
August 2024 Patch Tuesday Highlights: 89 CVEs, 6 Zero-Day Vulnerabilities Under Exploitation
[Update] September 4, 2024: “Details of CVE-2024-38106 and PoC Exploit”
[Update] August 20, 2024: “Lazarus Group Targets CVE-2024-38193 to Deploy Stealthy Rootkit” & “PoC Exploit Available for Windows Zero-Days, Enabling Downdate Attacks”
Microsoft has rolled out the August 2024 Patch Tuesday updates, enhancing its products to address a wide array of security threats through various fixes and improvements.
The August 2024 Patch Tuesday update tackles 89 CVEs, including nine that are critical. Six vulnerabilities are actively being exploited as zero-days, and some had been publicly disclosed prior to the release of patches.
Here’s a breakdown of the vulnerabilities addressed in the August 2024 Patch Tuesday updates:
- 36 Elevation of Privilege (EoP) Vulnerabilities
- 27 Remote Code Execution (RCE) Vulnerabilities
- 8 Information Disclosure Vulnerabilities
- 6 Denial of Service (DoS) Vulnerabilities
- 5 Spoofing
- 2 Memory Corruption Vulnerabilities
- 2 Security Feature Bypass
- 2 Cross-site Scripting (XSS) Vulnerabilities
- 1 Tampering Vulnerability
Notably, this update also includes a patch for a vulnerability that was originally fixed in June, but Microsoft had not released an advisory for it until the August 2024 Patch Tuesday updates.
SAP has also issued its Security Patch Update for this month, addressing a critical vulnerability that potentially leads to system compromise.
Numerous Exploited Zero-Days Addressed in August 2024 Patch Tuesday
In the August 2024 Patch Tuesday, Microsoft patched several zero-day vulnerabilities, including six that have been actively exploited. Among these, three involve local privilege escalation, allowing attackers to gain SYSTEM-level privileges on compromised systems.
Below are the key details of the zero-day vulnerabilities addressed:
CVE-2024-38189 (CVSS: 8.8): This vulnerability affects Microsoft Project, allowing RCE when a user opens a malicious file with security features like macro-blocking and notifications are disabled. Exploitation requires tricking the user into opening the file, typically through phishing attacks.
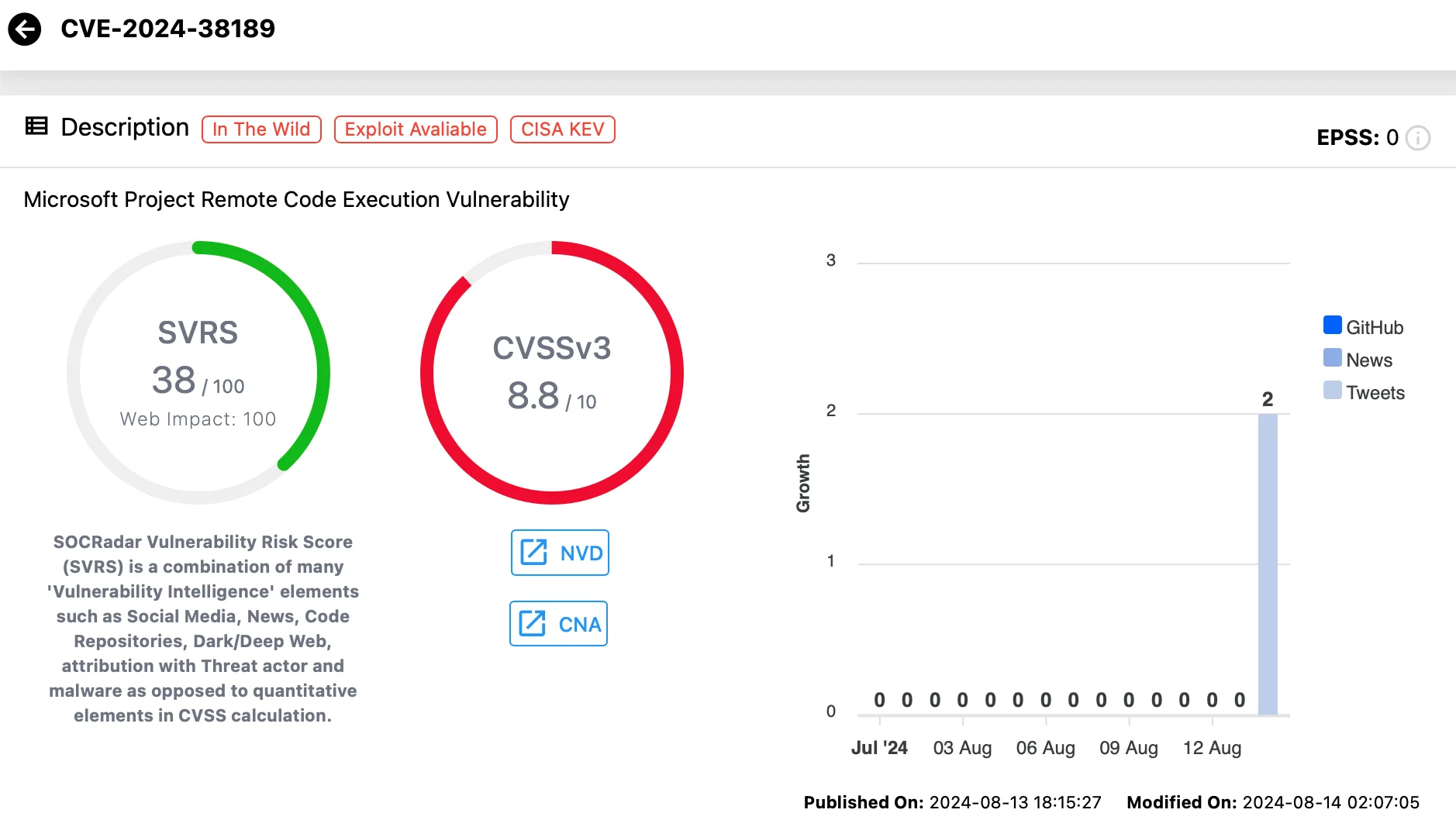
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-38189 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
CVE-2024-38193 (CVSS: 7.8): This flaw, residing in Windows Ancillary Function Driver for WinSock, poses a risk of privilege escalation, enabling attackers to gain SYSTEM privileges.
CVE-2024-38107 (CVSS: 7.8) This vulnerability also allows privilege escalation to SYSTEM level on Windows devices. Specific details regarding its discovery and exploitation have not been shared by Microsoft.
CVE-2024-38178 (CVSS: 7.5): Exploitation of this flaw requires user interaction, specifically clicking a malicious link in Microsoft Edge’s Internet Explorer mode. Despite these conditions, it has been exploited in attacks disclosed by the South Korean NCSC and AhnLab, enabling attackers to perform RCE.
CVE-2024-38106 (CVSS: 7.0): This Windows Kernel vulnerability allows SYSTEM-level access through a race condition. Microsoft has not provided details on the discovery or exploitation method.
CVE-2024-38213 (CVSS: 6.5): Initially patched in June 2024, this zero-day vulnerability, dubbed “copy2pwn,” allows attackers to bypass Windows SmartScreen protections. An advisory for this vulnerability is now available with August 2024 Patch Tuesday.
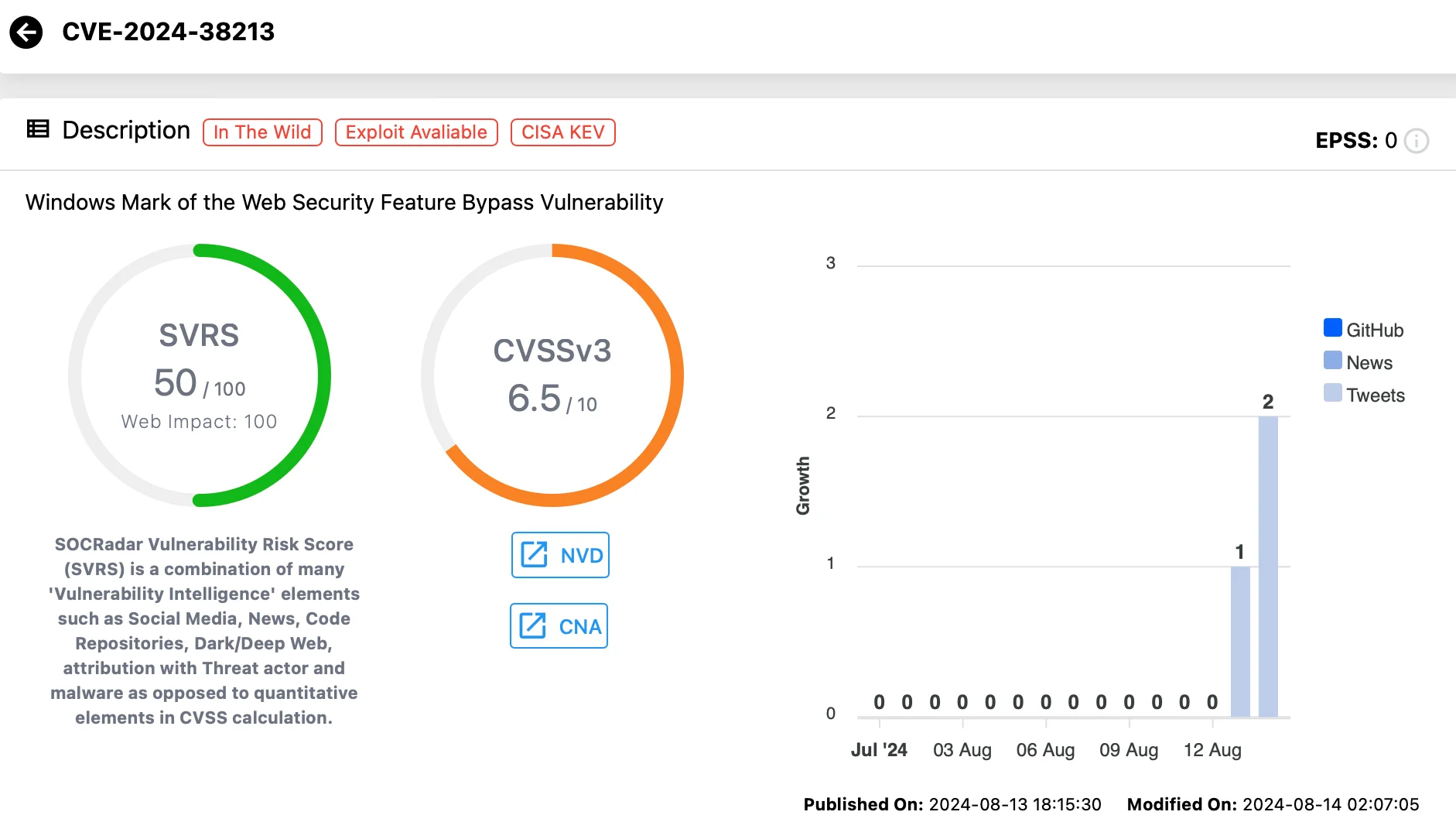
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-38213 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
The flaw allows attackers to bypass Windows SmartScreen protections by exploiting files from WebDAV shares. Normally, files downloaded from the internet are tagged with a Mark of the Web (MotW), which triggers SmartScreen warnings to prevent the execution of malicious content. CVE-2024-38213 enables these files to bypass the MotW protections, posing a significant security risk despite requiring user interaction for exploitation.
