
Streamlining Cloud Security Strategy to Reduce Attack Surface
As businesses increasingly shift their operations to the cloud, the importance of a comprehensive cloud security strategy cannot be overstated. According to Gartner, by 2027, more than 70% of organizations will leverage industry cloud platforms to accelerate their business initiatives. This rapid adoption of cloud technology underscores the critical need for businesses to implement effective cloud security strategies to safeguard their data and minimize vulnerabilities.
The growing complexity of cloud environments presents significant challenges. A study by Microsoft found that 95% of security professionals are concerned about the security of public cloud environments. These concerns are well-founded, as data breaches related to cloud security vulnerabilities have proven to be extremely costly. For example, IBM’s 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report reveals that the average cost of a cloud-related data breach now exceeds $5.17 million USD.

An illustration of “Streamlining Cloud Security Strategy to Reduce Attack Surface”, generated by OpenAI’s DALL-E
Given these stakes, developing a cloud security strategy that effectively reduces the attack surface is crucial for any organization. In this article, we will explore the key challenges organizations face in securing cloud environments and provide a detailed roadmap for creating a strong cloud security strategy. By addressing these challenges head-on, businesses can better protect their assets, ensure compliance with regulatory standards, and maintain the trust of their customers.
Key Challenges in Cloud Security
Organizations adopting cloud environments face several critical security challenges. From managing a complex multi-cloud environment to mitigating the risks of human error, addressing these challenges is essential to reducing the attack surface. Below are some of the key obstacles organizations encounter when developing a cloud security strategy:
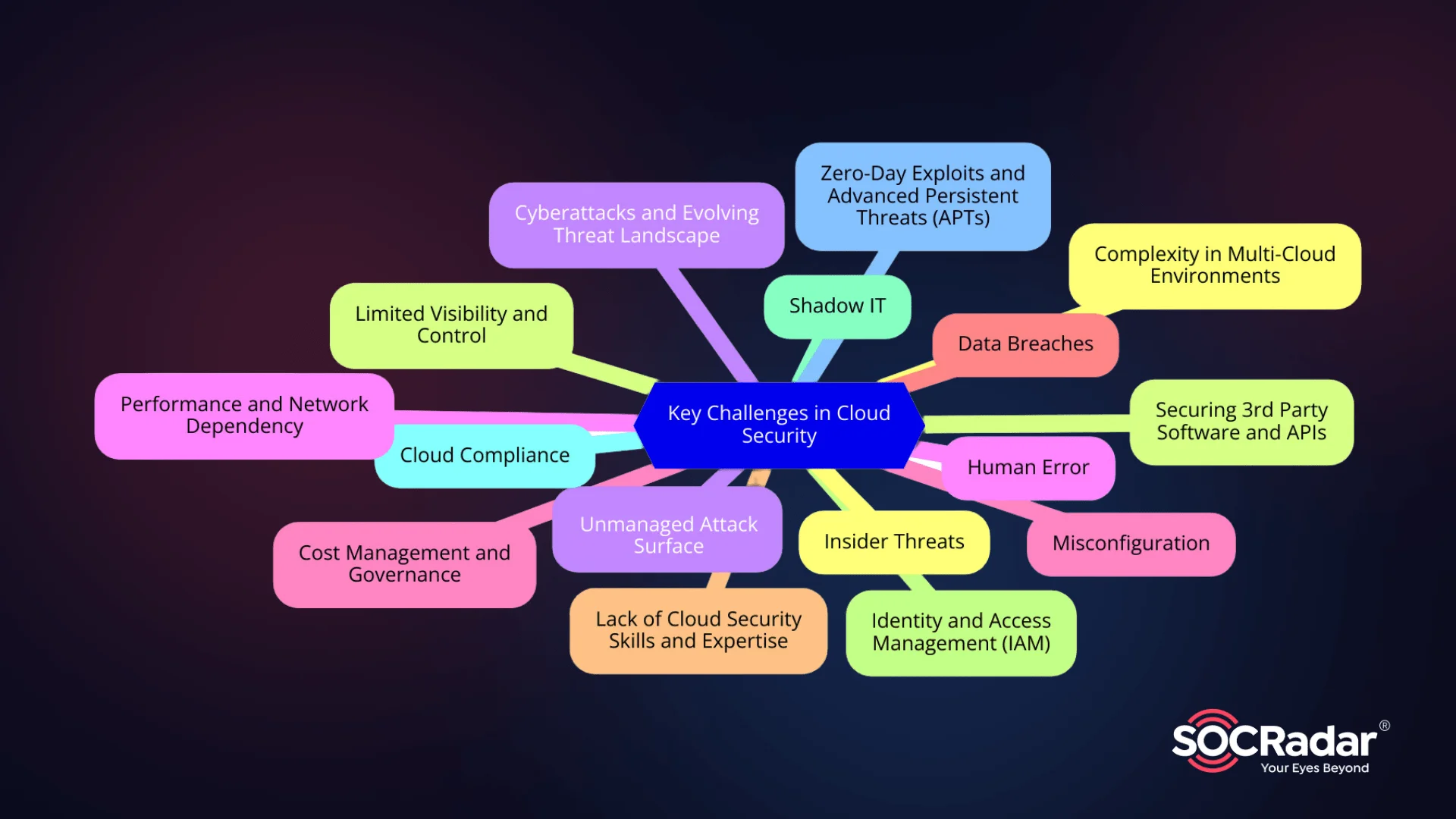
Major Obstacles in Cloud Security
- Complexity in Multi-Cloud Environments
As businesses adopt multiple cloud platforms, managing security across these environments becomes increasingly difficult. Different platforms have unique security features, which can lead to inconsistencies and gaps in protection. - Limited Visibility and Control
Maintaining full visibility over cloud data and services is a persistent challenge. Without proper monitoring, organizations may overlook vulnerabilities or active threats in their cloud infrastructure, making it difficult to respond in a timely manner. - Unmanaged Attack Surface
The rapid expansion of cloud services increases the attack surface. As organizations scale, it becomes harder to monitor and secure every endpoint, leaving opportunities for attackers to exploit unprotected areas. - Human Error
One of the leading causes of security incidents in the cloud is human error. Misconfigurations, weak passwords, and improper handling of sensitive data can open the door to cyberattacks and data breaches. - Misconfiguration
