
FortiGate Firewall Configs Dumped: Revisiting CVE-2022-40684 Exploitation
[Update] January 18, 2025: “Fortinet’s Official Statement on the Breach”
In a shocking development, the fallout from the 2022 Fortinet vulnerability, CVE-2022-40684, has resurfaced with severe consequences. A newly emerged group, Belsen Group, has released configurations from over 15,000 compromised FortiGate firewalls.
This breach not only exposes usernames, passwords (some in plaintext), and VPN credentials but also includes critical firewall rules, IP addresses, and digital certificates, underscoring the lingering impact of vulnerabilities even years after patching.
The Exploit: A Critical Authentication Bypass
Originally discovered in 2022, CVE-2022-40684 was a severe authentication bypass vulnerability with a CVSS score of 9.8. Exploited actively in the wild, it allowed remote attackers to gain administrative access to Fortinet devices via specially crafted HTTP or HTTPS requests. Vulnerable versions included FortiOS (7.0.0–7.0.6 and 7.2.0–7.2.1), FortiProxy (7.0.0–7.0.6 and 7.2.0), and FortiSwitchManager (7.0.0 and 7.2.0).
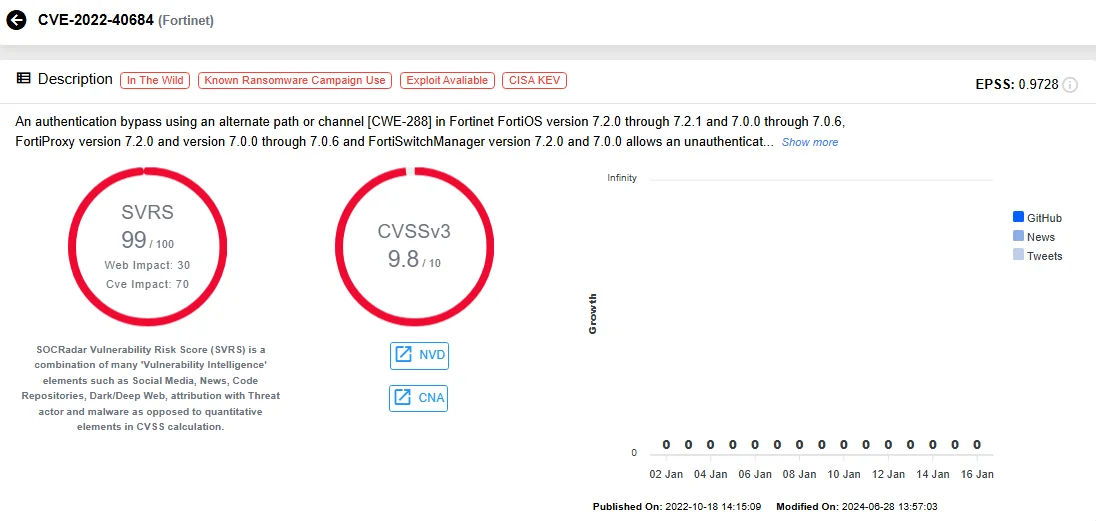
Vulnerability card of CVE-2022-40684 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
Though patches were promptly issued by Fortinet, reports emerged of attackers exploiting unpatched systems, leading to unauthorized access to sensitive configurations. GreyNoise and Shodan searches during the exploit’s peak highlighted over 165,000 publicly exposed FortiGate firewalls, indicating the scope of the threat.
The Fallout: 2022 Exploits Surface in 2025
The Belsen Group’s recent release of compromised firewall configurations reveals that many organizations were exploited before patching their systems. The leaked data includes detailed configurations and plaintext VPN credentials, posing significant risks:
- Network security compromised: Attackers now have access to detailed firewall rules, potentially enabling them to evade defenses.
- Credential exposure: Plaintext usernames and passwords increase the risk of further breaches.
- Geographical exposure: The dump is categorized by country, making it easier for threat actors to target specific regions.
