
Could Your Email be Hacked? 2024 Analysis of Top Email Providers in Stealer Logs
With the ever-present concern surrounding the security of email addresses and the accounts linked to them, there arises a necessity to examine the vulnerabilities and threats present in the digital landscape.
In our analysis of some of the top email providers’ domains through stealer logs, we have targeted data shared in the first quarter of 2024 to illustrate the most recent occurrences and provide the latest insights.
Everyone is aware of the ease with which people share their email addresses online, frequently without thinking through the possible risks. This inadvertently exposes users to exploitation. Even if you are not one to frequent suspicious corners of the internet, the sites you regularly visit may one day become compromised. Threat actors keenly exploit these opportunities, deploying infostealer malware to stealthily pilfer valuable data.
It is not just a risk for end-users; affected platforms or websites may become unreliable in the eyes of their customers, or, as a business owner, your information may end up in these stealer logs, spelling potential doom.
By examining the widely used email domains in stealer logs, with the help of SOCRadar’s Threat Hunting feature, we aim to discern which have been targeted the most and gauge the level of caution exercised by users. While such statistics are influenced by the user base of each provider, this analysis nonetheless offers important insights into the overall landscape of email security.

SOCRadar’s Threat Hunting
Now, let’s proceed to identify the providers and domains under examination in this article.
- Gmail, operated by Google, stands as one of the most widely used email services globally, with its domain primarily being gmail.com.
- Outlook, a service provided by Microsoft, offers email solutions under the domain outlook.com. Known for its integration with Microsoft Office and widespread corporate usage, Outlook is a prominent player in the email service domain.
- Yahoo Mail, offered by Yahoo, utilizes the domain yahoo.com. While its popularity has declined in recent years, Yahoo Mail still retains a significant user base, particularly among older demographics.
- ProtonMail distinguishes itself by offering end-to-end encryption and a focus on privacy. Its domains include @proton.me, @protonmail.com, @pm.me, and @protonmail.ch. ProtonMail is often favored by individuals seeking heightened security and privacy in their communications.
- Tuta, formerly known as Tutanota, positions itself as a privacy-focused email and calendar service. Its free tier offers email addresses with domains including tutamail.com, tuta.io, tutanota.com, tutanota.de, and keemail.me. Tuta is also particularly popular among users who prioritize privacy and data security.
Note: Although some providers offer custom domain names, our analysis focuses on primary domains.
Here’s What We Found About Email Providers in Stealer Logs
After reviewing stealer logs from top email providers, we discovered a significant data breach landscape in Q1 2024. With a total of 1,904,497 user records sourced from 2,841 compromised victim IP addresses, these stealer logs expose a wide range of personal information and login credentials, painting a troubling picture of user vulnerability.
The compromised data consists of:
- 216,395 unique email addresses (and usernames), exposing tens of thousands to potential cyber threats like phishing and identity theft.
- 63,103 unique passwords, posing a substantial security risk, granting unauthorized access to sensitive accounts and information.
- 3,013 Credit Card (CC)/Bank Identification Number (BIN) details count, highlighting financial implications, increasing the risk of fraudulent transactions.
- 11,021 hashes, representing sensitive data cryptographically; their compromise enables unauthorized access and manipulation, worsening the security impact.
Moreover, during our analysis, various threat actors and malware entities emerged, including Starz, Crypton, Vidar, HubHead, AirBender, ArtHouse, OnionLABS, Hulk Logs, and Zero Logs.
Why Does It Matter?
The data we uncover in stealer logs often serves as the merchandise for threat actors during their illicit shopping sprees. They buy or freely obtain sensitive information from leaks, using it to fuel various malicious activities. Common occurrences include phishing schemes, fraudulent transactions, and unauthorized access to critical assets.
Of utmost concern is when corporate credentials find their way into these stealer logs. Threat actors can leverage such information to launch targeted attacks against entire organizations, resulting in significant financial and reputational damage.
Understanding which domains are most frequently targeted or included in these logs provides a clearer picture of where the greatest risks lie.
You can easily identify compromised accounts using SOCRadar’s free Account Breach Check service. As a critical component of the SOCRadar Labs suite, it enables users to search for their domain or email address in a breach database to determine whether their accounts have been compromised.
