
Unleashing the Domino Effect: Google’s Deletion of Unused Emails and the Cascade of Account Compromises
Email accounts are the primary key to accessing various online services in today’s digital age. They are used to create accounts and serve as login credentials for platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram. However, some individuals create email accounts solely to sign up for online services. They subsequently forget important details like their email address and password or fail to regularly check their mailboxes. While these online services remain active as long as they are being used, there is no mechanism to determine if an email account is still active or not, as long as the user has the correct email address and password combination associated with their account on social platforms.
What happens when an email address used to create an online service account is deleted by an email provider? Essentially, that address becomes available for someone else to claim, as it will no longer be in use.
“Starting later this year, if a Google Account has not been used or signed into for at least 2 years, we may delete the account and its contents – including content within Google Workspace (Gmail, Docs, Drive, Meet, Calendar) and Google Photos.”
(From Google’s company blog)
While mainly targeting personal accounts, Google’s choice to delete inactive email accounts can impact key organizational personnel, including CEOs, CFOs, and other C-level executives. These executives commonly utilize personal email addresses for communication and account management, so the risk of compromised or deleted email addresses can extend to the business domain.
This article explores Google’s recent decision, delves into the potential risks associated with it, and examines the domino effect it may have on various aspects of online security.
Account Takeover: A Serious Threat
Upon discovering that the email address associated with a targeted account no longer exists, an attacker can register it under their name. They can then initiate a “forgot password” process on the targeted service, ultimately gaining control over the account.
Exploiting Data Breach Lists
Malicious actors have been known to exploit data breach lists to carry out password reuse attacks or generate wordlists for brute force attacks. After Google started to apply its plan late this year, these data breach lists may now be utilized by attackers to identify unused email addresses.
Which Sensitive Data is Under Risk?
Once an attacker takes ownership of a deleted email address, they can access the targeted account’s order history, friend lists, and messages on various platforms.
- Personal Identifiable Information (PII): Online platforms often require users to provide personal information during registration. This includes full names, addresses, phone numbers, and sometimes even social security numbers. Protecting personally identifiable information (PII) is critical for C-level executives and key employees. If an attacker gains control of an account associated with a deleted email address, they can access sensitive information like full names, addresses, phone numbers, and social security numbers. Threat actors can exploit this data for identity theft, phishing, or selling on the dark web. Safeguarding against account takeovers is crucial for businesses as it protects personal information, maintains reputation, and ensures overall security.
- Financial Data: Many online services, including e-commerce websites, banking platforms, and payment processors, are linked to email accounts. When an attacker gains control of a deleted email address, they can potentially access the account holder’s financial data. This includes credit card information, bank account details, transaction history, and billing addresses. Armed with this information, the attacker can carry out unauthorized transactions, make fraudulent purchases, or even empty the victim’s bank account.
- Social Media Accounts: Email addresses are commonly used to create and manage social media accounts. The attacker gains control over the victim’s social media presence by compromising a deleted email address associated with a particular social media platform. This includes access to their profile, friend lists, private messages, and potentially compromising photos or posts. The attacker can misuse this information for identity theft, impersonation, spreading malware or scams, or even posting malicious content under the victim’s name.
- Online Shopping and Order History: E-commerce platforms often send order confirmations, invoices, and shipping notifications to the email address linked to the user’s account. When an attacker takes over a deleted email address, they can access the victim’s order history, which may reveal their purchasing habits, preferences, and even shipping addresses. This information can be exploited for targeted phishing attacks, sending spam emails, or conducting fraudulent activities using the victim’s account.
- Communication and Messaging: Email accounts are used for formal communication and serve as a recovery option or verification method for other messaging services like instant messaging apps or forums. By gaining control of a deleted email address, an attacker can access the victim’s chat history, private conversations, and any confidential or sensitive information shared through these platforms. This can lead to further privacy breaches, blackmail attempts, or unauthorized access to other accounts linked to those messaging services.
Recognizing the value of the data stored within online accounts and the potential risks associated with compromised email addresses is crucial. Maintaining strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, regularly monitoring account activity, and promptly reporting suspicious or unauthorized access attempts are essential to protect oneself from these threats.
