
Dark Web Profile: Big Head Ransomware
While ransomware groups such as ALPHV and Lockbit 3.0 continue to hit big companies and make headlines with the large-sized files they steal, there are also actors who do not even have a TOR page or a ProtonMail account but ask to be contacted via Gmail, and they operate only as a variant of another ransomware. Who are we talking about? In this article, we will discuss one of them, Big Head Ransomware.
Who is Big Head Ransomware?
Big Head Ransomware is a relatively new player in the cyber threat landscape, first emerging in May 2023. This malicious software is not just a single entity but consists of multiple variants with unique characteristics and capabilities. The threat actor behind Big Head Ransomware has been elusive, with only a few details known about them. The actor has been observed engaging with victims via email and Telegram.
There is also speculation about a potential connection to Bahasa-speaking countries, and the actor is probably Indonesian but this remains unconfirmed.
The actor’s malware suggests a level of experience, but their actions indicate they might not be sophisticated actors. Despite this, this nascent malware’s diverse and multifaceted nature has caused significant concern among cybersecurity researchers.

How Does Big Head Ransomware Attack?
Big Head Ransomware employs various deceptive techniques to infiltrate systems and execute its malicious activities. One of its most notable methods is using fake Windows updates and counterfeit Microsoft Word installers. These deceptive techniques trick users into executing the ransomware, thinking they perform a legitimate software update or installation.

Researchers observed that during the encryption process, Big Head Ransomware displays the screen that purports to be a legitimate Windows update. This clever disguise further deceives the victim, allowing the ransomware to complete its encryption process without interruption.
Initial Access: Big Head Ransomware probably gains initial access to systems through malvertising campaigns and also phishing emails, malicious attachments, or compromised websites.
Tools Used: The ransomware uses several tools for its operation. Some of these tools include:
- Mimikatz: A post-exploitation tool that dumps passwords from memory, as well as hashes, PINs, and Kerberos tickets.
- PsExec: A lightweight telnet replacement that lets users execute processes on other systems.
- Cobalt Strike: A threat emulation software. Its Beacon payload enables red teams and attackers to simulate an advanced actor and deploy payloads.
- Empire PowerShell: A post-exploitation framework that includes a pure PowerShell2.0 Windows agent and a pure Python 2.6/2.7 Linux/OS X agent.
Impact: The ransomware encrypts files on the victim’s system and demands a ransom to decrypt the files. It has caused significant damage to various organizations, disrupting their operations and causing financial losses.
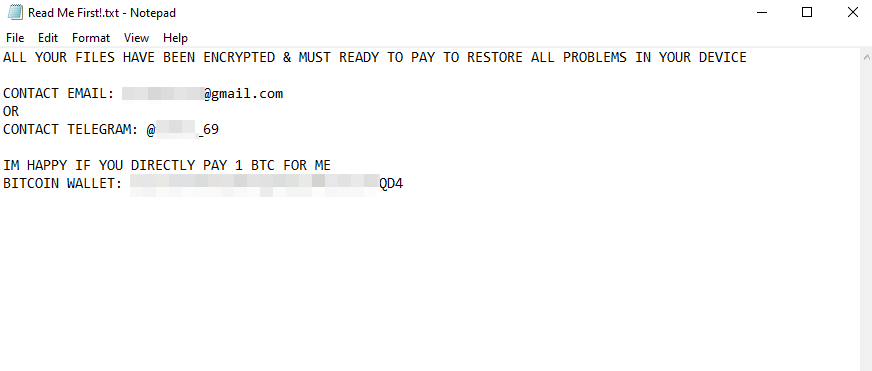
When we do research on Alienvault, we see that this ransomware is mostly referred to as “Ransom:MSIL/Ryzerlo.A”, meaning that it is likely to be a variant of Ryzerlo ransomware.