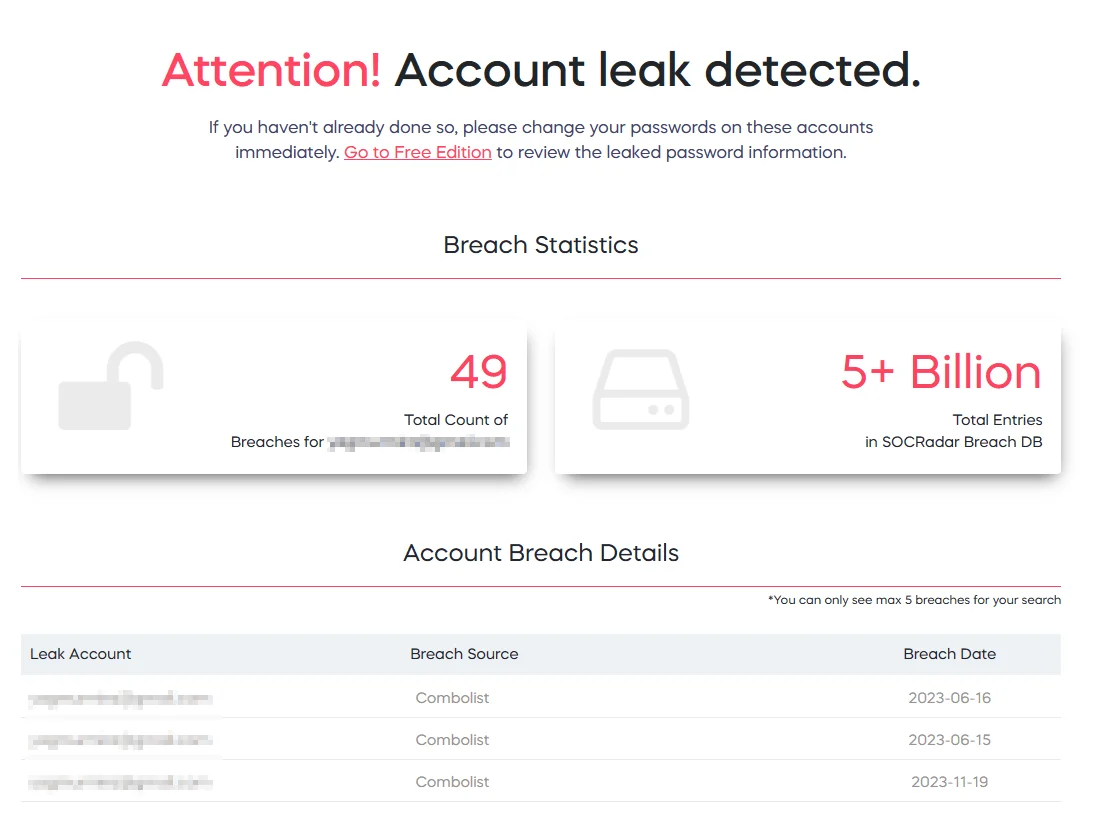
Account Breach Check, SOCRadar Labs
Which Countries’ Users Were More Frequent in Stealer Logs?