Cloud misconfigurations, such as leaving storage buckets publicly accessible or failing to set up proper security protocols, are common and can lead to severe data exposure. Misconfigurations remain one of the top causes of cloud-related breaches. - Data Breaches
The risk of data breaches in the cloud is ever-present. With sensitive data moving between different environments, it becomes more vulnerable to interception or unauthorized access, leading to costly breaches. - Lack of Cloud Security Skills and Expertise
As cloud technology evolves, there is a growing gap in cloud security expertise. Many organizations struggle to find qualified professionals who can manage and secure cloud environments effectively. - Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Weak or improperly configured IAM policies can result in unauthorized access to sensitive resources. Managing user identities and permissions across cloud environments is a complex but crucial part of maintaining security. - Shadow IT
The use of unauthorized cloud applications and services, or “shadow IT,” increases security risks, as these applications are often not vetted or monitored by IT departments, leaving them vulnerable to exploitation. - Cloud Compliance
Navigating the complexities of data protection laws, such as GDPR and HIPAA, is a major challenge in cloud environments. Ensuring that data is compliant across various regulatory frameworks can be difficult, especially when data is stored in multiple locations. - Zero-Day Exploits and Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
Cybercriminals are constantly evolving their attack methods. Zero-day exploits and APTs pose significant risks, as they often target previously unknown vulnerabilities in cloud environments. - Insider Threats
Whether intentional or unintentional, insider threats remain a critical concern. Employees or contractors with access to sensitive data can inadvertently or maliciously compromise cloud security. - Securing 3rd Party Software and APIs
The integration of third-party services and APIs into cloud systems increases the risk of vulnerabilities. Organizations must ensure that these integrations are secure and do not introduce exploitable gaps in their defenses. - Cyberattacks and Evolving Threat Landscape
The frequency and sophistication of cyberattacks continue to grow. Cloud environments are often targeted by ransomware, DDoS attacks, and other cyber threats, which can severely disrupt operations. - Performance and Network Dependency
Cloud systems heavily rely on network performance. If network connectivity is compromised, it can lead to downtime, delayed services, or security breaches. Maintaining a high level of performance and availability is critical for cloud environments. - Cost Management and Governance
The cost of managing and securing cloud services can escalate quickly, especially when trying to maintain a strong security posture. Implementing governance practices to control costs while ensuring security is a balancing act for many organizations.
