DDoS Attack Trends: Key Takeaways from Cloudflare’s Q4 2024 DDoS Report
Cybersecurity threats continue to evolve, with Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks leading the charge in their scale and sophistication. As digital infrastructure becomes the backbone of business operations worldwide, safeguarding against these attacks has become a top priority. Cloudflare’s latest DDoS Report for Q4 2024 sheds light on this escalating battle, offering critical insights into the tactics of cybercriminals and the strategies required to defend against them.
Among the report’s most striking revelations is a record-breaking DDoS attack that occurred during the Halloween week of 2024. This attack peaked at a staggering 5.6 Tbps, the largest ever recorded, lasting just 80 seconds but involving over 13,000 IoT devices. Such hyper-volumetric assaults showcase the immense capability of adversaries and emphasize the immediate need for organizations to adopt automated, high-capacity defenses.
While the focus areas of the report remain consistent with previous editions, the evolving data provides a fresh perspective on the strategies attackers are using and the defenses required to counter them. In this blog, we will explore the most critical findings from the Q4 2024 DDoS Report, highlighting key trends, attack patterns, and their implications for businesses worldwide. By breaking down these findings, we aim to provide actionable guidance to help organizations strengthen their defenses.
Changing Attack Strategies and What They Mean
Attack methods used by cybercriminals are evolving rapidly, reflecting their ingenuity in exploiting vulnerabilities. The Q4 2024 DDoS Report reveals some of the most significant trends shaping this shift, including amplification attacks and the continued exploitation of IoT devices.
