
How SOCRadar Can Help Fraud Teams?
Fraud refers to transactions made using card information without the knowledge of cardholders in the card payment sector in cybersecurity or purchases made by using fake or stolen credit cards.
Today, with the advantages of the rapid digitalization of the world, stealing non-physical information is getting more easily. Problems experienced in shopping transactions, whether customer-related or not, cause distrust.
By avoiding problems caused by fraud (stolen/fake credit card transactions), you prevent losing money and customer trust. In this context, companies have started to take precautions by forming fraud teams within their organization.
On internet/mobile shopping, your payment system must offer a secure infrastructure due to transactions made without physically using a credit card (CNP).
It is tried to hold companies responsible for phishing domains created on the Internet, malware that infects the user’s computer or phone, and the resulting victimization by obtaining user information. Entering card information manually in mobile shopping, not using your card physically during the transaction, obliges you to take extra security measures against malicious use.
Utilize CTI to Strengthen SecOps Efficiency: Findings from Gartner’s Report
SecOps (Security Operations) is an important practice in cybersecurity that integrates security with an organization to reduce risks. SecOps helps organizations detect and respond to security incidents quickly, reducing the impact and cost of a potential breach. It could also help DevOps teams by proactively identifying and addressing security threats throughout the development process, promoting a culture of security awareness and responsibility, all in all creating DevSecOps.
Organizations should identify their intelligence needs to improve security operations and understand potential threats to their system. Many organizations struggle with this because they rely solely on their SOC and have a fragmented approach to threat intelligence, making it difficult to prioritize their needs. To address this, organizations can create a matrix linking business criticality and information sensitivity to the intelligence available for analysis.
Gartner has recently published its “Define Threat Intelligence Requirements to Improve SecOps Efficiency” report to detail the musts of achieving a better SecOps plan.
The report suggests 4 key processes that can enhance SecOps efficiency. These are:
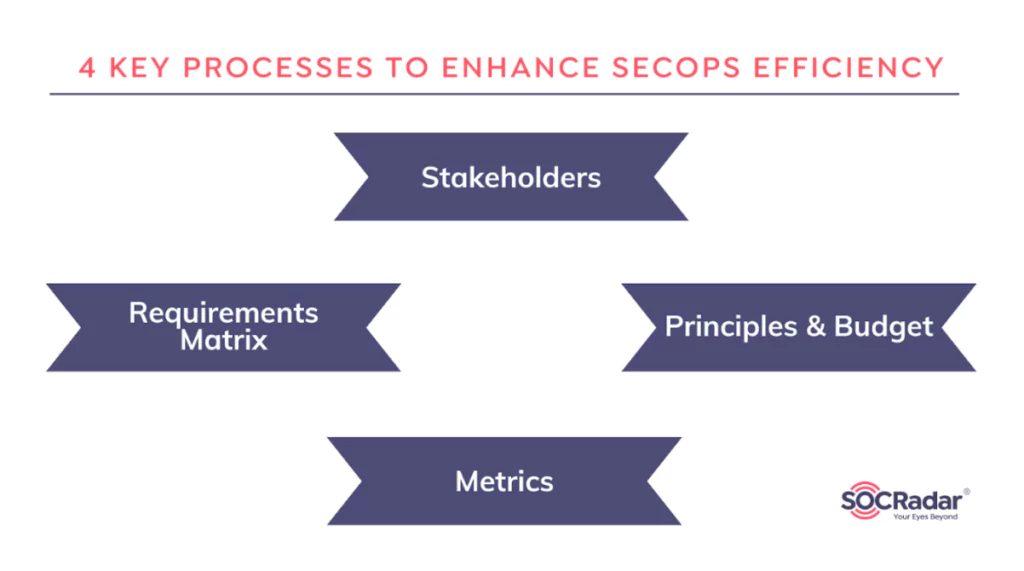
- Identify stakeholders, comprehend their needs, and provide them with actionable insights during a security incident. This will help to improve communication and prevent missed opportunities.
- Develop a requirements matrix to better understand security needs and improve the use of intelligence by SecOps.
