
Top 10 Identity Attacks in 2024: Protecting Credentials in a Digital World
In 2024, identity attacks have advanced to new levels of sophistication, targeting credentials with ruthlessness. From wreaking havoc on healthcare supply chains to exposing millions of user records in the cloud, cybercriminals are now using deepfake video calls, polymorphic loaders, and RDP exploits to breach even the strongest systems. A single stolen password has the potential to disrupt critical services and cause cascading data breaches across multiple industries.
According to the 2024 Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR), credentials continue to play a pivotal role in enabling cyberattacks. A staggering 24% of initial breach actions involved the use of stolen or abused credentials, solidifying their status as a prime target for attackers. This highlights the critical importance of securing identity credentials against exploitation.
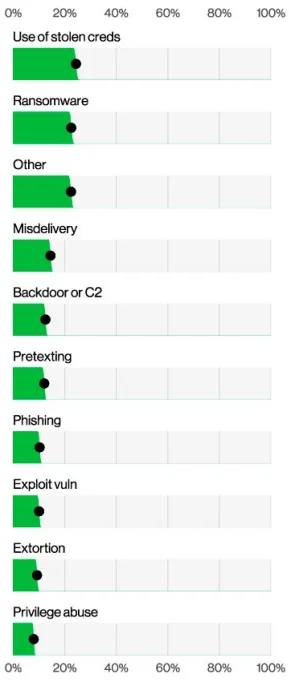
Use of stolen credentials of initial breach (source :DBIR)
The report also underscores the prevalence of credential abuse methods, such as phishing and unauthorized access through stolen credentials, as key components in system intrusion breaches. These tactics have become increasingly sophisticated, allowing attackers to infiltrate systems and compromise sensitive data. With credentials forming the backbone of identity and access management, their protection is paramount to mitigating risks across industries.
The Top 10 Identity Attacks of 2024 are listed below, revealing a complex web of threats and emphasizing the importance of credential protection in a rapidly changing digital landscape.
1. Change Healthcare Breach
The ransomware attack on Change Healthcare in early 2024, attributed to the ALPHV (BlackCat) group, underscored the critical risks of inadequate access controls, particularly the absence of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). By exploiting single-factor authentication vulnerabilities, attackers infiltrated the healthcare giant’s systems, causing significant disruptions to nationwide prescription drug distribution for over ten days. This breach severely impacted hospitals and pharmacies, disrupting the supply chain critical to patient care.
Reports suggest that UnitedHealth Group, a key partner of Change Healthcare, may have paid a $22 million ransom to recover encrypted data, although neither the company nor the attackers officially confirmed this payment. However, the situation took a darker turn when an ALPHV affiliate, known as “Notchy,” accused the group of withholding the ransom proceeds and claimed to still possess sensitive data from Change Healthcare and its partners. This revelation pointed to the possibility of an exit scam by ALPHV, heightening concerns about the stolen data being leaked or used for further extortion.
Notchy claimed that additional healthcare organizations affiliated with Change Healthcare were also compromised during the attack, complicating the breach even further. Despite the potential ransom payment, the affiliate’s claims about data retention point to a larger threat to the US healthcare sector. ALPHV’s announced shutdown and plans to sell its ransomware source code increase the risk of derivative attacks using BlackCat variants. The Change Healthcare incident demonstrates the devastation caused by insufficient identity and access protections in critical industries.
2. Snowflake Data Breach
The Snowflake data breach in 2024 exemplified the multifaceted dangers of identity attacks, impacting not just the company but also its high-profile clients, including Santander Bank and Ticketmaster. Threat actors leveraged Lumma Stealer, a credential-stealing malware, to gain access to a compromised Snowflake sales engineer’s account. This served as the entry point, allowing attackers to exploit single-factor authentication vulnerabilities and infiltrate multiple environments.
