
ChatGPT Users in Stealer Logs: A 2023 Stealer Analysis of OpenAI
Stealer logs serve as the underground repositories of stolen data, filled with sensitive information such as payment card details and credentials. These logs, traded in dark web forums, are exploited by cybercriminals for fraudulent activities and breaches, impacting numerous industries and websites. Unfortunately, even ChatGPT users have not been immune to stealer logs, as their credentials, acquired through stealer malware infiltrating OpenAI domains, have surfaced on the dark web.
Recent reports indicate that there are 180 million users on ChatGPT, and openai.com receives an astounding 1.6 billion visits each month. Since its establishment in late 2022, the AI platform has experienced rapid growth. However, with such rapid growth comes the unwelcome attention of threat actors, who apparently waste no time in targeting extensive user communities.
Between January and October 2023, researchers identified 225,000 stealer logs containing compromised information on ChatGPT users.
This blog post is powered by SOCRadar’s Threat Hunting module, a powerful tool for defenders to proactively identify and neutralize threats within collected stealer logs. Using this module, we expand on previous findings and delve into the available data to uncover trends and provide insights.
SOCRadar’s Threat Hunting page
Join us on a journey through the labyrinth of cybercrime in this blog post, as we shed light on the imminent threats faced by ChatGPT users.
What Was Found in the ChatGPT / OpenAI Stealer Logs?
In our analysis of ChatGPT / OpenAI stealer logs, we identified 701,884 user records from the year 2023, originating from a total of 2,164 compromised victim IP addresses. These records encompass a wide range of information, including personal details and login credentials, providing a comprehensive overview of the users affected by these breaches.
The compromised data from users of the renowned AI platform included:
- 69,731 User IDs/Emails: Among the compromised data are tens of thousands of user IDs and email addresses, potentially exposing individuals to a range of cyber threats, including phishing attacks and identity theft.
- 67,660 Passwords: The compromised passwords pose a significant security risk, as they grant unauthorized access to users’ accounts and sensitive information, leading to potential data breaches and privacy violations.
