What’s New in the NIS2 Directive? Requirements, Affected Organizations & All You Need to Know
The European Union is ushering in a new era of stringent regulations with the introduction of the NIS2 Directive, officially designated as E.U. Directive 2022/2055.

NIS2 Directive – E.U. Directive 2022/2055
Standing for “Network and Information Systems,” NIS aims to fortify critical infrastructure across EU member states, marking a pivotal step toward bolstering cyber resilience. With an estimated impact on over 100,000 companies, NIS2 sets forth rigorous cybersecurity mandates akin to its predecessor.
While its scope may not match that of GDPR, NIS2 is poised to become a benchmark for critical infrastructure globally, mirroring the far-reaching influence of similar EU regulations.
As organizations prepare for this transition, understanding the nuances of NIS2 and its implications is extremely important.
This article explores the NIS2 Directive, offering insights into its requirements, affected organizations, and general cybersecurity implications.
What is NIS2 (E.U. Directive 2022/2055)?
The NIS2 Directive is a significant cybersecurity regulation established by the European Union to safeguard critical infrastructure. Officially named “Directive (EU) 2022/2555 on measures for a high common level of cybersecurity across the Union,” it was released on December 14, 2022, and enacted in January 2023.
It replaces the prior version, NIS (Directive 2016/1148), which was introduced in 2016, marking a significant step forward in EU cybersecurity legislation.
NIS2 is a directive that allows each EU member state to create its own cybersecurity regulations based on the framework outlined. While NIS2 establishes the minimum cybersecurity standards, individual countries may impose more stringent requirements through local laws. This decentralized approach ensures customized cybersecurity measures while adhering to a unified standard.
The directive is slated to take full effect on October 18, 2024, which is the deadline for member states to enact cybersecurity laws in accordance with NIS2.
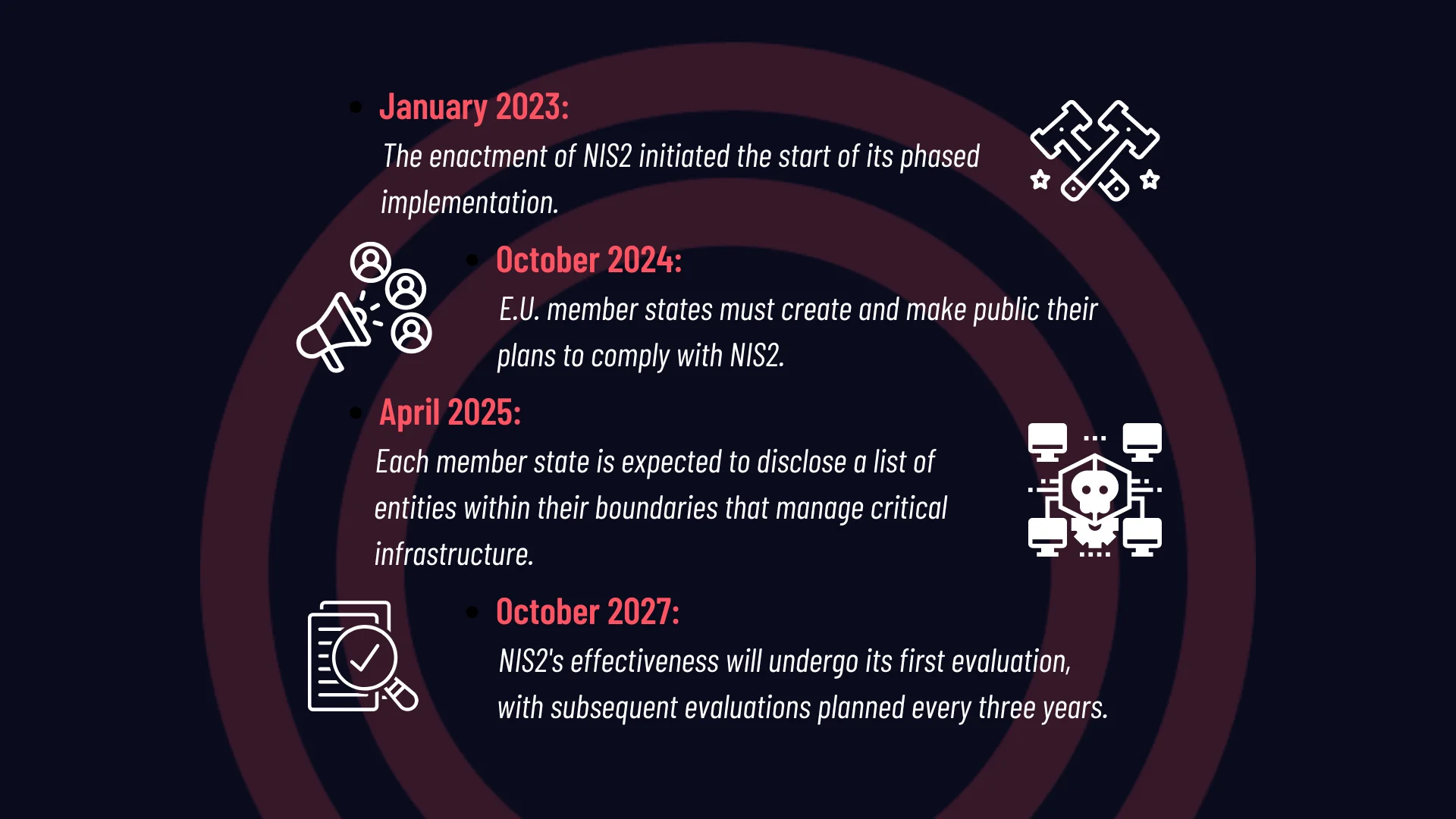
Planned timeline for the NIS2 Directive’s implementation