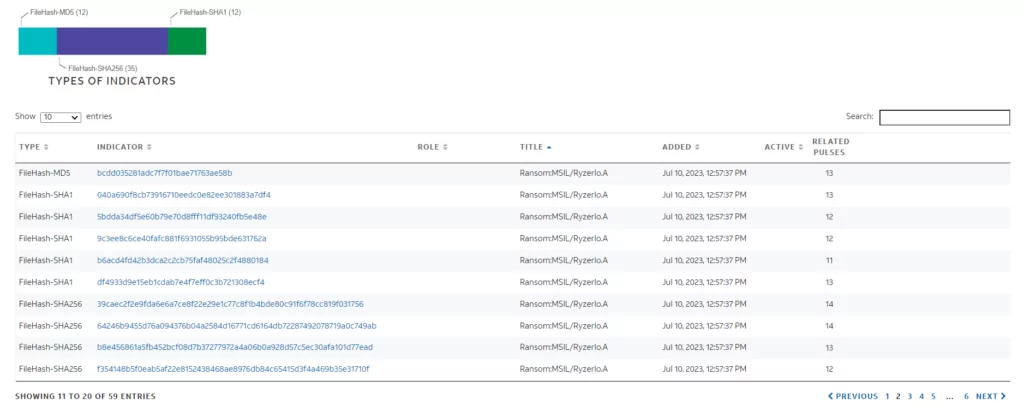
When we did research on Malwarebazaar with the Ryzerlo tag, we ran the sample with the hash value “0dbfd3479cfaf0856eb8a75f0ad4fccb5fd6bd17164bcfa6a5a386ed7378958d” and observed that it was Big Head ransomware, although it was marked as Ryzerlo.

When we search the hash value on Virus Total, we see that the malware communicates with the address “https[:]//t[.]me/dme69”. Earlier versions of the ransomware contacted “https[:]//t[.]me/temon_69” and “https[:]//github[.]com/temon_69” and the ransom note had instructions to contact “temon_69”. From this, we can see that the threat actor has changed his username one more time (we think his previous username was poop69).
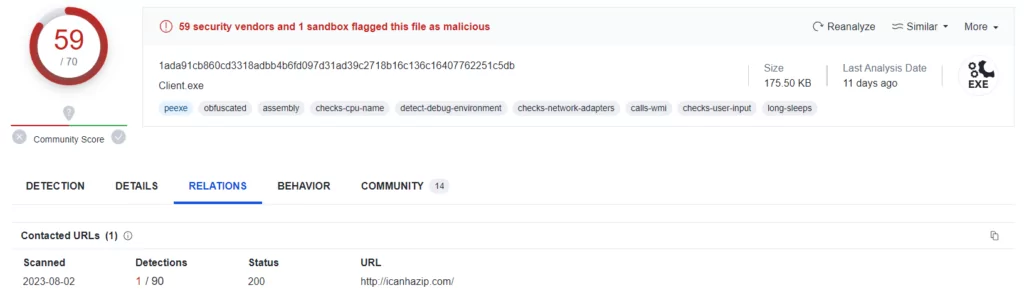
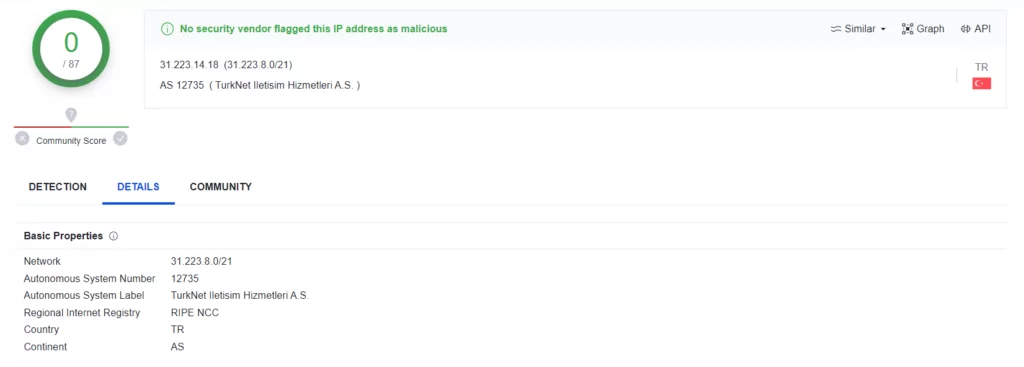
When we looked at other hashes associated with Big Head Ransomware on VirusTotal, we noticed a malware that worked as “Client[.]exe” and when we looked at the communications established by the malware, we observed that it communicated with the “icanhazip” domain.
