
Threat Actors Impersonate GitHub, Zoom, and Cloudflare to Steal User Information
Hackers frequently look for ways to trick users and organizations, as the weakest link in security is the human factor. This makes phishing one of the most common entry attacks. During the last two months, well-known names such as CloudFlare, GitHub, and Zoom were used as a disguise by hackers to deceive victims.
GitHub Credentials Stolen in Phishing Attack
On September 16, GitHub discovered phishing attacks by hackers impersonating CircleCI. During the attack, users are warned of session expiration and directed to log in again using their GitHub credentials.
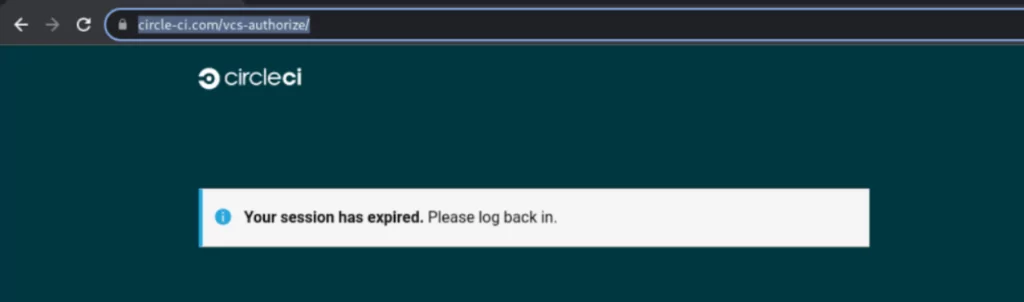
GitHub was unaffected, but many organizations’ login information and 2FAs were compromised.
The attack allows the attacker to compromise accounts with TOTP (time-based one-time passwords) as well by relaying it to the attacker in real-time. Those who use hardware security keys can not be affected by this attack.
They informed all known-affected individuals and organizations, reset passwords, and removed threat actor-added credentials for impacted users.
Zoom is Impersonated by Russian FIN11 Hackers in Phishing Attacks
The research team of Cyfirma has come across fake Zoom application download URLs on the web. Financially motivated FIN11 is thought to be behind the campaign. Additionally, an IP address that was previously linked to AsyncRAT was seen.
A large attack surface was the aim of FIN 11’s installation of Information Stealer (Vidar), which was done using Zoom download pages.
Recently, Russian threat actor FIN11 has been linked to the ransomware gang CLOP. This connection raises the risk of infected computers becoming potential ransomware victims.
The discovered hosts (first six links in Zoom IoCs at the end of the post) are pointing to malicious .exe, .rar, .apk, .lnk, and .pdf files, showing that FIN 11 is running a well-thought-out campaign that targets all operating systems.
Technical Details
When the download button is clicked, a malicious zip package that contains a malicious Zoom[.]exe file downloads and appears as a legal Zoom app with a Zoom icon. It is a 64-bit SFX (Microsoft Cabinet) file.
Once “Zoom[.]exe” has been extracted, it contains two files: ZOOMIN~1[.]exe, which is the legitimate zoom application setup, and Decoder[.]exe which is a malicious downloader.
These executables are dropped by Zoom[.]exe at the location “C:UsersUsernameAppDataLocalTempIXP000.TMP“.
When Decoder[.]exe is run, it connects to “hxxp[:]//193[.]106[.]191[.]223/CharSequence[.]TextPaint[.]setAlignment.module8_Rkbbnqyt[.]png” and downloads a .PNG file that has been encoded.
The IP address (193[.]106[.]191[.]223) is associated with AsyncRAT and is linked to Russia.
Later, Decoder[.]exe uses PowerShell to carry out a command that is Base64 encoded.
The decoded string “UwB0AGEAcgB0AC0AUwBsAGUAZQBwACAALQBTAGUAYwBvAG4AZABzACAAMQAyAA==” equivalent to “S t a r t-Sleep-Seconds 12” can be used to sleep for 12 seconds before performing the next operation.
Additionally, it generates a child process called MSBuild[.]exe. The Microsoft Build Engine (MSBuild) was previously misused by malware developers to distribute remote access tools (RATs) and malware that steals passwords.
To summarize, the threat actor uses phishing URLs that pretend to be official Zoom website and apps to distribute malicious Zoom apps. When a malicious Zoom[.]exe is run, it drops Decoder[.]exe, a downloader for additional payloads (RAT and information stealers), and ZOOMIN~1[.]EXE, the installer for the legal zoom software. Additionally, the infected MSBuild.]exe downloads DLLs associated with the Vidar information stealers.
Trojan Brought With Fake CloudFlare Captcha
Last month, DDoS alert pages impersonating CloudFlare DDoS protection were discovered. Here is the attack scenario:
Users are instructed to download a file to proceed when they visit a malicious website. This file is actually a remote access trojan (RAT) that grants attackers full system access. From here onward, attackers can launch other attacks on the compromised system, such as ransomware or credential theft.
A fake CloudFlare Captcha check is included in the new wave of attacks. After entering values in it, the victim is prompted to make a download to skip further Captcha checks.
