
CISA Launches New Resources to Help Combat Vulnerabilities and Weaknesses Exploited by Ransomware Groups
[Update] November 17, 2023: See the subheading: “CISA Intensifies Security Efforts Against Ransomware: Latest Advisories on Royal Ransomware, Rhysida, Scattered Spider.”
[Update] October 20, 2023: CISA, NSA, FBI, and the MS-ISAC have collaboratively released an updated version of the joint Stop Ransomware Guide. See the subheading: “Collaborative Update on #StopRansomware Guide: October 2023.”
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, the importance of staying ahead of threats cannot be overstated. With digital adversaries growing more sophisticated by the day, understanding which vulnerabilities are actively exploited is crucial. This is where CISA takes center stage, offering valuable resources for organizations. CISA KEV catalog now not only identifies known vulnerabilities but also explores their connections to ransomware campaigns, ushering in a new era in the fight against ransomware. Moreover, CISA has launched the “Misconfigurations and Weaknesses Known to be Used in Ransomware Campaigns” table, featured on StopRansomware.

In this blog post, we will explore how CISA’s role in tackling ransomware through these new resources is a game-changer in the realm of cybersecurity, and more.
How Does CISA Work to Mitigate Ransomware Threats?
Ransomware continues to pose a severe threat to organizations worldwide, often capitalizing on known vulnerabilities. Organizations may remain unaware if they harbor a vulnerability targeted by ransomware threat actors, potentially making them the next target if appropriate action is not taken.
In response to this pressing concern, CISA introduced the Ransomware Vulnerability Warning Pilot (RVWP) in January 2023. The RVWP stands as a groundbreaking initiative designed to preemptively address vulnerabilities before organizations fall victim to ransomware attacks. Through this program, CISA actively identifies vulnerabilities commonly associated with ransomware exploitation and proactively alerts entities within critical infrastructure sectors that are susceptible to these vulnerabilities.
Moreover, CISA has added a new resource to its RVWP toolkit as part of the StopRansomware initiative – an informative table titled “Misconfigurations and Weaknesses Known to be Used in Ransomware Campaigns.” According to CISA, this table identifies common misconfigurations and weaknesses frequently leveraged by ransomware campaigns. It also features a column that identifies the Cyber Performance Goal (CPG) action to rectify each misconfiguration or weakness.
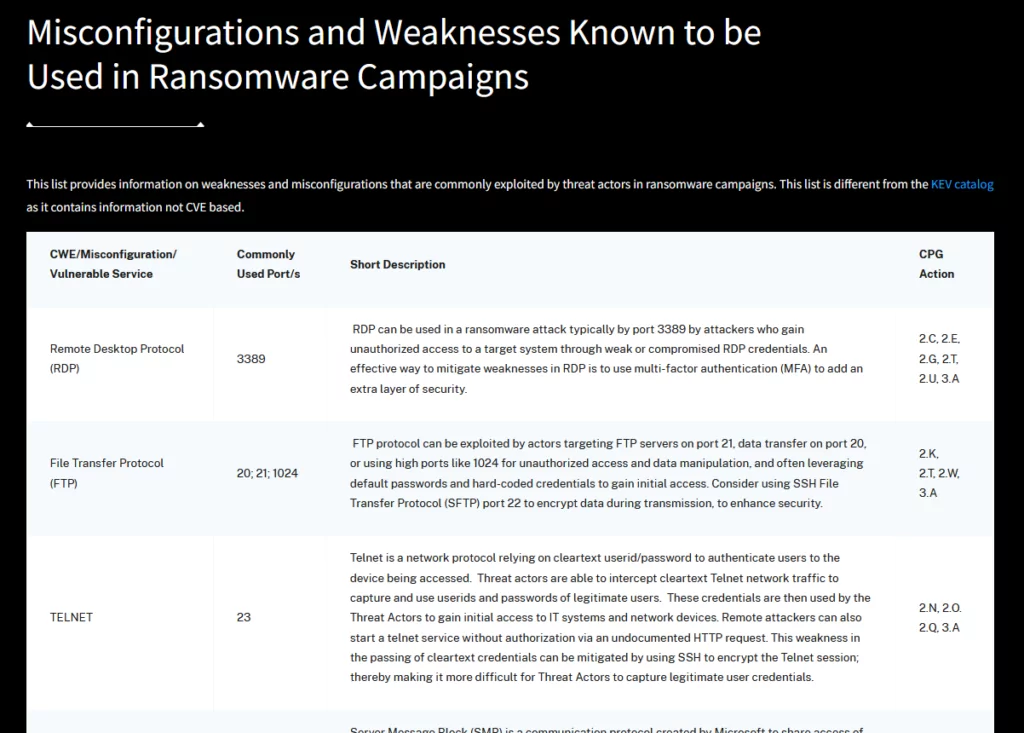
Along with the table, CISA has augmented its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog by adding the label “known to be used in ransomware campaigns.” This significant enhancement provides organizations with crucial insights into vulnerabilities recognized by CISA as exploited by ransomware groups, enabling them to prioritize their patching efforts effectively.