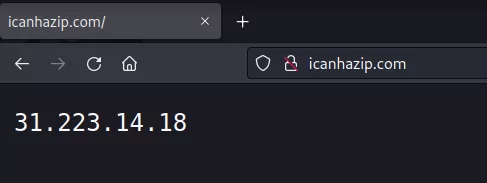
We received an IP address as an output that we went to the site, we think that this domain provides the IP address of the current C2 server to the malware. When we checked the IP address on VirusTotal, we observed that it was not marked as malicious by any tool and appeared completely clean, and in addition, it was an IP address located in Turkey.
Variants of Big Head Ransomware
According to observations, there are two variants of Big Head ransomware.
The first variant’s key attributes are:
- Fake Windows update screen,
- Encodes filenames by using Base64.,
- Generates an ID for the victim as seen in the ransom note,
- Changes background after running successfully.
Second variant’s key attributes are:
- It’s observed that the ransomware doesn’t encrypt the files in some test cases,
- Drops ransom note without generating any victim ID or unique value,
- Changes background after running successfully.
What are the targets of Big Head Ransomware?
Sectors
Big Head Ransomware, like many of its counterparts, does not discriminate when it comes to its victims. It targets a wide range of sectors, with a particular focus onconsumers rather than enterprises. This is evident from the relatively low ransom fee it demands, which is typically around one Bitcoin.
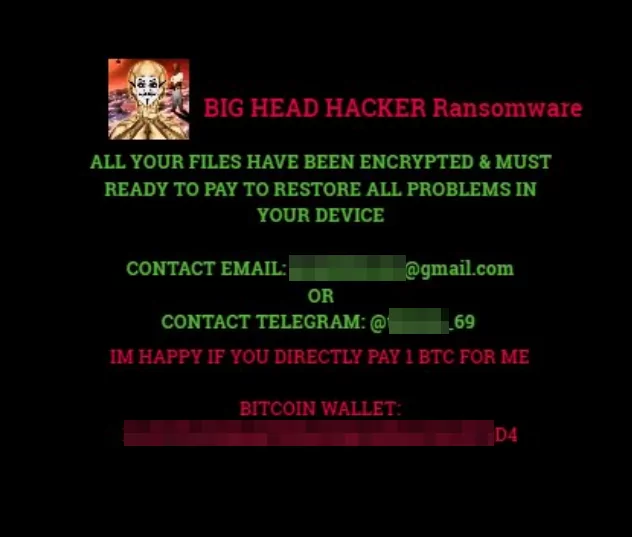
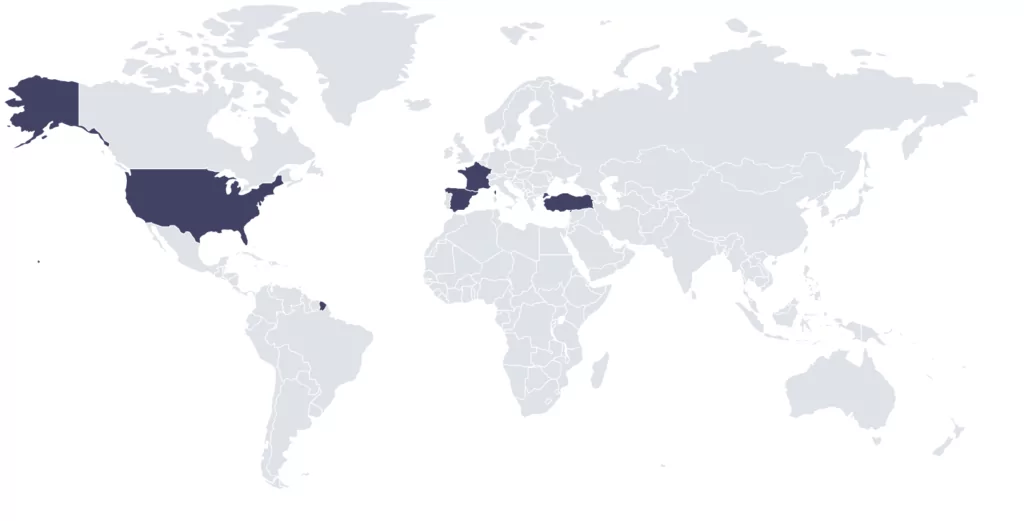
Countries
In terms of geographical distribution, Big Head Ransomware has a global reach. However, most of the samples of this ransomware were submitted from the United States. Other countries where submissions have been made include Spain, France, and Turkey, indicating that Big Head Ransomware has also affected these regions.