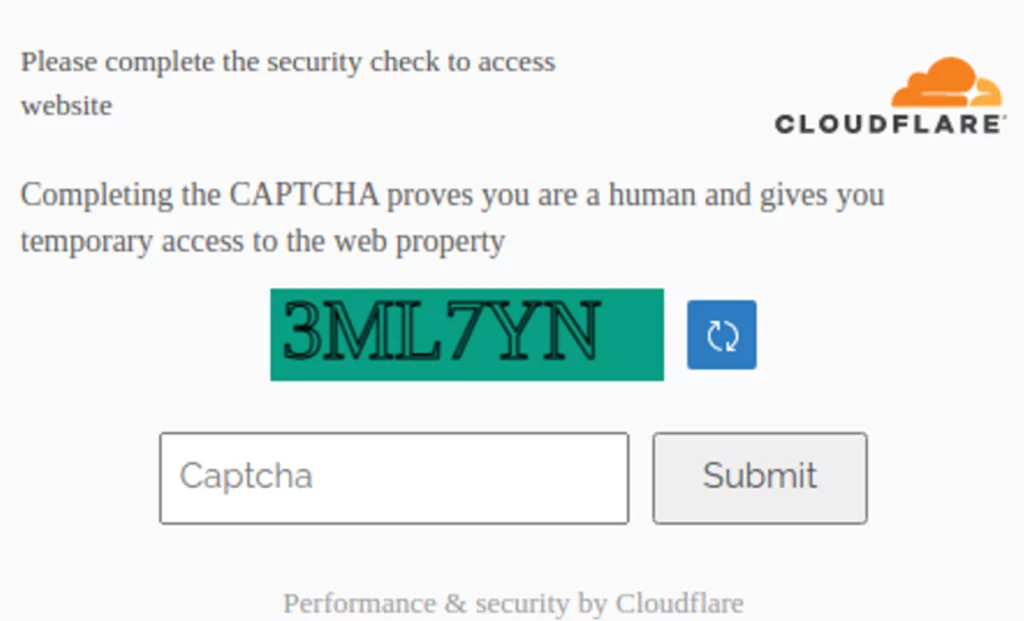
A .iso file is downloaded as a result, which contains an executable named Cloudfla[.]exe or Cloudflare_security_installer[.]exe. A Google Chrome update is launched in Russian to hide the RAT process by distracting users.
The RAT used is bundled with Raccoon Stealer. A MalwareBytes researcher also suggests the malware is the Amadey Stealer.
Several new variants emerged this month as the campaign continued. One of the variations uses a JavaScript string, and the attacks specifically target WordPress websites. For the time being, fewer than a thousand sites were impacted by new variants. The infection was usually found in /wp-includes/js/jquery/jquery.min[.]js.
Recommendations
Using MFA and unique passwords are always recommended. Consider using hardware security keys for some cases.
Browser-integrated password managers can be used to autofill on trusted sites. In a phishing website you just encountered, the password manager will not recognize the fields for autofill.
Check indicators of compromise, and only download from trusted sources. Check files for any malicious intentions before executing them.
Use web application firewalls (WAF) and employ a routine scanning or a complete monitoring method for your assets.
GitHub IoCs
Domains:
- circle-ci[.]com
- emails-circleci[.]com
- circle-cl[.]com
- email-circleci[.]com
Zoom IoCs
URLs:
- https://zoom-download[.]host – 92[.]53[.]96[.]41
- https://zoom-download[.]space – 2a03:6f00:1::5c35:6029
- https://zoom-download[.]fun – 92[.]53[.]96[.]41 pDNS 5.101.159[.]26; 87.236.16[.]226
- https://zoomus[.]host – 92[.]53[.]113[.]155
- https://zoomus[.]tech – 92[.]53[.]114[.]144
- https://zoomus[.]website – 92[.]53[.]114[.]172
- hxxp://116.202.179[.]139
- hxxp://193.106.191[.]223
Web applications (used in the past):
- www.zo0m[.]info – 23[.]82[.]19[.]170
- www.app-zoom[.]com – 198[.]54[.]116[.]220
- zoom-meetings[.]net – 2607:f1c0:100f:f000::2ce
- zoom-update[.]online – 192[.]254[.]185[.]80
- zoomcyber[.]nl – 2606:4700:3030::6815:970
- zoomclient[.]nl – 2606:4700:3037::ac43:a1d6
- https://veehy[.]com/download-zoom/ – 5[.]39[.]216[.]178
- http://videoconfer[.]xyz/ – 2606:4700:3035::ac43:87c5
- zoom-download.huvpn[.]com–5[.]39[.]216[.]179
- https://zoom[.]cheap/ – 2606:4700:3031::ac43:9b36
- www.user01zoom[.]website – 161[.]35[.]144[.]236
SHA256:
- b76cad93d0501d69746c84db3f7bfc158968900c2e472121019efe5d234ffa34,
MD5:
- 19AFF3D6ED110A9037AFF507CAC4077F
- 98C8C28B790BBCE2BC2F20CC8FF2BD8E
- 21ABAC012CAA151DA5ED7C760198FAC6
IPs:
- 92.53.96[.]41
- 5.101.159[.]26
- 87.236.16[.]226
- 92.53.113[.]155
- 92.53.114[.]144
- 92.53.114[.]172
- 79.124.78[.]206




































