
Top Phishing Tricks Attackers Use to Target Employees & The Recent ‘You’re Fired’ Campaign
Phishing remains one of the most prevalent and effective cyber attack methods, thriving on deception to steal sensitive information or deliver malware. These attacks manipulate human behavior, using fear, urgency, and curiosity as tools to trick victims into clicking malicious links or downloading dangerous attachments.
Phishing tactics have evolved significantly, becoming both more targeted and widespread. In fact, phishing is the most common email attack method, accounting for nearly 40% of all email threats, while a staggering 94% of organizations in a study reported experiencing email security incidents in 2024. These statistics emphasize how deeply phishing continues to infiltrate today’s cybersecurity landscape.
One of the latest examples is the “You’re Fired” phishing campaign, a scheme that preys on employees’ fear of job termination. This campaign showcases how phishing continues to evolve, combining emotional manipulation with technical obfuscation to bypass traditional defenses. In this article, we’ll examine this campaign and explore broader phishing tactics, their effectiveness, and how organizations and individuals can defend against them.
The Recent ‘You’re Fired’ Phishing Campaign as an Example
Phishing campaigns constantly evolve, exploiting timely and emotionally charged themes to maximize their success. The “You’re Fired” phishing scam has emerged as a recent and highly manipulative example, using fear and urgency to exploit victims.
As the campaign leverages the sensitive topic of job loss, it serves as a case study of how attackers adapt their tactics to prey on human vulnerabilities and current events.
This scam begins with an email disguised as an official employment termination notice, designed to alarm and prompt immediate action from the recipient. Its emails are crafted to appear highly authentic, often using subject lines such as “Action Required: Tribunal Proceedings Against You.”
In one instance that was observed, the attacker used supposedly official components in their email, such as the UK coat of arms or fake Employment Tribunal case numbers, in an attempt to win the victim’s trust.
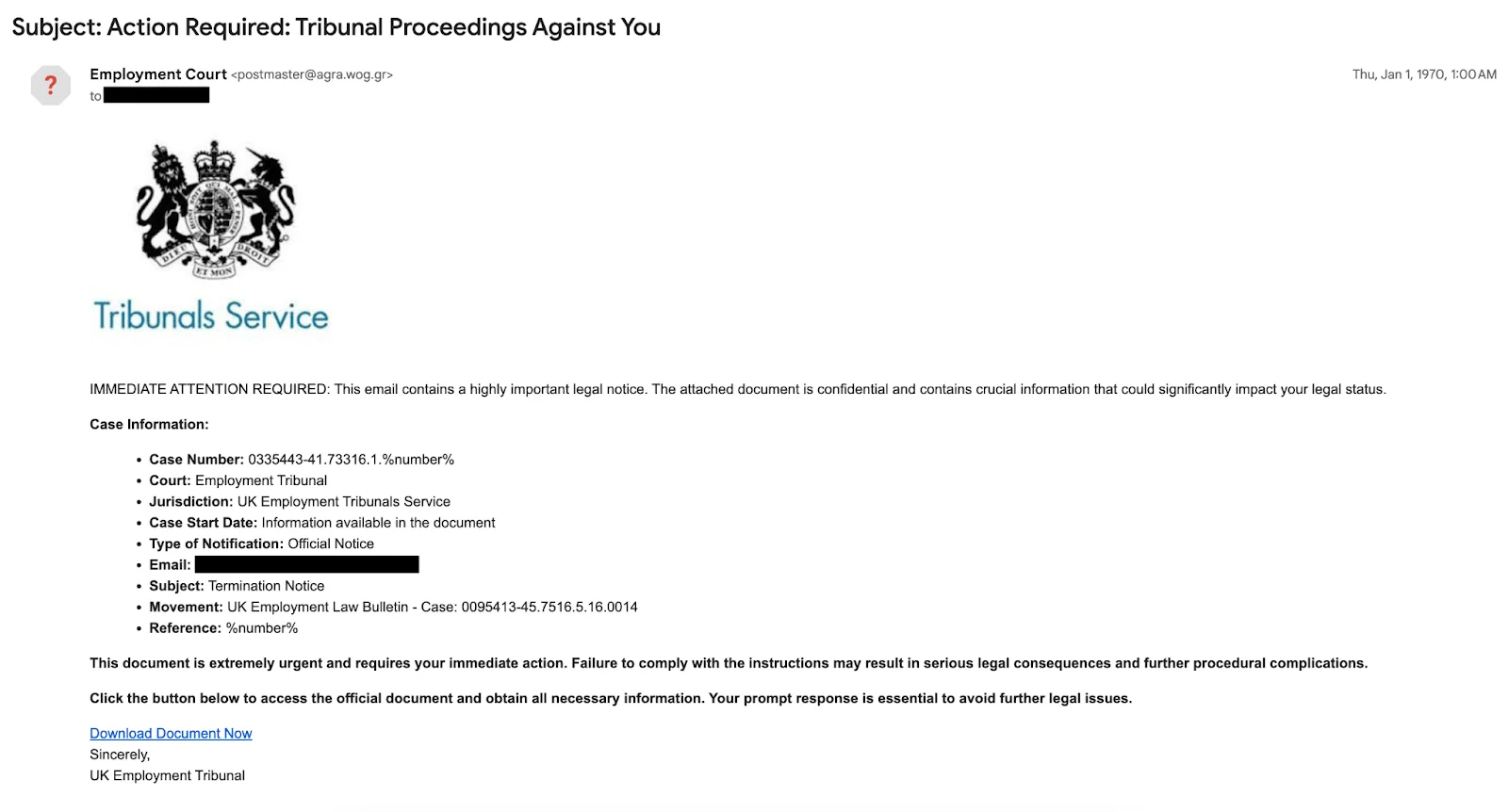
Attacker’s phishing email, disguised as a “termination notice” (Source: Cloudflare)
Breaking Down the Tactics
The campaign relies on a range of manipulative tactics to deceive its targets and compel them to engage with the fraudulent content. Common elements in these phishing emails include:
- Fake termination letters: These often come with malicious attachments claiming to provide more details about the termination.