Specific Victims
While Big Head Ransomware is not known to target specific individuals or organizations, it exploits general users’ lack of awareness and vigilance. By posing as a fake Windows Update or counterfeit software, it manages to trick users into executing the ransomware, leading to the encryption of their files.
In conclusion, Big Head Ransomware is a global threat that targets consumers across various sectors and countries.
In addition, a question arises: Is it successful?
We checked the Bitcoin wallet written in the ransom note, and only four transactions were made in 2022.
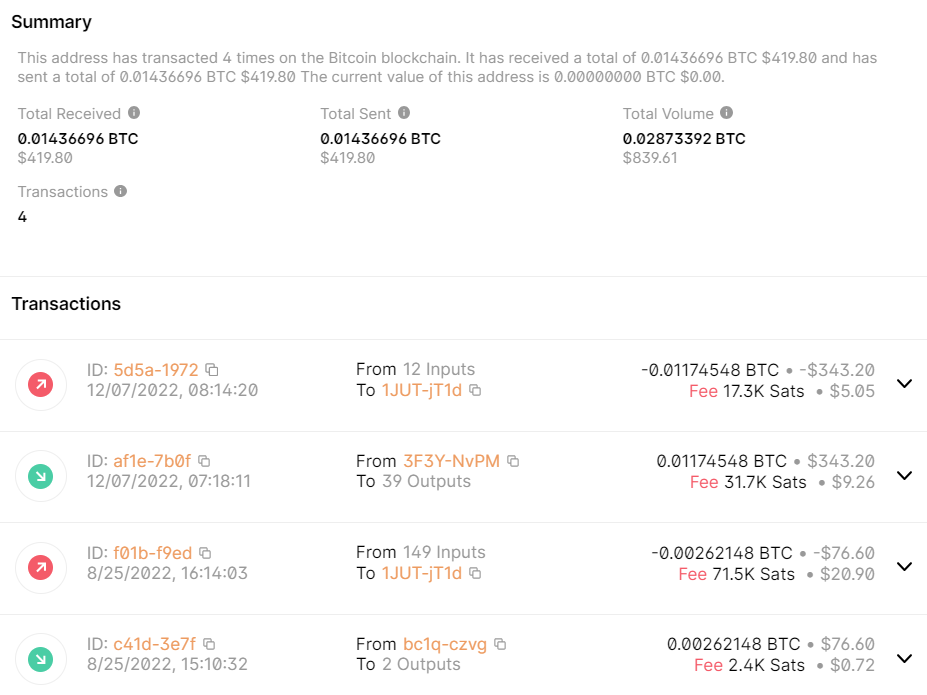
Conclusion
Big Head Ransomware is a sophisticated and evolving threat that targets consumers globally. Its deceptive tactics, such as posing as a fake Windows Update or counterfeit software, make it particularly dangerous. Despite its relatively low ransom fee, the damage it can cause to individuals and their data is significant.
The ransomware is not widespread at the moment. Still, its stealthy operations and the fact that it has already been submitted from various countries, including the United States, Spain, France, and Turkey, indicate that it is a growing threat.
The attacker behind Big Head Ransomware has also been linked to another ransomware variant, further highlighting the need for robust cybersecurity measures. The attacker’s Bitcoin wallet recorded two transactions, but these do not appear to be related to the ransomware variant, suggesting that the attacker may be involved in other illicit activities.