- IP Address Context: Each folder in the leaked dump includes IP addresses linked to individual configurations, making it simpler for attackers to target and exploit devices.
Top Countries Affected
Through analysis of the affected IP addresses, SOCRadar identified the top countries impacted by this breach. Mexico and the United Arab Emirates led the list, with 1,603 devices (10.34%) and 1,081 devices (6.98%) affected, respectively. Notably, the top 10 affected countries accounted for more than 51% of the impacted devices across the 144 affected countries. The remaining top 10 countries, including Thailand, Malaysia, and the United States, are displayed in the accompanying graph.
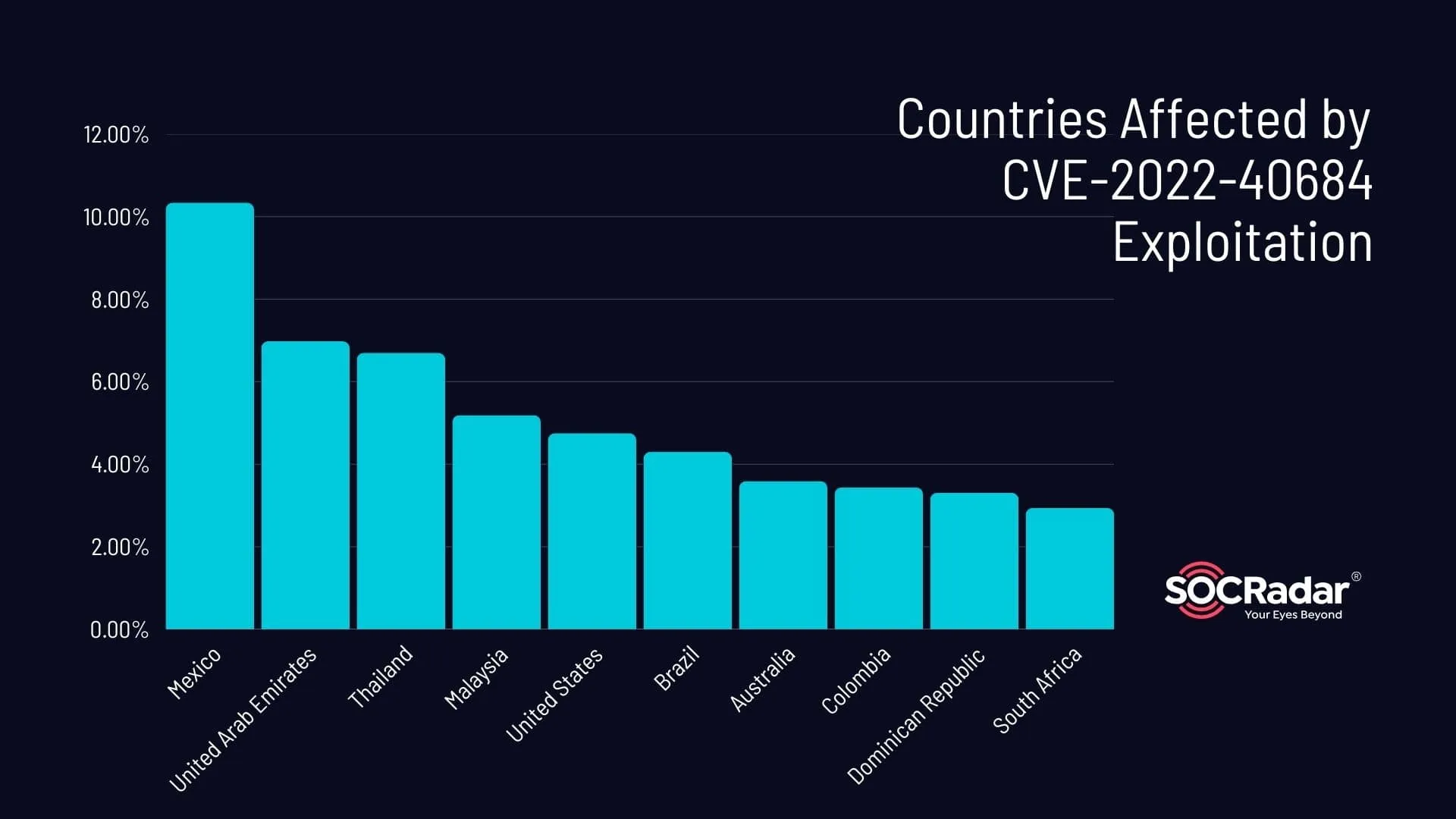
This data showcases the widespread nature of the exploit, leaving organizations across various regions vulnerable to potential attacks.