- Links to fraudulent HR portals: Victims are directed to fake login pages designed to steal their credentials.
- Requests for personal information: Attackers gather sensitive details under the guise of processing termination claims.
- Threats to financial stability: Claims of losing access to paychecks or benefits if immediate action isn’t taken.
The combination of these techniques heightens the pressure on victims, making them more likely to comply without verifying the legitimacy of the email.
How the Attack Unfolds: From Email to Malware
The scam follows a structured process that begins with a phishing email and escalates into malware deployment:
- Deceptive Links: Victims are urged to click a “Download Document Now” button, which leads to a fraudulent Microsoft page. This page uses branding and plausible messaging, such as “This file cannot be opened on this device,” to manipulate the victim into downloading malware.
- Malware Download: The victim downloads a file, often a RAR archive containing a malicious Visual Basic script, such as “Processo Trabalhista.vbs” or “Labor Lawsuit.vbs.”
- Malware Execution: Once executed on a Windows device, the script installs additional malware, which could include banking trojans or infostealers.
This well-crafted scam demonstrates how attackers use both psychological manipulation and technical obfuscation to bypass security measures and achieve their objectives.
Note: Indicators of compromise (IOCs) for this campaign, including malicious URLs and file hashes, will be provided in a dedicated section at the end of this blog.
Why Such Phishing Tricks Are So Effective
The effectiveness of phishing campaigns like “You’re Fired” lies in their calculated exploitation of human emotions and psychological triggers. By invoking fear, anxiety, and urgency, these scams manipulate victims into taking impulsive actions, bypassing critical thinking. The fear of job loss, combined with the sense of immediacy created by formal notices, leads recipients to respond without verifying the legitimacy of the message.
Scammers amplify their success by leveraging perceived authority and authenticity. Official-looking email addresses, professional formatting, and the use of recognizable symbols, such as government crests or organizational logos, foster trust. Victims are more likely to comply with demands when they believe the communication is from a credible source, a legitimate company.
Phishing campaigns also capitalize on victims’ lack of familiarity with cybersecurity best practices. On the other hand, many employees remain unaware of the red flags associated with phishing attempts, such as unexpected links, unusual email formatting, requests for sensitive information, or impersonation attempts involving an executive, colleague, or HR. This lack of awareness significantly amplifies the effectiveness of these scams.
For a broader understanding of phishing’s impact, explore SOCRadar’s blog on essential cybersecurity statistics for 2024.
Protect Your Brand with SOCRadar’s Brand Protection Module
