DarkGate Malware: Exploring Threats and Countermeasures
As we get increasingly digitized, the threat posed by malware has reached unprecedented levels in parallel. From individual users to large corporations, no entity is immune to the detrimental effects of malicious software. Among the vast array of threats lurking in the depths of the internet, DarkGate emerges as a particularly formidable adversary.
Initially surfacing around 2017, DarkGate has since undergone a metamorphosis, evolving into a sophisticated malware toolkit with a broad spectrum of capabilities. From its humble beginnings, DarkGate has matured into a versatile weapon capable of executing remote code, evading detection mechanisms, and efficiently stealing sensitive data.
Especially after law enforcement agencies seized the QakBot infrastructure, DarkGate became a more prominent threat as of 2024, quickly replacing QakBot in new malware campaigns. Most recently in January 2024, phishing campaigns have exploited Microsoft Teams group chat invitations to disseminate malicious attachments, facilitating the installation of DarkGate malware payloads on targeted systems.
DarkGate Emergence
Allegedly in development in 2017, DarkGate began its journey as a relatively obscure entity, but its ascent to prominence has been relatively swift. Initially, DarkGate lurked in the shadows, quietly spreading its tendrils through various digital channels. However, as its capabilities expanded and its tactics grew more sophisticated, DarkGate emerged from the shadows, asserting itself as a potent force in cybercrime.
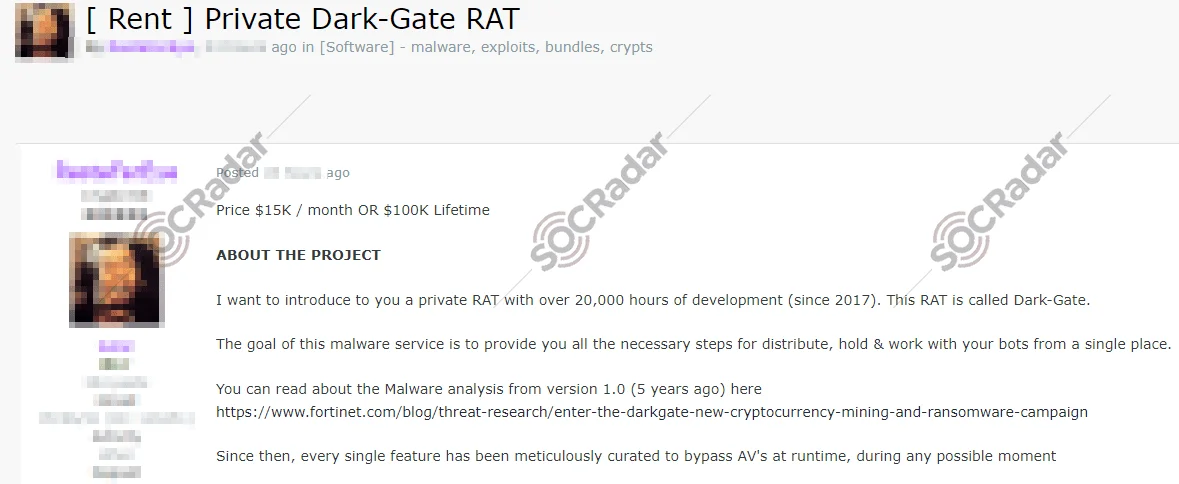
Sale of DarkGate on Russian eCrime forums
Developed by the underground user RastaFarEye, DarkGate is offered through a subscription-based model, with prices reaching up to $15,000 per month. While it surfaced in 2018, gaining traction in 2021 under the alias MehCrypter, DarkGate’s popularity surged with the release of updated versions incorporating advanced techniques like AutoIt scripting and remote access tools.