Google’s Approach
Google has stated that all data belonging to inactive accounts, including Google Drive, Google Photos, and emails, will be gradually deleted. However, data related to inactive accounts on other online services will remain intact. Consequently, when an attacker gains control of a deleted email address, they can exploit the account’s associated information on various platforms.
The Paradox of Account Compromise
Ironically, Google acknowledges that even with their protective measures, an account that has been inactive for an extended period is more likely to be compromised. Deleting these allegedly compromised email accounts could inadvertently lead to the compromise of other accounts linked to those email addresses.
Google plans to implement this decision gradually, starting from December 2023. They will send notification emails to both the affected email addresses and the recovery addresses associated with them. It’s important to note that this action plan applies only to personal addresses.
Conclusion
Deleting email accounts by Gmail can have significant implications for online security. Attackers can exploit this situation by claiming deleted email addresses and executing account takeovers, thereby gaining access to personal information and potentially compromising other accounts. While Google aims to gradually delete data from inactive accounts, caution is advised regarding the security of your online presence. Regularly updating passwords, monitoring account activity, and being aware of potential vulnerabilities can help safeguard your digital identity.
Safeguard Key Executives and Business Networks from Account Theft
SOCRadar VIP Protection
Although primarily focused on personal accounts, Google’s decision to delete inactive email accounts can have implications for key employees within an organization, such as CEOs, CFOs, and other C-level executives. As these executives often use personal email addresses for communication and account creation, the potential risk of compromised or deleted email addresses can extend to the business realm.
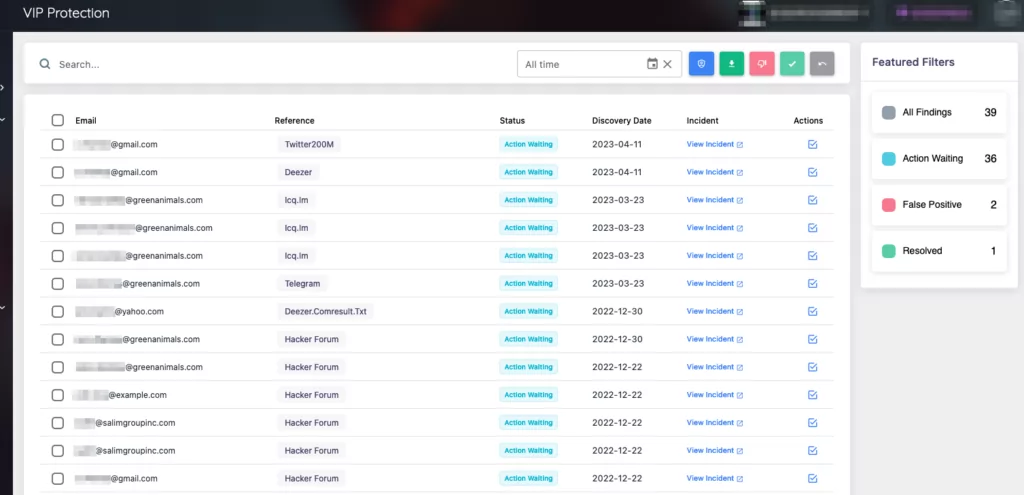
SOCRadar’s VIP Protection feature for searching and monitoring the personal email addresses of key executives provides organizations with a proactive solution to combat the issues discussed in the previous article. By leveraging SOCRadar’s extensive breach database, security teams can identify potential threats and monitor for impersonation attempts targeting CEOs, CFOs, and other top-level employees.
With the ability to search for personal email addresses within the database, organizations can promptly detect any exposed personal data and take appropriate action. Monitoring these email addresses helps prevent cyberattacks, physical harm, and reputational damage. By leveraging SOCRadar’s capabilities, organizations enhance their incident response readiness and strengthen their security posture, safeguarding their executives and business networks from potential threats.
SOCRadar Breach Database
With a vast Breach Database of SOCRadar comprising over 10 billion records, individuals can leverage this feature to proactively check if their personal information is in the database. By searching for their records, users can identify any instances of exposed data, enabling them to take immediate action and mitigate the risk of compromised accounts. This proactive approach empowers individuals to safeguard their online presence and protect themselves from security threats.



