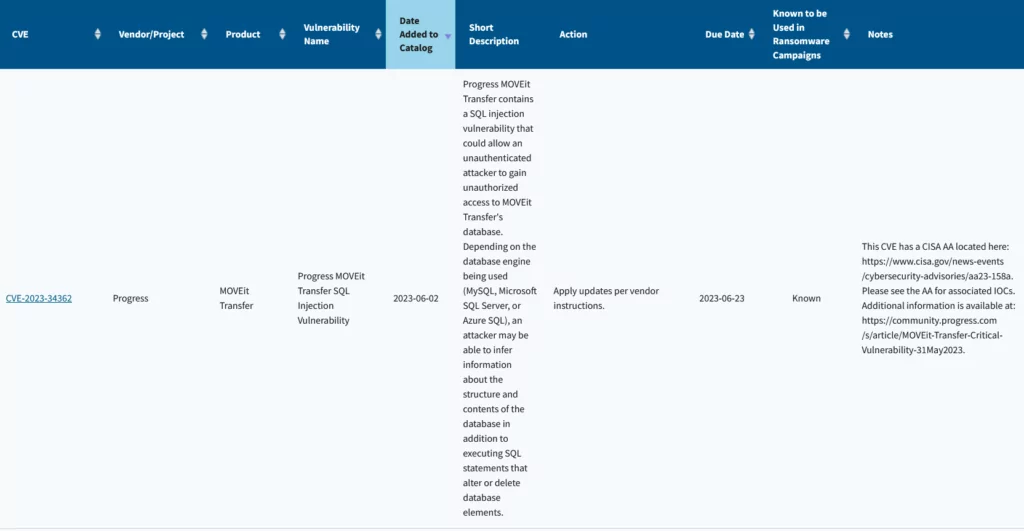
With these strategic enhancements, CISA is not only raising awareness about the ransomware threat but also equipping organizations with the tools they need to fortify their defenses and thwart potential ransomware threats before they manifest.
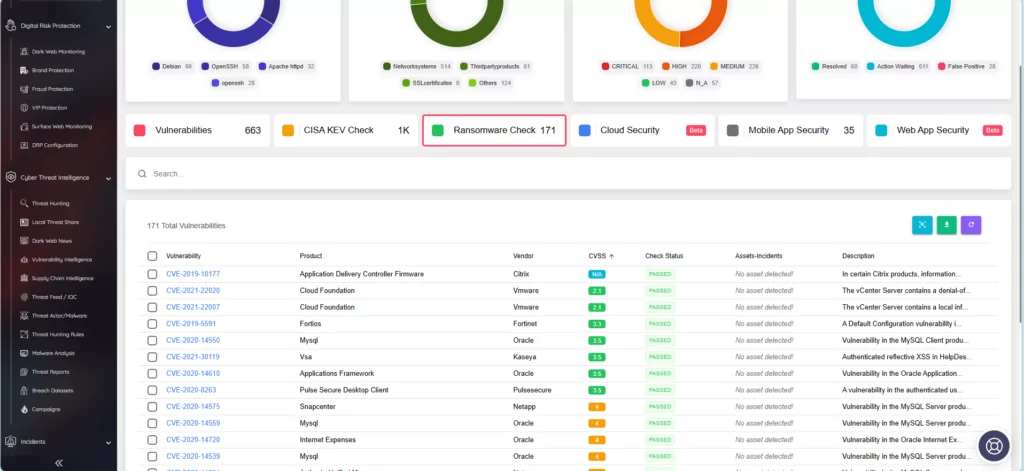
The SOCRadar platform has previously incorporated a feature called “Ransomware Check,” offering the same utility as CISA’s newly added feature in the KEV catalog. When you search for a vulnerability here, you can see if it has been targeted by ransomware operations, assess its impact on your assets, and access its information.