The breach exposed sensitive customer data from well-known organizations, highlighting the dangerous consequences of inadequate identity security. For example, Santander reported the compromise of databases containing sensitive customer information, whereas Ticketmaster disclosed unauthorized access to user records in a cloud database environment. These incidents collectively affected millions of customers worldwide, raising concerns about third-party risks in interconnected digital ecosystems.
The primary threat actor, “Whitewarlock,” took to Russian dark web forums to claim responsibility, offering exfiltrated data from Snowflake accounts for sale. This included 500 demo environment instances and data associated with several major organizations, highlighting the risks posed by compromised credentials and single-factor authentication.
The Snowflake breach also revealed the attackers’ use of a custom tool dubbed “RapeFlake” for data exfiltration and persistent access. This tool took advantage of the lack of robust access controls to successfully target sensitive databases. Cybersecurity researchers report that the attackers gained access to millions of customer records, including financial and personal information.
The 2024 Snowflake breach revealed the critical vulnerabilities in third-party ecosystems, where compromised credentials led to data exposure for major organizations like Santander Bank and Ticketmaster. SOCRadar’s Supply Chain Intelligence empowers you to mitigate such risks by delivering comprehensive insights into over 50 million companies globally.
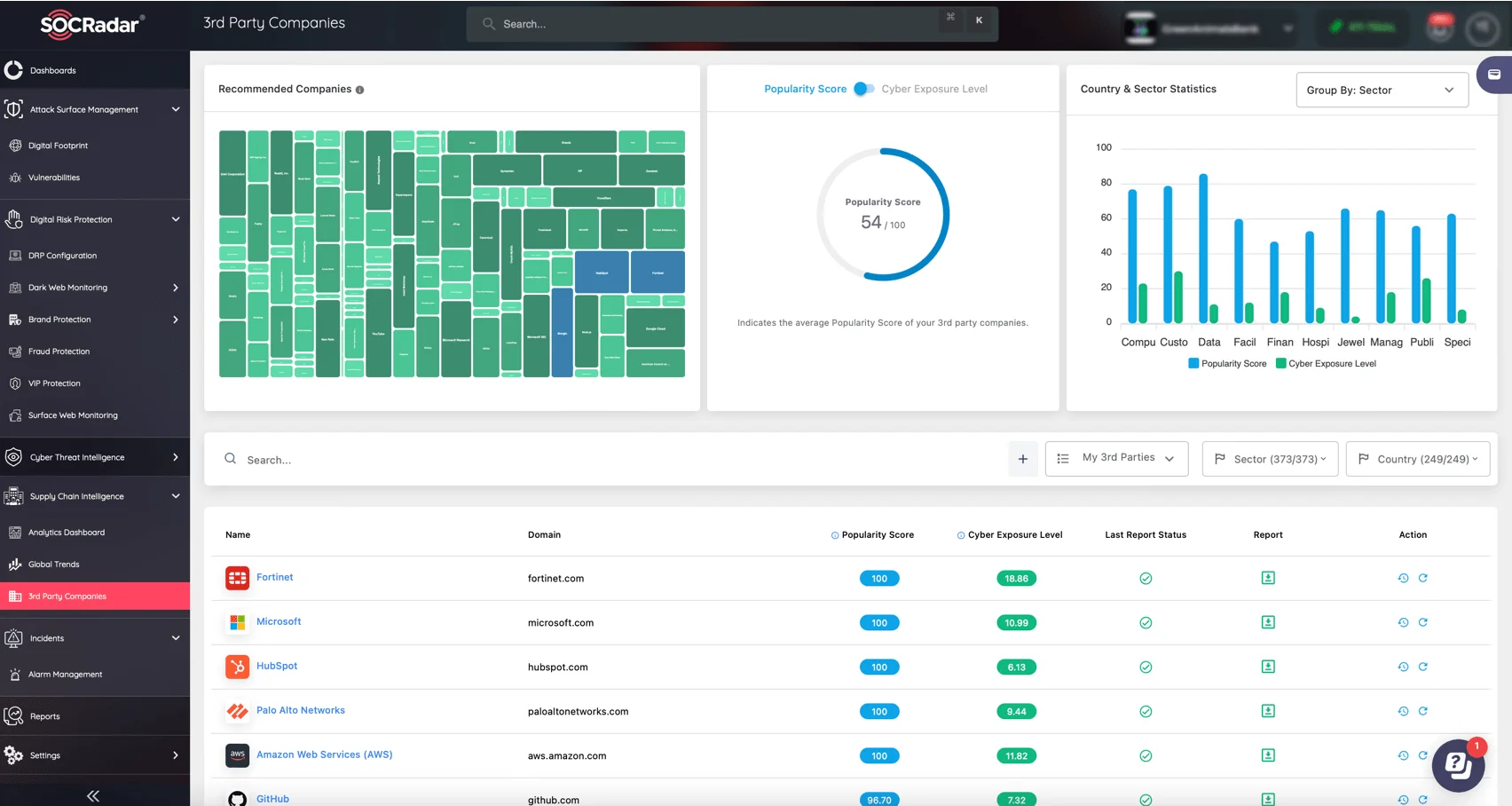
Stay ahead of cyber threats with SOCRadar’s Supply Chain Intelligence—monitor, analyze, and secure your third-party ecosystem effortlessly
Leverage real-time Cyber Exposure Levels, dynamic risk scoring, and automated recommendations to identify and secure high-risk third-party environments. With SOCRadar, businesses can prioritize threats, enhance visibility across their supply networks, and protect sensitive data from advanced cyberattacks targeting interconnected ecosystems. Stay proactive—secure your supply chain today!
3. Ticketmaster Breach