NIS2’s implementation unfolds gradually, allowing member states and organizations time to adapt to the new regulations. By April 2025, member states must identify entities operating critical infrastructure within their jurisdictions, thereby facilitating targeted compliance efforts.
Additionally, a crucial milestone in October 2027 will mark the first review of NIS2’s functionality, followed by subsequent evaluations every three years. This cyclical assessment ensures the directive remains effective and adaptive to evolving cybersecurity landscapes.
While the progressive rollout offers some time frame for preparation, organizations involved in critical infrastructure management should start readiness initiatives right away.
What has changed in NIS2 Directive?
NIS2 represents significant advancements over NIS (Directive 2016/1148), with the goal of building a more unified and robust cybersecurity scenery across the European Union.
An important development is the growing list of sectors that need to adhere to cybersecurity regulations. By including more sectors than just critical infrastructure, NIS2 covers much more territory than NIS and improves overall cyber resilience. In addition, registration is now required for organizations that manage critical infrastructure.
One other important aspect of NIS2 that stands out is enhanced cooperation amongst EU members. Because member states are required to establish reporting teams and designate a key person within each organization, the directive promotes improved mechanisms for collaboration and ensures streamlined responses to cyber threats and incidents on a pan-European scale.
NIS2 changes the timelines for incident reporting, requiring entities to notify relevant authorities within 24 hours of a breach. This prompt reporting allows for quick mitigation measures, improving overall cybersecurity posture.
SOCRadar XTI’s suite of security solutions, including Attack Surface Management (ASM), Vulnerability Intelligence, and Dark Web Monitoring, provide organizations with real-time tracking of digital assets, identification of vulnerabilities, and continuous visibility into potential threats, thereby helping prevent breaches and enhancing overall cybersecurity posture.