- 1,238 CC/BIN Count: The presence of credit card and BIN (Bank Identification Number) data highlights the financial implications of these breaches, with over a thousand records compromised, increasing the likelihood of fraudulent transactions and financial loss.
- 3,305 Hashes: Hashes serve as cryptographic representations of sensitive data, and their compromise can lead to unauthorized access and manipulation of information, further exacerbating the security implications of these breaches.
What Are the Top Countries Observed in the ChatGPT / OpenAI Stealer Logs?
Examining the geographic data within ChatGPT / OpenAI logs from stealer malware, we found that certain countries appeared more frequently than others, suggesting increased vulnerability to cyber threats such as phishing, fraud, and impersonation.
To gain a deeper understanding of this distribution, let’s examine the victim country distribution by percentage. This metric enables us to assess the relative impact of stealer logs across different countries. The breakdown of victim country distribution is as follows:
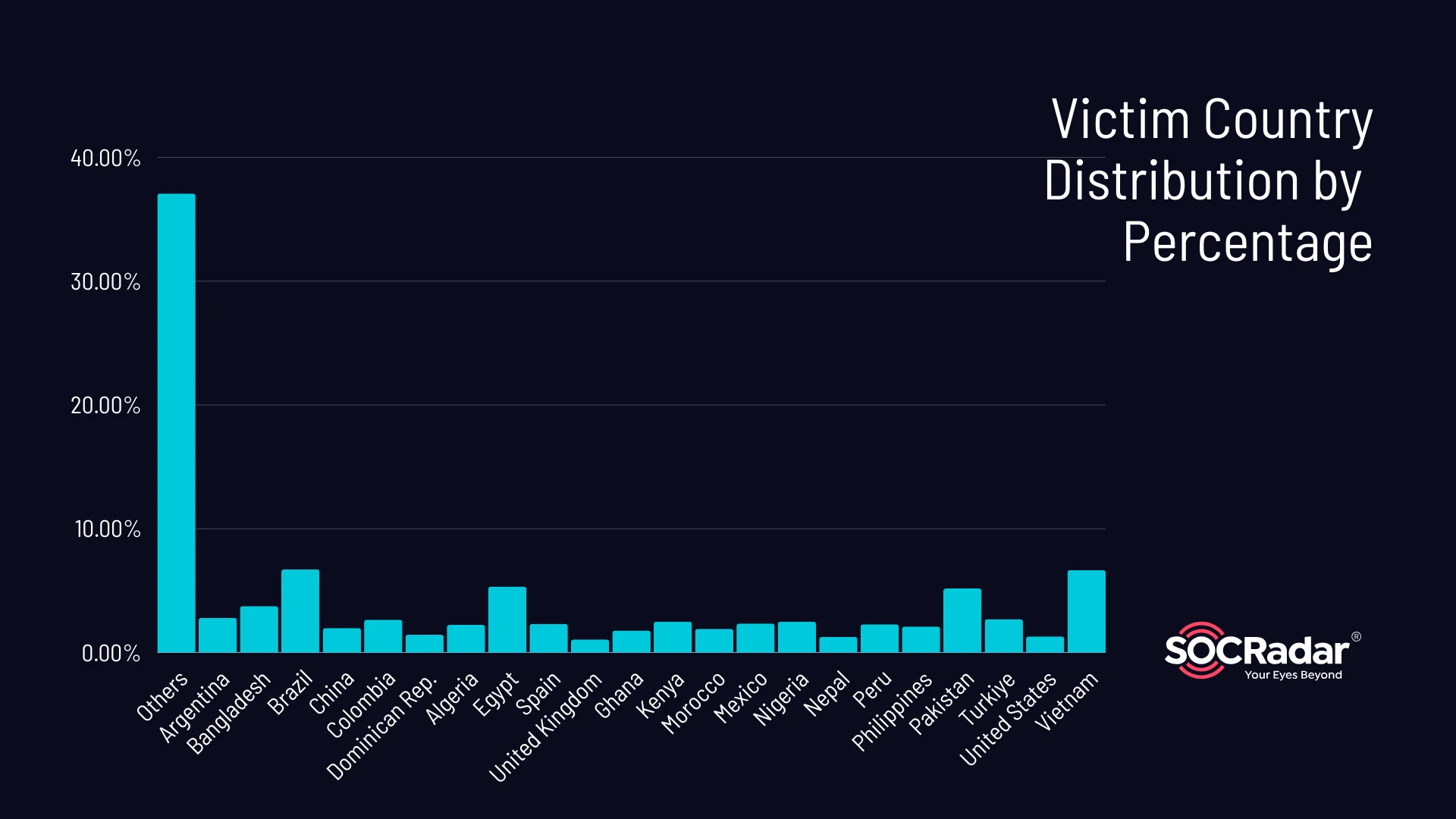
Victim country distribution by percentage
The logs we examined contained 132 country domains; however, some of them were not assigned a specific country code or contained mixed information. Our analysis shows that the top five countries by percentage of stealer logs are Brazil (6.66%), Vietnam (6.59%), Egypt (5.28%), Pakistan (5.12%), and Bangladesh (3.72%).
As users from these countries embraced the capabilities of ChatGPT, threat actors deployed stealthy stealer malware to harvest their valuable information in the background, unbeknownst to the victims.
On the contrary, these rankings do not represent the highest traffic received by OpenAI. United States (21.29%), India (12.46%), Brazil (5.69%), Indonesia (5.49%), and the Philippines (5.05%) are the countries generating the most traffic to the OpenAI domain.
Interestingly, Brazil is the only country that appears in both the top 5 victim countries identified in our analysis of stealer logs and the top 5 for website traffic.
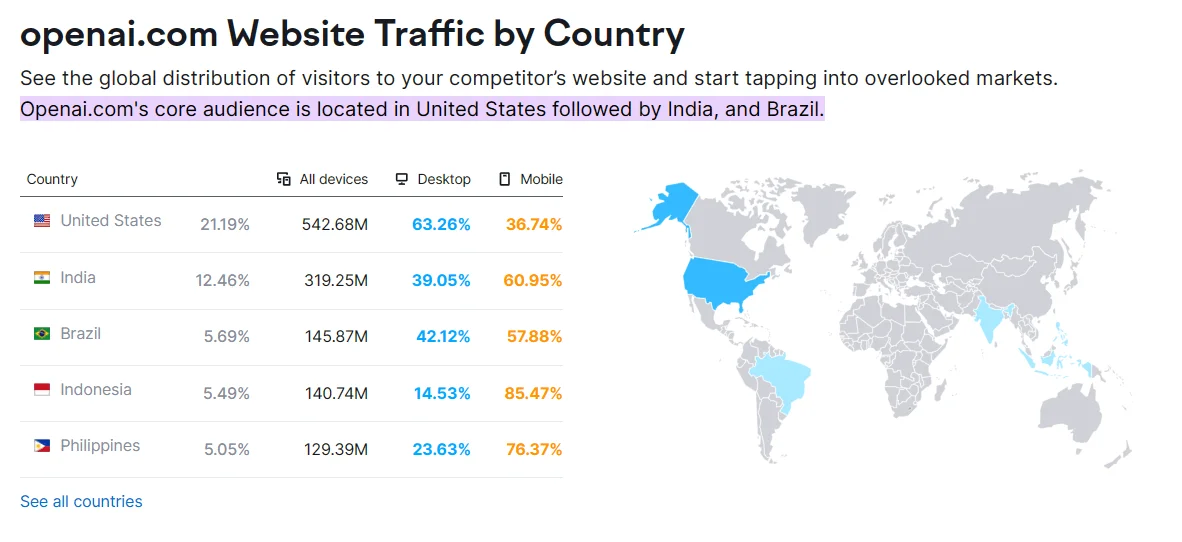
openai.com website traffic (Semrush)
Organizations can improve their security measures and mitigate potential threats earlier by leveraging SOCRadar’s proactive threat intelligence approach and insightful alarms.