Role of CISA in Ransomware Defense: Navigating the Recent Vulnerabilities Used in Ransomware Operations
Ransomware groups have a multifaceted approach to their operations. They commonly target diverse industries across various regions, often driven by the desire for financial gain. These threat actors deploy a wide array of strategies to infiltrate their victims’ networks, including phishing, social engineering, and the exploitation of known vulnerabilities.
Some vulnerabilities have become notorious for their persistent exploitation by ransomware groups. These actors continuously search for weaknesses they can leverage to gain unauthorized access. By identifying these vulnerabilities, we can better understand how these attacks occur and take proactive steps to mitigate risks.
Let’s explore the more recent vulnerabilities that have drawn the attention of ransomware threat actors:
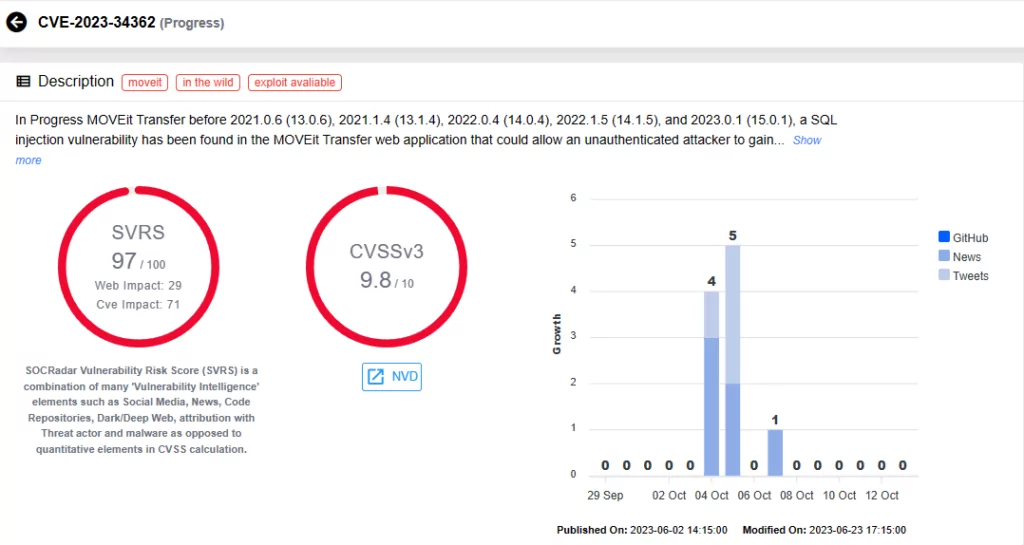
MOVEit Transfer Vulnerability (CVE-2023-34362)
CVE-2023-34362, a recent zero-day vulnerability in MOVEit Transfer software, enables remote code execution and data extraction via SQL injection. The Cl0p Ransomware group has exploited this vulnerability, resulting in significant data breaches worldwide.
Fortra GoAnywhere MFT Vulnerability (CVE-2023-0669)
CVE-2023-0669, another recent zero-day vulnerability, has fueled an increase in ransomware attacks. Malicious actors like Cl0p Ransomware and BlackCat (ALPHV) have exploited it, with a significant impact on the healthcare sector.