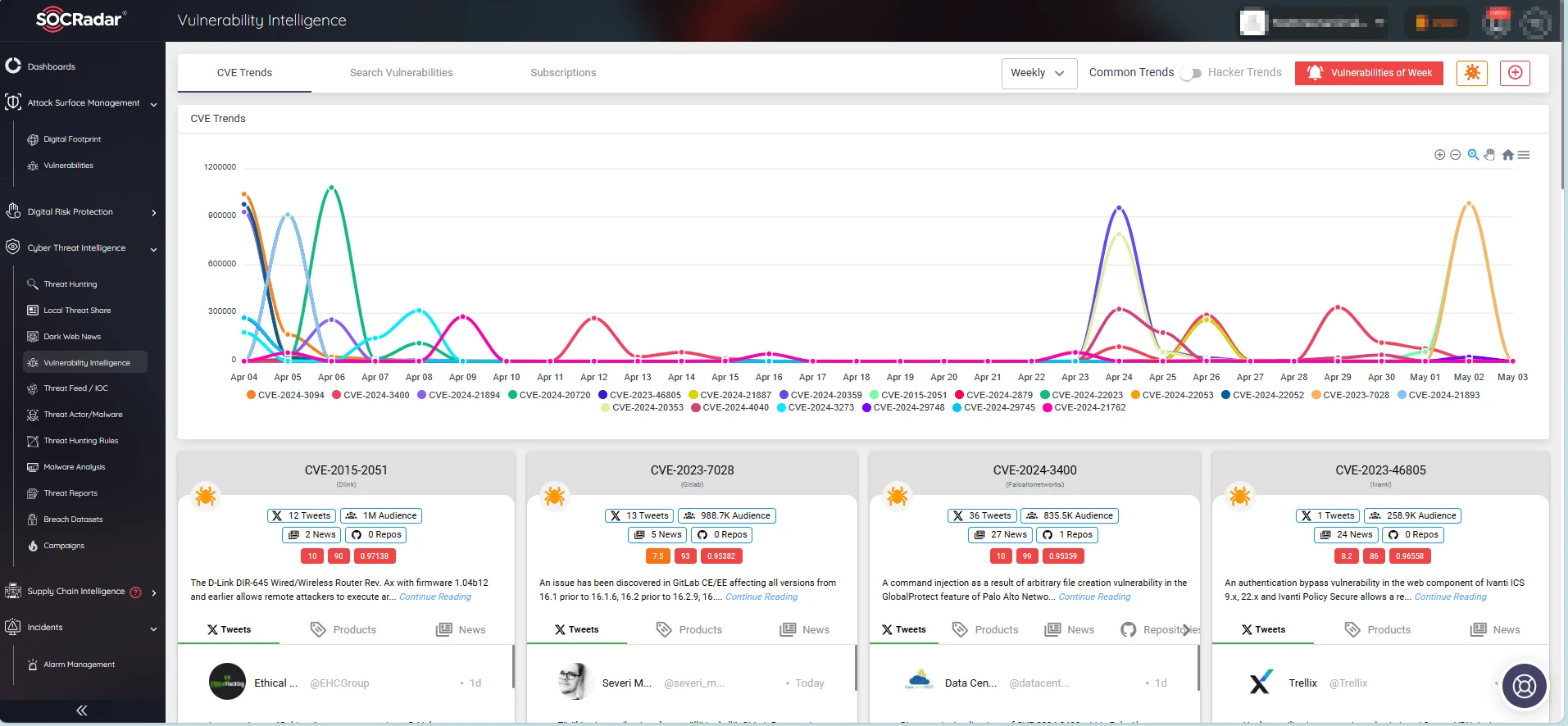
Monitor the emerging vulnerabilities and trending exploits using SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence
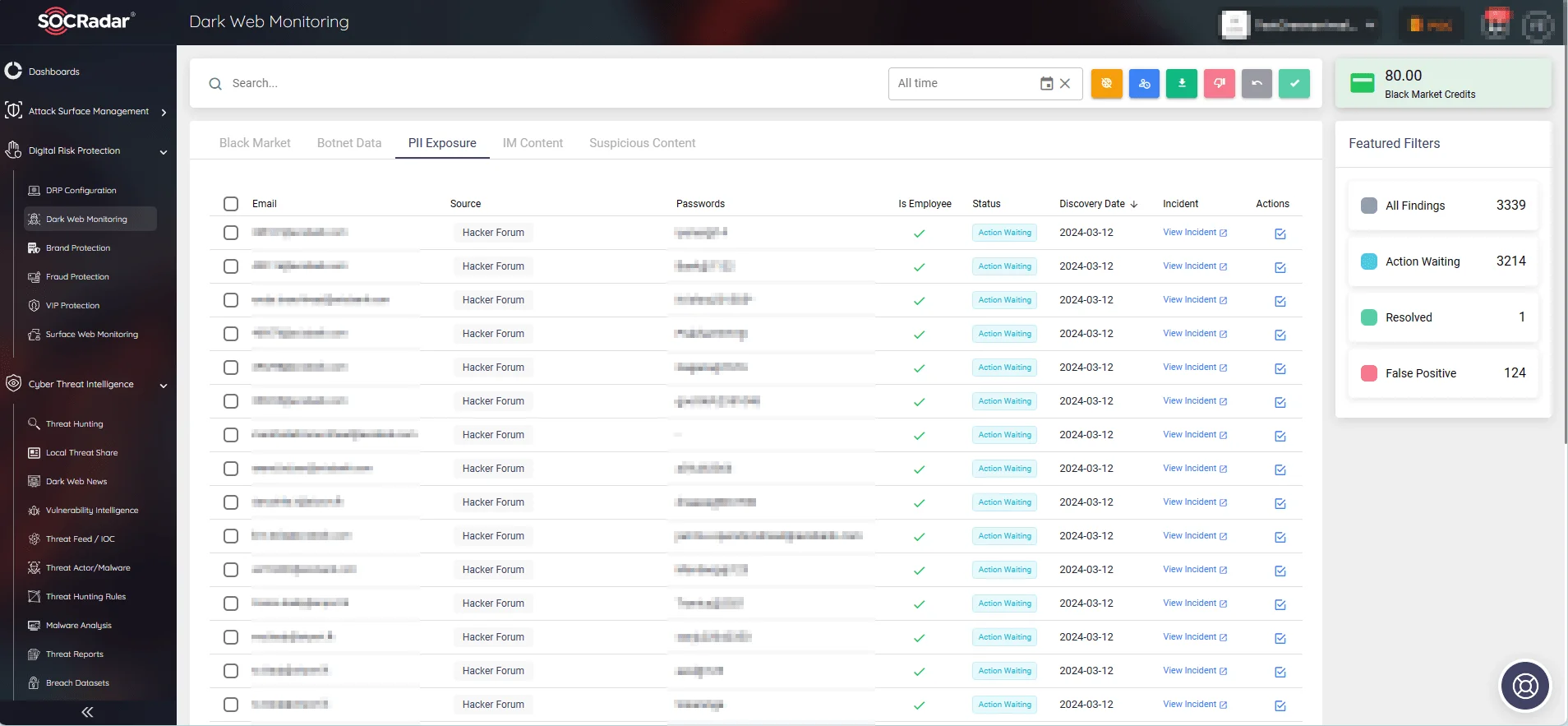
SOCRadar’s Dark Web Monitoring helps you keep an eye out for potential exposures and threats.
The directive also prioritizes supply chain security in response to the evolving threats. It emphasizes the importance of securing supply chains in order to strengthen resilience against cyberattacks originating from interlinked ecosystems.
Organizations can proactively secure their supply chain with SOCRadar’s Supply Chain Intelligence module, accessing real-time cybersecurity updates, reports, and alerts.
SOCRadar enables organizations to swiftly detect and respond to cyber threats from the dark web by tracking incidents such as ransomware attacks, defacements, and breaches over time.
The platform also offers insights into global attack trends specific to countries and sectors. This enables organizations to anticipate and protect against threats emerging from the dark web, targeting their supply chain.