Similarities to CVE-2024-55591
The recent disclosure of CVE-2024-55591 underscores the ongoing risks associated with Fortinet devices. While the security researcher Kevin Beaumont confirmed that the Belsen Group exploited CVE-2022-40684 to gain access to and leak FortiGate configurations, he also warned that similar threat actors may target the newly discovered CVE-2024-55591. Despite their technical differences, both vulnerabilities exposed critical administrative controls on Fortinet systems, allowing attackers to make unauthorized configuration changes and compromise VPN credentials.
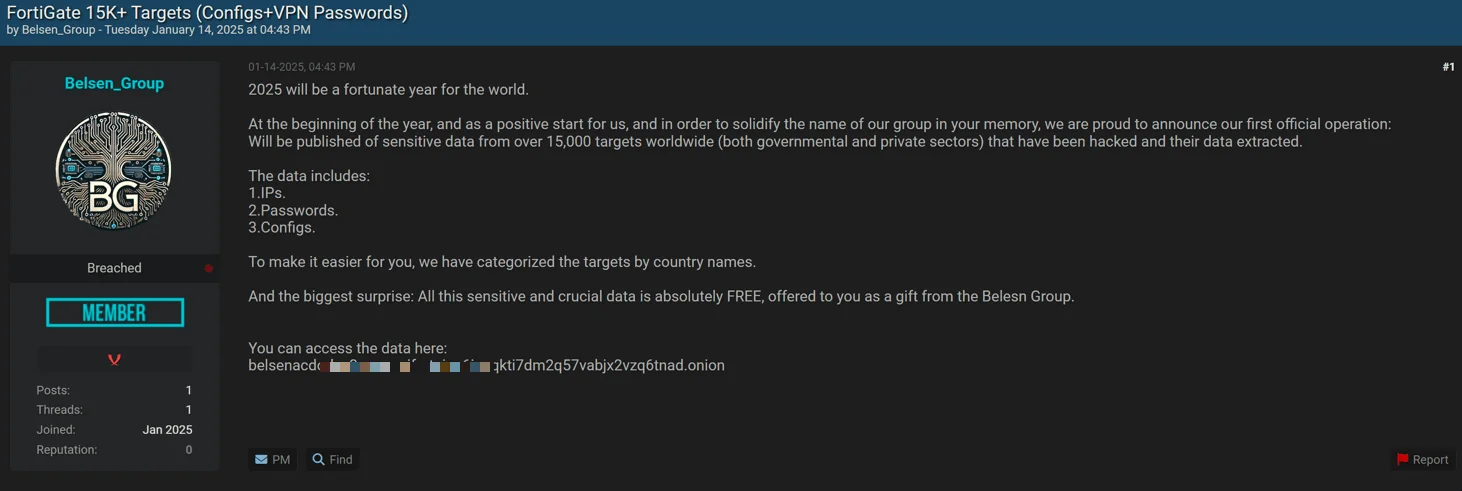
Dark web announcement by Belsen Group showcasing leaked configurations and credentials
Kaushík Pał emphasized the importance of patching both vulnerabilities, noting that attackers who exploited the 2022 zero-day may already be planning how to exploit CVE-2024-55591. This is consistent with broader trends in the cybersecurity landscape, in which advanced threat actors frequently repurpose successful methodologies for new vulnerabilities to broaden their attack scope. Both incidents highlight the importance of securing administrative interfaces, applying patches quickly, and constantly monitoring for signs of compromise.