In 2024, Cloudflare’s autonomous defense systems blocked an impressive 21.3 million DDoS attacks, reflecting a 53% increase compared to 2023. On average, this equated to 4,870 attacks blocked per hour. During Q4 alone, 6.9 million attacks were mitigated. Of these, 49% were Layer 3/Layer 4 DDoS attacks, while 51% were HTTP DDoS attacks, with 73% of HTTP DDoS attacks launched by known botnets.
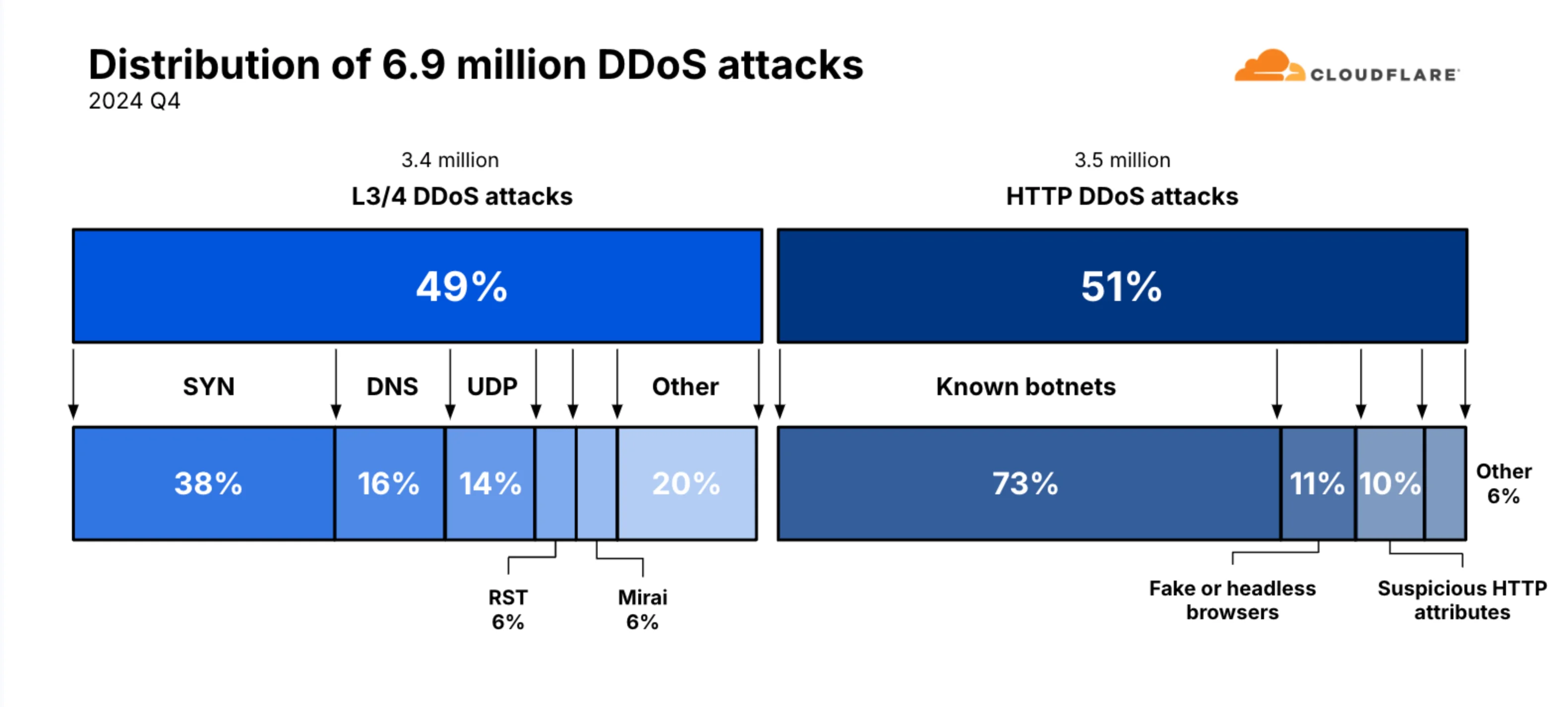
Distribution of 2024 Q4 DDoS attacks (Cloudflare)
What follows is an exploration of the tactics used in these attacks and their implications for cybersecurity defenses.
The Amplification Effect: Memcached and BitTorrent
The resurgence of Memcached amplification attacks is a key finding from Q4 2024, with these attacks increasing by 314% quarter-over-quarter. Attackers exploit misconfigured Memcached servers to amplify attack traffic, causing significant disruption. Similarly, BitTorrent DDoS attacks saw a 304% rise, leveraging the protocol’s infrastructure to flood victims with spoofed traffic. These methods demonstrate how cybercriminals adapt overlooked technologies for malicious purposes.
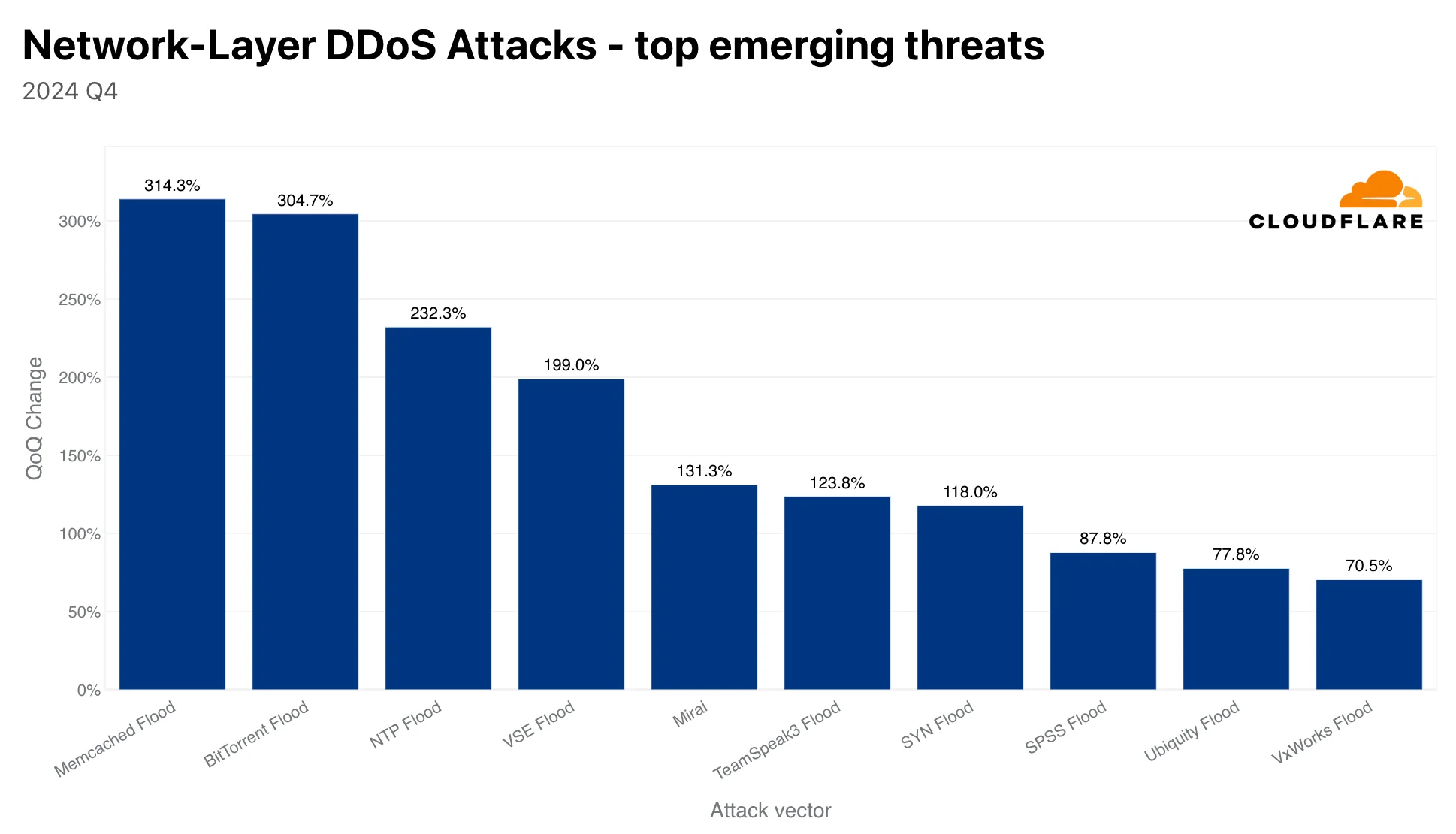
DDoS threats on the network layer (Cloudflare)
IoT Devices Under Siege: The Mirai Botnet Factor
Mirai botnets, notorious for hijacking IoT devices, accounted for 6% of all network-layer DDoS attacks this quarter. The largest recorded attack of Q4 – the 5.6 Tbps assault – originated from a Mirai variant, emphasizing the ongoing threat posed by unsecured IoT devices. Securing these devices is critical to minimizing their role in future botnet-driven attacks.