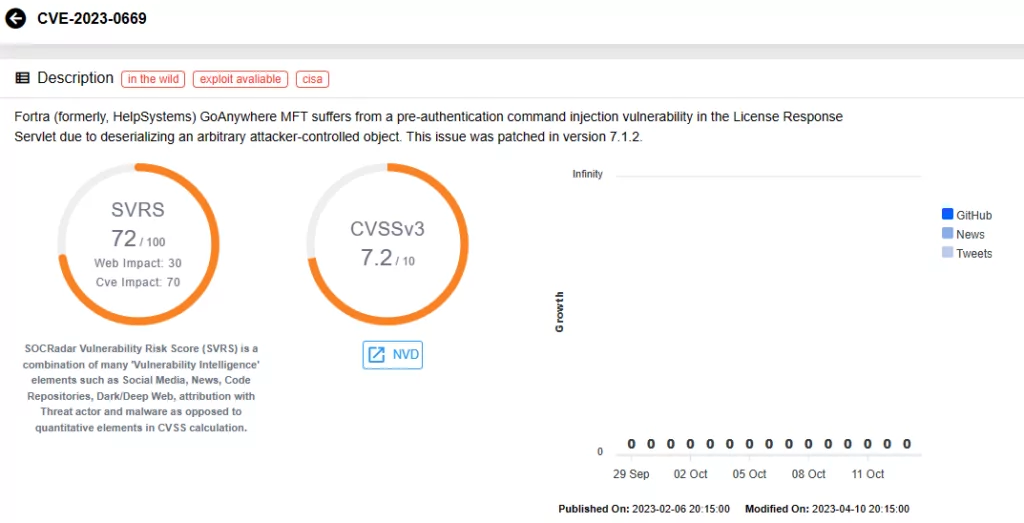
3CX VOIP Desktop Client (CVE-2023-29059)
CVE-2023-29059 is linked to a supply chain attack known as “SmoothOperator,” targeting the 3CX VoIP desktop client. Attackers exploited this vulnerability for arbitrary code execution, facilitating ransomware attacks through compromised software updates.
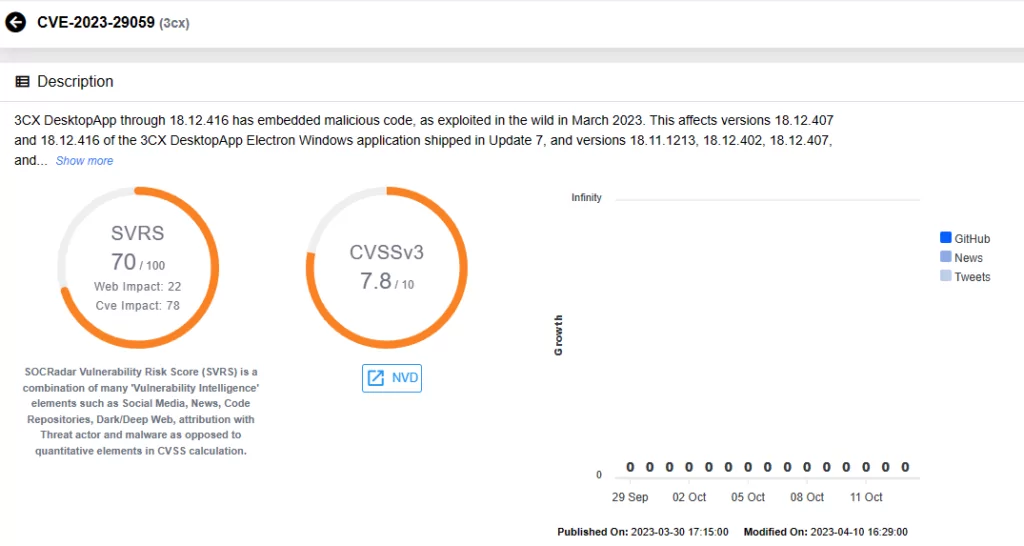
These vulnerabilities have proven their criticality, especially when used in ransomware operations, leading to substantial consequences. For instance, the MOVEit Transfer vulnerability facilitated data breaches at over 2,000 organizations, serving as a primary attack vector for the Cl0p ransomware group. The Fortra GoAnywhere MFT Vulnerability resulted in a significant surge in ransomware attacks, with a 91% increase in March 2023, and 459 attacks during the month. The compromise of the 3CX VOIP Desktop Client allowed attackers to manipulate downloadable files and distribute backdoored software updates for data theft and system compromise.
These real-world examples emphasize the pressing need for organizations to address these vulnerabilities effectively to prevent data breaches, ransomware incidents, and cyber disruptions. To address these growing concerns, CISA’s recent enhancements provide organizations with a vital resource to stay proactive against such vulnerabilities.
Collaborative Update on Stop Ransomware Guide: October 2023
CISA, NSA, FBI, and the MS-ISAC have collaboratively released an updated version of the joint #StopRansomware Guide. This update introduces fresh prevention tips, including the reinforcement of SMB protocols, revised response procedures, and additional insights for threat hunting.
The comprehensive #StopRansomware guide builds upon CISA’s initial ransomware guide released in September 2020, with the FBI and NSA joining forces as co-authors in 2023 to contribute their expertise and operational insights.