Cybercriminals increasingly target trusted brands, leveraging impersonation tactics to steal sensitive information, conduct fraud, and harm your reputation. SOCRadar’s Brand Protection module offers comprehensive monitoring to track your brand’s presence across the web, including social media platforms, domains, and dark web marketplaces.
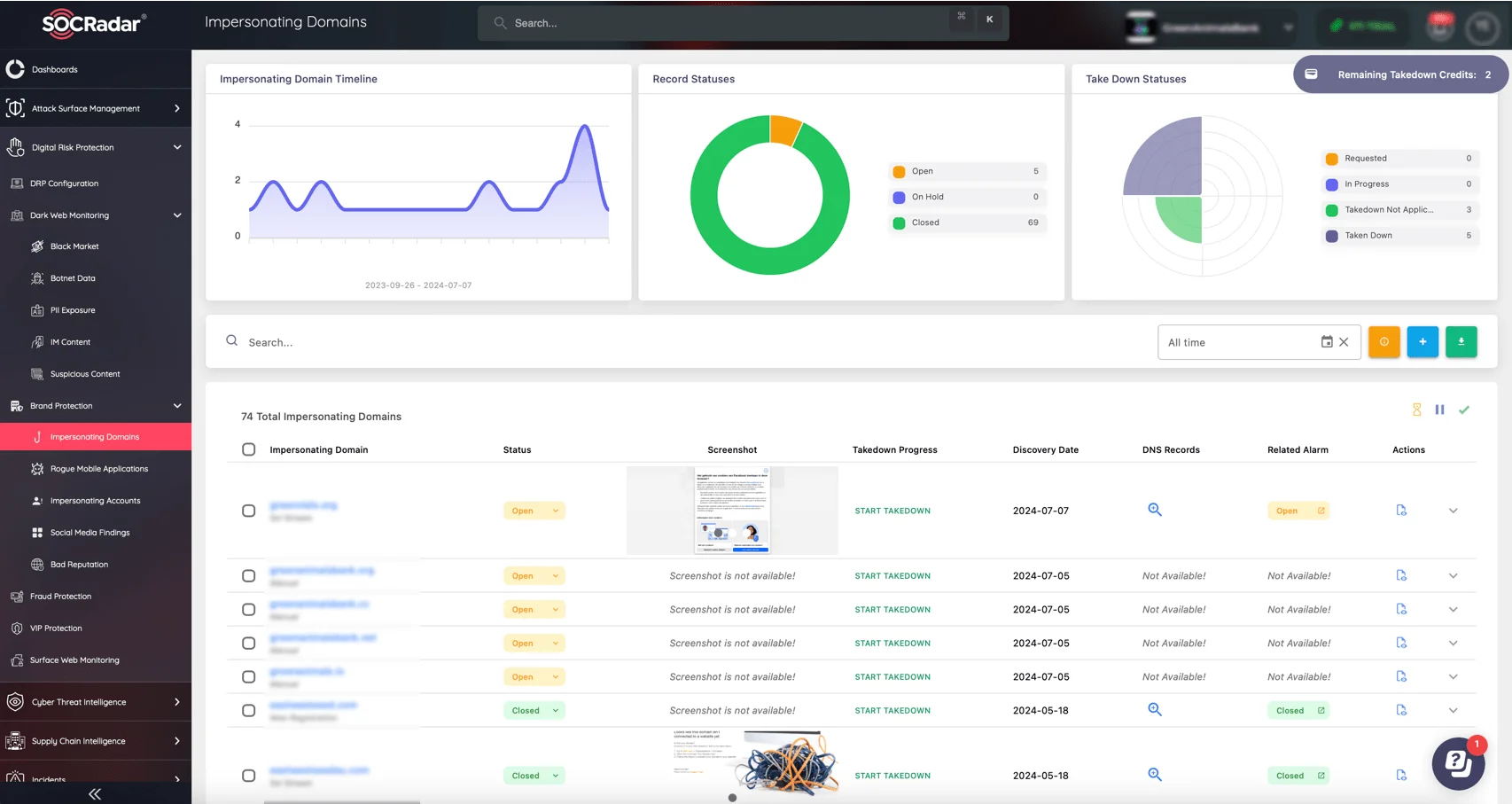
SOCRadar’s Brand Protection module, Impersonating Domains
The module identifies counterfeit websites, fraudulent social media profiles, and brand impersonations, providing a layer of defense against attacks that could impact your reputation and customers.
- Detect Brand Impersonation: Automatically identify fake domains, social media accounts, and mobile apps impersonating your brand.
- Real-Time Alerts: Receive instant notifications when a new threat is detected, enabling rapid response and mitigation.
- Take Action Quickly: Streamline the process of investigating and removing counterfeit assets to minimize damage to your brand’s trust and integrity.
- VIP Protection: C-suite executives are prime targets for phishing and impersonation attacks. SOCRadar continuously monitors for exposed personal data, compromised credentials, and potential CEO fraud.
Ensure your brand stays protected across all online channels. With SOCRadar’s Brand Protection module, you can confidently monitor, detect, and take action against brand misuse and impersonation attempts.
Common Phishing Ploys and Red Flags
Following our discussion of the “You’re Fired” phishing campaign, it’s clear that phishing is a highly flexible attack method, with cybercriminals using various strategies to deceive their victims. While triggering a sense of urgency was central to that particular scam, phishing attacks employ many different tactics to achieve success.
Attackers often craft convincing scenarios to exploit common human behaviors, increasing the likelihood of their targets falling victim. Let’s look at some of the most common ploys and the tactics that make them so effective.
What Are the Top Tricks Used in Phishing?
Here’s a look at some of the most prevalent strategies cybercriminals use in phishing campaigns. These strategies appear across various attack methods, including but not limited to fraudulent emails, voice scams, fake advertisements, spear phishing, Business Email Compromise (BEC), and SEO poisoning.
Fake Invoices and Payment Requests
Attackers often send emails posing as vendors or suppliers, claiming unpaid invoices or overdue payments. Victims are tricked into clicking malicious links or downloading fake invoice attachments, which can lead to credential theft or malware installation.
For instance, a recent phishing campaign exploited DocuSign’s Envelopes API to send fake invoices that appeared legitimate, tricking recipients into sharing sensitive financial information. This scam leveraged DocuSign’s credibility, and also impersonated high-profile names like Norton and PayPal, making it particularly deceptive and effective in targeting businesses globally.
