
What is Operational Cyber Threat Intelligence and How to Use It
Organizations of all sizes are building security teams to deploy network solutions and address threats. A key component to the success of these initiatives is access to up-to-date cyber threat intelligence.
This blog describes the significance of operational threat intelligence for organizations. Don’t forget to look at the other blog posts where we talk about tactical, technical, and strategic cyber threat intelligence.
What is Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI)?
CTI, by definition, is a form of threat intelligence that can be used to understand current or future threats better.
Collecting, analyzing, and classifying cyber threat information is used for providing firms with an actionable vision to identify, measure and rank vulnerabilities and mitigate cyber risks. Better knowledge about cyber CTI gives the latest threat trends on the cyber threat landscape. For your cybersecurity strategy to be effective, you must understand the different types of cyber information.
What are the Types of Cyber Threat Intelligence?
Threat intelligence falls into four categories within the framework of applicable information: Strategic, Tactical, Operational, and Technical. For these four types of intelligence, data collection, analysis, and consumption of intelligence differ. SOCRadar generates intelligence at different levels with the information it collects and ensures the best use of information.
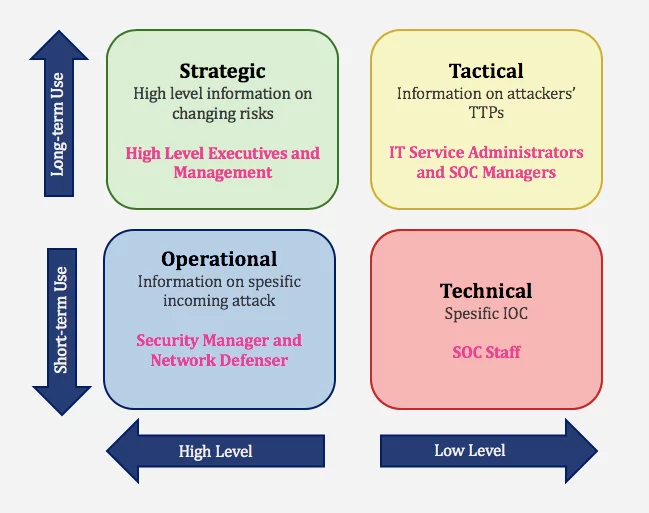
- Strategic Cyber Intelligence: The audience does not need technical knowledge. High-level information on changing risks. High-level information on risk-based intelligence is used by high-level decision-makers (Executives and management). Whitepapers, policy documents, and publications are examples of strategic cyber intelligence.
- Operational Cyber Intelligence: Actionable information about specific incoming attacks. They are infiltrating hacker chat rooms to anticipate the incoming attacks.
- Tactical Cyber Intelligence: Details of threat actor tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs).
- Technical Cyber Intelligence: Technical threat indicators such as specific IOC for SOC Staff.
What is Operational Cyber Threat Intelligence?
Operational CTI aims to answer “how” and “where” at the operational level. Detected threat actor TTPs explain “how.” How should the organization understand the extent of a breach and prepare a defense policy?
CTI helps organizations proactively pursue threat hunting before the compromise or after recovering the beginning of the incident. As a result, to better respond, you should know where to skim/scan. Tactical and Operational CTI’s features can overlap, but the main difference is Tactical CTI is more automated.
Operational CTI focuses on attack knowledge, which provides detailed insights into factors such as nature, motivation, timing, and attack methods. Ideally, information is collected through penetration from hacker chat rooms or online discussions, which is difficult to obtain.
Operational CTI provides a coherent framework to analyze and prioritize potential threats and vulnerabilities in the organization’s threat environment, thereby linking the possibility and impact of cyber attacks to their strategic implications.
Who Uses Operational CTI, Why, and How?
Operational CTI scope is Industry/Sector, Partners, Suppliers, Competitors, Customers, etc. OCT users in any firm include various personnel related to security such as malware analysts, incident responders/teams, network defenders, host analysts, etc. Technical background crucial for using Operational CTI. They use threat hunting procedures for counterintelligence. And they also use Operational CTI to provide warning intelligence.
Operational CTI Use Case: Threat Hunting
Threat hunting for operational users uses CTI to proactively search for evidence of threat actor activity, leveraging all relevant IOCs. A hypothesis based on the hunter’s intuition, or one or two seemingly unrelated pieces of evidence, is often the starting point for threat hunting. The hunter uses the CTI to explore the theory’s details further, either confirming it or moving on to the next issue. Successful Threat Hunting is nearly impossible without a specialized and reliable CTI.
What are the Difficulties in Collecting Operational Intelligence:
- Threats usually communicate over encrypted or private chat rooms, and access to these channels is not easy.
- It is not easy to manually gather relevant intelligence from vast data of chat rooms or other communication channels.
- Threat groups may use confusing and ambiguous language so that no one can understand their conversation.
What SOCRadar Provides
SOCRadar® provides ;
- Phishing Domain Lists
- Vulnerability Intelligence
- Critical Open Port
- Configuration weakness
- Integrate its feeds with the existing security system to support incident triage
Discover SOCRadar® Free Edition
With SOCRadar® Free Edition, you’ll be able to:
- Discover your unknown hacker-exposed assets
- Check if your IP addresses tagged as malicious
- Monitor your domain name on hacked websites and phishing databases
- Get notified when a critical zero-day vulnerability is disclosed
Free for 12 months for 1 corporate domain and 100 auto-discovered digital assets.
Try for free


