To proactively defend your systems, SOCRadar LABS offers the DoS Resilience service. This free tool provides valuable insights into your domain’s or subnet’s resilience against various DoS attack types. By leveraging this service, you can identify vulnerabilities and implement preventive measures to ensure strong defenses.

Free DoS Resilience service available on SOCRadar LABS
Attack Intensity: Magnitude and Frequency on the Rise
As attackers grow more resourceful, the size and frequency of DDoS assaults have reached unprecedented levels. The Q4 2024 DDoS Report reveals striking statistics about hyper-volumetric attacks and their implications for defenses. These trends set the stage for understanding both the exceptional and everyday challenges organizations face in mitigating DDoS threats.
The Era of Hyper-Volumetric Assaults
Cloudflare mitigated over 420 hyper-volumetric attacks exceeding 1 Tbps in Q4 2024, a remarkable figure reflecting a 1,885% increase quarter-over-quarter. Similarly, attacks exceeding 100 million packets per second grew by 175%.
These record-breaking assaults highlight the intensifying scale of DDoS threats and the imperative for defenses capable of handling such overwhelming traffic.
The Role of Encryption in DDoS Attacks
DDoS attackers are increasingly leveraging HTTPS traffic to disguise their malicious activity, with 92% of attack requests in Q4 conducted over encrypted connections. This is in stark contrast to legitimate traffic, where 94% used HTTPS. Such encrypted attacks complicate mitigation efforts, demanding higher computational resources from defenses.
At the network layer, SYN floods dominated with 38% of attacks, followed by DNS floods (16%) and UDP floods (14%), highlighting the diverse vectors attackers employ to overwhelm systems.