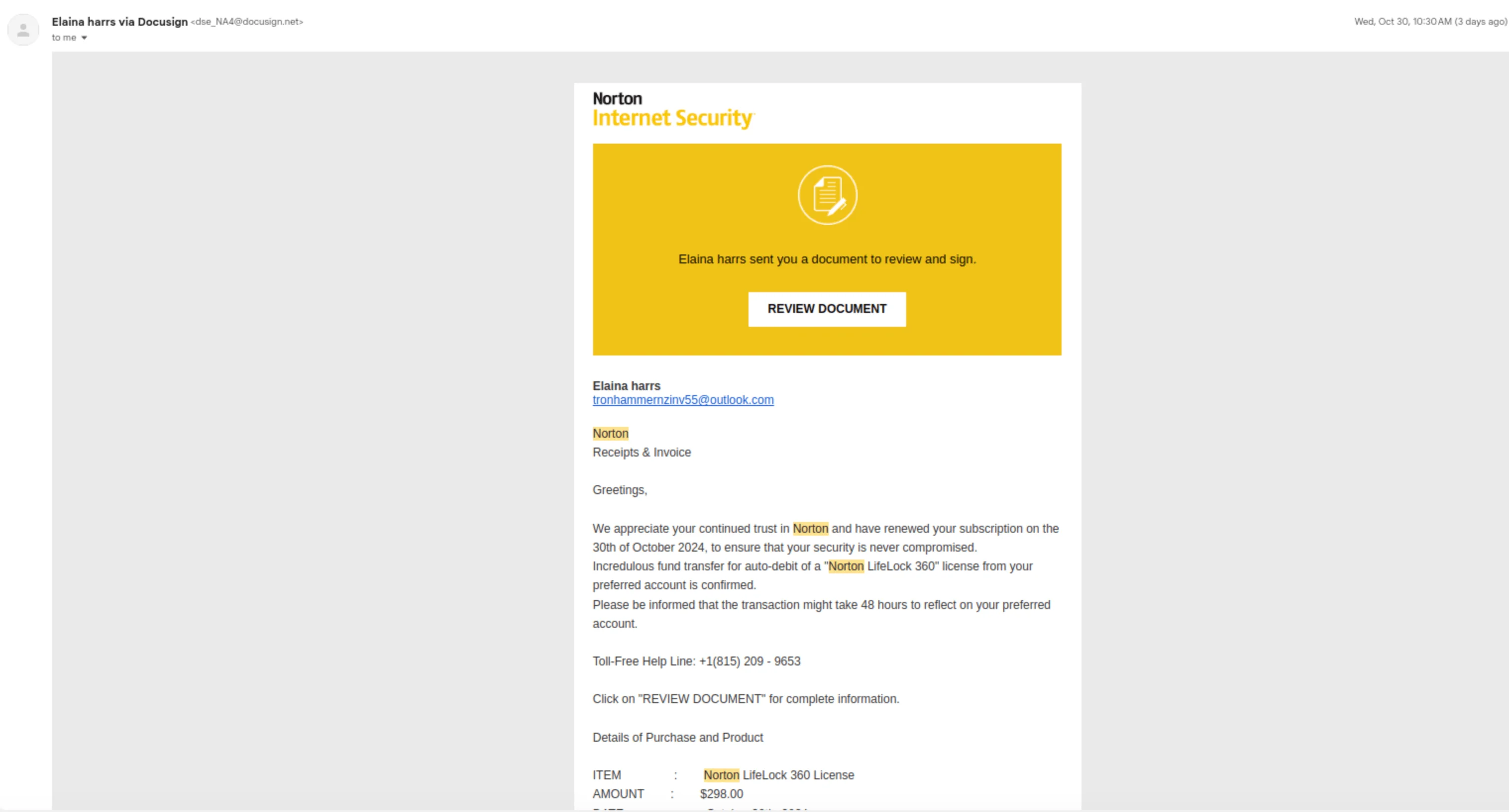
Fake invoice email by DocuSign, impersonating Norton (Source: wallarm)
Password Reset and Verification Scams
Phishers send fake password reset or verification requests, frequently claiming suspicious activity on accounts among other scenarios. These emails include links to convincing but fraudulent login pages where victims unknowingly reveal their credentials.
In 2024, attackers exploited Apple’s password reset feature using “MFA bombing.” Victims were bombarded with password reset notifications across their devices, followed by calls from scammers impersonating Apple support. The attackers sought to obtain reset codes or trick users into pressing “Allow,” enabling them to reset Apple IDs and gain account access.
Event-Based Phishing
Major events like the Olympics, elections, natural disasters, and also other high-profile occasions are frequently exploited by attackers. These scams often include fake ticket sales, fraudulent donation requests, or deceptive event updates, impersonating trusted organizations and domains.
During the Paris 2024 Olympics, a phishing campaign dubbed “Ticket Heist” used over 700 fake domain names to sell fraudulent tickets.
Stay ahead of phishing threats with SOCRadar LABS’ free Phishing Radar service. By leveraging AI-powered Digital Risk Protection, Phishing Radar scans millions of domain registrations to detect malicious domains and provides real-time alerts on suspicious activity. Protect your organization from targeted scams with advanced detection capabilities.

Possible phishing domains that targeted the official Olympics event (SOCRadar LABS’ Phishing Radar)
Tech Support Scams
Pretending to be from a well-known tech company, attackers claim there’s an issue with your device or account. Victims are urged to download software or provide remote access, leading to further exploitation.
In 2023, a deceptive Google search result for “YouTube” directed users to a tech scam. The link led to a fake “Windows Defender – Security Warning” pop-up, falsely claiming the user’s computer was infected and urging them to call a fraudulent support number. This scam exploited search engine rankings and the familiarity of trusted platforms to mislead users into disclosing sensitive information or making payments.
The impersonation of Microsoft by the attackers in this attack seems to be a common tactic; in 2024, Microsoft was the most impersonated brand in phishing schemes, accounting for over 43% of all attempts.
Tax and Refund Scams
Leveraging the fear of audits or the lure of tax refunds, scammers pose as tax authorities. They request personal and financial information, which is then used for identity theft or fraudulent transactions.
