Fortinet Rolls Out Patches for Critical RCE Vulnerability in SSL VPN Devices (CVE-2023-27997)
[Update] July 04, 2023: Recent findings reveal that despite a recent update from Fortinet, hundreds of thousands of FortiGate firewalls remain vulnerable to CVE-2023-27997, with over 300,000 devices exposed and reachable via the internet. Added the subheading: “FortiGate Firewalls Still Vulnerable: Over 300,000 at Risk.”
[Update] June 13, 2023: Cybersecurity researchers examined the differences in the software’s assembly code between the vulnerable and fixed versions. Added the subheading: “Fortinet’s Bug Fix Under the Microscope: What Does the Analysis Reveal About CVE-2023-27997.”
The vulnerability CVE-2023-27997, announced by security researchers over the weekend and immediately patched by the manufacturer, was enough to keep system administrators up at night. Although the manufacturer and researchers have not yet shared the details, breaths are being held for June 13, when the specifics will be disclosed. As SOCRadar, we have compiled what you need to know about the CVE-2023-27997 vulnerability and the necessary steps to secure your systems. You can follow the updates on this blog post.
What Is the Critical Vulnerability in Fortigate Firmware? Who Discovered the Vulnerability?
Fortinet has recently issued Fortigate firmware updates to fix an undisclosed, critical vulnerability in SSL VPN products. The vulnerability poses a significant risk of pre-authentication remote code execution(RCE) attacks.
The release notes by Fortinet did not explicitly mention the vulnerability; however, security professionals and administrators have suggested that the recent updates silently addressed it.
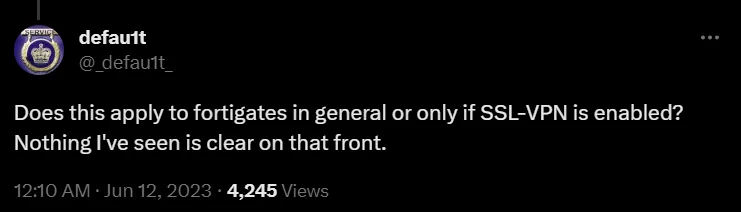
The remote code execution vulnerability, according to French cybersecurity firm Olympe Cyberdefense, could allow a threat actor to interfere with the VPN even if multi-factor authentication (MFA) is enabled. The firm has also mentioned that all versions are likely affected, pending confirmation with the release of CVE, which is scheduled for June 13, 2023. Fortinet has a history of releasing patches ahead of vulnerability disclosure to allow customers to update their devices before threat actors can attempt to exploit them.
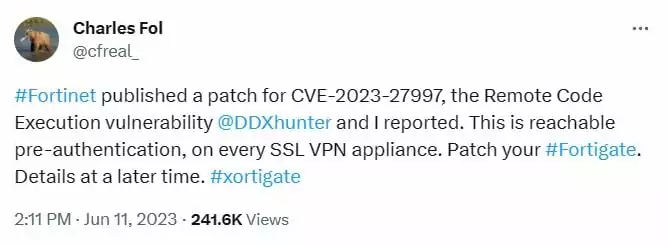
Vulnerability researchers from Lexfo Security, Charles Fol and Rioru, were who initially reported the critical remote code execution vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2023-27997. Fol took to Twitter to share that the patch addressed the CVE-2023-27997 vulnerability, describing it as a reachable pre-authentication vulnerability that affects every SSL VPN appliance.
Which Firmware Versions Were the Security Fixes Released In?
Fortinet has released the security fixes in the following FortiOS firmware versions:
- 6.0.17
- 6.2.15
- 6.4.13
- 7.0.12
- 7.2.5
Why Are Fortinet Devices Attractive Targets for Attacks?
Fortinet devices are attractive targets for attacks because they are among the most popular firewall and VPN devices in the market.
In recent years, Fortinet vulnerabilities have garnered increased attention from attackers. An analysis is available on our blog, but here is a summary of notable threats that have emerged across Fortinet products:
One critical vulnerability, CVE-2022-42475, affected FortiOS and allowed the remote execution of arbitrary code. Exploited since October 2022 by alleged Chinese threat actors using the BoldMove malware, this heap-based buffer overflow vulnerability had a CVSS score of 9.3.
Another significant vulnerability, CVE-2022-40684, an authentication bypass, enabled threat actors to exploit various Fortinet products through specific HTTP and HTTPS requests. Exploit techniques and tools for this vulnerability were sold on dark web forums.
The third critical vulnerability, CVE-2022-39952, allowed attackers to gain root authority and establish a backdoor, attracting attention from threat actors after its disclosure. Additionally, the SOCRadar Platform recorded SSL-VPN access credentials through Fortinet products as a prominent initial access method in 2022, contributing to the growth of the initial access market by almost 50% from 2021 to 2022.
Threat actors have historically exploited SSL-VPN flaws just days after patches are released. These vulnerabilities are commonly used to gain initial access to networks and carry out activities such as data theft and ransomware attacks.
