
Microsoft’s June 2023 Patch Tuesday Fixes Six Critical Vulnerabilities
Microsoft has released the Patch Tuesday update for June 2023, which addresses 78 security vulnerabilities. While six of the listed vulnerabilities are critical, there were no zero-day vulnerabilities in this month’s patch.
The number of vulnerability types covered in June’s Patch Tuesday is as follows:
- 32 Remote Code Execution (RCE) Vulnerabilities
- 17 Elevation of Privilege (EoP) Vulnerabilities
- 10 Denial of Service (DoS) Vulnerabilities
- 10 Spoofing Vulnerabilities
- 5 Information Disclosure Vulnerabilities
- 3 Security Feature Bypass Vulnerabilities
- 1 Edge – Chromium Vulnerabilities
Critical Vulnerabilities of June 2023 Patch Tuesday
CVE-2023-29357 (CVSS Score: 9.8, Critical): This is an Elevation of Privilege (EoP) vulnerability that allows attackers to gain Administrator privileges on the SharePoint host by using spoofed JWT tokens.
Although Microsoft has not seen any public disclosure or active exploitation, they consider the possibility of exploitation to be higher.
Both SharePoint Enterprise Server 2016 and SharePoint Server 2019 are affected. The June security update does not explicitly reference CVE-2023-29357, and the advisory for the vulnerability still does not mention a patch for SharePoint 2016.
Defenders should closely monitor the situation as there is currently no patch available that addresses CVE-2023-29357 for SharePoint 2016.
Microsoft notes that multiple patches may be necessary for a specific version of SharePoint, and all patches for that version must be installed to address this vulnerability, regardless of the order.
CVE-2023-29363, CVE-2023-32014, and CVE-2023-32015 (CVSS Score: 9.8, Critical): Three critical Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerabilities have been identified in Windows PGM.
PGM is a multicast protocol known for its reliability and scalability. It allows receivers to identify and address data loss, request the retransmission of missing data, or inform an application about loss that cannot be recovered.
Microsoft has not observed any exploitation or public disclosure, and they believe the likelihood of exploitation is low.
Exploiting these vulnerabilities requires sending a specially-crafted file over the network to execute malicious code on the target system.
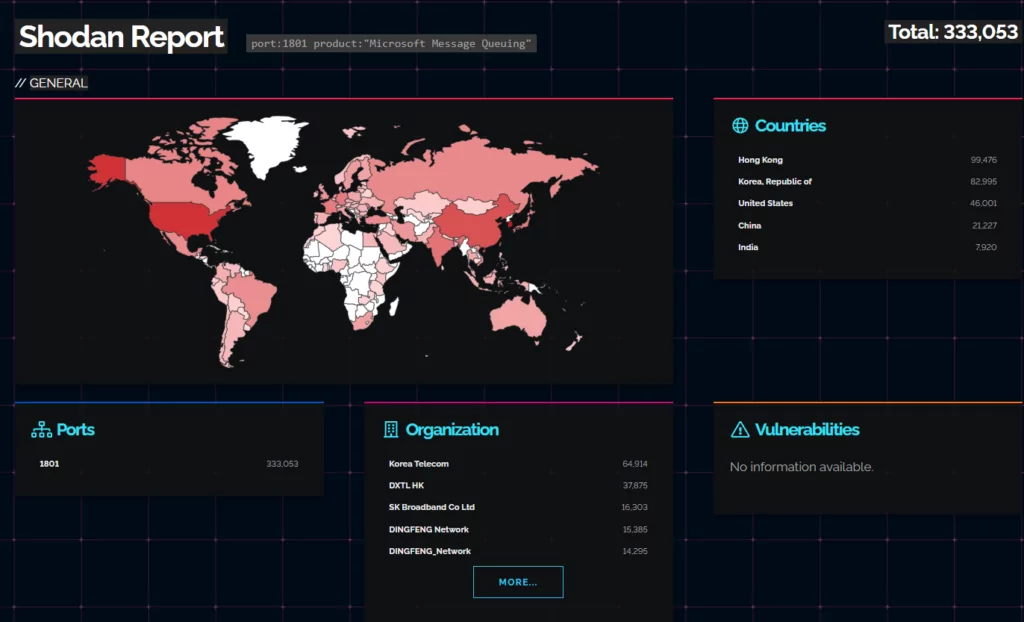
To exploit this vulnerability, the Windows message queuing service, which is a built-in component of Windows, must be enabled on the system.
To verify if the service is running, check if there is a service named “Message Queuing” and ensure that TCP port 1801 is actively listening on the machine.
CVE-2023-24897 (CVSS Score: 7.8, High): Another RCE that affects .NET, .NET Framework, and Visual Studio. Despite it having a CVSS score of 7.8, Microsoft classified the vulnerability’s max severity as Critical in the advisory. Exploiting this vulnerability requires convincing the victim to open a specially-crafted malicious file, usually from a website.
Although there have been no reports of public disclosure or exploitation, the extensive list of patches dating back to .NET Framework 3.5 on Windows 10 1607 indicates that this vulnerability has existed for years.