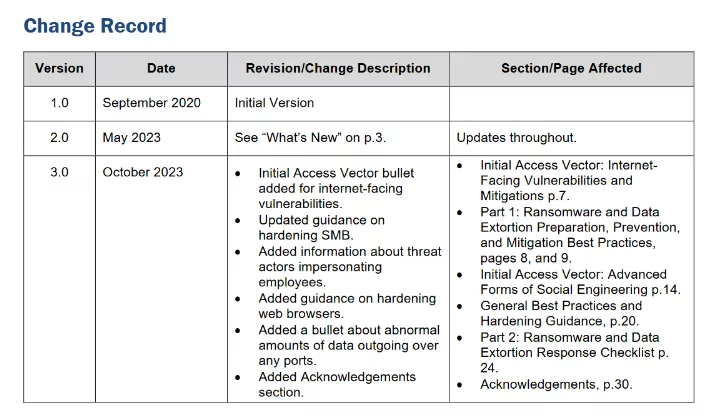
In the latest update, released in October 2023, the guide has been further fortified with several key enhancements, including an Initial Access Vector bullet addressing internet-facing vulnerabilities, updated guidance on hardening SMB, insights on threat actors impersonating employees, tips on hardening web browsers, a crucial addition highlighting abnormal data traffic over various ports, and the inclusion of an Acknowledgements section. Here is the change record of the guide:
Discover the latest insights to safeguard your digital realm – your indispensable shield against rising ransomware threats. Explore the official updated guide here.
CISA Intensifies Security Efforts Against Ransomware: Latest Advisories on Royal Ransomware, Rhysida, Scattered Spider
Now celebrating its fifth anniversary, CISA stands as a stalwart guardian at the forefront of cybersecurity. The agency has been intensifying its efforts against ransomware threats, and in alignment, has recently released several advisories to disseminate the latest identified information about threat actors to public.
The latest advisory release on November 16, 2023, is about Scattered Spider. Scattered Spider is a cybercriminal group that targets large companies and their contracted IT help desks. Scattered Spider threat actors, per trusted third parties, have typically engaged in data theft for extortion and have also been known to utilize BlackCat/ALPHV Ransomware alongside their usual tactics.
The FBI and CISA encourage critical infrastructure organizations to implement the recommendations in the advisory to reduce the likelihood and impact of a cyberattack by Scattered Spider actors.
Another advisory issued before was for Rhysida, while there was an update to an existing Royal Ransomware advisory. The update discloses that Royal Ransomware has targeted over 350 victims globally since September 2022, with ransom demands surpassing $275 million. It is also noted that there are signs that it might undergo re-branding or introduce a variant, Blacksuit, evidenced by shared coding characteristics.
Regarding Rhysida, CISA highlights the RaaS group’s diverse sector targeting, utilizing external-facing remote services and exploiting vulnerabilities like Zerologon and using phishing. Rhysida employs Living Off the Land techniques, which allow them to blend in with normal Windows activities to evade detection.
These advisories include comprehensive lists of Indicators of Compromise (IOCs), such as tools, software, and commands utilized by these threat actors, as well as their latest Tactics, Techniques, Procedures (TTPs). CISA aims to provide an extensive resource to organizations with such advisories, guiding them in the road of cybersecurity, as part of the #StopRansomware initiative.
Here are the links to advisories:
Conclusion
By identifying and cataloging vulnerabilities exploited by ransomware groups, CISA not only offers a comprehensive defense strategy but also enables organizations to implement proactive security measures that safeguard their digital environments. Prioritizing patching efforts, bolstering security protocols, and enhancing incident response strategies become more achievable with these early insights, reducing the risk of falling victim to ransomware attacks.
By staying informed about the dynamic landscape of ransomware vulnerabilities, organizations can maintain a robust cybersecurity posture. In a world where cyber threats continually evolve, this knowledge serves as a crucial tool for defenders. To delve deeper into the intricacies of the vulnerabilities mentioned in this blog and explore trends related to ransomware groups, you can visit our other blog post, linked below. It provides a wealth of information and analytics to aid organizations in their mission to protect against ransomware threats.
Journey into the Top 10 Vulnerabilities Used by Ransomware Groups
How Can SOCRadar Help?