Organizations such as CISA, NCSC, the FBI, and HHS caution ransomware victims against paying a ransom, as payment does not guarantee that files will be recovered. Furthermore, ransom payments may embolden adversaries to target additional organizations, encourage other criminal actors to distribute ransomware, and fund illicit activities.
In conclusion, Big Head Ransomware is a cybersecurity concern that requires comprehensive and proactive measures to mitigate. Its global reach, deceptive tactics, and stealthy operations make it a formidable threat that should not be underestimated.
MITRE ATT&CK TTPs of Big Head Ransomware
|
Technique |
ID |
|
Resource Development |
|
|
Acquire Infrastructure: Malvertising |
T1583.008 |
|
Initial Access |
|
|
Phishing |
T1566 |
|
Execution |
|
|
User Execution |
T1204 |
|
Persistence |
|
|
Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder |
T1547.001 |
|
Privilege Escalation |
|
|
Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder |
T1547.001 |
|
Defense Evasion |
|
|
Obfuscated Files or Information |
T1027 |
|
Software Packing |
T1027.002 |
|
Masquerading |
T1036 |
|
File Deletion |
T1070.004 |
|
Deobfuscate/Decode Files or Information |
T1140 |
|
Virtualization/Sandbox Evasion |
T1497 |
|
Disable or Modify Tools |
T1562.001 |
|
Hidden Window |
T1564.003 |
|
Discovery |
|
|
Query Registry |
T1012 |
|
Remote System Discovery |
T1018 |
|
System Owner/User Discovery |
T1033 |
|
System Information Discovery |
T1082 |
|
File and Directory Discovery |
T1083 |
|
Account Discovery |
T1087 |
|
Virtualization/Sandbox Evasion |
T1497 |
|
Impact |
|
|
Inhibit System Recovery |
T1490 |
|
Data Encrypted for Impact |
T1486 |
Appendix
IoCs of Big Head Ransomware
|
SHA256 |
ff900b9224fde97889d37b81855a976cddf64be50af280e04ce53c587d978840 |
|
SHA256 |
f6a2ec226c84762458d53f5536f0a19e34b2a9b03d574ae78e89098af20bcaa3 |
|
SHA256 |
f59c45b71eb62326d74e83a87f821603bf277465863bfc9c1dcb38a97b0b359d |
|
SHA256 |
f354148b5f0eab5af22e8152438468ae8976db84c65415d3f4a469b35e31710f |
|
SHA256 |
0dbfd3479cfaf0856eb8a75f0ad4fccb5fd6bd17164bcfa6a5a386ed7378958d |
|
|
poop69news@gmail[.]com |
|
IP |
104.86.182[.]43:443 |
|
IP |
118.215.185[.]110:443 |
|
IP |
13.107.21[.]200:80 |
|
IP |
185.199.108[.]154:443 |
|
IP |
185.199.109[.]154:443 |
|
IP |
185.199.110.154:443 |
|
IP |
185.199.111[.]154:443 |
|
IP |
192.168.0[.]1:137 |
|
IP |
192.229.211[.]108:80 |
|
IP |
192.30.255[.]113:443 |
|
IP |
20.99.133[.]109:443 |
|
IP |
20.99.184[.]37:443 |
|
IP |
204.79.197[.]200:443 |
|
IP |
204.79.197[.]200:80 |
|
IP |
23.193.135[.]106:443 |
|
IP |
23.216.147[.]64:443 |
|
IP |
23.216.147[.]76:443 |
|
IP |
23.41.86[.]106:443 |
|
IP |
23.62.81[.]152:443 |
|
IP |
23.78.114[.]164:443 |
|
IP |
31.223.14[.]18 |
|
IP |
a83f[:]8110:0:0:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:53 |
|
IP |
a83f[:]8110:4747:47ff:4747:47ff:4747:47ff:53 |
|
IP |
a83f[:]8110:cce1:d301:10:0:0:0:53 |
For more IoCs, you can visit the Threat Actor/Malware page under the CTI module of SOCRadar XTI Platform.




