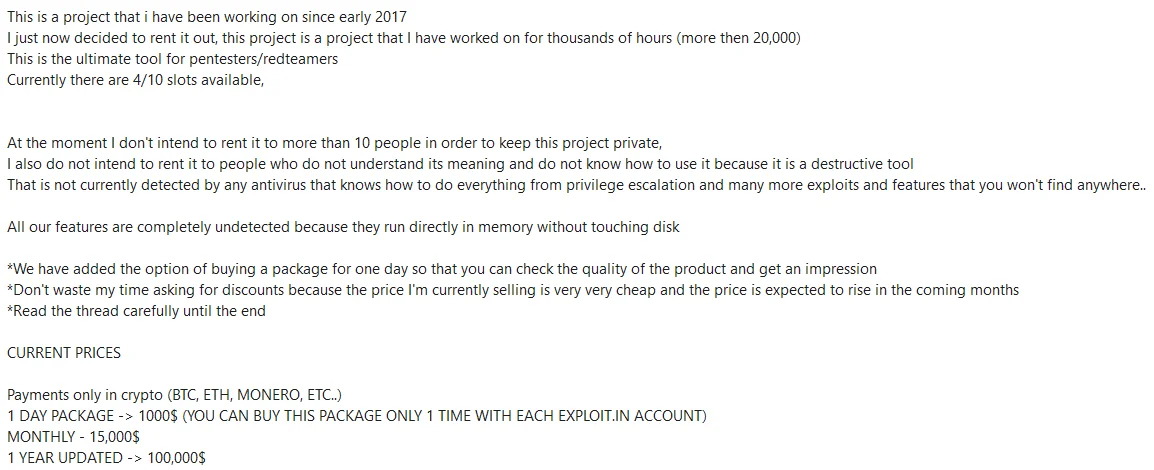
Threat actor’s statements and prices
In June 2023, RastaFarEye introduced DarkGate v4, boasting new features such as hVNC, file manager, Discord and Browser stealer, keylogger, and a rootkit module. This version promised evasion of security products and offered a command and control panel for convenient control by buyers. As security firms began uncovering campaigns using DarkGate v4 in August 2023, RastaFarEye responded by releasing updates to evade detection.

Alleged main features of DarkGate
Continuing to refine the malware, RastaFarEye announced the development of DarkGate version 5 in September 2023, scheduled for release in October. Meanwhile, DarkGate has been documented on forums since May 2023, with an observed increase in initial entry attacks. The malware’s capabilities include executing discovery commands, self-management, remote access, cryptocurrency mining, keylogging, browser data theft, and privilege escalation.
At its inception, DarkGate may have been just one among many malware variants circulating the internet. Still, its developer’s pursuit of innovation and adaptability to changing circumstances set it apart. DarkGate was not content with remaining static; it constantly evolved, incorporating new features and techniques to stay ahead of detection mechanisms and security protocols.
A possible rebranding in the near future
A twisting point is DarkGate’s developer has recently been banned from forums such as Exploit and XSS, it may be looking for new avenues, and perhaps DarkGate may undergo an identity change ahead of us.
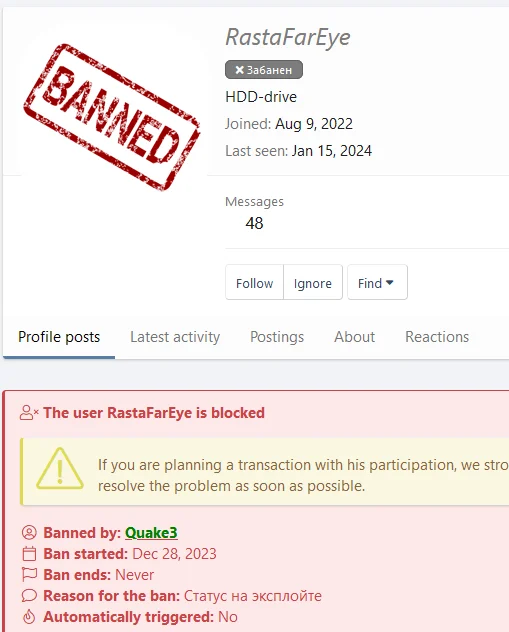
Developer’s banned account in XSS.in forum
One of its last activities before it was banned was to promote a crypto miner it was working on.
Crypto Miner ads of the Threat Actor
Attack Overview of DarkGate
DarkGate, a sophisticated malware toolkit, utilizes various distribution mechanisms to infiltrate victim systems, including phishing emails, malvertising, and malicious attachments in collaboration tools like Microsoft Teams. Phishing campaigns often employ malicious VBScript or MSI files disguised as legitimate documents to initiate the infection chain.