Developing a Roadmap for Robust Cloud Security Strategy
To effectively protect cloud environments from evolving threats, organizations must develop a comprehensive cloud security strategy. This roadmap should address the key challenges and provide actionable steps to safeguard data and reduce the attack surface. Below is a structured approach for building a resilient cloud security framework:
- Assess Current Security Posture
Begin by evaluating your existing cloud security measures. Conduct a thorough audit to identify any gaps or vulnerabilities in your current setup. SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management tools provide visibility into your organization’s external assets and digital footprint, identifying vulnerabilities and exposed services across your cloud infrastructure. This proactive monitoring can help prevent attacks by alerting you to weaknesses before they are exploited.
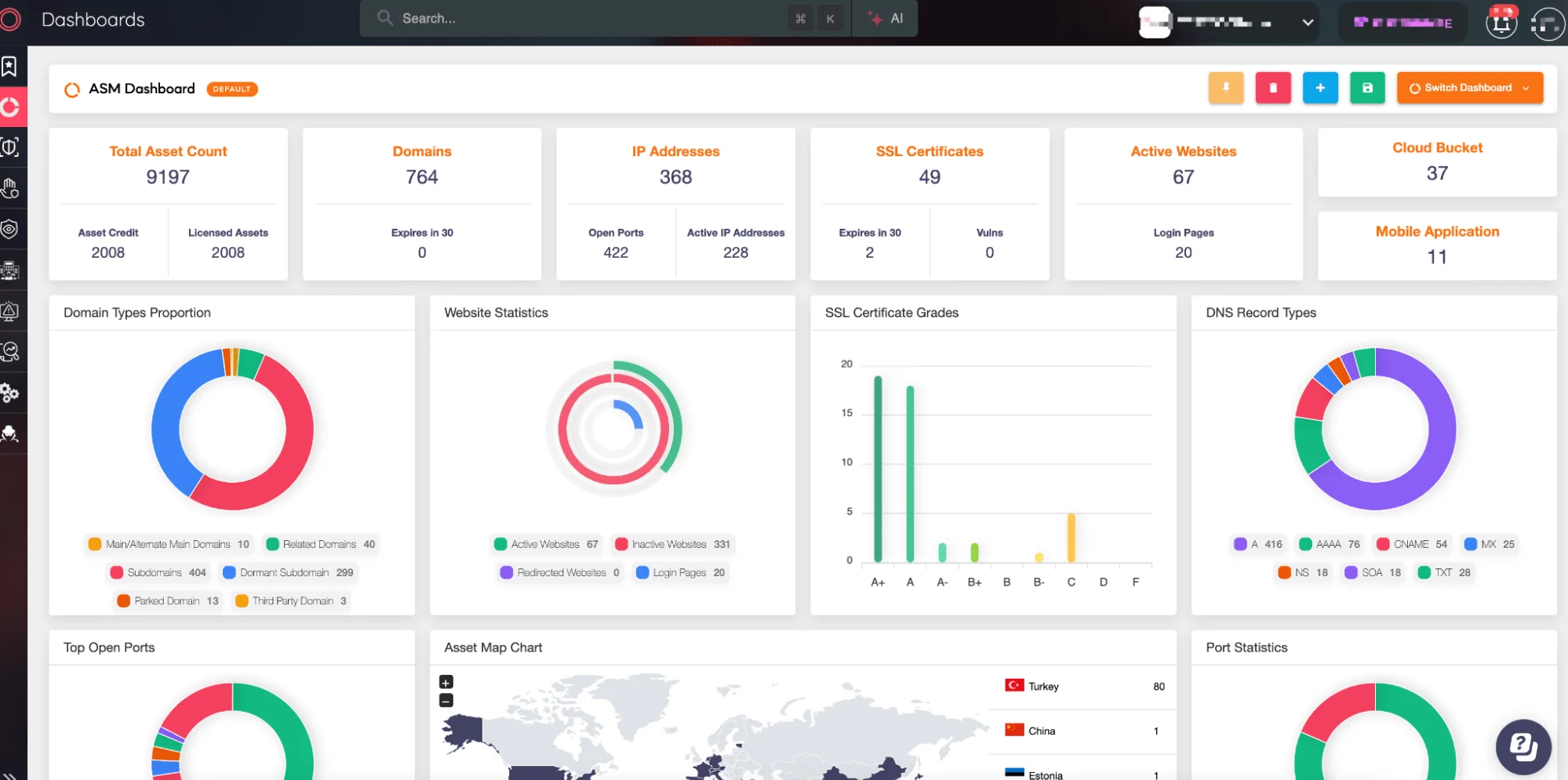
SOCRadar Attack Surface Management
- Prioritize Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection
Continuous monitoring tools that offer real-time insights into cloud environments are essential for identifying and responding to threats quickly. SOCRadar’s Extended Threat Intelligence and Dark Web Monitoring capabilities can alert organizations to emerging threats targeting their specific cloud assets. By providing real-time alerts on new vulnerabilities, exploits, and cybercriminal activity, SOCRadar helps organizations stay ahead of potential threats.