- Establish principles and allocate budgets that allow SRM leaders to use priority intelligence requirements to create a threat intelligence program that meets stakeholders’ expectations.
- Establish metrics, govern and validate threat intelligence efficiency, and establish guidelines for reporting it.
Intelligence Requirements for SecOps Teams
To establish a successful CTI system, taking an all-encompassing approach to collect and address intelligence requirements is crucial. This involves establishing three types of IRs: Intelligence Requirements (IRs), Priority Intelligence Requirements (PIRs), and Specific Intelligence Requirements (SIRs).
Gartner’s report states that, by 2026, half of the intelligence programs will be unable to effectively address organizational risk as they will lack efficient priority intelligence requirements (PIRs). Building a requirements matrix is considered one of the steps in a strategic plan to improve the efficiency of security operations, and SecOps teams define the priority intelligence requirements (PIR) in the matrix.
In the matrix, IR expands to PIR, and PIR expands to SIR. This progressive approach emphasizes three steps for improving security operations; the PIR translation of these steps are:
- Continuous assessment of the attack surface must involve vulnerable points, TTPs, IOCs, insecure protocols, and more.
- Stakeholders must be notified of compromised data immediately, which may be detected on the dark web, cybercriminal forums, and channels.
- Actively analyze threat actors, and obtain IOCs, create threat actor profiles. Identify when a known threat actor is targeting related companies or industries.
Implementation of Cyber Threat Intelligence: Tactical, Strategic, and Operational CTI
According to the report, organizations must also plan a CTI deployment strategy in order to achieve their priority intelligence requirements (PIR). Three levels of CTI analysts or CTI functions are common in large organizations:
Tactical CTI identifies how threat actors plan to attack organizations, with examples such as malware signatures and blacklisted IPs/URLs.
SOCRadar offers multiple levels of intelligence to help organizations protect their systems, including phishing domain lists, tracking cybersecurity incidents, and integrating feeds with existing security systems. Using Tactical CTI can help organizations quickly determine if there is a cause for concern and reduce the time analysts spend trying to differentiate between trusted and malicious information.
Strategic Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) refers to high-level information about changing cyber risks used by senior decision-makers for management.
This includes non-technical staff, such as CEOs, CFOs, and CIOs, who need data to better understand patterns and high-level threats to the organization for making risk-based decisions related to personnel, technologies, cybersecurity requirements, and, ultimately, budgets.
Brand reputation is critical for strategic CTI users, who need to consider multiple data points, including phishing campaigns, fake domains, fake social media accounts, and exploited web pages, to understand how and why threat actors target their brands.
SOCRadar provides various services like digital asset management for attack surface risk, industry-specific and geopolitical cyber attack information, popular threat actor monitoring, cyber security reports, brand monitoring, and executive intelligence reports to monitor company risk.
Operational Cyber Threat Intelligence is actionable information about incoming identified attacks. Operational CTI is crucial for organizations to identify and mitigate potential cyber threats.
It focuses on specific threat actor TTPs, correlating findings from various sources to identify likely threat actors exploiting vulnerabilities in the attack surface.
CTI helps organizations pursue threat hunting before or after a cyber attack, but knowing where to skim/scan to respond better is essential.
Operational CTI provides detailed insights into factors such as nature, motivation, timing, and attack methods and is used by security personnel to prioritize potential threats and vulnerabilities in the organization’s threat environment.
It integrates with existing security systems to support incident triage, but a technical background is crucial to effectively use it. Threat hunting for Operational CTI users proactively searches for evidence of threat actor activity, leveraging all relevant indicators of compromise (IOCs), which is nearly impossible without specialized and reliable CTI.
SOCRadar provides several CTI feeds, including phishing domain lists, vulnerability intelligence, critical open port, and configuration weakness. These feeds can be integrated with existing security systems to support incident triage.
Global Fraud Loss: How Much?
Frauds in payments made without physically using a credit card (Card Not Present-CNP) continue to increase year by year in Europe. Within the Single Euro Payment Area (SEPA), CNP fraud increased by 17.7% compared to the previous year, resulting in a loss of €1.43 billion in 2018. In contrast, ATM fraud decreased by 14.7% from 2017 to 2018 with the increase in Chip & Pin enabled cards.