Once triggered, DarkGate executes a series of steps to establish control over the victim’s system, typically involving downloading and executing additional payloads from remote servers using techniques like DLL side-loading or obfuscated PowerShell commands. The malware employs sophisticated evasion techniques to avoid detection by security solutions, such as obfuscating malicious code within AutoIT scripts and shellcode encryption.
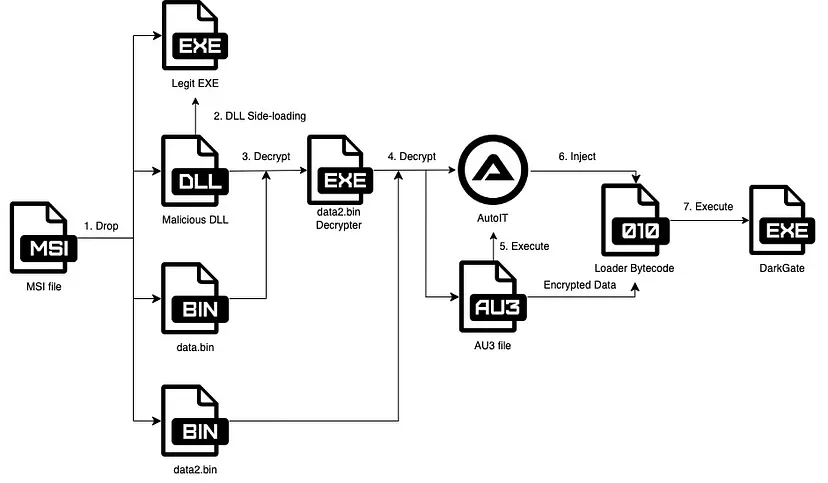
Infection chain of DarkGate Malware (Source)
DarkGate communicates with its Command-and-Control (C2) server using HTTP POST requests, often employing custom Base64 encoding to obfuscate data. The malware encompasses a wide range of malicious functionalities, including keylogging, credential theft, remote code execution, privilege escalation, and cryptocurrency mining.
To maintain control over infected systems, DarkGate employs various persistence mechanisms, such as creating malicious registry keys or injecting code into legitimate processes. Additionally, DarkGate is capable of detecting installed antivirus software and taking action accordingly to avoid detection or removal.
The malware supports a multitude of commands sent by the C2 server, enabling actions such as keylogging, collecting information, managing files, stealing credentials, removing data/backups, privilege escalation, cryptocurrency mining, inspecting network activity, controlling the Graphical User Interface (GUI), establishing reverse shells, managing processes, and configuring DarkGate settings.
The characteristics of DarkGate underscore its potency as a cyber threat, posing severe risks to data confidentiality, operational integrity, financial stability, and regulatory compliance for affected individuals and organizations. Mitigating these risks requires robust cybersecurity measures, including user awareness training, endpoint protection, network monitoring, and threat intelligence capabilities. By understanding DarkGate’s tactics, techniques, and procedures, individuals and organizations can better defend against this pervasive malware threat and safeguard their digital assets.
Recent Microsoft Teams Campaign
According to ATT’s blog on January 30, 2024, phishing attacks leveraging Microsoft Teams group chats were being used as a vector to distribute. In these attacks, malicious attachments disguised as legitimate files are sent to victims through over 1,000 compromised Teams group chat invites. Once users accept the chat request and download the attachment, named ‘Navigating Future Changes October 2023.pdf.msi,’ the DarkGate malware is installed on their systems. This malware then connects to its command-and-control server at hgfdytrywq[.]com, a known part of DarkGate’s infrastructure confirmed by Palo Alto Networks.