Ticketmaster suffered a significant breach when attackers used vulnerabilities in Snowflake’s infrastructure to gain access to a third-party cloud database. The incident affected 560 million users, exposing personal information like names, email addresses, and partial payment details. The breach disrupted operations and highlighted the risks of weak security in third-party integrations. With the attackers using stolen credentials, the breach highlighted the importance of implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and conducting rigorous audits of external service providers. These steps are critical for avoiding future incidents and protecting sensitive customer information.
4. AT&T Breach
The AT&T breach, caused by vulnerabilities in Snowflake’s cloud platform, exposed sensitive data for nearly 109 million customers. Attackers used compromised credentials and weak authentication protocols to gain access to call logs, phone numbers, and location data stored in a third-party database. While call and text content remained secure, the disclosure of metadata revealed critical flaws in cloud security configurations. To address the breach, AT&T reportedly paid a $370,000 ransom, but there are questions about whether the stolen data was truly deleted. This incident highlighted the risks of relying on third-party cloud environments without strong access controls and monitoring.
These incidents demonstrated how vulnerabilities in third-party platforms could cascade into large-scale compromises, affecting millions of customers and exposing organizations to significant financial and reputational risks. To mitigate such threats, businesses must enforce multi-layered authentication measures, regularly audit third-party security practices, and leverage real-time monitoring tools, such as SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management, to detect and address risks proactively.
SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management module
5. OpenAI Phishing Campaign
Cybercriminals launched a large-scale phishing campaign impersonating OpenAI, preying on the platform’s widespread adoption and reputation. Attackers sent fraudulent emails to over 1,000 recipients, urging them to update payment information for their ChatGPT subscriptions. The emails mimicked OpenAI’s communication style, using a mix of urgency, legitimate-looking support details, and obfuscated hyperlinks to deceive users. However, the sender’s domain, which did not match OpenAI’s official domain, raised a significant red flag.
This incident highlights how threat actors exploit trusted brands to conduct credential harvesting. As AI technology becomes more integral to businesses, phishing attacks targeting AI services like OpenAI are likely to increase, emphasizing the importance of advanced email security and regular employee training.