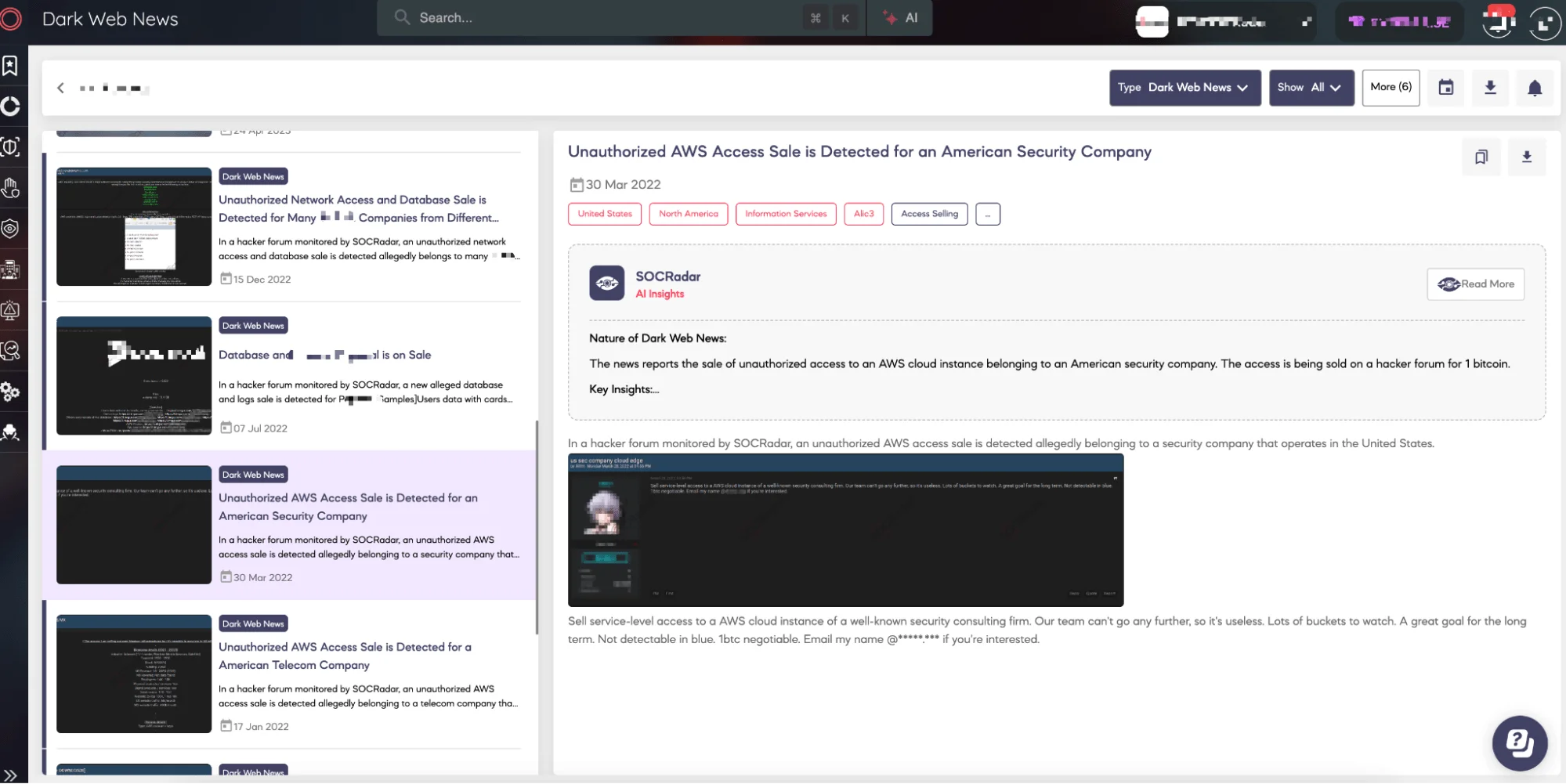
SOCRadar Dark Web News
- Strengthen Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Implement robust IAM practices to manage user identities and control access to critical cloud resources. Ensure that Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is mandatory for all users, and regularly review user access levels to enforce the principle of least privilege.