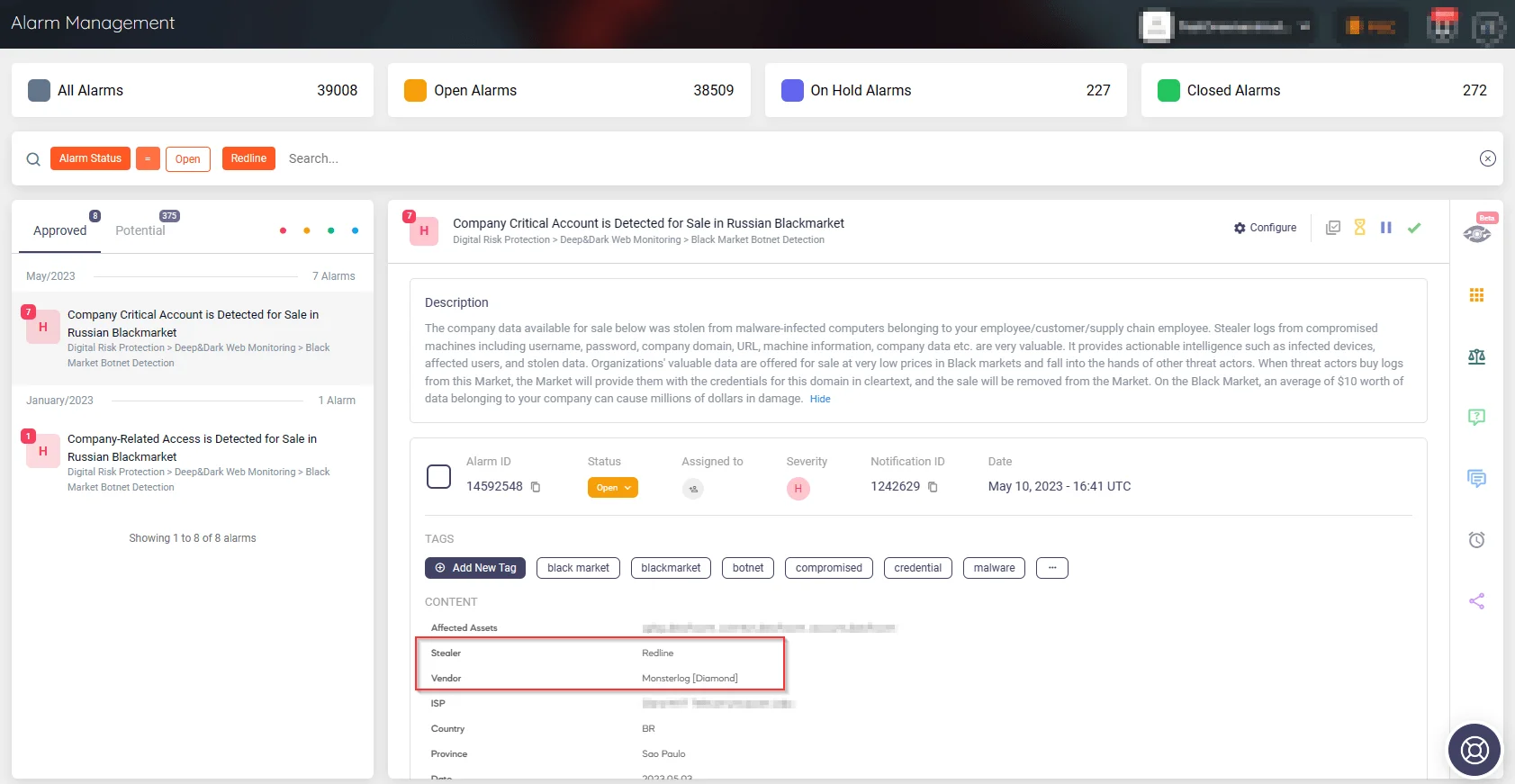
Alarm by SOCRadar: Company account detected on blackmarket
E-mail, Credit Card (CC), and Hash Inclusion
In this section, we delve into the e-mail, credit card (CC), and hash information extracted from the OpenAI stealer logs, alongside the top countries associated with each type of data.
E-mails emerge as the most prevalent information in stealer logs, indicating cybercriminals’ focus on acquiring e-mail addresses due to their utility in various cyber activities. The top five countries associated with email inclusion are Brazil (6.14%), Vietnam (5.53%), Egypt (5.32%), Nigeria (4.92%), and Argentina (4.58%).