As in Europe, CNP fraud accounts for 76% of fraud losses worldwide. UK Payment losses through fraudulent card payments, remote banking, and checks totaled £824.8m in 2019. While paying with lost, stolen, or counterfeit cards using a card machine is still a significant problem, the vast majority of losses are CNP frauds totaling £470.2m.
Global losses from payments fraud tripled from $9.84 billion in 2011 to $32.39 billion in 2020. Payment fraud is expected to increase and cost $40.62 billion in 2027.
The number of transactions reported as fraud and their total records are presented below.
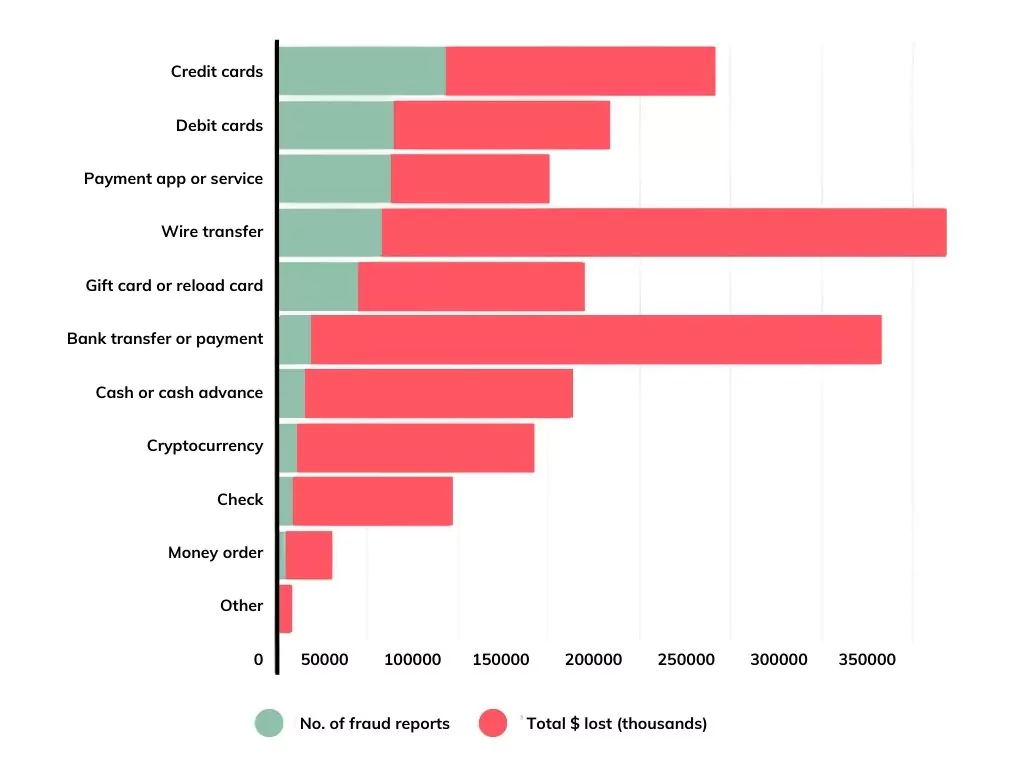
According to the 2021 edition of the “Financial Costs of Fraud Report” published annually by the University of Portsmouth and Crowe since 2009, the loss from fraud for 2020 is more than even the global Gross Domestic Product (GDP) ($83.85 trillion). If such losses from individual organizations are reduced by 40%, more than $2.1 trillion in GDP, more critical than all GDP outside the seven major economies, would be avoided.
You can access the details of this report and more on the Threat Reports page on the SOCRadar Platform.
How Can Fraud Teams Benefit from SOCRadar?
Unlike traditional CTI products, SOCRadar’s unified structure and the concept of Extended Threat Intelligence (XTI) create alarms that allow you to forward the email structure of the relevant alarms to your fraud teams without connecting to the platform. In addition, you can feed your fraud systems with relevant alarms with the filtering structure it brings in the incident API. You can also process the relevant alarm via the API with the bidirectional API structure (false positive, resolved, etc.).