Previously, cybercriminals distributed the Emotet malware through emails impersonating the IRS, urging recipients to complete a fake W-9 tax form. Once opened, the attachment downloaded Emotet, enabling attackers to steal sensitive information like login credentials and financial data.
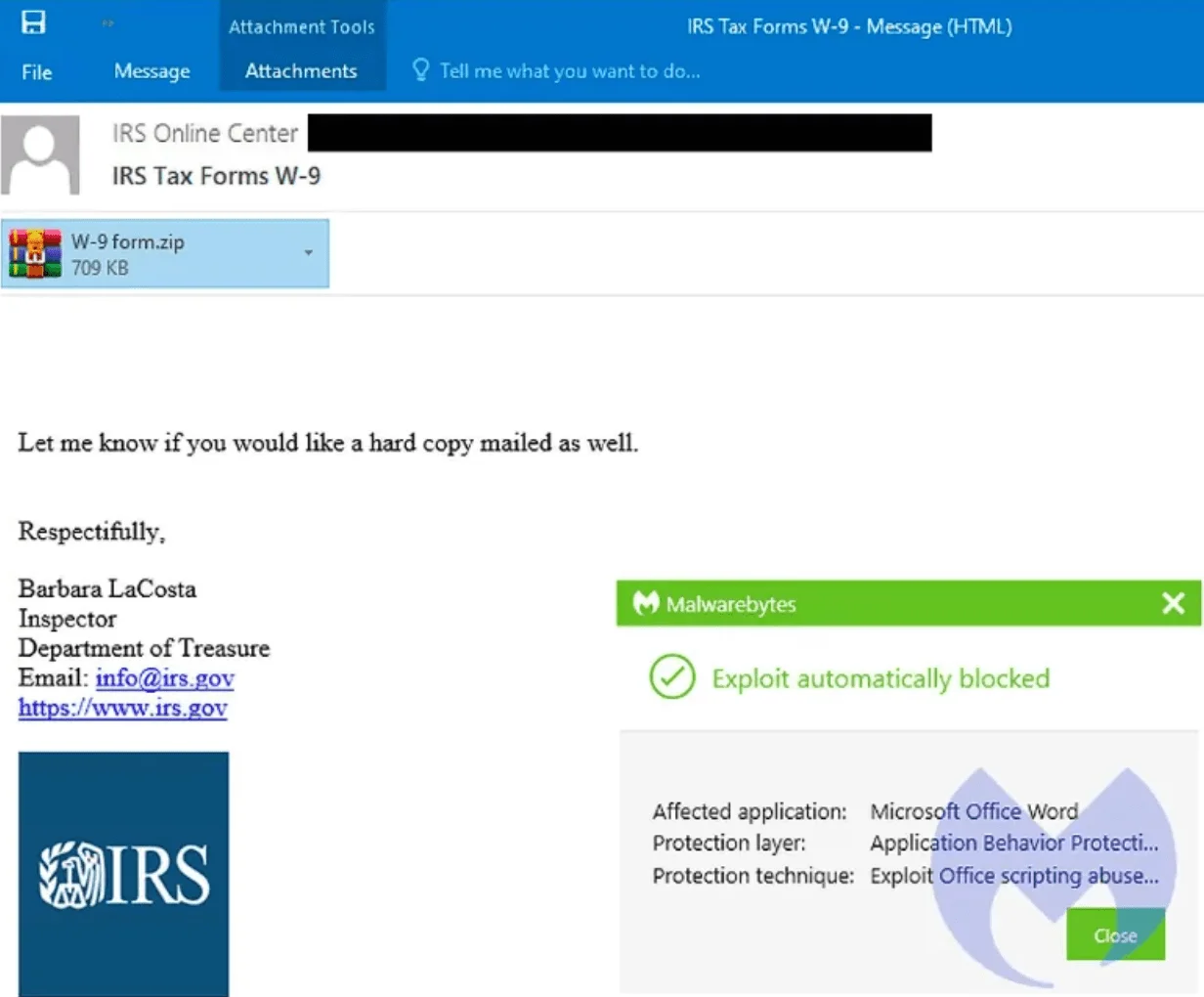
An Emotet phishing email impersonating IRS
Phishing Kits on the Dark Web
Many phishing campaigns are fueled by readily available phishing kits sold on the Dark Web. These kits provide templates, tools, and instructions, enabling even novice attackers to launch sophisticated scams. Advanced kits include features like automated credential harvesting and integration with malware payloads, making phishing attacks more accessible and dangerous.
On November 8, 2024, SOCRadar’s Dark Web News module detected a hacker forum post advertising an advanced phishing script. Fully controllable via Telegram, the script can allegedly be used to target platforms like Shopify, Ecwid, OpenCart, and WooCommerce, capturing OTPs (One-Time Passwords) and enabling payment-handling phishing with advanced features and easy instructions.