Analyzing geographic data within email providers affected by stealer malware reveals distinct patterns, indicating varying susceptibility to cyber threats. The victim country distribution by percentage provides critical insights into the impact of these logs across different regions:
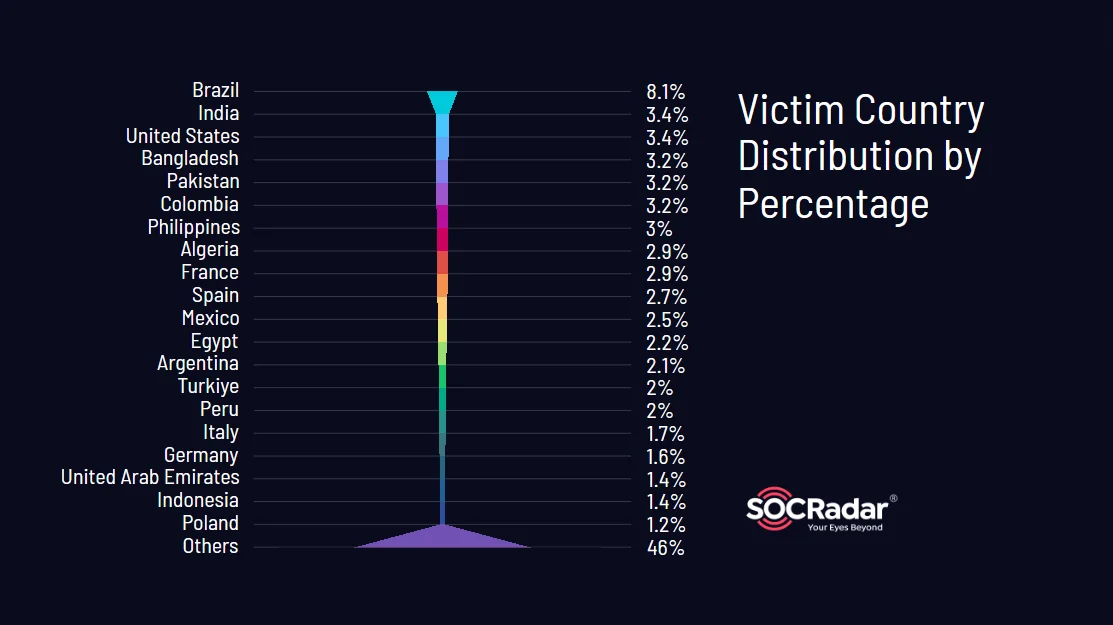
Victim country distribution in stealer logs related to different popular email domains
While 166 different country domain codes were identified in the logs, over 600 lacked specific country codes and contained mixed information. Nonetheless, our analysis pinpointed the top five countries most affected by stealer logs as Brazil (8.1%), India (3.4%), the United States (3.4%), Bangladesh (3.2%), and Pakistan (3.1%).
These findings suggest that users in these countries may have been more prolific in their online activities, making them prime targets for stealer malware, thus compromising their information online.
Analysis of Email Providers’ User Presence in Stealer Logs
The presence of users from certain email providers in stealer logs does not necessarily reflect the safety of those platforms. Yet, we can say that attackers adapt their tactics based on the prevalence and usage patterns of email domains.
Below, we depict which email provider’s users ended up more frequently in stealer logs, through percentages of user records found in each of them:
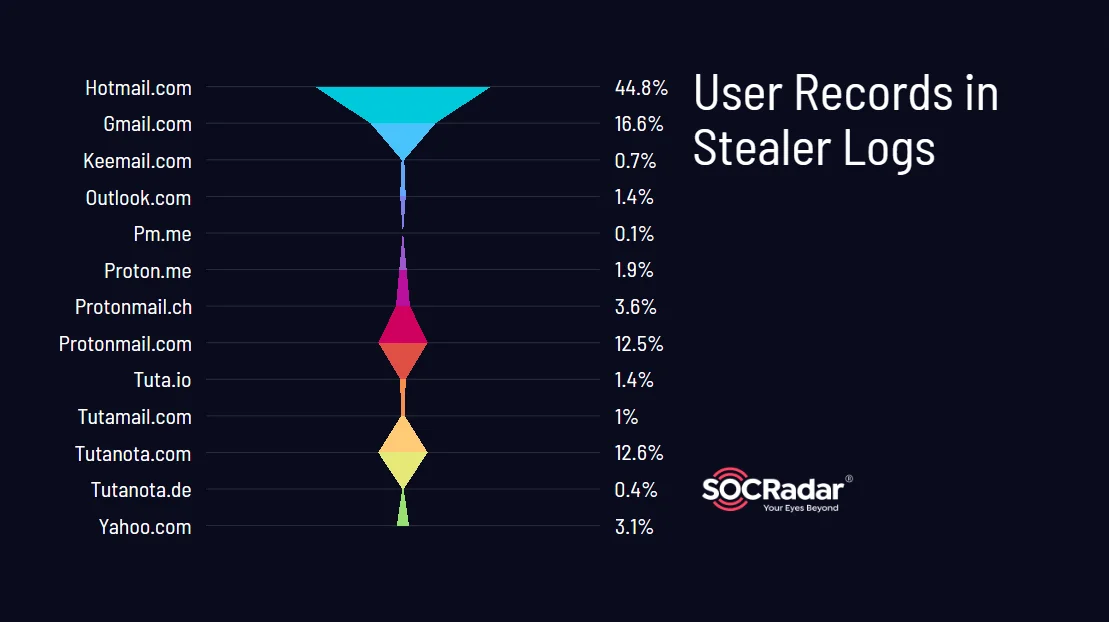
User records in stealer logs
These statistics highlight the prevalence of certain email providers and user records in stealer logs, with Gmail leading the pack followed closely by various ProtonMail domains. While percentages may vary, the risk posed by stealer malware underscores that any user or site is vulnerable if best practices are not followed diligently.