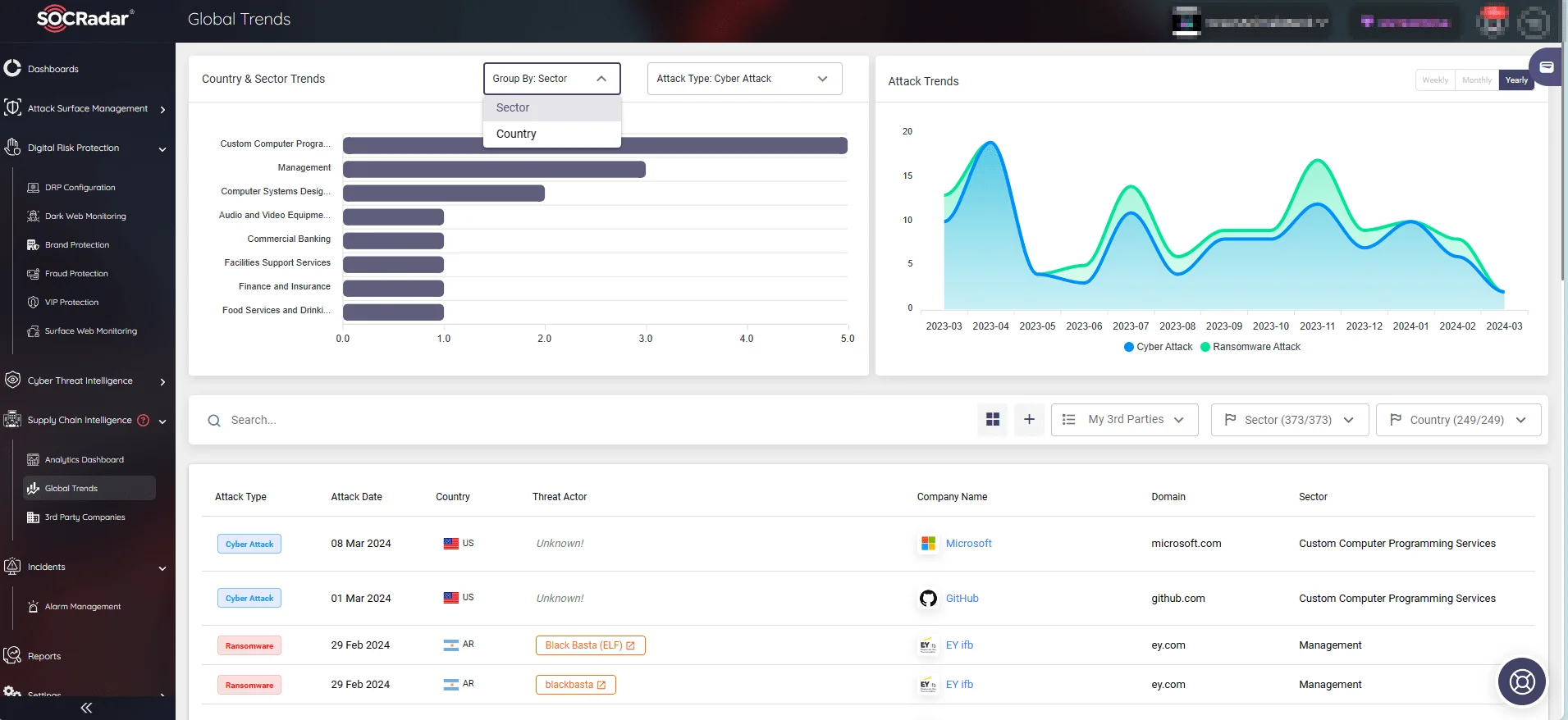
SOCRadar’s Supply Chain Intelligence, Global Trends
The NIS2 Directive imposes stricter penalties and accountability measures, emphasizing the responsibility of top management within organizations to maintain cybersecurity standards. This shift emphasizes the need for proactive risk management and compliance efforts at all organizational levels.
A structured framework with nine chapters is provided by NIS2 that covers a variety of topics, including coordinated cybersecurity frameworks, mechanisms for cooperation, risk management strategies, and enforcement, promoting compliance with the directive’s mandates.
Targets Industries and Organizations
Under NIS2, compliant entities are categorized as ‘essential’ or ‘important’ based on specific criteria. All entities that meet the following criteria are required to comply:
- Location and Size: Entities operating within any EU member state with over 50 employees and revenue exceeding 10 million euros.
- Industry: Organizations in critical sectors such as energy, transport, banking, healthcare, digital infrastructure, and manufacturing. Find more details in the official text of NIS2.