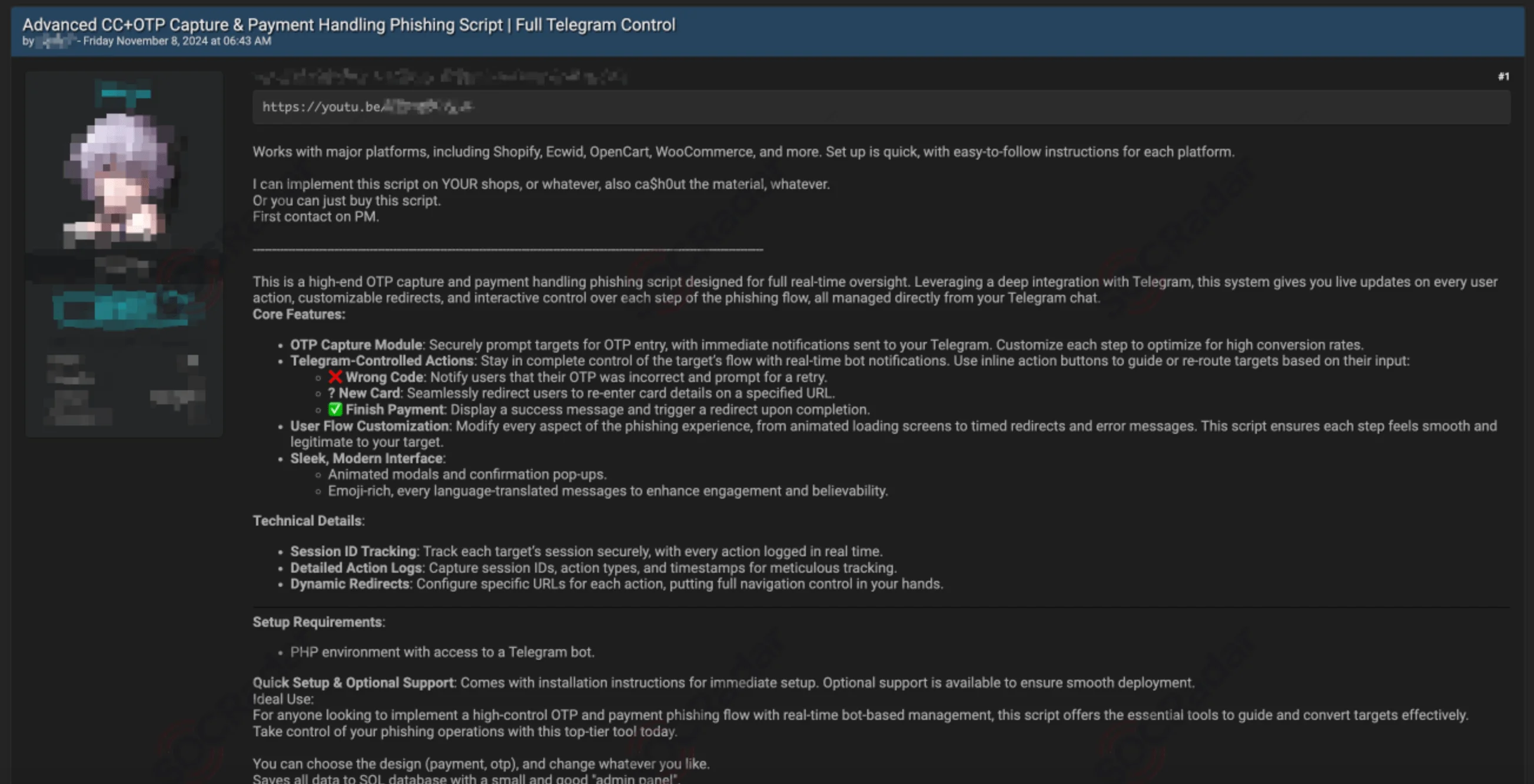
Threat actor sells advanced phishing script on a Dark Web forum (SOCRadar Dark Web News)
By continuously monitoring hacker forums and underground marketplaces, SOCRadar’s Dark Web News module identifies posts and discussions that indicate potential risks, such as phishing kits and other malicious tools targeting your platforms. You can easily filter and search through these findings to identify emerging threats that could affect your organization.
SOCRadar Dark Web Monitoring: The Complete Solution for Your Protection
While Dark Web News helps you stay informed on the latest discussions, SOCRadar’s Dark Web Monitoring takes it a step further by proactively safeguarding your brand.