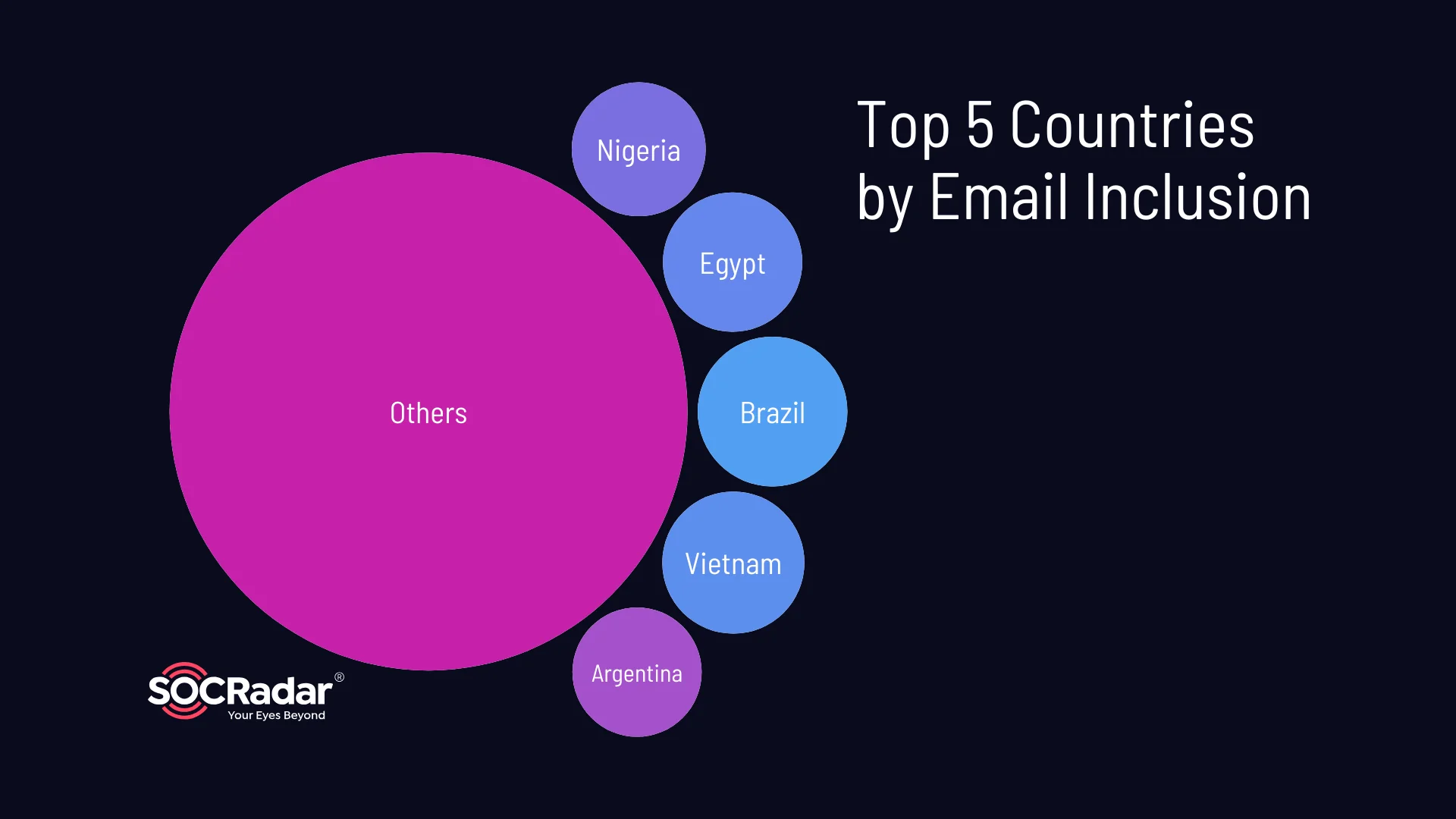
Top 5 countries by email inclusion
E-mail accounts often hold personal or professional information, making them lucrative targets for phishing, identity theft, or unauthorized access to online services.
Credit card (CC) and Bank Identification Number (BIN) information feature in approximately 27.09% of the logs, signifying a notable risk for financial fraud or unauthorized transactions. The top five countries associated with CC inclusion are Egypt (14.46%), Dominican Republic (8.32%), Colombia (6.7%), Brazil (4.52%), and Nigeria (4.04%).
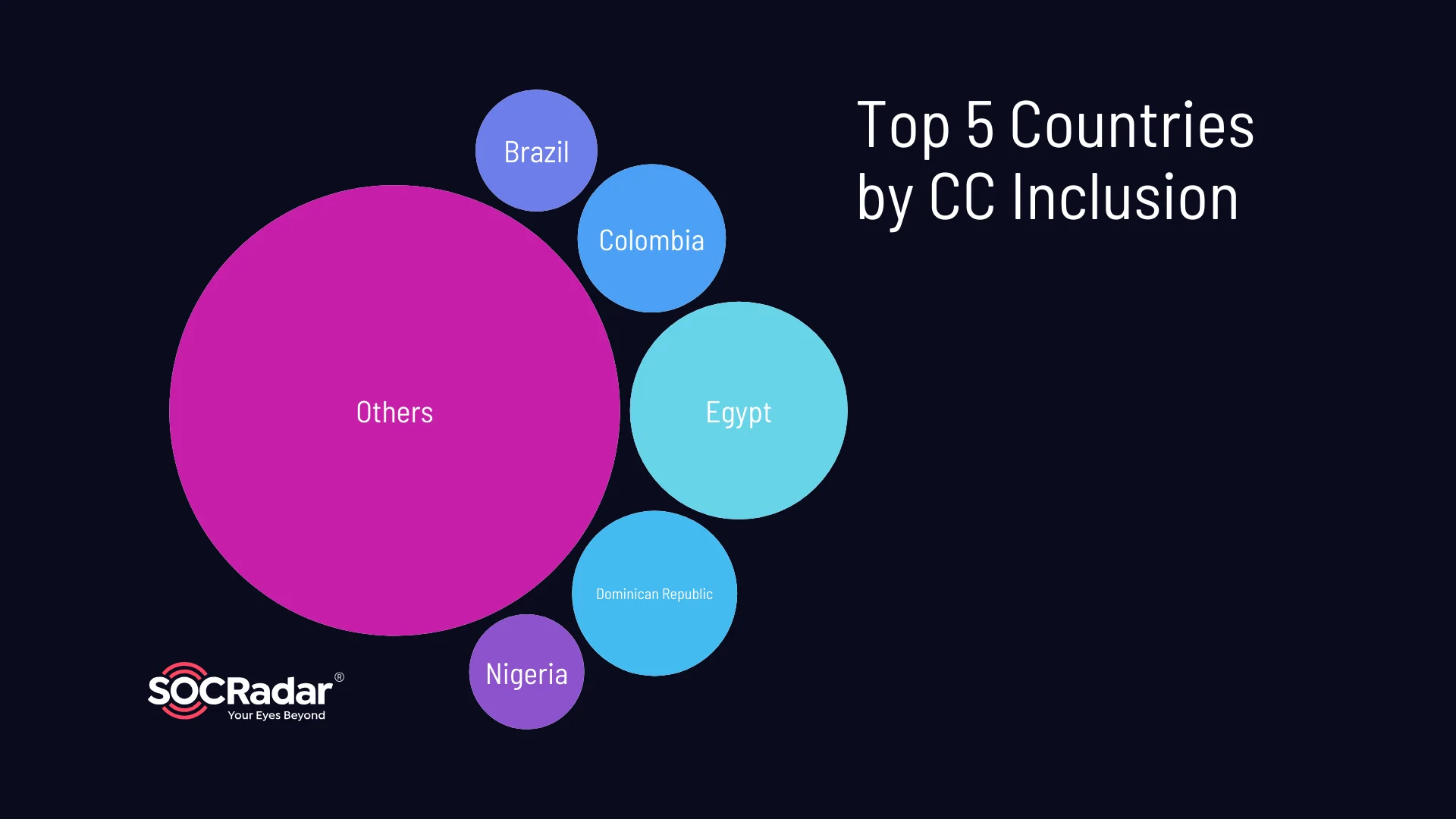
Top 5 countries by credit card information inclusion
These countries exhibit a heightened concentration of compromised credit card information within the stealer logs, indicating an increased risk of financial fraud or misuse of credit card details.