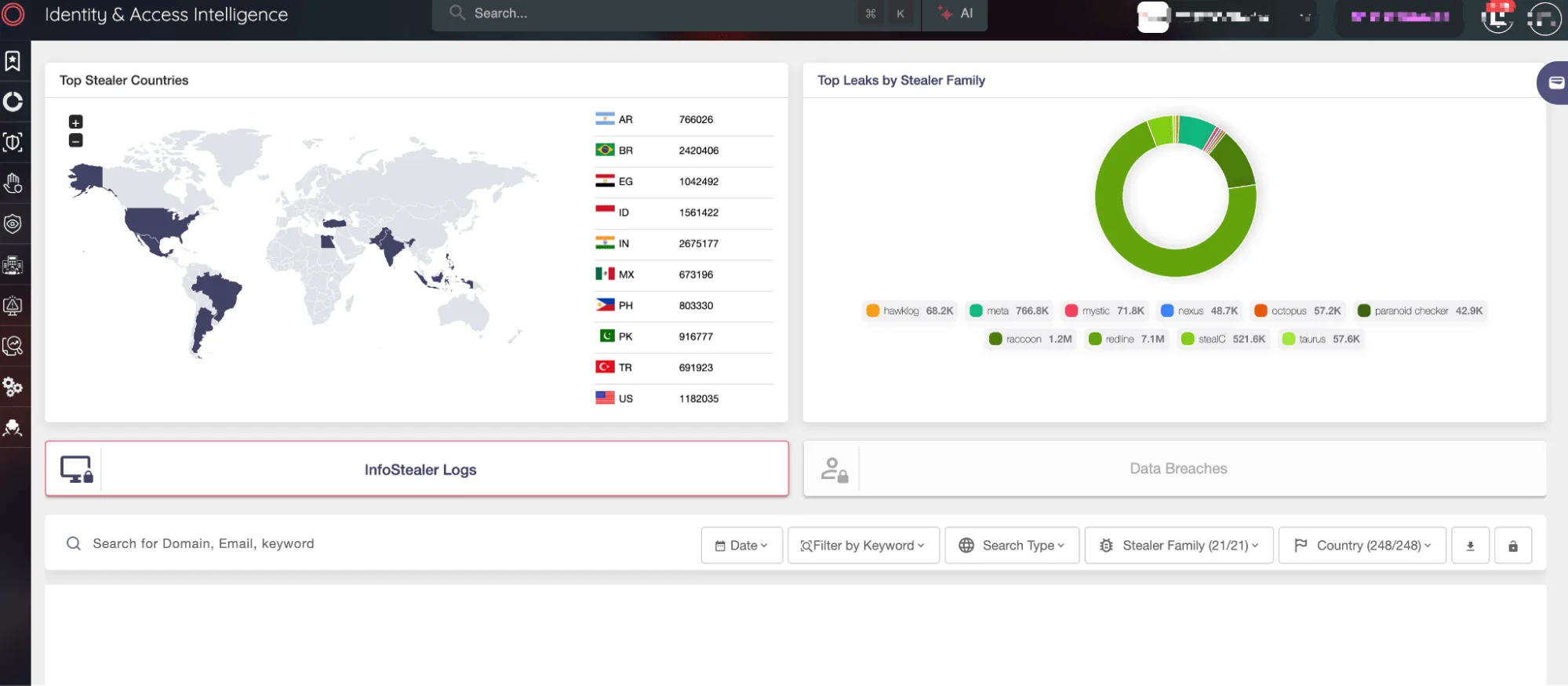
SOCRadar’s Identity & Access Intelligence
Additionally, SOCRadar’s Identity & Access Intelligence can detect leaked credentials in stealer logs and notify organizations before those credentials are used for malicious purposes. For example, SOCRadar helped prevent further breaches by identifying compromised credentials from a stealer trojan, enabling the organization to remove the threat and protect user access effectively.