DarkGate malware operators have actively exploited this vulnerability, disguising their payloads as legitimate software installers like Apple iTunes and NVIDIA to deceive users.
CVE-2024-38213 is part of a series of SmartScreen bypasses, including CVE-2024-21412, which itself bypassed an earlier vulnerability, CVE-2023-36025. The financially motivated Water Hydra (DarkCasino) group has leveraged these vulnerabilities in various cyberattacks. This vulnerability is typically part of an exploit chain, enhancing the overall threat level when used in combination with other security flaws.
CISA had added these vulnerabilities to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog and also issued an alert to highlight the availability of patches. Federal organizations are mandated to mitigate potential risks before assigned deadlines. For more details, check the KEV Catalog.
Lazarus Group Targets CVE-2024-38193 to Deploy Stealthy Rootkit
The Lazarus Group, a well-known North Korean hacking organization, has been actively exploiting the CVE-2024-38193 vulnerability to gain elevated system privileges and install the FUDModule rootkit on compromised systems. This rootkit is particularly dangerous due to its ability to disable Windows monitoring features, effectively evading detection.
This vulnerability falls under the Bring Your Own Vulnerable Driver (BYOVD) category, allowing attackers to manipulate a system’s driver to their advantage. Lazarus previously used this technique to exploit vulnerable Dell drivers.
A significant concern with CVE-2024-38193 is that AFD.sys is a default driver installed on all Windows devices. This widespread presence allows attackers to exploit the flaw without the need to introduce drivers.