Hash information, representing hashed passwords or other sensitive data, is present in approximately 72.36% of the logs, posing a significant risk as cybercriminals can attempt to crack these hashes to access user accounts or decrypt sensitive data. The top five countries associated with hash inclusion are the United Kingdom (8.77%), Argentina (8.02%), Brazil (6.84%), Spain (4.36%), and Colombia (4.3%).
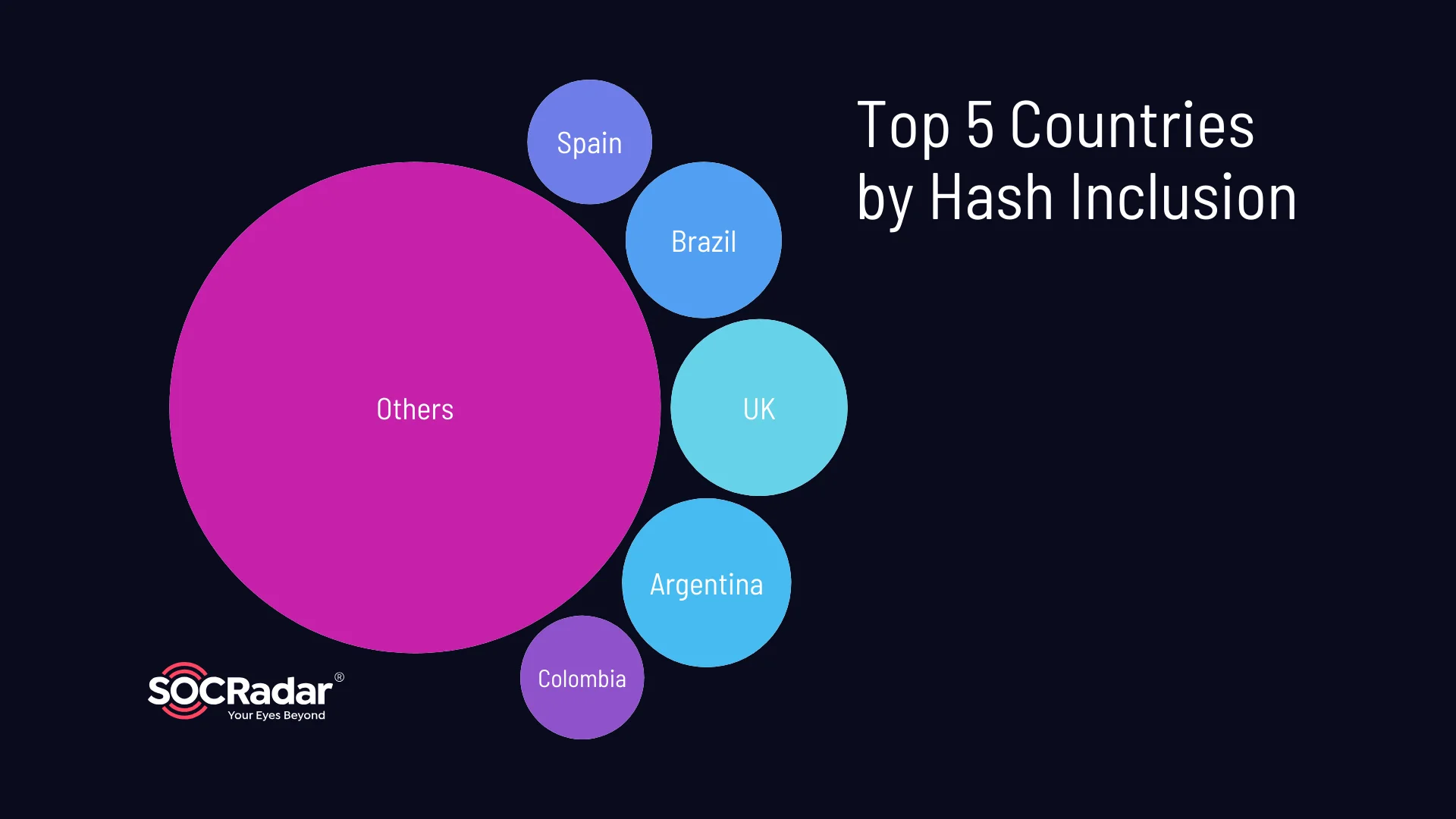
Top 5 countries by hash inclusion
These countries demonstrate a heightened prevalence of compromised hash information within the stealer logs, suggesting a potential risk to user accounts and sensitive data.