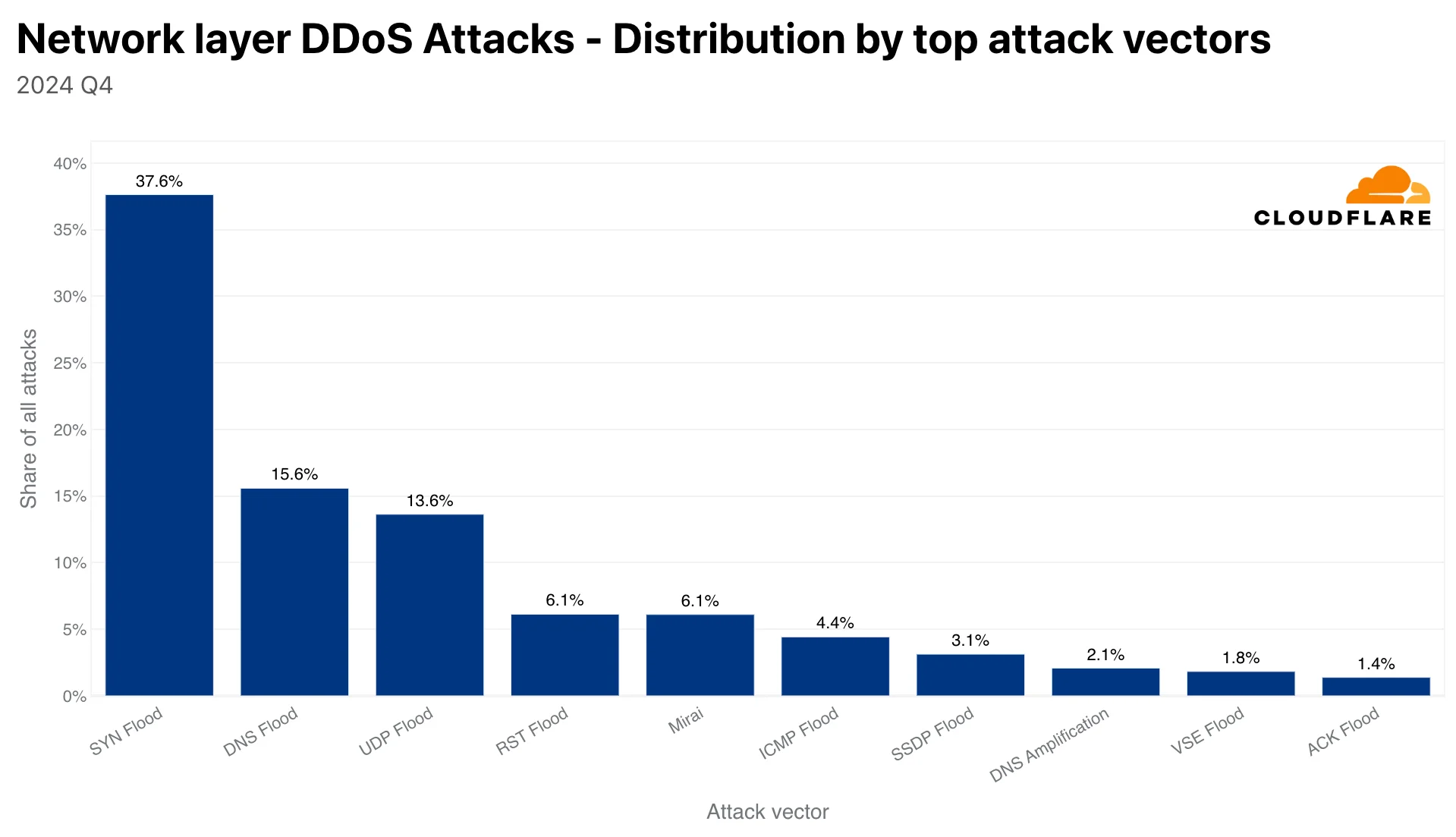
DDoS attack vectors on the network layer (Cloudflare)
Measuring the Typical Attack: Sizes and Durations
While extreme attacks grab headlines, most network-layer assaults (93%) remained under 500 Mbps, with HTTP DDoS attacks (63%) not surpassing 50,000 requests per second. Yet, the 3% of HTTP DDoS attacks that exceeded 100 million requests per second underline the potential for massive disruption even in a minority of cases. Most attacks lasted less than 10 minutes, demonstrating the importance of swift, automated mitigation strategies.