Essential entities include large-scale organizations with more than 250 employees or more than 50 million euros in revenue within sectors like energy, finance, healthcare, and public administration. This category also includes trust and DNS service providers, as well as public electronic communication networks. Plus, it includes any entity identified as critical under the Critical Entities Resilience (CER) Directive, as well as entities specified by member states.
Meanwhile, important entities are organizations that do not meet the criteria for essential entities but are initially deemed important due to their size, revenue, and industry.
Both essential and important entities have cybersecurity and reporting obligations, with essential entities subject to stricter requirements and potentially higher fines for non-compliance.
The newer directive expands its scope beyond EU-based entities to include non-EU organizations that manage critical infrastructure within the EU’s jurisdiction. This global applicability exemplifies the directive’s comprehensive approach to cybersecurity governance.
Main Requirements
The NIS2 Directive outlines key compliance requirements, including governance structures, risk management, and coordinated security assessments of critical supply chains. It also sets forth reporting obligations and the potential use of European cybersecurity certification schemes.
It is important to note that while NIS2 does not require certification for essential and important entities, it allows member states to mandate the use of certified IT products or services in line with the Cybersecurity Act (EU Regulation 2019/881).
The rules broadly stipulate readiness to protect critical infrastructure, encourage EU-wide cooperation, and promote a shared culture of security. It compels EU organizations with critical infrastructure to implement cybersecurity measures, including risk analysis and incident response.
With the directive’s overarching objectives in mind, organizations need to customize their strategies to effectively meet these requirements, taking into account their unique operational contexts and threat landscapes.
What happens if organizations do not comply with NIS2?
Non-compliance with NIS2 requirements can lead to significant consequences for affected organizations, including substantial fines and additional legal repercussions. The severity of penalties varies based on the classification of entities and the extent of non-compliance.
Under NIS2, both essential and important entities face the risk of fines for non-compliance. Essential entities could incur fines of up to €10 million or 2% of their total annual turnover, while important entities may face fines of up to €7 million or 1.4% of their total annual turnover. However, the implications of non-compliance extend beyond monetary penalties.
In addition to fines, non-compliant organizations may face legal actions, reputational damage, temporary managerial bans, and the appointment of monitoring officers. They may also be subject to additional reporting requirements and, in severe cases, criminal sanctions for violating NIS2 regulations.
To comply with NIS2, entities must send notifications about significant incidents to a Computer Security Incident Response Team (CSIRT) or competent authority, as well as recipients of their services. This includes various types of reports, such as early warnings, incident notifications, intermediate reports, final reports, and progress reports.
SOCRadar provides critical alerts enriched with actionable insights to streamline the way organizations respond to security events. Assisted by SOCRadar, organizations can acquire a comprehensive understanding of the threat landscape, thoroughly protect their assets, and uphold regulatory compliance.