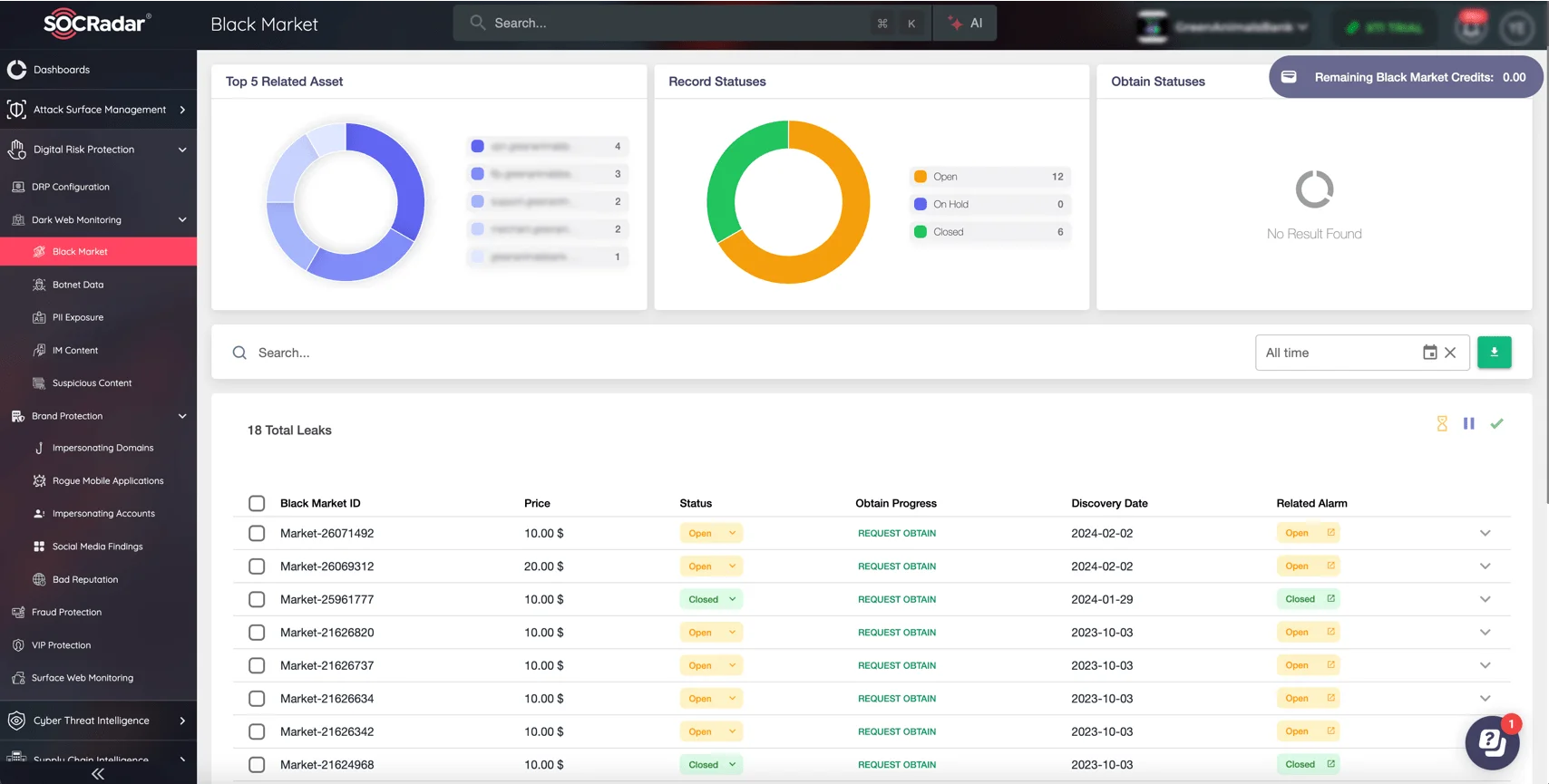
SOCRadar Dark Web Monitoring empowers you to detect and act on threats quickly, ensuring your organization’s data stays protected against evolving cybercrime tactics.
With comprehensive monitoring, this module:
- Identifies stolen credentials, leaked company data, or cyber attack attempts across hidden corners of the internet.
- Provides immediate notifications about threats targeting your organization, giving you the time to respond effectively before attacks escalate.
- Allows you to monitor hacker activities, identify vulnerabilities, and prevent future attacks with thorough analysis and tracking.
Recognizing the Red Flags
While phishing emails are often polished, certain red flags can help identify them:
- Statements like “Your account will be suspended!” aim to create panic.
- Emails from unknown senders or unsolicited communications should raise suspicion.
- Hover over links to verify the URL before clicking.
- Legitimate organizations rarely request credentials or financial data via email.
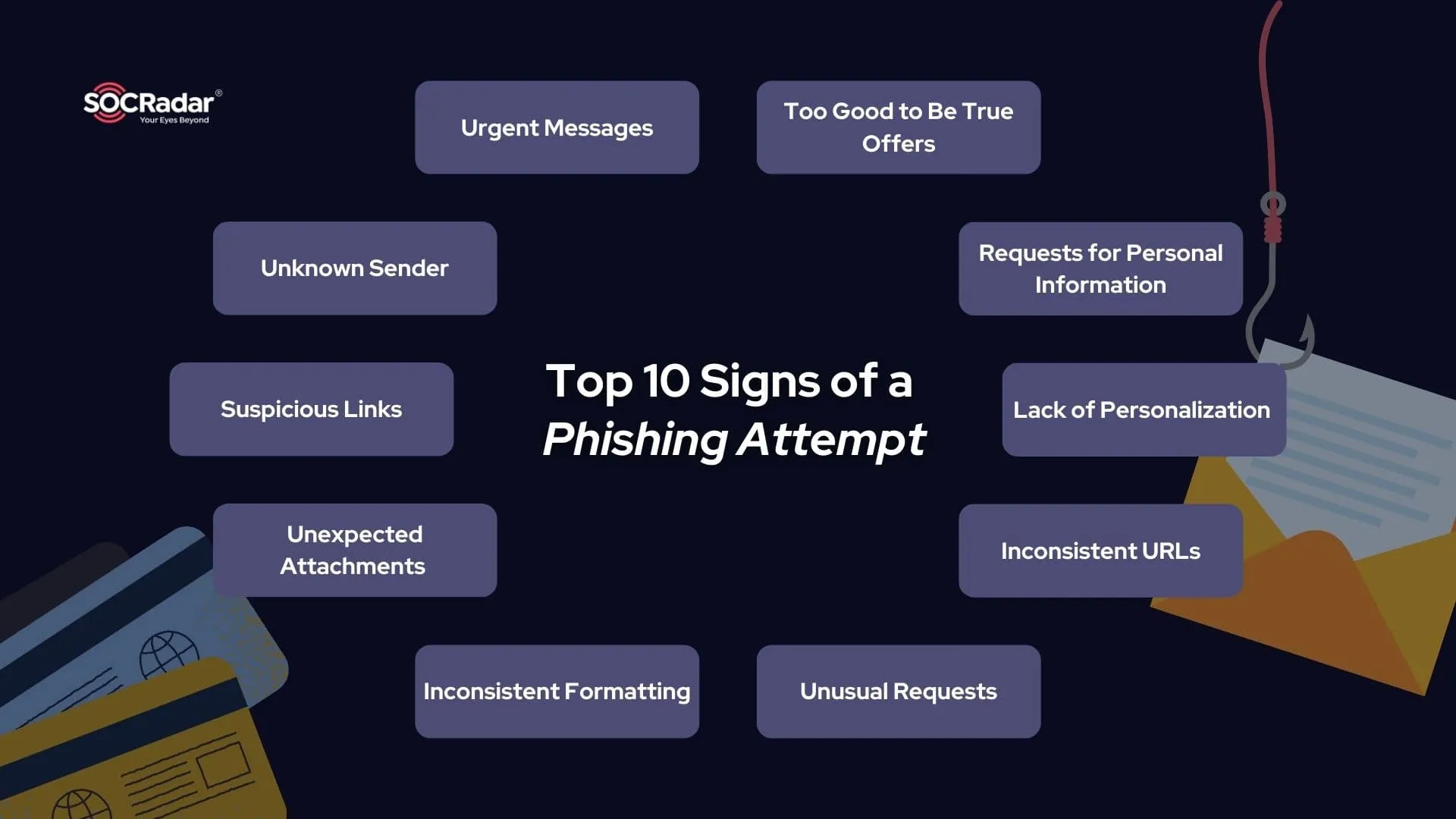
The top 10 signs of a phishing attempt
For deeper insights into the changing phishing landscape, explore the latest phishing trends shaping 2024 and equip yourself with tools to stay one step ahead.
How Organizations Can Protect Employees Against Social Engineering Scams
Phishing attacks are increasingly sophisticated, making it critical for organizations to adopt proactive measures to safeguard employees from social engineering scams. Here are actionable steps organizations can take:
- Awareness Training: Equip employees with knowledge about phishing tactics, emotional manipulation, and common red flags through regular training sessions. Educated employees are less likely to fall victim to scams.
- Simulated Phishing Exercises: Test employees’ vigilance by conducting simulated phishing attacks. These exercises help identify weaknesses and improve response strategies.
- Email Security Measures: Deploy advanced email filtering systems that can detect and block phishing emails. This includes tools that analyze email headers, links, and attachments for malicious content.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Require MFA for all accounts to add an extra layer of protection. Even if credentials are compromised, MFA can prevent unauthorized access.
- Verification Protocols: Establish clear processes for verifying the legitimacy of emails, especially those requesting sensitive information or financial actions. Encourage employees to confirm suspicious requests through alternative communication channels.