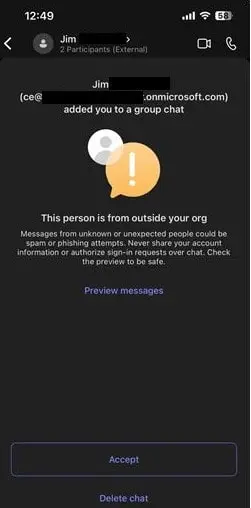
Phishing message received by a user (ATT)
This attack exploited Microsoft Teams’ default setting, allowing external users to message users in other tenants. Similar tactics were observed in previous campaigns where DarkGate malware was distributed via compromised outer Office 365 and Skype accounts. The surge in DarkGate attacks followed the disruption of the Qakbot botnet in August, leading cybercriminals to pivot towards DarkGate as their preferred method of gaining initial access to corporate networks. This surge is further fueled by the developer’s attempts to sell DarkGate subscriptions, offering a range of capabilities, including tools to bypass Windows.
Impact of DarkGate Malware
DarkGate’s extensive array of malicious functionalities, such as keylogging, credential theft, and data exfiltration, poses a significant threat to the security of sensitive information. The malware’s infiltration capabilities can result in severe privacy breaches and financial losses for individuals and organizations.
Moreover, DarkGate’s ability to execute remote code, escalate privileges, and install cryptocurrency mining software can disrupt normal business operations, leading to performance degradation and operational disruptions. The financial impact of DarkGate extends to expenses related to remediation efforts, regulatory penalties, and legal liabilities. Additionally, DarkGate infections can damage an organization’s reputation, erode customer trust, and trigger regulatory compliance obligations.
Therefore, the evolving threat landscape underscores the importance of robust cybersecurity measures, including comprehensive security frameworks, threat intelligence capabilities, and employee training initiatives. In conclusion, understanding the implications of DarkGate and implementing proactive cybersecurity measures are essential for mitigating risks and safeguarding digital assets against future threats.
Mitigation Measures
In response to the escalating threat posed by DarkGate malware, organizations must adopt comprehensive countermeasures and mitigation strategies to effectively mitigate risks and safeguard their digital assets. Implementing a multi-layered defense approach and proactive security measures is crucial for detecting, preventing, and responding to DarkGate and similar advanced malware threats. Here are key countermeasures and mitigation strategies:
Endpoint Protection Solutions: Deploy robust endpoint protection solutions such as antivirus software, Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) tools, and advanced threat detection technologies. These solutions help detect and block malicious activities, including DarkGate infections, at the endpoint level.
Network Security Controls: Strengthen network security controls by implementing firewalls, Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS), and network segmentation. These measures help prevent unauthorized access to network resources and mitigate the spread of DarkGate malware within the network.
Email Security Gateways: Enhance email security defenses with advanced email security gateways, spam filters, and email authentication mechanisms. These solutions help detect and block phishing attempts and malicious email attachments commonly used to distribute DarkGate malware.
Web Filtering and Content Security: Implement web filtering and content security solutions to block access to malicious websites hosting DarkGate payloads and Command-and-Control (C2) servers. Proactive monitoring of web traffic helps identify and mitigate potential threats in real-time.
User Awareness Training: Provide comprehensive cybersecurity awareness training to employees to educate them about the risks associated with phishing attacks, malicious attachments, and social engineering tactics used by DarkGate attackers. Empowering users to recognize and report suspicious activities can help prevent successful DarkGate infections.
Patch Management: Maintain up-to-date software and security patches on all systems and applications to address known vulnerabilities exploited by DarkGate and other malware variants. Regular patching helps reduce the attack surface and minimizes the risk of exploitation.
Behavioral Analysis and Threat Intelligence: Leverage behavioral analysis techniques and threat intelligence feeds to identify and analyze anomalous behavior and Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) associated with DarkGate malware. Proactive threat hunting and intelligence-driven defense strategies enhance detection and response capabilities.