Details of CVE-2024-38106 and PoC Exploit
An analysis and Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit for the CVE-2024-38106 vulnerability is now publicly available.
This flaw, exploited as a zero-day, played a role in attacks by the North Korean threat group Citrine Sleet (also known as AppleJeus, LabyrinthChollima, and UNC4736). The group used it alongside a Chrome RCE vulnerability (CVE-2024-7971) to deploy the FudModule rootkit, bypassing Windows sandbox protections and manipulating kernel security mechanisms.
CVE-2024-38106 allows attackers to escalate privileges via a race condition within the ntoskrnl.exe process. Two key functions, VslGetSetSecureContext() and NtSetInformationWorkerFactory(), were updated with proper locking mechanisms and flag checks to mitigate the issue.
Check out the analysis by researcher Sergey Kornienko here for further information.
Publicly Disclosed Vulnerabilities in August 2024 Patch Tuesday
In addition to the exploited zero-days, several vulnerabilities that were publicly disclosed as zero-days were addressed in this month’s updates:
- CVE-2024-38199 (CVSS: 9.8) –Affects the deprecated LPD (Line Printer Daemon) service, though its exploitability is noted to be ‘less likely.’
- CVE-2024-21302 (CVSS: 6.7) – An Elevation of Privilege (EoP) Vulnerability that allows attackers to replace Windows files with outdated versions.
- CVE-2024-38200 (CVSS: 6.5) – A medium-severity spoofing flaw impacting NTLM authentication.
To proactively prevent potential breaches, it’s vital to continuously track new exploits and developments across different platforms. SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence module offers a comprehensive analysis of identified security vulnerabilities, delivering critical insights into emerging threats.
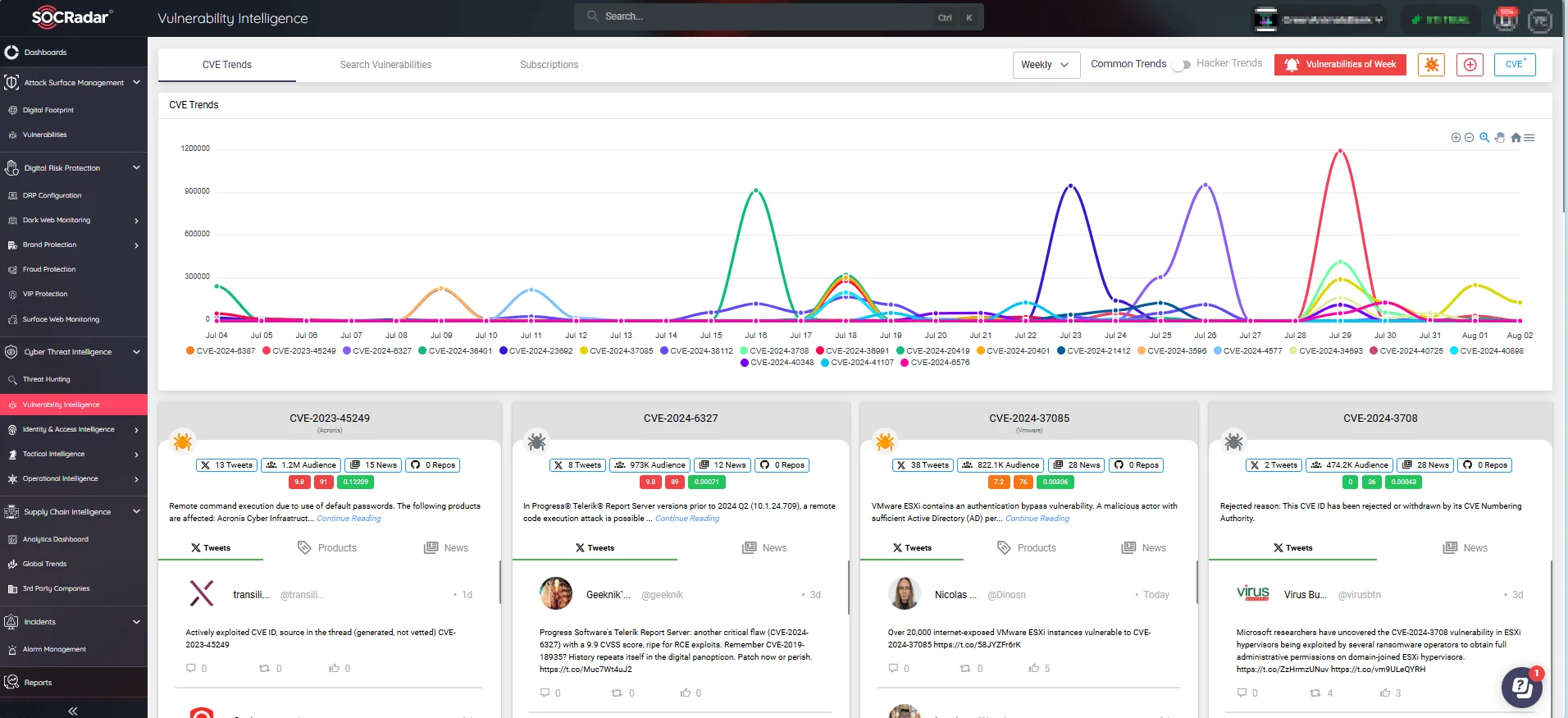
SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence module
The module also allows you to refine vulnerability searches using parameters such as vendor, product, and severity scores, and more. With Vulnerability Intelligence, you can identify and prioritize the most critical vulnerabilities affecting your digital assets, ensuring a more targeted and effective response.