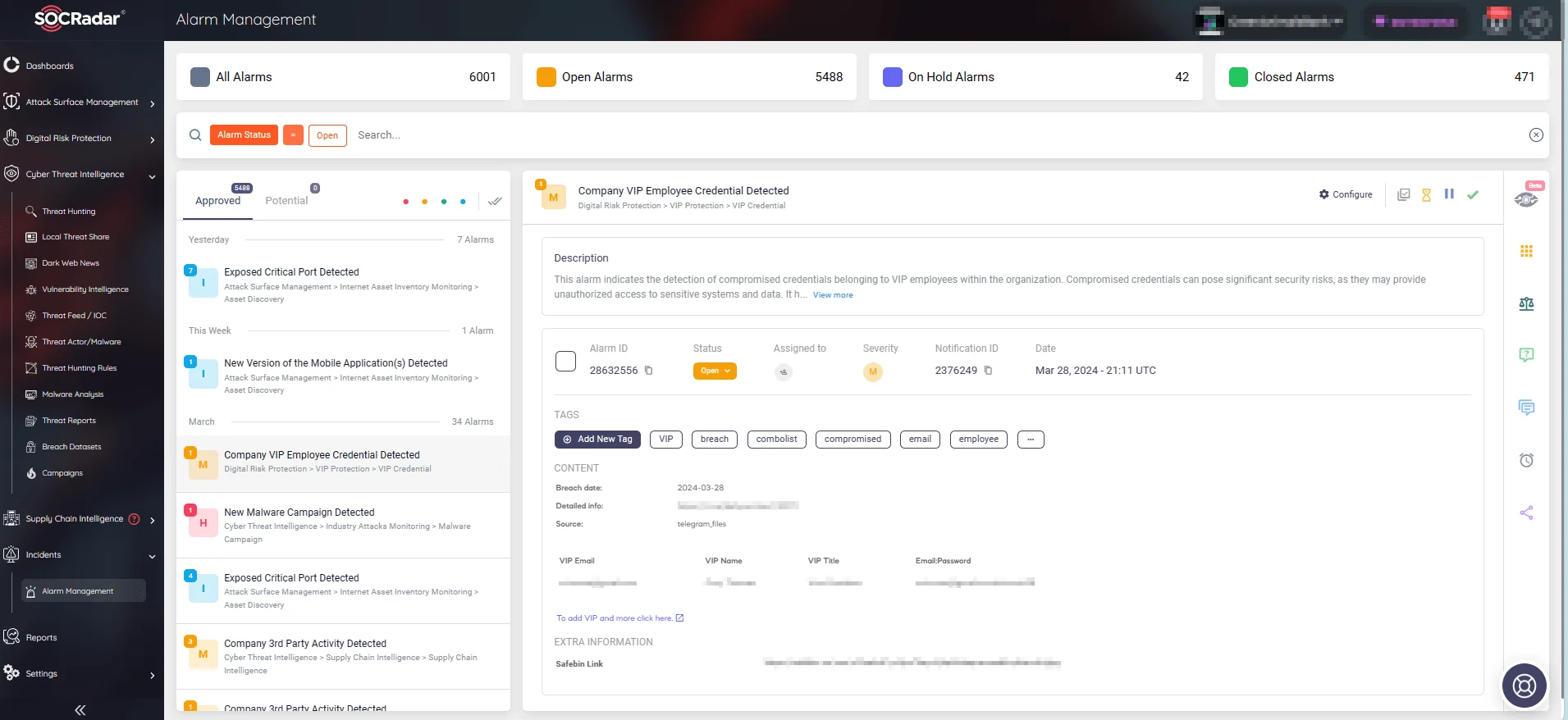
View all alerts by SOCRadar through the Alarm Management tab
Conclusion & How SOCRadar can help comply with the NIS2 Directive
In conclusion, the introduction of the NIS2 Directive marks a significant milestone in EU cybersecurity regulation, aiming to fortify critical infrastructure and enhance cyber resilience across member states and beyond.
As organizations navigate this new regulatory landscape, understanding the requirements and implications of NIS2 is fundamental.
SOCRadar provides a comprehensive suite of security solutions to help organizations prevent breaches and effectively meet compliance requirements, including those outlined in the NIS2 Directive.
Here’s how SOCRadar can help:
- Continuous Monitoring and Alerts: Benefit from continuous monitoring of your digital assets and receive instant alerts for any suspicious activities or potential security threats detected by SOCRadar.
- Vulnerability Intelligence: Stay updated on emerging vulnerabilities and trending exploits..
- Dark Web Monitoring: Keep an eye out for potential exposures and threats lurking in deep and dark web forums, and various other hacker channels.
- Supply Chain Intelligence: Proactively secure your supply chain with SOCRadar, accessing real-time cybersecurity updates, reports, and alerts. Gain insights into global attack trends specific to countries and sectors, enabling proactive protection against threats targeting your supply chain.
- Attack Surface Management (ASM): Monitor your digital assets in real time and receive alerts when critical vulnerabilities are cross-referenced to your exposed software assets.
- Threat Intelligence Feeds Integration: SOCRadar integrates with various threat intelligence feeds, providing organizations with enriched data on potential threats and enabling proactive threat detection and response.