Email Security Grader from SOCRadar Labs will be very helpful if you wish to evaluate the security of your email servers, even though, as we previously mentioned, these counts do not reflect the safety of email providers.
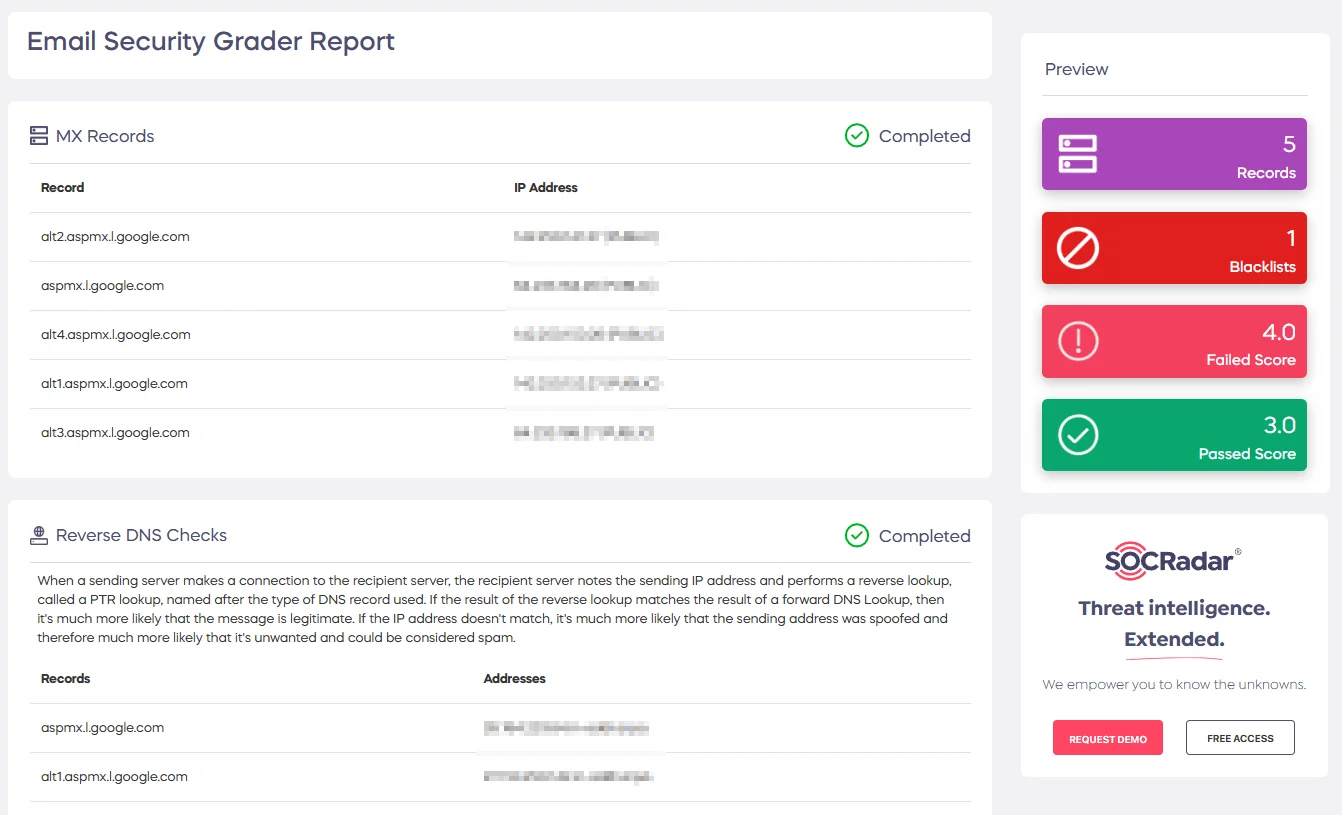
A section from a report generated by SOCRadar’s Email Security Grader
The Email Security Grader is one of the complimentary SOC Tools offered by SOCRadar. It quickly assesses your email server to find vulnerabilities, provides information about the email server’s risk profile, and offers actionable guidance to enhance email security.