While Microsoft does not specify the file type associated with the vulnerability, it does require local user interaction, and the remote qualifier refers to the location of the attacker.
CVE-2023-32013 (CVSS score: 6.5, Medium): This denial of service vulnerability in Windows Hyper-V has a maximum severity of Critical on the Microsoft advisory. To successfully exploit this vulnerability, an attacker must first prepare the target environment to improve exploit reliability.
Other Important Fixes the Patch Includes
CVE-2023-28310 and CVE-2023-32031 (CVSS scores: 8.0 and 8.8, High): The attacker must have previously obtained an authenticated role on the Exchange server to exploit these RCE vulnerabilities. An attacker who successfully exploits these vulnerabilities could use PowerShell remoting sessions to gain remote code execution. Microsoft anticipates that both of these vulnerabilities will be exploited.
CVE-2023-21565 (CVSS score: 7.1, High): The vulnerability exists in the Azure DevOps Server and could allow an attacker to gain access to data such as organization/project configuration, groups, teams, projects, pipelines, boards, and wiki. To exploit this vulnerability, an attacker must have valid service credentials but does not need elevated privileges.
To protect your environment and enhance your security posture, we strongly advise you to apply the patches as soon as possible. See Microsoft’s Release Note for more information on the vulnerabilities mentioned in this update.
Enhance Security with SOCRadar
SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence offers additional security protection by detecting and tracking potential security risks like vulnerabilities.
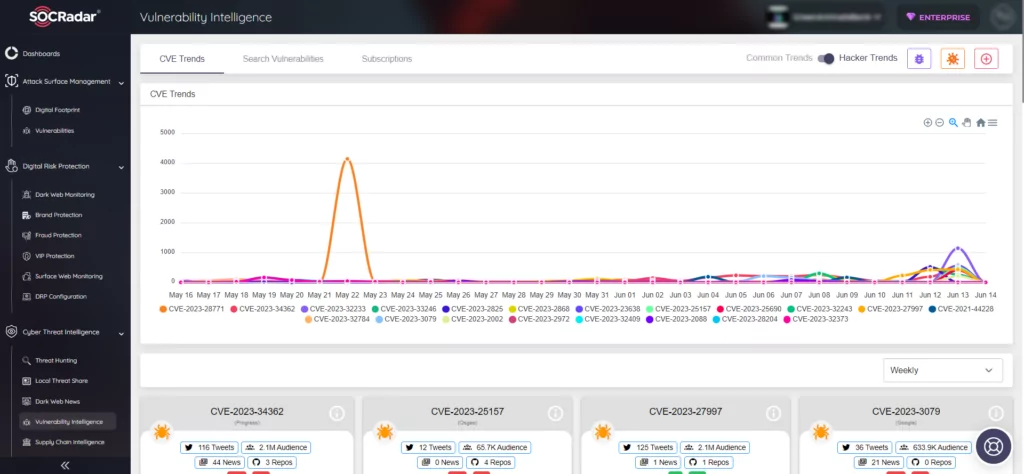
Additionally, its External Attack Surface Management (EASM) feature helps identify your digital assets and notifies you of any emerging issues. By providing actionable insights, the platform enhances security measures and aids in patch management.
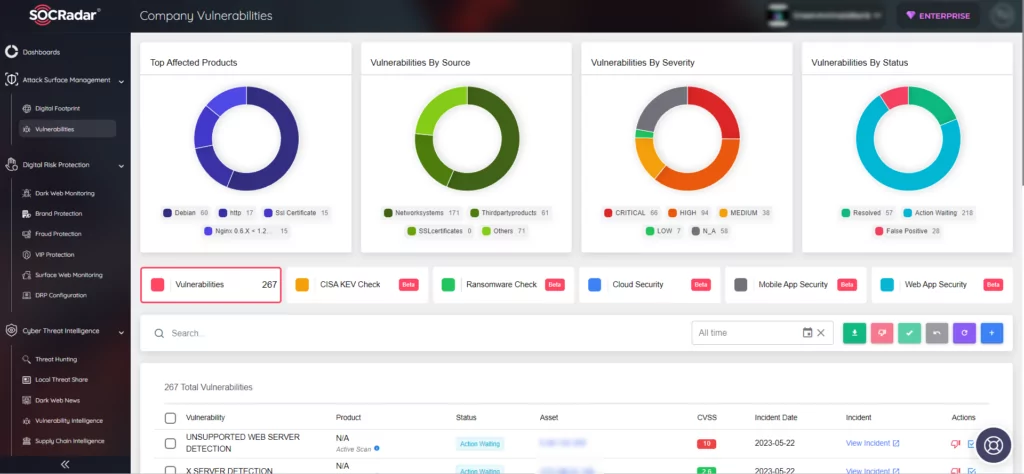
To gain more knowledge and stay informed about the latest vulnerabilities, you can sign up for a demo of the SOCRadar platform.



