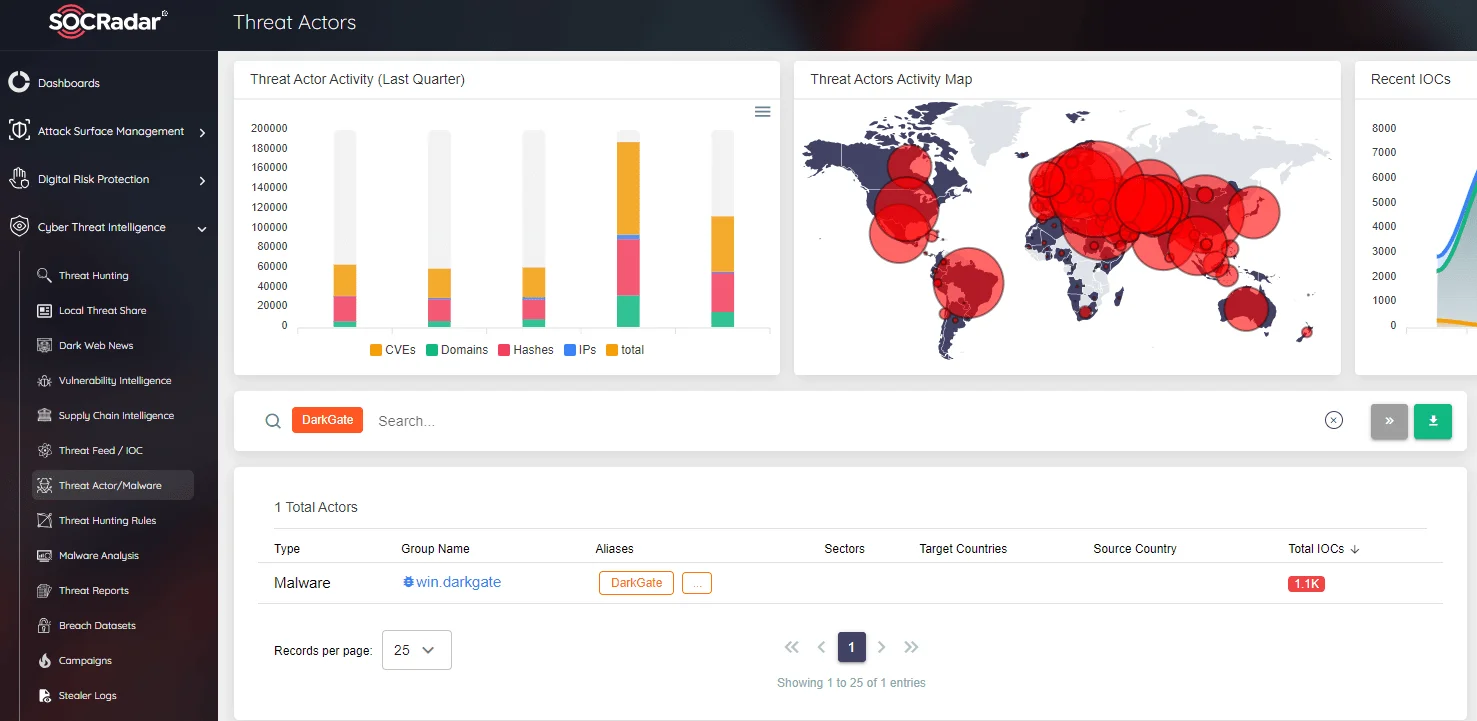
SOCRadar Threat Actors/Malware page includes more than 1,000 IoCs of DarkGate
Incident Response Planning: Develop and implement comprehensive incident response plans and procedures to effectively respond to DarkGate infections and cybersecurity incidents. Establish clear roles, responsibilities, and communication channels to facilitate prompt incident detection, containment, and remediation.
Data Backup and Recovery: Implement regular data backup and recovery procedures to ensure the availability and integrity of critical data in the event of a DarkGate infection or ransomware attack. Maintain offline backups and test restoration processes regularly to mitigate the impact of data loss.
Continuous Monitoring and Threat Hunting: Implement continuous monitoring and threat hunting capabilities to proactively identify and mitigate emerging threats, including DarkGate malware. Real-time monitoring of network and endpoint activity enables early detection and response to potential security incidents.

SOCRadar Platform could help you with Threat Hunting endeavors
Conclusion
In conclusion, the continuing campaigns of DarkGate malware represent a significant challenge for individuals, businesses, and organizations operating in today’s interconnected digital environment. With its evolving capabilities and sophisticated deployment methods, DarkGate poses a formidable threat to data integrity, confidentiality, and system security. However, by understanding the technical intricacies of DarkGate and implementing comprehensive countermeasures and mitigation strategies, organizations can effectively mitigate the risks associated with this pervasive malware.