PoC Exploit Available for Windows Zero-Days, Enabling Downdate Attacks
Researchers have published a Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit for two critical Windows zero-day vulnerabilities, CVE-2024-38202 and CVE-2024-21302, first revealed at the 2024 Black Hat conference. These flaws affect Windows Update and allow attackers to roll back the system components, bringing back previously patched vulnerabilities.
The “Windows Downdate” tool, released alongside the PoC, demonstrates how these vulnerabilities can be exploited. Attackers can downgrade critical system components, such as dynamic link libraries (DLLs) and the NT Kernel, leaving systems vulnerable to serious attacks while appearing fully updated.
Although no active exploits have been reported, the release of the PoC significantly increases the risk to affected systems. Microsoft urges users to follow mitigation steps to protect against potential exploitation.
Critical Vulnerabilities Addressed in August 2024 Patch Tuesday
The August 2024 Patch Tuesday updates include fixes for nine critical security vulnerabilities as outlined in Microsoft’s advisories. These vulnerabilities pose significant risks, including remote code execution and privilege escalation.
- CVE-2024-38063 (CVSS: 9.8) – A Windows TCP/IP Remote Code Execution vulnerability that is particularly concerning due to its zero-click nature. This vulnerability can be exploited without any user interaction.
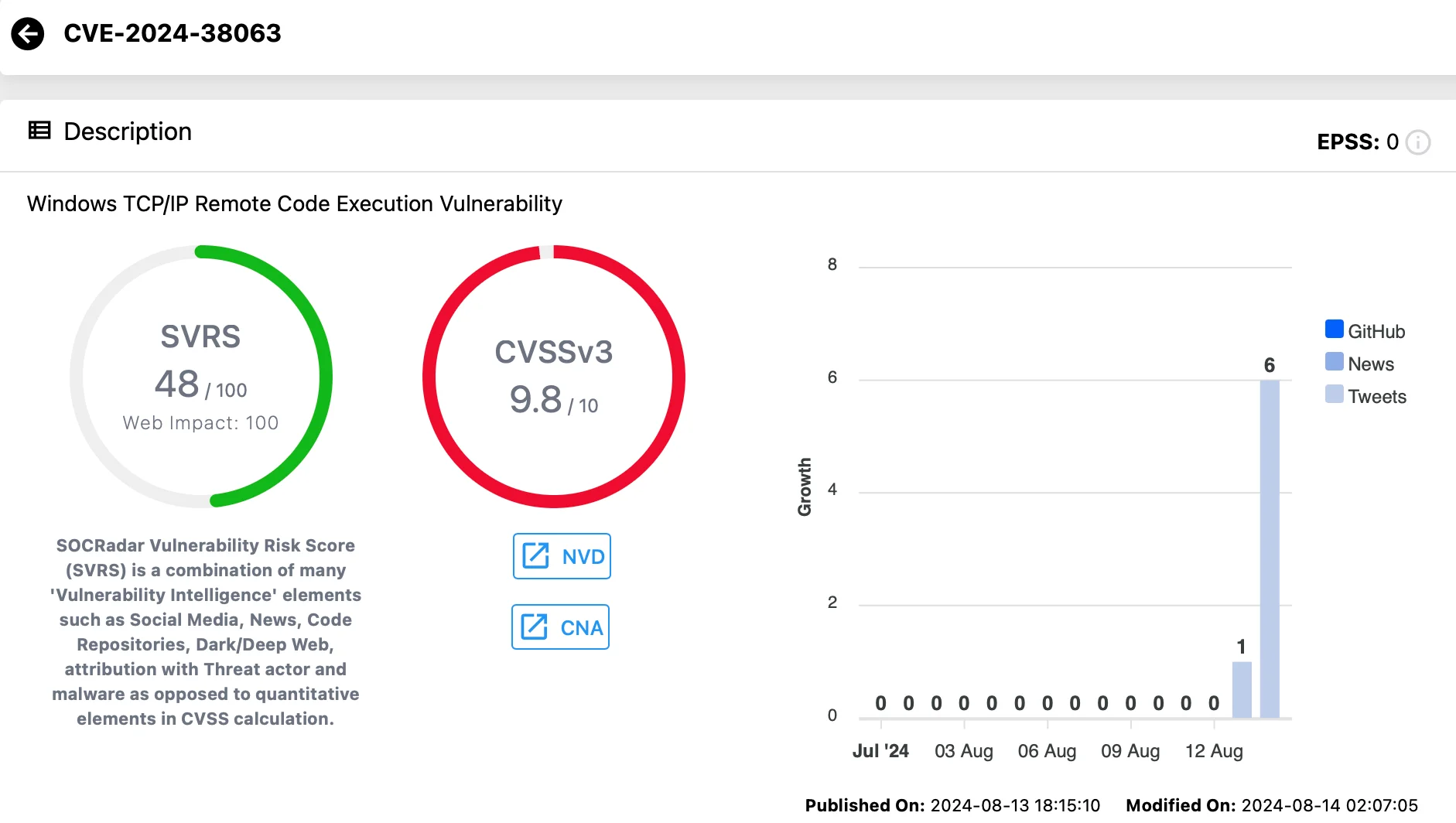
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-38063 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