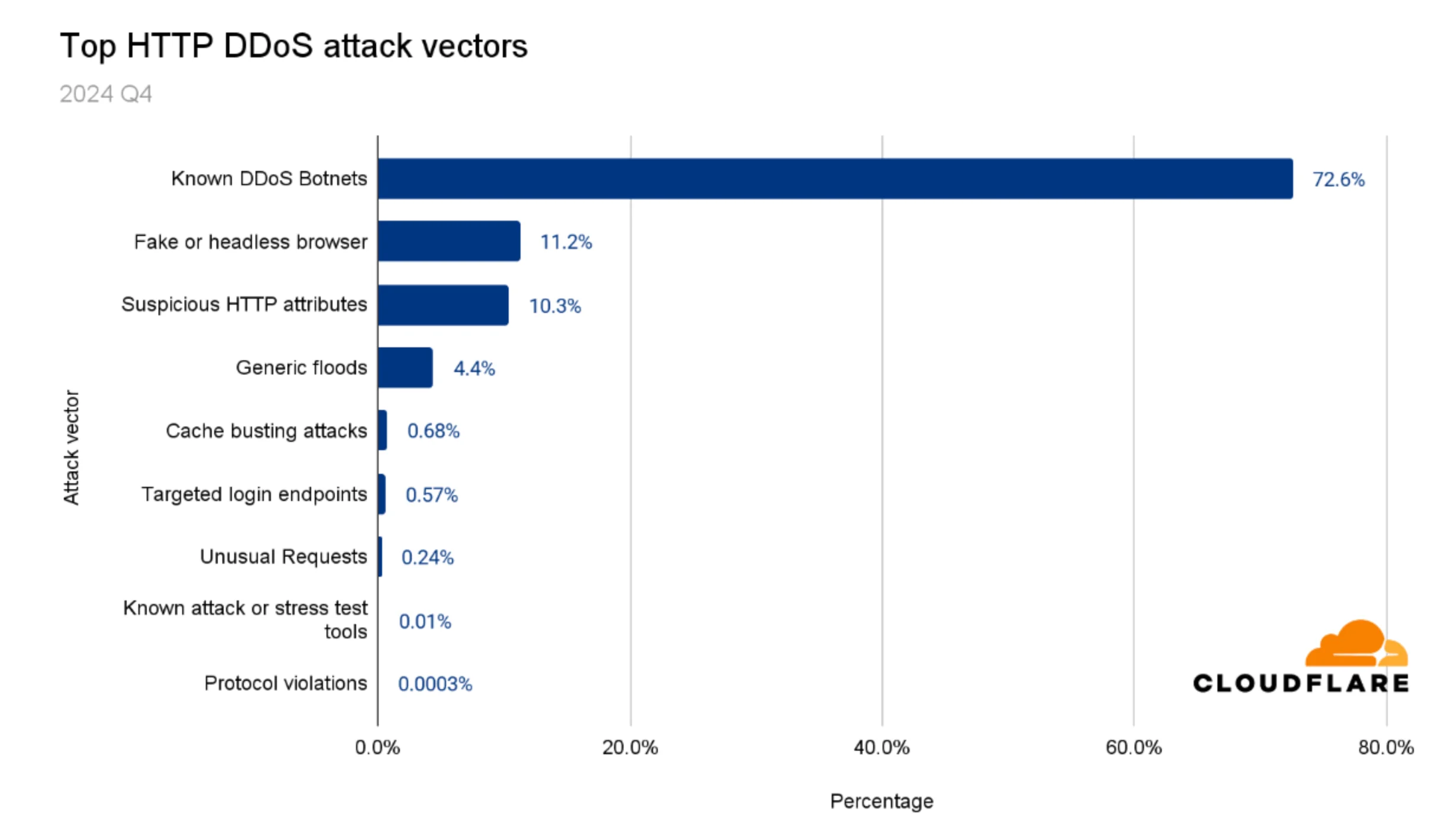
HTTP DDoS attack vectors in 2024 Q4 (Cloudflare)
Global Footprint: Where Attacks Come From and Who They Target
The reach of DDoS attacks spans the globe, with certain regions and industries bearing the brunt of malicious activity. Understanding the origins of these attacks and identifying their primary targets is important for developing effective defenses. In this section, we explore the hotspots for attack traffic, the nations most impacted, and the industries that remain in the crosshairs of cybercriminals.