Browser Information of Victims in ChatGPT / OpenAI Stealer Logs
Understanding the browsers used by victims when their information was compromised provides valuable insights into the attack vectors exploited by cybercriminals.
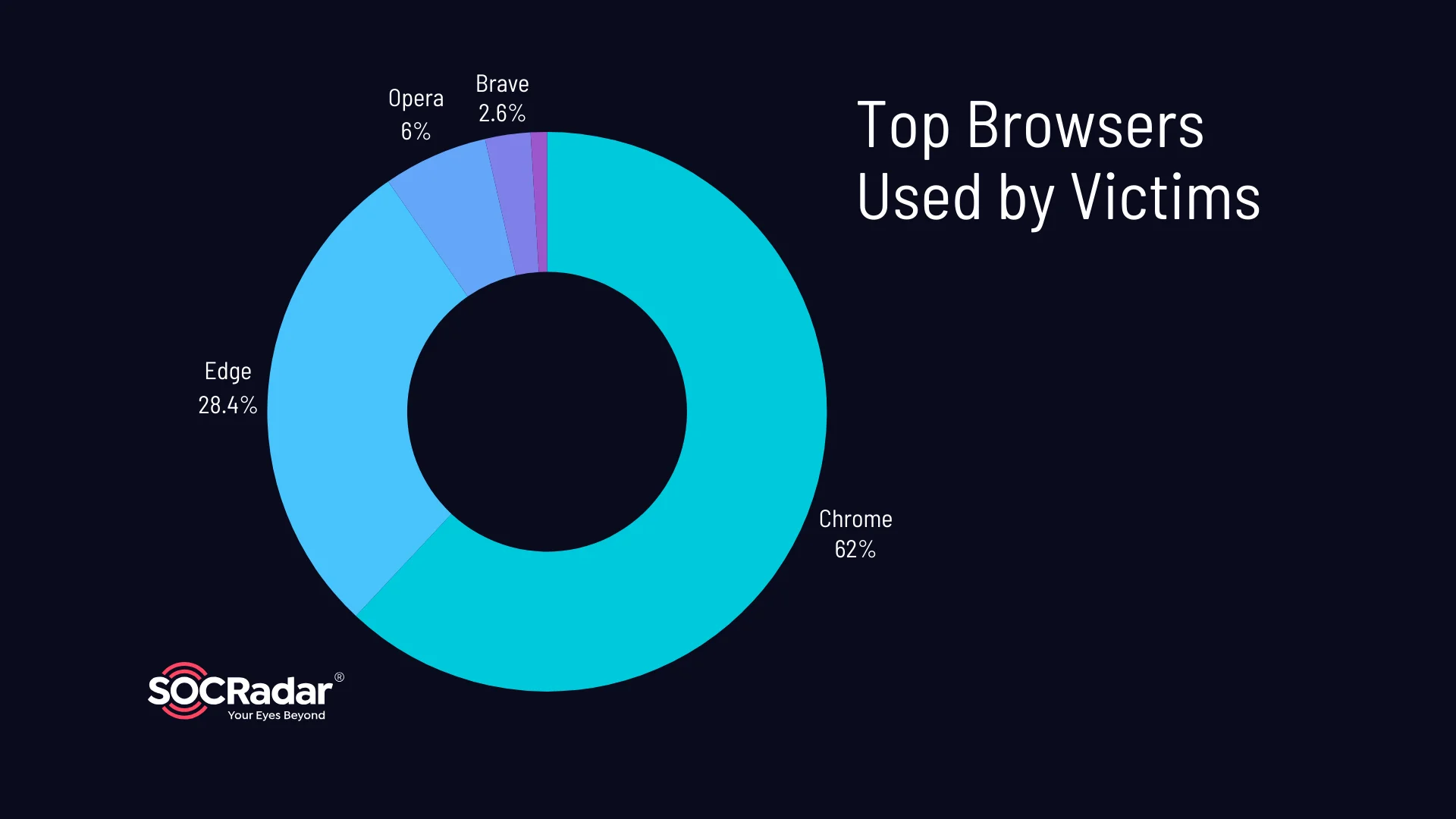
Top browsers used by ChatGPT users found in stealer logs
Chrome emerges as the most commonly used browser among victims, with a significant number of compromised user records attributed to this platform (61.97%). Edge (28.42%) and Opera (6.05%) follow in ranks, with substantial representation in the stealer logs.
Other browsers such as Brave, CocCoc, Firefox, and Vivaldi also appear, albeit in smaller numbers.
The prevalence of Chrome and other widely used browsers underscores the importance of securing browser environments against various attack vectors, including malware and phishing attempts. Organizations and individuals should prioritize implementing robust security measures to safeguard against browser-based threats and protect sensitive information from falling into the hands of cybercriminals.