Attackers can remotely exploit CVE-2024-38063 by sending specially crafted IPv6 packets to a target system, potentially allowing them to execute arbitrary code with SYSTEM privileges.
This vulnerability affects all supported versions of Windows and Windows Server, including Server Core installations. Microsoft rates this vulnerability as ‘more likely’ to be exploited and recommends disabling IPv6 if not necessary to mitigate its impact.
- CVE-2024-38140 (CVSS: 9.8) – A Windows Reliable Multicast Transport Driver (RMCAST) Remote Code Execution vulnerability.
- CVE-2024-38109 (CVSS: 9.1) – An Azure Health Bot Elevation of Privilege vulnerability.
- CVE-2024-38160 and CVE-2024-38159 (CVSS: 9.1) – Two vulnerabilities in Windows Network Virtualization that could lead to remote code execution.
In addition to these, other vulnerabilities with lower CVSS scores but still marked as critical (in maximum severity) include:
- CVE-2024-38206 (CVSS: 8.5) – Microsoft Copilot Studio Information Disclosure Vulnerability
- CVE-2023-40547 (CVSS: 8.3) – Redhat: Shim – Windows Secure Boot Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
- CVE-2024-38166 (CVSS: 8.2) – Microsoft Dynamics 365 Cross-site Scripting Vulnerability
- CVE-2022-3775 (CVSS: 7.1) – Redhat: grub2 – Windows Secure Boot Heap-based Out-of-Bounds Write Vulnerability
Microsoft has made patches available for these vulnerabilities in the August 2024 updates, and it is strongly advised to apply them immediately to mitigate the risk of exploitation.
What Are the Vulnerabilities That Are More Likely to Be Exploited?
The August 2024 Patch Tuesday release includes several vulnerabilities flagged as ‘more likely to be exploited,’ requiring immediate attention.
