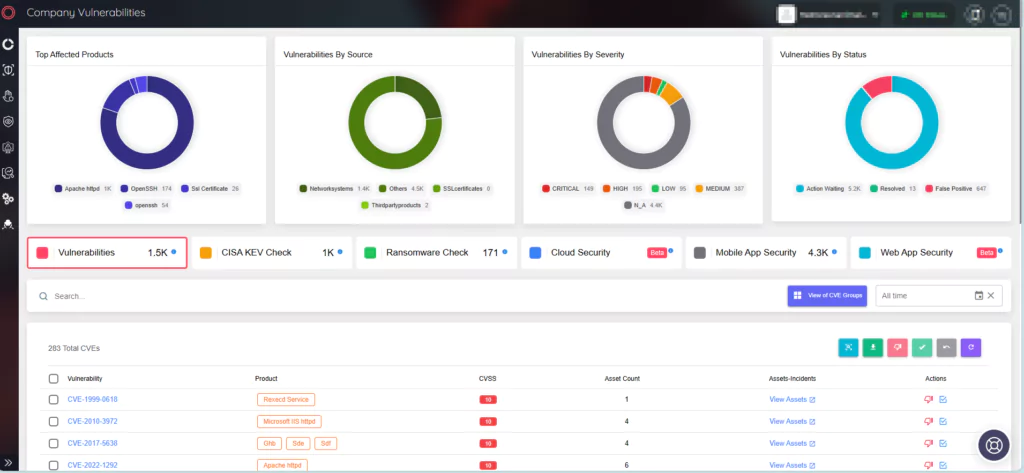
Over a Dozen Critical RCE Vulnerabilities in Ivanti Avalanche; Actively Exploited Chrome Zero-Day, CVE-2023-7024
Ivanti has issued security updates to address a total of 22 vulnerabilities identified in its Avalanche Mobile Device Management (MDM) product. Among these, 13 are of critical severity, demanding immediate attention.
Avalanche MDM is a system designed for centralized device management via an internet connection, facilitating supply chain mobility. With Ivanti Avalanche MDM, users can oversee device details, including battery power and location, manage device settings like Wi-Fi and GPS, and distribute or remove software.
These vulnerabilities impact older versions of Avalanche, confirmed back to 6.3.1, with a likelihood of affecting any 6.X versions.
Details of Vulnerabilities Affecting Ivanti Avalanche
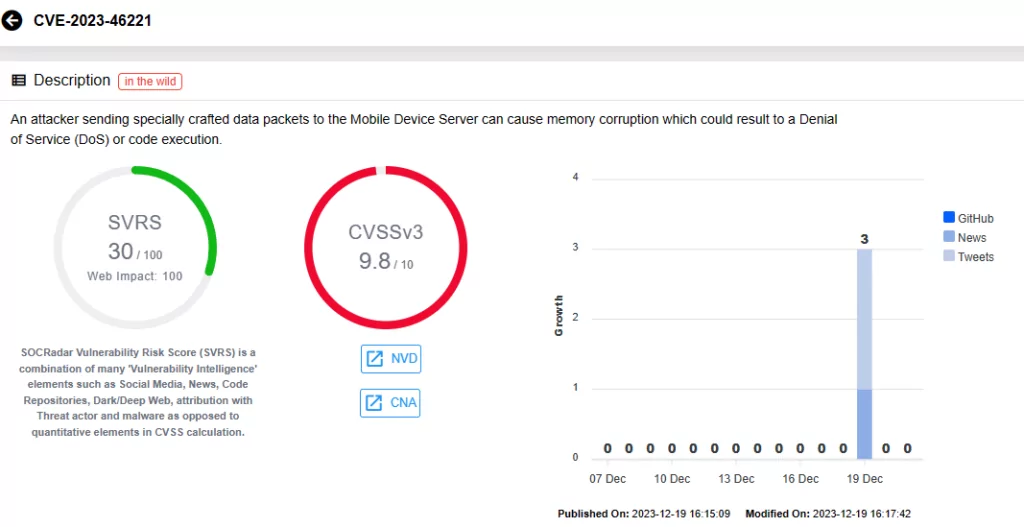
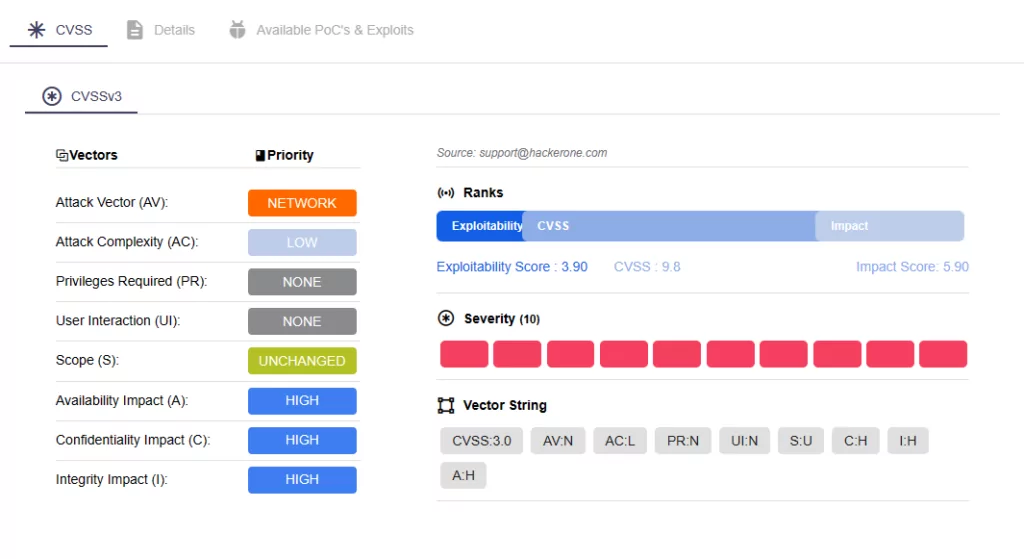
On the Ivanti advisory, there are 22 vulnerabilities that have been patched in the latest release of Avalanche version 6.4.2. Of these, 13 are critical with CVSS scores of 9.8. Attackers could exploit these vulnerabilities by sending crafted data packets to the Mobile Device Server, causing memory corruption, which could enable Remote Code Execution (RCE). Moreover, exploitation of these vulnerabilities does not require user interaction.