How Can You Enhance Security Measures Against Stealers?
Not only OpenAI, but all organizations need effective strategies to protect their data against cyber threats like stealer malware. Here are some best practices:
- Organizations need to implement strict controls over employee account access, which can include adopting robust authentication methods such as Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) or Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) to enhance defense against unauthorized access.
- Encouraging the use of password managers among employees can significantly enhance security measures. Stressing the importance of creating strong, unique passwords for each account and regularly updating them helps reduce the risk of credential exposure.
- Regularly updating software is essential to safeguard organizational systems. Ensuring that all software is up-to-date with the latest security patches helps address vulnerabilities that may be exploited by stealer malware.
- If stealer malware is identified on employee devices, it is vital to immediately isolate infected devices from the network. Taking swift action against affected users and systems can help contain the breach and prevent further data compromise.
- Educating employees about the risks associated with stealer logs is required. Providing training on how to recognize and avoid suspicious emails and attachments empowers employees to actively contribute to cybersecurity efforts.
- Emphasizing the importance of downloading applications only from trusted sources endorsed by the organization can help minimize the risk of inadvertently installing malicious software or compromised versions of legitimate applications.
- Regularly conducting checks for credential leaks in publicly accessible services is important. Platforms such as popular chat platforms and cloud storage services are frequent targets for cybercriminals seeking to exploit sensitive data.
Stay Informed with SOCRadar’s Dark Web Monitoring Solution
In addition to implementing proactive measures, using CTI tools like SOCRadar’s Dark Web Monitoring provides continuous surveillance of the web, including the deep and dark web, to detect compromised sensitive information related to your customers, employees, or the organization itself.
With real-time alerts on recently compromised account credentials and credit card numbers relevant to your organization, SOCRadar helps mitigate the risks of identity theft and fraud associated with stealer logs.
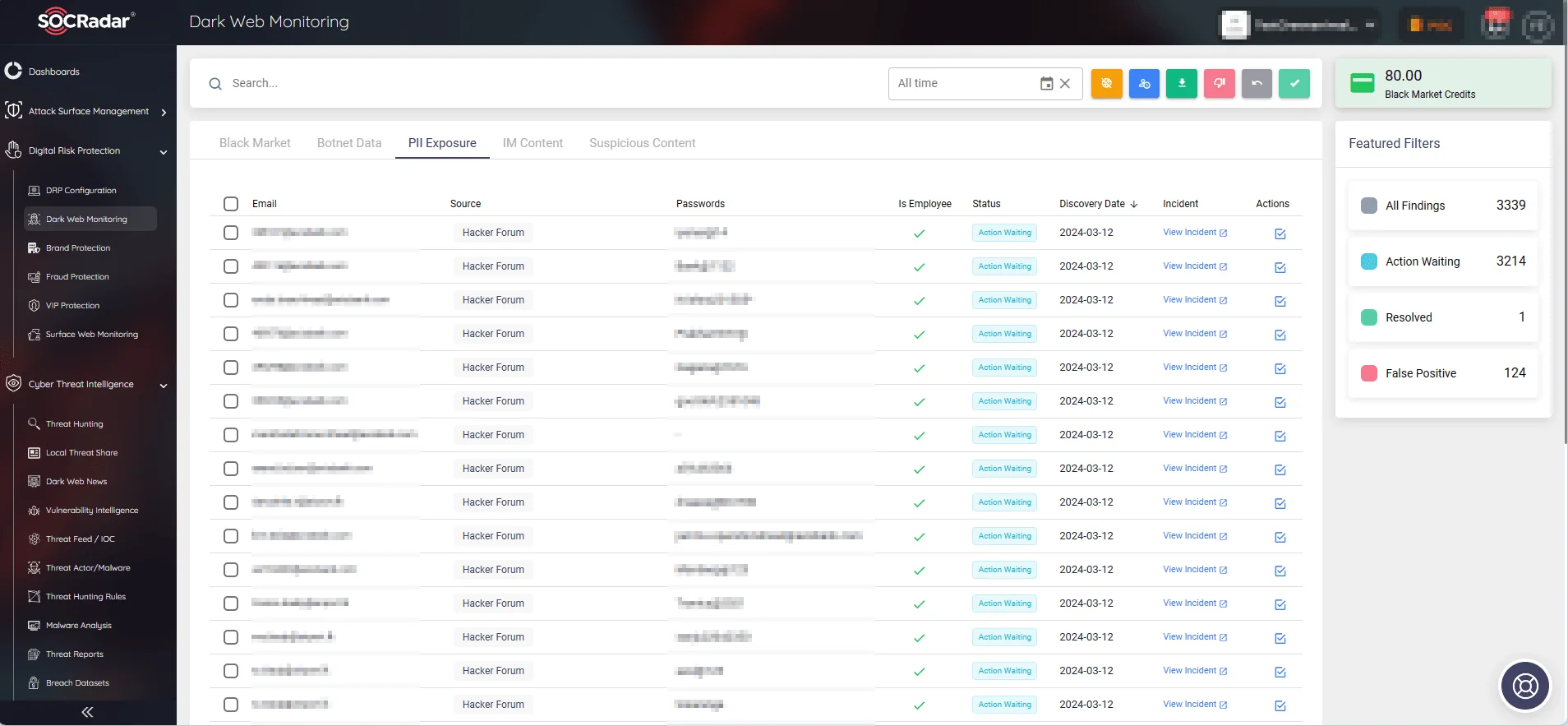
SOCRadar’s Dark Web Monitoring
SOCRadar’s “Snapshot of 70 Million Stealer Logs” whitepaper can help organizations stay up to date on the latest trends surrounding stealer malware and their dangers.