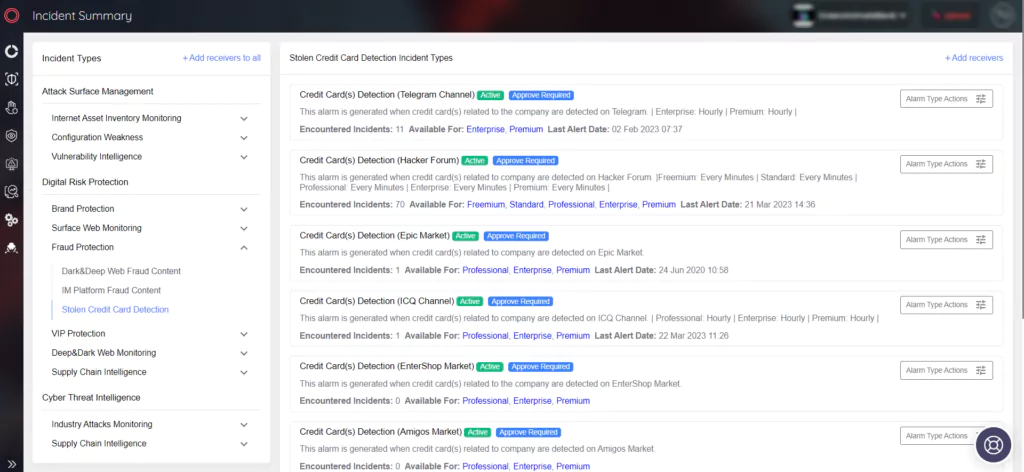
Its structure that provides role distribution to your security teams offers your fraud teams the opportunity to monitor and control the relevant alarms and dashboards on the platform. In this way, fraud teams can take action regarding alarms instantly and turn off alarms.
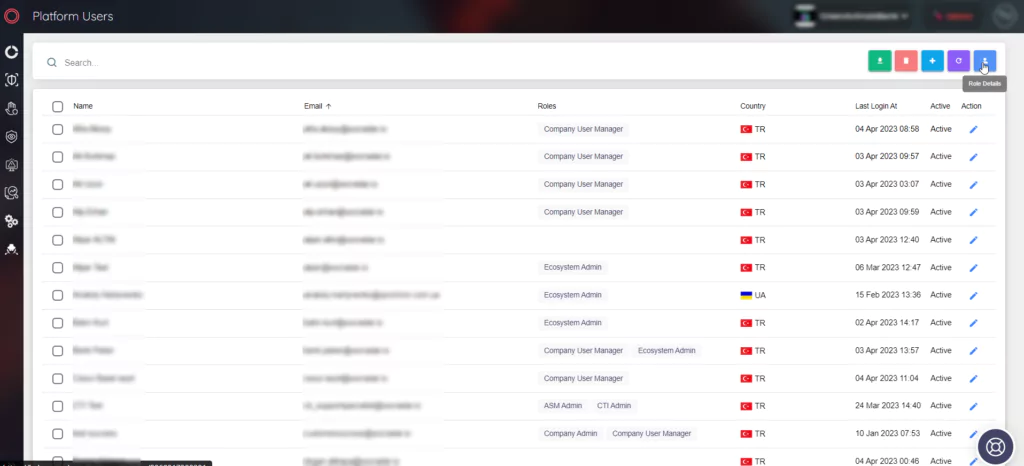
With SOCRadar Digital Risk Protection,
- You can check whether your credit card information is leaked on malicious channels.
- You can search in black markets, IRC channels, Telegram, etc. It provides you with fraud activities that take place in places.
In the SOCRadar Cyber Threat Intelligence;
- You can access the most recent incidents in the Dark Web News section.
- Combolist service is received by companies that provide payment transactions on credit cards belonging to banks. Combolist sharing is provided, and action is taken before the payment is made.




































