
What is Customer Identity and Access Management (CIAM)?
CIAM (Customer identity and access management) is part of the identity and access management (IAM) system integrated into applications for external users such as customers/consumers. The primary goal of CIAM is to manage and control end users’ access to digital services. However, it also includes collecting, analyzing, managing, and storing customer data. And when it comes to all these processes, security is the top priority. In this context, CIAM is designed with a high perspective.
CIAM must provide a secure, simple, and seamless path for external use cases while protecting sensitive data against malicious intrusions and preventing data breaches. Realizing those attributes requires identity management, privacy and access management, and fraud detection and prevention capabilities.
CIAM solutions generally include:
- customer registration
- password, permission, and preference management
- self-service account management
- profiling and management
- authentication and authorization in applications
- identity repositories
- directory services
- reporting and analytics
- APIs and SDKs for mobile applications
- single sign-on (SSO)
- multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- social sign-in (BYOI)
- fraud detection or behavior monitoring
What Should be Considered When Establishing a Robust CIAM System?
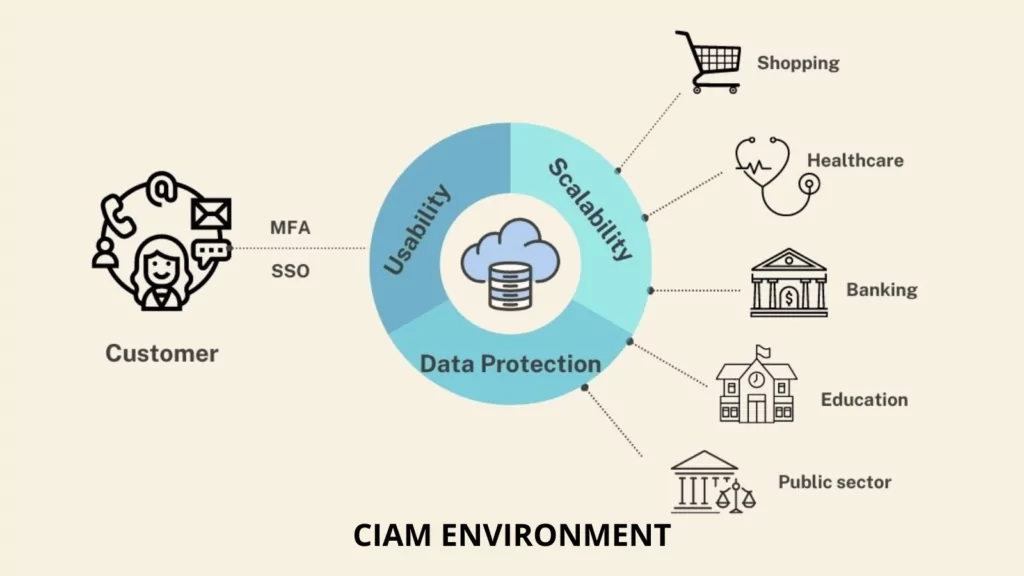
1. Scalability
To respond to fluctuating customer demands for several reasons and exponentially increasing data from a single customer, the CIAM system must be scalable. So, the system can handle many users, roles, and connections.
2. Usability
External users of the CIAM system do not receive formal employee training and have no motivation to follow instructions. They prefer not to read manuals or go through learning to use a system if everything is easy to use. As a result, a CIAM system should be designed to be highly user-friendly. The following CIAM applications will make it easier to use:
- Self-Service Account Management: Self-service account management empowers users by giving them control and visibility over their data and how it is used. Customers can thus efficiently perform various tasks such as profile data and preference management, password reset, and help requests.
- Personalization: CIAM provides customers consistent access to their data across all channels by providing a central profile synchronizing across all digital channels.
- Single Sign On (SSO): This feature allows users to automatically sign in to several other apps when they sign in to one. The most common type of SSO is social login, enabling users to log in using credentials from a third-party provider such as Facebook, Google, or Apple.
3. Data Protection
CIAM solutions collect personally identifiable information due to the nature of CIAM, which involves the user logging in, managing his profile, and accessing services. The amount of data processed at CIAM has expanded as customers increasingly share information with organizations and partners. Security issues with these data types can result in financial losses and loss of the organization’s reputation and trust. As a result, CIAM must offer security solutions that protect both organizations and customers.
Passwords, usernames, phone numbers, credit card numbers, and other pieces of personal information are frequently compromised through data breaches by threat actors. Data leaks can sometimes occur by insiders or because of an error. CIAM systems track who has access to customer data and notify administrators of any suspicious activity. This tracking ensures that neither an employee nor a bad actor accesses sensitive data.
CIAM also protects customers’ data while it is in storage or transit by encrypting it. Even if the information is captured, it will be useless.
Fraud is another security issue that customers may face. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is helpful against fraud attempts. MFA requires a different form of authentication besides username and password. This verification can be in the form of a one-time PIN, an email, or a biometric credential like facial recognition or fingerprint sent to the user instantly.
CIAM is a system that allows customers to access digital assets, establish and keep customer data, authenticate legitimate users, and deny access to threat actors. The goal is to make digital application access more straightforward and more secure.
CIAM solutions are distinguished from traditional IAM solutions, designed for accessing internal IT systems, by focusing on authentication and authorization processes of the public face of corporate applications and services.
Strong Together: CIAM & CTI
Because of the digital transformation in many areas, identity now includes a diverse range of data such as financial, medical, educational, purchases, preferences and behavioral patterns, and more. Managing and securing identity requires managing and securing all of this data. Additionally, access-related breaches are one of the most well-known security breaches. Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) is an option to establish identity and access security in this framework.
CTI allows security professionals to take proactive measures about possible threats. When the CIAM solution is associated with CTI, it can detect suspicious activity discovered by CTI analysis and prevent the threat from escalating into an incident. In a system where CTI and CIAM inform each other, based on intelligence from CTI, customized authentication processes can be performed for specific users, activities, or risk levels. In this context, using the CTI product to support the CIAM system creates a more robust security posture.



