SOCRadar, through its Attack Surface Management module, plays a crucial role in fortifying an organization’s defenses. Our platform provides real-time alerts about vulnerabilities that impact your digital assets. This feature ensures that you have access to the latest information about these vulnerabilities and their potential impact on your organization.
Additionally, within the Company Vulnerabilities page, you will find a dedicated tab for CISA KEV Check. Here, you can search for specific vulnerabilities and determine whether they have been added to CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog.
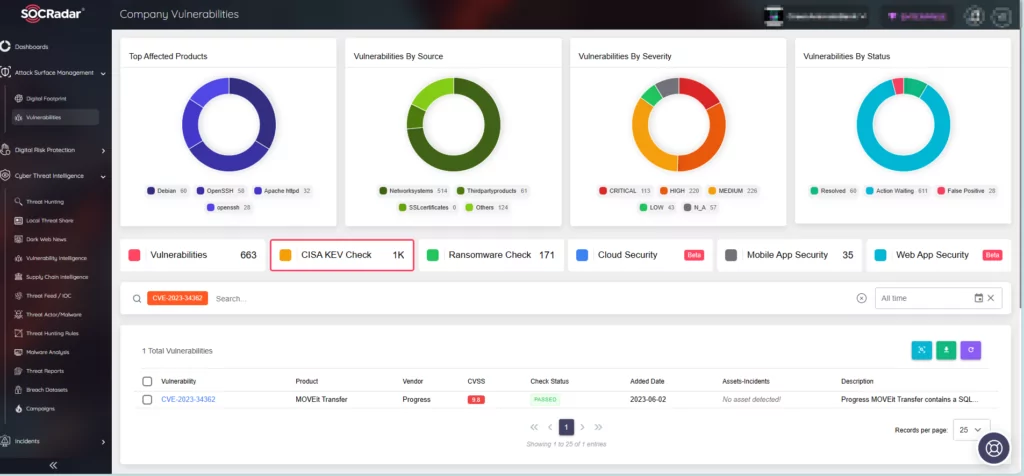
To further bolster your security posture and stay ahead of emerging threats, SOCRadar offers CVE Radar, a free SOCRadar Labs feature. CVE Radar allows you to monitor vulnerability trends with clarity, providing insight into the most frequently mentioned vulnerabilities, their associated exploits, repos, and the latest updates through tweets and news blogs. In addition, you can access relevant repositories for each vulnerability.
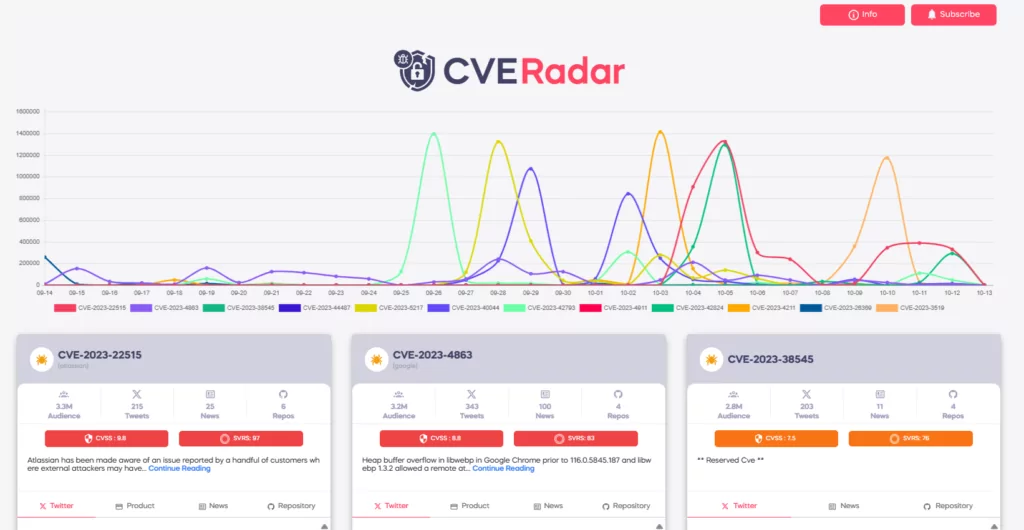
Unlock the full range of features offered by the SOCRadar platform to enhance your security management efforts by signing up for the Free Edition.


