Conclusion
The prevalence of stealer logs poses a significant threat to digital security, with cybercriminals exploiting stolen data for illicit purposes on a daily basis. Our analysis illustrates the pervasive nature of these logs across OpenAI domains, underscoring the potential vulnerability of ChatGPT users to cyber intrusion.
In this blog post, leveraging SOCRadar’s Threat Hunting module, we sifted through vast volumes of data within stealer logs to identify trends and illuminate imminent threats.
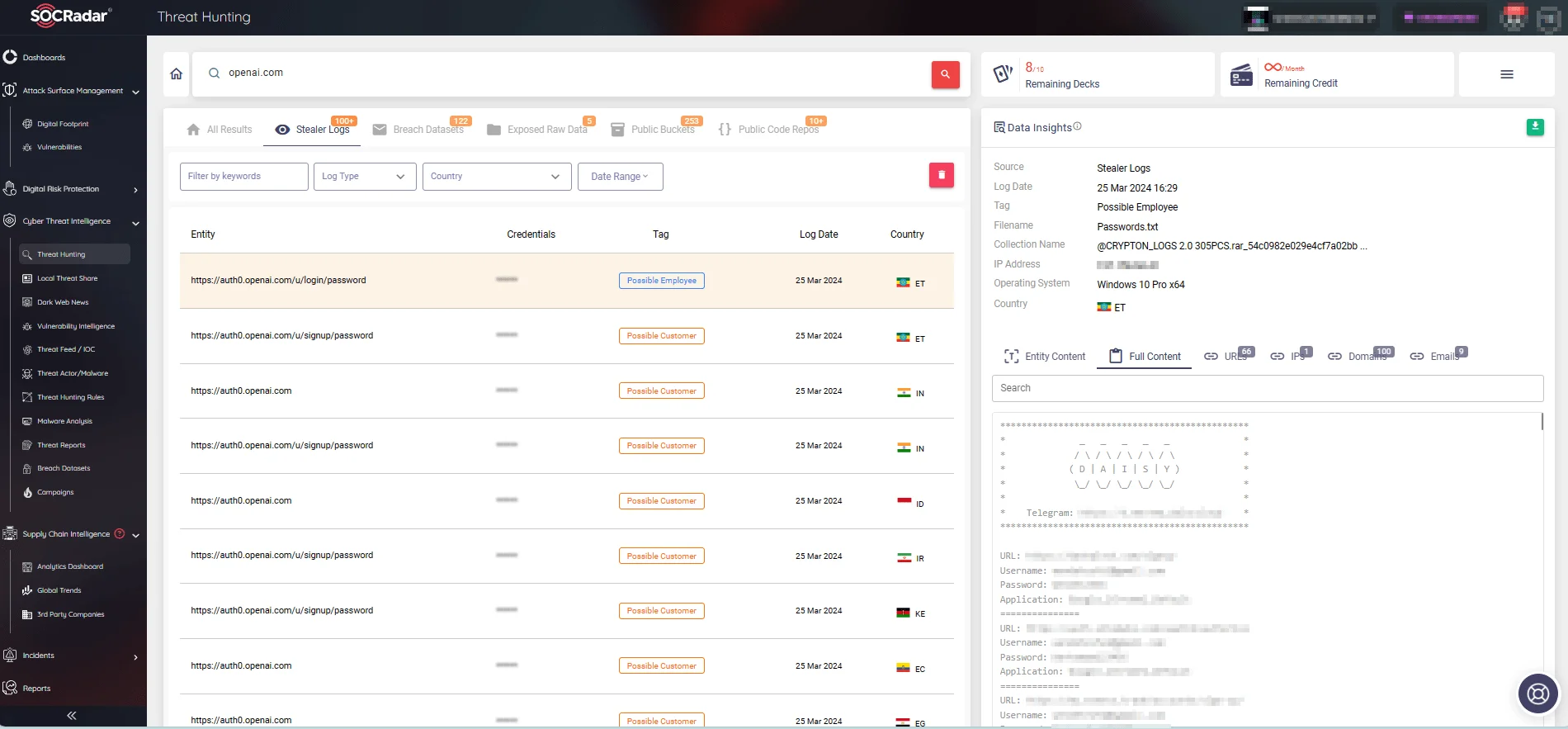
Search on stealer logs for OpenAI (SOCRadar Threat Hunting)
Analyzing stealer malware logs yielded valuable insights into the complex cybersecurity environment surrounding OpenAI and ChatGPT, including the most targeted countries and those at risk of fraud, phishing, and impersonation attacks.
Organizations can use similar analyses to anticipate threats, identify patterns, and strengthen their cybersecurity defenses.
Tools like SOCRadar’s Threat Hunting and Dark Web Monitoring, when combined with strong security measures, can provide critical layers of defense against stealer logs and other cyber threats, providing organizations with timely intelligence for effective threat detection and response.



