How Many of These E-mails Came with CC (Credit Card) / Hash Information?
In this section, we will explore the credit card (CC) details found in stealer logs from our exploration of the compromised users of prominent email providers, ranking the domains based on exposure of such information.
Before starting, it is important to mention that credit card (CC) and Bank Identification Number (BIN) data appear in roughly 24% of the logs, indicating a significant risk of financial fraud or unauthorized transactions.
Among the top five domains with CC inclusion are protonmail.com (33.72%), hotmail.com (15.41%), tutanota.com (11.90%), protonmail.ch (9.44%), and yahoo.com (6.78%).

Top domains by CC inclusion
These domains exhibit a heightened concentration of compromised credit card information within the stealer logs, indicating an increased risk of financial fraud or misuse of credit card details.
While one might expect Gmail to have the most compromised financial information due to its vast user base and significant presence in our stealer logs search results, it is possible that Protonmail and Tutanota, being associated with heightened security, attract users who associate their financial information with these email providers, making them prime targets for attackers seeking financial data.
On the other hand, hash information, representing hashed passwords or other sensitive data, is present in approximately 47% of the logs. A little over half of the stealer logs we examined include hashed information, posing a significant risk as cybercriminals can attempt to crack these hashes to access user accounts or decrypt sensitive data.
The top five email domains associated with hash inclusion are protonmail.com (29.97%), tutanota.com (13.73%), hotmail.com (12.61%), protonmail.ch (11.23%), and gmail.com (8.21%).

Top domains by hash inclusion
Breakdown of Browser Information Among Victims
Knowing which browsers were used by victims when their data was compromised provides important information about the channels that threat actors use to get around restrictions.
The top five most commonly used browsers in the stealer logs we examined for this article were:
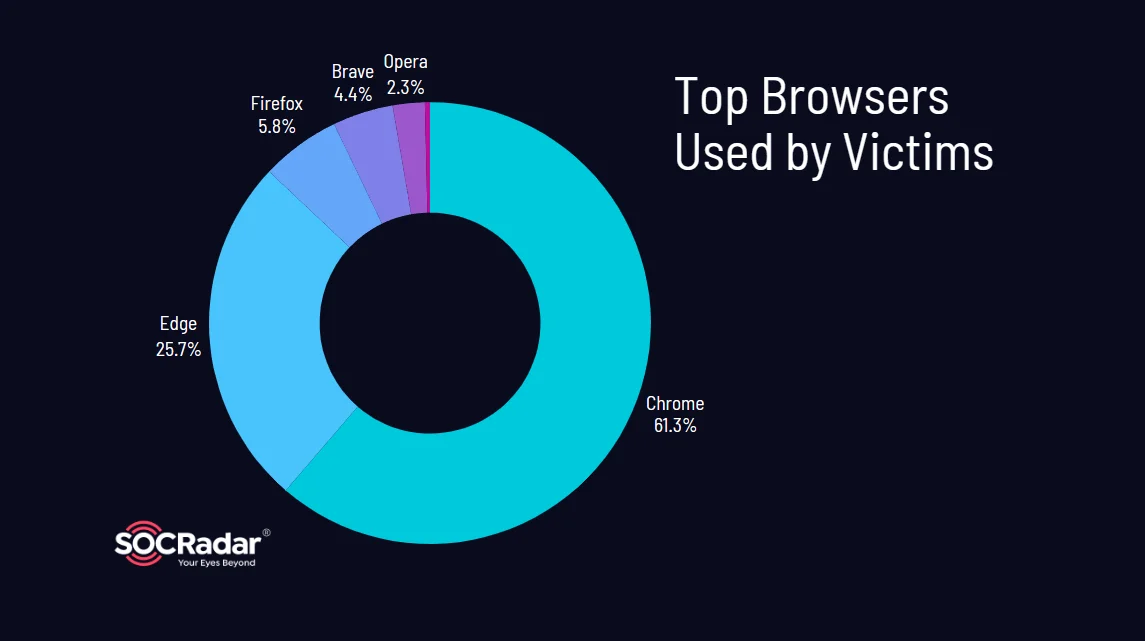
Top browsers used by victims
Chrome emerges as the predominant browser choice among victims, with a significant majority of compromised user records (61.32%) attributed to this platform.