6. Mercku Support Portal Compromise
Cybercriminals exploited Mercku’s Zendesk support portal to distribute phishing emails targeting MetaMask users. When users submitted support tickets, they received automated responses titled “Mandatory Metamask Account Update Required.” These messages included malicious links designed to harvest login credentials under the guise of improving account security. The phishing emails abused URL structures to appear legitimate, misleading recipients into believing the links directed them to MetaMask’s official site.
This breach underscores the dangers of compromising trusted platforms to propagate phishing campaigns. Organizations relying on third-party support systems must ensure their portals are secured to prevent such malicious exploits.
7. ARUP’s $25 Million Deepfake Scam
In one of the most sophisticated identity attacks of 2024, British multinational design and engineering firm ARUP fell victim to a $25 million deepfake scam. Fraudsters used advanced AI-generated audio and video to impersonate ARUP’s CFO and other staff members during a video call. Convincing a finance employee to authorize 15 transactions totaling $25.6 million, the attackers exploited the realism of deepfake technology to execute the fraud seamlessly.

ARUP Headquarters – Source ESG News
The attack, which targeted ARUP’s Hong Kong office, highlights the escalating threat of deepfake-enabled social engineering. Despite initial skepticism from the victim, the attackers’ realistic impersonations overrode any doubts, showcasing the effectiveness of deepfake technology in bypassing human suspicion. The funds were rapidly transferred offshore, leaving recovery efforts futile.