- Incident Response Plans: Develop an incident response plan tailored to phishing attacks. This includes identifying, containing, and mitigating threats, as well as notifying affected parties promptly.
How Individuals Can Protect Themselves
Employees play a critical role in defending against phishing attacks. Here’s how they can stay safe:
- Verify Sources: Always verify the sender’s email address or contact information before engaging with unexpected messages. Avoid clicking on links or downloading attachments from unknown sources.
- Be Skeptical of Urgency: Exercise caution with emails or messages that use urgent or threatening language to pressure you into immediate action.
- Double-Check Requests: If an email requests sensitive information, such as login credentials or payment details, confirm its legitimacy by contacting the sender through an official channel.
- Report Suspicious Activity: Encourage employees to report suspicious emails or messages to the IT department promptly. Early detection can prevent further damage.
- Keep Software Updated: Regularly update devices and applications to ensure they have the latest security patches, reducing vulnerabilities.
Empowering individuals with the tools and knowledge to recognize and respond to phishing threats is essential in combating social engineering scams.
Conclusion
Cybercriminals continue to refine their tactics, making phishing one of the most significant and persistent threats. The “You’re Fired” campaign, along with other advanced phishing attacks, illustrates how cybercriminals can manipulate individuals into disclosing sensitive information or downloading malware.
Organizations must adopt a proactive approach to protect their employees by implementing strong security practices, such as awareness training, simulated phishing exercises, and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). Likewise, individuals should stay alert and follow best practices for verifying emails and avoiding suspicious links or attachments.
With phishing threats constantly evolving, integrating advanced tools like SOCRadar’s Brand Protection and Dark Web Monitoring can help you stay ahead of attackers. Brand Protection provides real-time monitoring of your brand’s digital presence, ensuring counterfeit websites and fraudulent impersonations are swiftly detected. Meanwhile, Dark Web Monitoring helps track stolen credentials, leaked company data, and emerging cyber threats, enabling early responses to prevent attacks before they escalate.
Equip your organization with the necessary tools to defend against phishing and defend your reputation – stay proactive, stay secure.





