Among these high-priority vulnerabilities is CVE-2024-38063, previously highlighted in our article as particularly concerning due to its critical nature. Additionally, the following vulnerabilities are also deemed highly exploitable:
- CVE-2024-38144 (CVSS: 8.8) – Microsoft Streaming Service
- CVE-2024-38125 (CVSS: 7.8) – Microsoft Streaming Service
- CVE-2024-38133 (CVSS: 7.8) – Windows Kernel
- CVE-2024-38141 (CVSS: 7.8) – Windows Ancillary Function Driver for WinSock
- CVE-2024-38147 (CVSS: 7.8) – Windows DWM Core Library
- CVE-2024-38150 (CVSS: 7.8) – Windows DWM Core Library
- CVE-2024-38163 (CVSS: 7.8) – Windows Update Stack
- CVE-2024-38196 (CVSS: 7.8) – Windows Common Log File System Driver
- CVE-2024-38198 (CVSS: 7.5) – Windows Print Spooler Components
- CVE-2024-38148 (CVSS: 7.5) – Windows Transport Security Layer (TLS)
Due to exploitation of these flaws being more likely, it is important to prioritize patches for these vulnerabilities to safeguard your systems.
For more detailed information on the vulnerabilities addressed in the August 2024 Patch Tuesday update, please refer to Microsoft’s official Release Note.
Monitor Assets and Pinpoint Vulnerabilities with SOCRadar
To improve your defense against the constant emergence of new vulnerabilities, SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) module offers a powerful solution.
SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) module
With ASM, SOCRadar ensures the real-time monitoring of your digital assets, delivering prompt alerts on potential security issues. By utilizing the actionable insights provided by SOCRadar, your organization can swiftly address threats and effectively manage security posture.
SAP Security Patch Update: Addressing Critical Vulnerability CVE-2024-41730
Another major software provider, SAP, has also recently issued its monthly security updates, including a particularly critical vulnerability tracked as CVE-2024-41730.
In its August 2024 Security Patch Day, SAP released 17 new Security Notes and updated 8 previously issued ones. Among these, the most critical vulnerability, CVE-2024-41730, carries a CVSS score of 9.8, underscoring its severity.
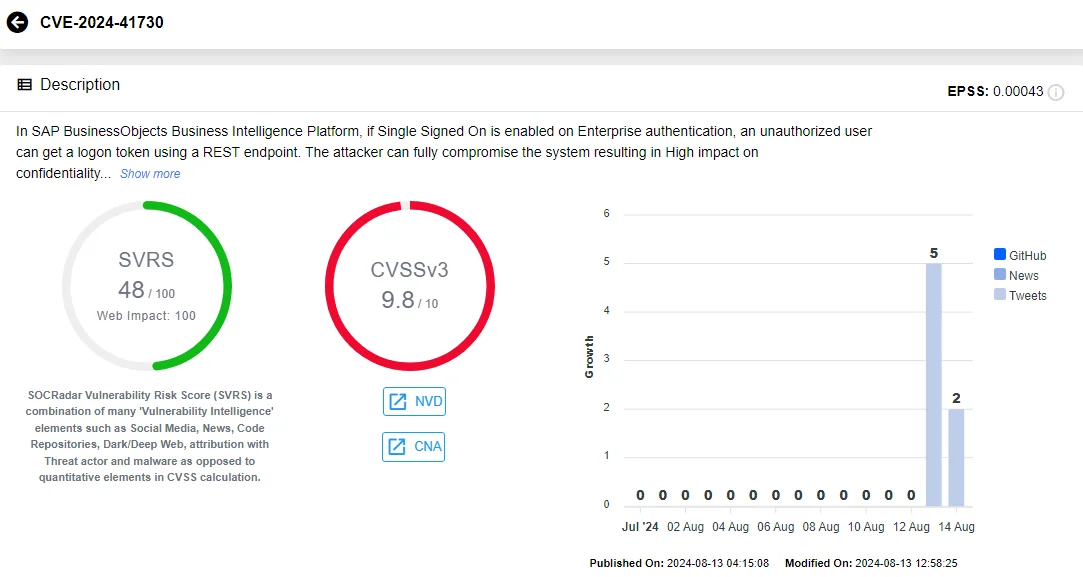
Vulnerability card of CVE-2024-41730 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
This flaw impacts the Single Sign-On (SSO) functionality in SAP BusinessObjects Business Intelligence Platform. Exploiting this vulnerability, an unauthorized attacker can obtain a logon token via a REST endpoint, potentially leading to a full system compromise.
SAP has released patches to secure the affected versions, ENTERPRISE 430 and ENTERPRISE 440. Organizations using these versions should apply the patches immediately to mitigate the risk, as there are no available workarounds.
For further details, you can refer to the official SAP advisory.




































