technical knowledge. High-level information on changing risks. High-level information on risk-based intelligence is used by high-level decision-makers (Executives and management). Whitepapers, policy documents, and publications are examples of strategic cyber intelligence.
- Operational Cyber Intelligence: Actionable information about specific incoming attacks. It is infiltrating hacker chat rooms to anticipate the incoming attacks.
- Tactical Cyber Intelligence: Details of threat actor tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs).
- Technical Cyber Intelligence: It means technical threat indicators such as specific IOC for SOC Staff.
What is Technical Cyber Threat Intelligence?
Technical threat intelligence focuses on particular indicators or proof of an attack and serves as a foundation for analyzing such incidents. An analyst from Threat Intelligence looks for indicators of compromise (IOCs) and command and control channels, tools, etc., including reported IP addresses, phishing email content, malware samples, and bogus URLs. Because IOCs like rogue IPs or fraudulent URLs become outdated in a matter of days, communicating technical intelligence at the right time is crucial.
Who Uses Tactical CTI, Why, and How?
The difference between tactical and technical intelligence is that tactical CTI is malware used to carry out an attack, whereas technical CTI is the detailed information on the malware implementation.
Other examples of technical CTI include malicious endpoint IP addresses and domains, phishing email headers, malware hash checksums, and so on. SOC personnel and Incident Response Teams ingest technical threat intelligence.
Technical CTI indications are gathered through ongoing campaigns, attacks on other businesses, and data feeds given by external third parties. In most cases, these inculcators are collected as investigations into attacks on various organizations.
This information aids security experts in incorporating the discovered signs into defensive systems like 105/IPS, firewalls, and endpoint security systems, hence improving the detection processes used to detect attacks early on. It also aids in detecting malicious traffic and suspicious IP addresses that are used to transmit malware and spam.
Technical CTI Use Case: Triage & Blocking FW or Security Products
Technical CTI can help quickly determine whether or not there is cause for concern. In a triage case, technical users first check their local CTI store or call the APIs of their CTI sources such as SOCRadar Threat Feeds. If there is an IOC match, they proceed with their incident handling process. And it is blocked at FW level or other security products. If there is no match, they move on to the following message.
Using CTI on a “check “first, trust later” basis” can significantly reduce the number of time analysts spend at the technical level trying to distinguish between trusted and malicious information.
What SOCRadar Provides
SOCRadar® provides;
- Phishing Domain Lists, URLs
- Keeps track of cybersecurity incidents and informs organizations about attackers’
- Malicious Domain Lists, IPs, Hashes, URLs, etc.
- Integrate its feeds with the existing security products to support incident triage & block FW or other security products.
- Provide malware analysis
Discover SOCRadar® Free Edition
With SOCRadar® Free Edition, you’ll be able to:
- Discover your unknown hacker-exposed assets
- Check if your IP addresses tagged as malicious
- Monitor your domain name on hacked websites and phishing databases
- Get notified when a critical zero-day vulnerability is disclosed
Free for 12 months for 1 corporate domain and 100 auto-discovered digital assets.
Try for free

