According to the lifecycle findings in SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence module, CVE-2024-55591 has gained attention on social platforms like Telegram, where it has been mentioned multiple times across different channels.

SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence module Vulnerability Lifecycle
The timeline shows a significant increase in discussions and activity related to this vulnerability, indicating growing interest from users—and potentially threat actors. This highlights the urgency for organizations to monitor such developments and act swiftly to protect their systems.
Lessons Learned: Patch and Monitor
Even if organizations patched CVE-2022-40684 in late 2022, the stolen data may have already been exfiltrated and exploited. This emphasizes the importance of proactive patch management and monitoring for Indicators of Compromise (IoCs). Logs should be examined for suspicious activity, such as:
- user=”Local_Process_Access”
- user_interface=”Node.js” or “Report Runner”
Mitigation and Next Steps
To mitigate the risks associated with this breach, organizations should:
- Change device credentials immediately for all affected Fortinet devices.
- Reassess firewall rules to identify potential vulnerabilities revealed by the leaked configurations.
- Implement additional security layers, such as IP restrictions and disabling public-facing administrative interfaces.
- Adopt proactive vulnerability intelligence platforms like SOCRadar to monitor exposed data and mitigate risks.
Fortinet’s Official Statement on the Breach
Fortinet has issued a detailed statement responding to the Belsen Group’s recent claims about leaked FortiGate firewall configurations and VPN credentials. According to their analysis, the data comes from older campaigns that exploited CVE-2022-40684, not any recent vulnerabilities or incidents. The exposed data, organized by country and IP address, primarily consists of configurations from FortiOS 7.0.6 and 7.2.1, the last vulnerable versions before patches were released in 2022.
According to Fortinet’s investigation, the leaked data also includes IoCs related to previous vulnerabilities, such as FG-IR-22-377 and FG-IR-18-384, indicating that the threat actor repackaged outdated information to appear as a new disclosure. Organizations that have consistently followed Fortinet’s best practices, such as upgrading to supported versions of FortiOS and refreshing credentials, are at low risk from this vulnerability. Fortinet also confirmed that devices purchased after December 2022 or running FortiOS 7.2.2 and higher are unaffected by the leak.
Recommended Actions by Fortinet:
- Ensure your FortiGate devices are updated to the latest FortiOS versions.
- Validate configurations for unauthorized changes using Fortinet’s detailed IoCs.
- Adhere to routine credential-refreshing practices.
Boost Your Cyber Defense with SOCRadar’s Threat Hunting Module
In a space where advanced threats and zero-day vulnerabilities can go undetected for months, proactive threat hunting is no longer an option; it’s required. SOCRadar’s Threat Hunting module enables organizations to identify hidden threats before they escalate. Security teams can quickly identify malicious activities and improve incident response capabilities by leveraging actionable intelligence, automated IOC searches, and advanced correlation techniques.
Track and investigate emerging threats in real time with SOCRadar’s Threat Hunting module
SOCRadar provides real-time insights and in-depth analytics to help your team stay ahead of evolving cyber threats such as the recent FortiGate exploits. With SOCRadar’s Threat Hunting module, you can proactively defend your digital ecosystem rather than waiting for the next breach. Explore how it can improve your security operations today.
Looking Forward
The FortiGate exploit highlights the enduring danger of delayed patching and the long-term consequences of zero-day vulnerabilities. With over 15,000 firewalls exposed, the need for continuous monitoring, robust incident response plans, and comprehensive cybersecurity measures has never been clearer. Tools like SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence can play a critical role in helping organizations stay informed and secure against evolving threats.


