ARUP responded by strengthening its verification protocols, implementing biometric authentication, and adopting AI-based anomaly detection to prevent future scams. This incident underscores the growing threat posed by deepfake technology, which is increasingly used in attacks targeting businesses worldwide. As ARUP’s Chief Information Officer noted, the sophistication and frequency of such scams are rising sharply, demanding heightened vigilance and advanced cybersecurity measures.
SOCRadar’s Identity & Access Intelligence module offers organizations unparalleled visibility into global identity threats. From monitoring InfoStealer activity to analyzing leaked datasets, this module provides you with actionable intelligence to safeguard sensitive credentials and prevent identity-based attacks.
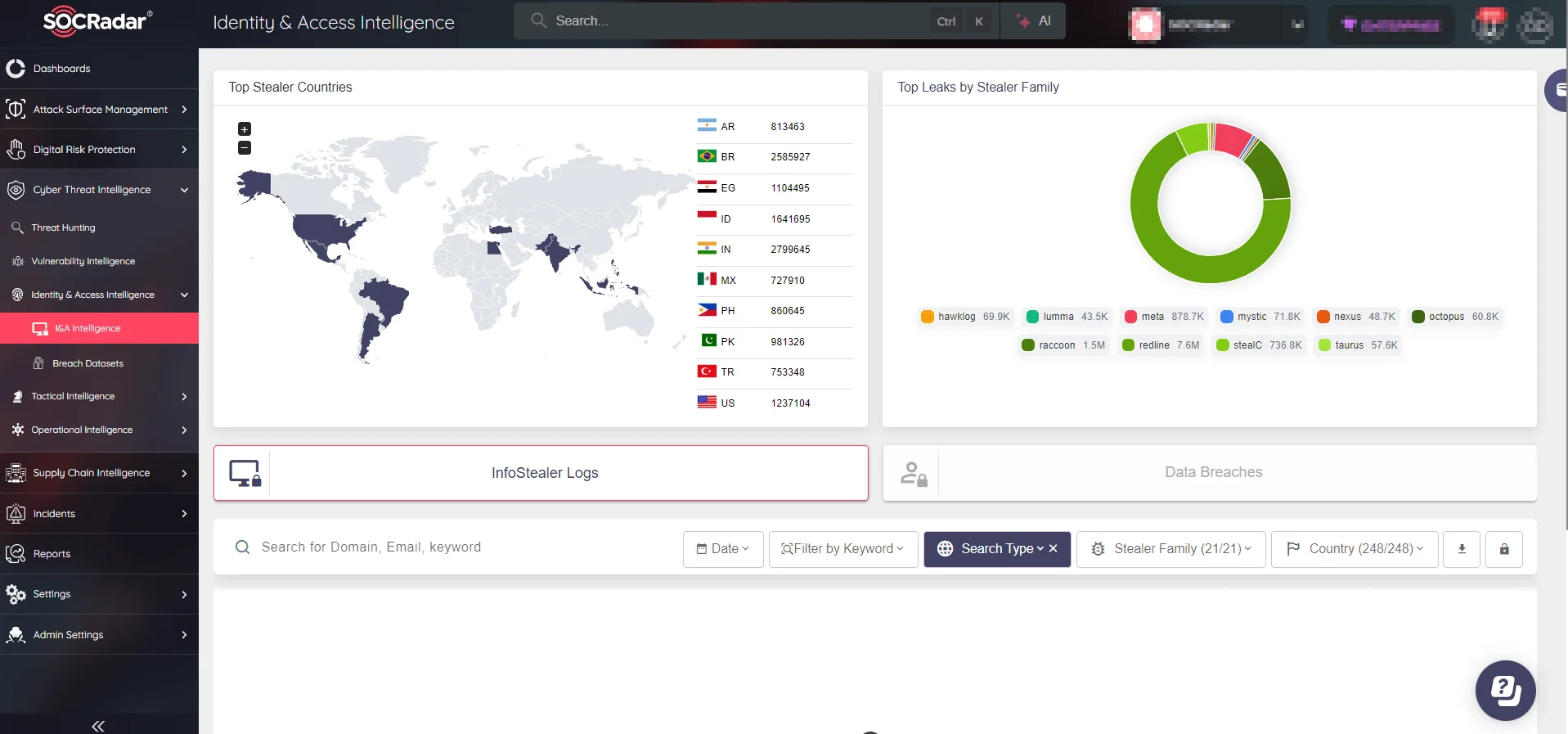
SOCRadar’s Identity & Access Intelligence: Track global InfoStealer activities and protect against evolving credential threats with actionable insights.
The Identity & Access Intelligence module, which uses real-time monitoring and tailored alerts, assists you in detecting potential breaches early, prioritizing remediation, and protecting your digital ecosystem. SOCRadar enables organizations to remain proactive in the face of evolving threats, whether by identifying leaked credentials, analyzing stealer family activities, or mitigating risks from data breaches.
8. Advanced Phishing Campaign Deploys Agent Tesla with Sophisticated Loader Techniques
In 2024, a novel phishing campaign demonstrated the increasing sophistication of malware deployment tactics, utilizing a polymorphic loader to deliver the Agent Tesla keylogger and infostealer. Disguised as a legitimate bank payment notification, the phishing email contained an attachment named “Bank Handlowy w Warszawie – dowód wpłaty_pdf.tar.gz.” Once executed, the loader bypassed traditional defenses through advanced obfuscation and packing techniques.