- Automate Security Processes
Automation can help streamline cloud security efforts by handling routine tasks such as patch management, security configuration, and incident response. Automating these processes reduces the risk of human error and ensures that security policies are applied consistently across cloud environments. It also enables faster response times in the event of an attack. - Implement Data Encryption and Backup Solutions
Encrypting data both at rest and in transit is crucial for protecting sensitive information in the cloud. Ensure that strong encryption protocols are in place to safeguard against data breaches. Additionally, maintain regular backups of critical data in a secure, offsite location. Backups should be regularly tested to ensure they are effective in case of an incident. - Enforce Cloud Governance and Compliance
Establish a governance framework to ensure that cloud security policies align with regulatory requirements and industry standards. Regularly review and update these policies to reflect changes in cloud usage, technology, or legislation. A solid governance structure helps maintain control over cloud resources and ensures compliance with frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS. - Educate and Train Your Workforce
A well-informed workforce is one of the most effective defenses against cloud security risks. Regularly train employees on cloud security best practices, phishing awareness, and incident response protocols. Ensure that both technical and non-technical staff understand the role they play in maintaining cloud security. - Conduct Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing
Regularly testing your cloud security through audits and penetration testing can help identify weaknesses before they are exploited. Simulating attacks can reveal vulnerabilities that might otherwise go unnoticed, allowing you to address them proactively.
SOCRadar Operational Intelligence Trends
SOCRadar’s threat actor tracking capabilities provide organizations with detailed intelligence on the latest attack methods and threat actor tactics. By understanding the most current threat landscape, businesses can conduct more focused penetration testing and prepare for potential vulnerabilities that are actively being targeted by cybercriminals.
- Collaborate with Trusted Cloud Service Providers (CSPs)
Partner with CSPs that offer strong security features and are transparent about their security responsibilities. Ensure that Service-Level Agreements (SLAs) with CSPs cover critical aspects of security, such as data protection, incident response, and compliance. Clear communication with your CSPs is essential for maintaining a secure cloud environment. - Develop an Incident Response Plan
Prepare for potential security incidents by developing a comprehensive incident response plan. This plan should include procedures for identifying, containing, and mitigating attacks, as well as steps for recovering affected systems. A well-designed incident response plan helps minimize downtime and data loss.
Conclusion
As organizations increasingly adopt cloud technologies, the need for a strong and well-structured cloud security strategy has never been more critical. The challenges of maintaining security across complex multi-cloud environments, managing identity and access, preventing data breaches, and navigating compliance requirements highlight the importance of proactive measures. With data breaches becoming more costly and cyberattacks more sophisticated, the stakes for cloud security are higher than ever.
To reduce the attack surface, organizations must take a comprehensive approach by continuously assessing their security posture, automating processes where possible, and implementing best practices such as encryption, robust IAM policies, and ongoing employee training. Partnering with trusted cloud service providers and conducting regular audits also ensure that vulnerabilities are addressed before they can be exploited.
By leveraging advanced tools such as SOCRadar Extended Threat Intelligence‘s Attack Surface Management and Identity & Access Intelligence, businesses can stay ahead of emerging threats and protect their cloud infrastructure. Developing a robust incident response plan and fostering a culture of security within the organization will further strengthen their defenses, ultimately safeguarding valuable data and maintaining trust with customers.
In a rapidly evolving digital landscape, an effective cloud security strategy is not only a necessity but also a key driver of business resilience and success.



