One critical vulnerability, CVE-2023-46261, affects WLInfoRailService, responsible for managing messages between servers and databases, typically installed with the Enterprise Server. The remaining 12 vulnerabilities are associated with WLAvalancheService (Mobile Device Server).
Critical vulnerabilities in the update are categorized as follows:
Stack-based Buffer Overflow:
- CVE-2023-46220
- CVE-2023-46221
- CVE-2023-46222
- CVE-2023-46223
- CVE-2023-46224
- CVE-2023-46225
- CVE-2023-46257
- CVE-2023-46258
- CVE-2023-46259
Unauthenticated Buffer Overflows:
- CVE-2023-41727
- CVE-2023-46216
- CVE-2023-46217
Heap-based Buffer Overflow:
- CVE-2023-46261
To proactively tackle critical vulnerabilities, SOCRadar XTI provides prompt notifications and thorough intelligence. The Vulnerability Intelligence feature enables users to obtain detailed information on vulnerabilities and monitor related activities, including hacker trends.
Additionally, Ivanti patched nine other vulnerabilities, ranging from medium to high severity, posing risks of Denial-of-Service (DoS), RCE, and Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) attacks upon successful exploitation. For details, review the Avalanche MDM 6.4.2 advisory here.
To address these vulnerabilities, it is strongly advised to update Avalanche to the latest release of version 6.4.2. The vulnerabilities mentioned in this blog have been addressed in Avalanche v6.4.2.313.
Previous Vulnerabilities Reported in Ivanti Products: Sentry, Avalanche, and EPMM (MobileIron Core)
Ivanti addressed several other significant CVEs this year, such as CVE-2023-32560, CVE-2023-38035, and CVE-2023-35078.
CVE-2023-32560 covers two RCE vulnerabilities affecting Avalanche, while CVE-2023-38035 is the previous latest vulnerability disclosed, impacting Ivanti Sentry. Furthermore, a critical zero-day vulnerability in Ivanti EPMM (formerly MobileIron Core) had raised alarms in July 2023.
Detailed information on these vulnerabilities is available in our previous blog posts:
Ivanti Avalanche Critical Buffer Overflow Vulnerabilities: CVE-2023-32560
Securing the Digital Gateways: The Ivanti Sentry Vulnerability (CVE-2023-38035)
Critical Zero-Day in Ivanti EPMM (Formerly MobileIron Core) Is Actively Exploited (CVE-2023-35078)
Actively Exploited Zero-Day Vulnerability in Google Chrome WebRTC: CVE-2023-7024
Google addressed a high-severity zero-day vulnerability in the Chrome web browser, tracked as CVE-2023-7024, which has been actively exploited in the wild.
CVE-2023-7024 is the 8th actively exploited zero-day in Chrome throughout 2023, described as a heap-based buffer overflow in the WebRTC (Web Real-Time Communication) framework. Its exploitation could lead to program crashes or arbitrary code execution, according to Google’s advisory.
There are no further details or any workaround methods, and Google recommends that users upgrade to the following Chrome versions to mitigate the risk of exploitation:
- For Windows: Chrome 120.0.6099.129/130
- For macOS and Linux: Chrome 120.0.6099.129
Chromium-based browser users are also advised to apply fixes as they become available.
CVE-2023-7024 Has Been Listed in CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog
On January 2, 2024, CISA included the Google Chromium WebRTC Heap Buffer Overflow vulnerability, CVE-2023-7024, in the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) Catalog, substantiated by evidence of active exploitation. The agency underscores that such vulnerabilities often serve as common attack vectors, posing substantial risks to the federal enterprise. Organizations are urged to promptly address CVE-2023-7024 by the designated deadline of January 23, 2024.
Easily Identify and Mitigate Vulnerabilities with SOCRadar
The External Attack Surface Management module provides organizations with tools for rapid identification, evaluation, and mitigation of vulnerabilities. With ASM, you can access details about their asset inventory and receive alerts about security vulnerabilities that could potentially affect organizational assets. These alerts provide quick and actionable insights, accelerating the response process.