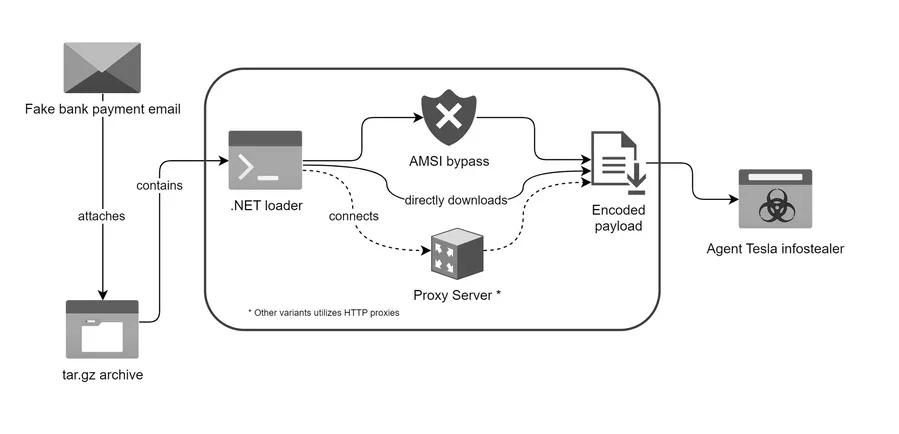
Agent Tesla infostealer deployment chain (Source: Trustwave)
The loader exhibited two distinct decryption routines and implemented AMSI bypassing mechanisms by patching the AmsiScanBuffer function. It also leveraged proxies and specific user-agent strings to retrieve and execute the payload entirely in memory, leaving no trace on disk. The exfiltrated data, including keystrokes and credentials, was transmitted via compromised email accounts for added anonymity. This campaign underscores the evolving capabilities of threat actors in integrating advanced techniques for maximum evasion and impact.
9. Midnight Blizzard Targets NGOs with RDP Phishing Campaign
In October 2024, according to research made by Microsoft the Russian state-sponsored group Midnight Blizzard launched a sophisticated spear-phishing campaign targeting NGOs, government agencies, and academic institutions. The phishing emails, sent to thousands of recipients across over 100 organizations, leveraged Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) configuration files signed with valid certificates. These malicious RDP files established connections to attacker-controlled servers, exposing victims’ devices and resources such as files, network drives, and authentication mechanisms.
Midnight Blizzard, also known as APT29 or Cozy Bear, aimed to gather intelligence through these attacks. The campaign highlighted advanced tactics, including exploiting compromised accounts to evade detection and maintain access. This operation underscores the critical need for phishing-resistant authentication methods, robust endpoint security, and continuous monitoring to counter persistent threat actors. Organizations are advised to implement multi-factor authentication (MFA), restrict RDP connections, and educate employees on identifying spear-phishing attempts.
10. 23andMe Data Breach Blamed on Recycled Passwords
The 23andMe data breach, which exposed sensitive information of 6.9 million users, has been linked to credential stuffing attacks that exploited recycled passwords. Hackers gained access to an initial 14,000 compromised accounts, leveraging these to access 5.5 million DNA Relatives profiles and 1.4 million Family Tree profiles. The breach disproportionately targeted users of Ashkenazi Jewish and Chinese heritage, with their data surfacing on the dark web.
While 23andMe attributed the breach to customers’ lax password practices, critics highlighted the company’s inadequate safeguards against credential stuffing. In response, 23andMe mandated two-factor authentication and password resets for all accounts. Despite these measures, the company faced a $30 million settlement to resolve a class-action lawsuit. The settlement includes three years of security monitoring for affected users and compensation for compromised accounts, marking a significant legal and financial outcome in the wake of the breach.
How to Protect Against Identity Attacks
- Adopt Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
MFA provides an additional security layer, reducing the risk of account compromise even if credentials are stolen. - Conduct Regular Security Training:
Educate employees on recognizing phishing attempts, social engineering, and secure password management to minimize human error. - Monitor for Credential Abuse:
Use advanced threat detection tools to identify and block credential stuffing attacks and suspicious login attempts. - Strengthen Third-Party Security:
Audit third-party integrations regularly to ensure they meet stringent security standards and mitigate risks from interconnected systems. - Implement Advanced Email Security:
Leverage tools that detect and block malicious attachments, phishing links, and sender spoofing, enhancing protection against identity-targeting campaigns. - Proactively Monitor the Dark Web:
Use solutions like SOCRadar’s Dark Web Monitoring to detect compromised credentials and prevent sensitive data from being exploited.
SOCRadar’s Dark Web Monitoring module
These targeted strategies address the most critical vulnerabilities and help fortify defenses against identity-related cyber threats.






