Following Chrome, Edge (25.71%) and Firefox (5.82%) also feature prominently in the logs, comprising substantial portions of the compromised data.
It is also noteworthy that the ranking of browsers varies slightly across different domains, with Chrome consistently occupying the top spot and Edge frequently following suit. The third position sees competition between Firefox and Brave.

Chrome and Edge consistently ranked first and second place for different domains
The dominance of Chrome and other widely used browsers underscores the critical need to fortify browser environments against diverse threats, including malware and phishing attacks.
While other browsers like Thunderbird, Vivaldi, and PaleMoon make appearances, they do so in smaller numbers.
Prioritizing the deployment of strong security measures is essential for both individuals and organizations to protect against browser-based threats and prevent sensitive data from getting into the hands of cybercriminals.
Enhancing Security Against Stealer Malware: Best Practices
To guard against stealer malware, organizations need to put in place strong security measures, such as:
- Tighten Account Access:
Implement stringent controls over employee account access, utilizing Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) or Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) to thwart unauthorized entry.
- Promote Password Managers:
Encourage the use of password managers among staff, emphasizing the creation of strong, unique passwords and regular updates to mitigate credential exposure risks.
- Keep Software Updated:
Regularly update software to fortify system defenses against vulnerabilities exploited by stealer malware.
- Act Swiftly:
Isolate infected devices from the network upon detecting stealer malware, swiftly containing breaches to prevent further compromise.
- Educate Employees:
Train staff to recognize and evade suspicious emails and attachments, empowering them to actively contribute to cybersecurity efforts.
- Use Trustworthy Sources:
Emphasize downloading applications solely from trusted sources endorsed by the organization to minimize the risk of installing malicious software.
- Monitor Credentials:
Regularly check for credential leaks in publicly accessible services, such as chat platforms and cloud storage, which are prime targets for cybercriminals.
Keep an Eye Out with SOCRadar’s Dark Web Monitoring
Use SOCRadar’s Dark Web Monitoring for continuous surveillance of the web, including the deep and dark web, to detect compromised sensitive information.
With Dark Web Monitoring, you can receive real-time alerts on recently compromised account credentials and credit card numbers relevant to your organization, mitigating the risks of identity theft and fraud associated with stealer logs.
Dark Web Monitoring (SOCRadar’s Digital Risk Protection module)
Learn more about how stealers operate and their purpose in the blog post, “The Anatomy of Stealers.” For further context and insights regarding stealer logs, you can also explore SOCRadar’s “Snapshot of 70 Million Stealer Logs” whitepaper.
Conclusion
Our investigation reveals that the pervasiveness of stealer logs poses a serious threat to digital integrity by acting as a haven for cybercrime. We delved into these logs through our Threat Hunting module, and revealed their effects across popular email services such as Gmail, Outlook, Yahoo Mail, and Tuta Mail.
During our investigation, we discovered alarming statistics: over 1.6 million compromised user records, as well as more than 2,500 instances of CC/BIN data that could potentially be used for fraud.
By using the knowledge gathered from similar analyses, organizations can strengthen their cybersecurity defenses, mitigate threats, and identify patterns more effectively. Integrating strong security procedures with technologies like SOCRadar’s Threat Hunting and Dark Web Monitoring will help you obtain the information needed for successful threat mitigation strategies.
Search on stealer logs for Gmail (SOCRadar Threat Hunting)
Monitor your email environment, make sure the websites you visit or host are secure, and keep a close eye on your online login credentials in order to protect yourself from stealer threats. Always keep in mind that your credentials are your online persona; be sure to protect them with utmost care.



