Hotspots of Malicious Traffic
Attack traffic predominantly originated from Indonesia, followed by Hong Kong and Singapore, regions known for high connectivity and large pools of compromised devices. These areas continue to serve as launching pads for widespread DDoS campaigns.
Threat actors, including competitors (40%) and state-sponsored groups (17%), leveraged opportunities to launch high-impact DDoS attacks.
Disguising Traffic via User Agents
Interestingly, some HTTP DDoS attacks were disguised using compromised user agents like HITV_ST_PLATFORM. The traffic of this user agent was 99.9% DDoS requests, pointing to the exclusive involvement of smart TVs in botnet activity.
Nations Under Siege
China, followed by the Philippines, and Taiwan ranked as the top targets of DDoS attacks in Q4 2024. These nations’ critical digital infrastructures and geopolitical importance make them prime objectives for cybercriminals.
Industries in the Crosshairs
The most attacked sectors included telecommunications, service providers, and carriers, reflecting their central role in digital connectivity. Surprisingly, the banking and financial services industry dropped to eighth place, suggesting a tactical shift in attacker priorities toward other high-value targets like internet services and marketing platforms.

Top 10 industries targeted by DDoS attacks in 2024 Q4 (Cloudflare)
For a deeper understanding of the threats targeting your region or country, check out SOCRadar LABS Country Threat Landscape & Industry Threat Landscape reports. These free resources offer insights into prevalent risks, including ransomware, phishing, and Dark Web threats, along with identifying the most active threat actors in your country/industry.
Download the Industry Threat Landscape Report to stay informed and prepared
Holiday Season Surge in Ransom DDoS
Ransom DDoS (RDDoS) attacks have become an increasingly disruptive threat, particularly during critical business seasons. Attackers often exploit unusual HTTP methods and vulnerable paths like /wp-admin/ to intensify their impact. Additionally, 12% of targeted customers reported ransom threats in Q4 2024, representing a 78% increase quarter-over-quarter.
This trend highlights the holiday season’s attractiveness for attackers aiming to exploit heightened digital activity. RDDoS campaigns are particularly disruptive for industries like e-commerce and SaaS providers, which rely heavily on uninterrupted online operations.
Practical Strategies to Mitigate Threats
To combat the growing DDoS threat, organizations can adopt several proactive measures:
- Automate DDoS mitigation: Deploy tools that detect and neutralize attacks in real time.
- Secure IoT devices: Prevent their exploitation by botnets through regular updates and proper configuration.
- Optimize network defenses: Use rate-limiting and adaptive filtering to manage high-volume attacks effectively.
- Monitor traffic anomalies: Stay alert to unusual patterns that might indicate an impending attack.
- Focus on vulnerable paths: Protect critical endpoints like /wp-admin/ and monitor usage of unusual HTTP methods.
- Foster collaboration: Share threat intelligence across the industry to enhance overall resilience.
In addition to these strategies, leveraging advanced tools like SOCRadar’s Extended Threat Intelligence (XTI) platform can provide a significant advantage in mitigating DDoS threats and other cyber risks. The XTI platform delivers real-time insights into emerging threats, enabling your organization to detect and respond to potential attacks before they escalate. By monitoring Surface, Deep, and Dark Web sources, it identifies critical vulnerabilities and evolving attacker tactics, ensuring your security team stays ahead of adversaries.
With its extensive threat intelligence capabilities, SOCRadar XTI helps enhance your defenses. Automated alerts, actionable insights, and continuous monitoring allow your team to prioritize threats and respond swiftly.
Conclusion: Building Resilience Against Growing Threats
The Q4 2024 DDoS Report by Cloudflare demonstrates how DDoS attacks are evolving in scale, complexity, and frequency. From hyper-volumetric assaults to innovative attack vectors, the findings emphasize the need for robust and adaptive defenses. By understanding these insights and taking proactive steps, businesses can safeguard their digital operations against the growing tide of cyber threats.