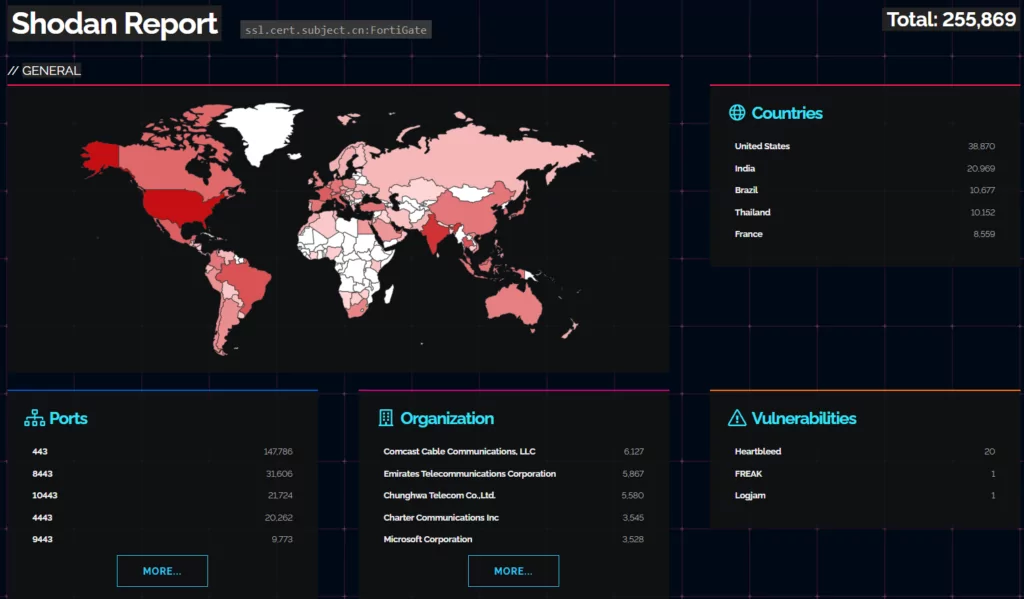
What Is the Scope of the Vulnerability? How Many Fortigate Firewalls Can Be Reached From the Internet?
According to a Shodan search, over 255,000 Fortigate firewalls can be reached from the Internet, and since the vulnerability affects all previous versions, the majority of these devices are likely exposed.
Fortinet’s Bug Fix Under the Microscope: What Does the Analysis Reveal About CVE-2023-27997?
After Fortinet released fixes for vulnerable devices, watchTowr took the initiative to examine the bug by performing a “patch diff.” This involved analyzing the vulnerable and patched versions of the software at the assembly level to identify specific details of the fix.
According to researchers, exploiting the heap overflow bug is challenging and requires expertise or access to a public exploit. Although widespread exploitation of the vulnerability is unlikely, it is important to note that unskilled attackers can still cause the targeted device to crash and reboot.
They focused on changes related to SSL VPN functionality. They discovered the addition of movzx instructions, indicating potential variable datatype mismatches:

The code snippet checks the encData parameter, ensuring its length is longer than 11 bytes and has an even length. It then processes the encData value by XORing it with the result of MD5‘ing a salt value combined with the first 8 bytes of the input string.
The code decodes the processed and extracts a payload length. However, there is a flaw in how it extracts it, as it only considers the bottom 8 bits, leading to truncation. The code compares the extracted payload length with the adjusted length of encData value minus 5 (to account for some header bytes). An error message is displayed if the extracted payload length exceeds this adjusted length.
Exploiting this vulnerability involves crafting a specially designed encData value where the truncated payload length appears valid, allowing the code to proceed. The code then performs XOR operations between the decoded data and an expanded salt array, with the array being updated using MD5 hashing every 16 bytes.
However, the code may access the expanded salt array out-of-bounds due to the incorrect payload length, resulting in undefined behavior such as crashes or data corruption.
In summary, the issue arises from the truncation of the payload length to 8 bits and the subsequent inadequate length check. This allows an attacker to construct an encData value with a payload length that exceeds the adjusted length check, leading to potential out-of-bounds access and unexpected behavior.
Are There Any Reports of Exploitation?
Concerning whether CVE-2023-27997 was exploited, Fortinet stated that they want to protect and secure their customers’ organizations by ensuring timely and ongoing communications and directed customers to the company’s Product Security Incident Response Team (PSIRT) page to learn more about their disclosure process.
Fortinet admins should urgently apply the patch because the CVE-2023-27997 vulnerability is likely to be quickly analyzed and discovered by threat actors, posing a potential risk to their systems.
How to Patch a Vulnerable Fortinet Fortigate Product?
Visit the Fortinet Support site frequently and apply newly released patches to keep your Fortigate VPN secure. To update your device:
- Check the firmware version: Check the “System Information” section of your device’s dashboard to see the current firmware version.
- Find the latest firmware: Go to the “Download” section after logging into the support site. In the product list, look for Fortigate VPN and select your Fortigate model. To view all available updates, click the “Firmware Images.” Look for and download the patch addressing CVE-2023-27997.
- Apply the patch: On the Fortinet Fortigate VPN dashboard, navigate to System > Firmware > Update > Upload File, then select the downloaded patch file. After the update, make sure to test your VPN. Check that all functions are operational and the device is stable.
FortiGate Firewalls Still Vulnerable: Over 300,000 at Risk
Hundreds of thousands of FortiGate firewalls are still vulnerable to a critical security issue known as CVE-2023-27997, despite a recent update from Fortinet.
Offensive security company Bishop Fox discovered over 300,000 vulnerable devices that can be accessed through the internet. They used the Shodan search engine to identify devices with exposed SSL VPN interfaces.
Out of the 489,337 devices found, 153,414 had been updated to a safe version. This means that around 335,900 FortiGate firewalls are still at risk, a higher number than previously estimated.
Bishop Fox also found that some devices had not received updates for eight years and are exposed to other critical vulnerabilities. To demonstrate the severity of CVE-2023-27997, Bishop Fox created an exploit that allows remote code execution on vulnerable devices.
How Can SOCRadar Help?
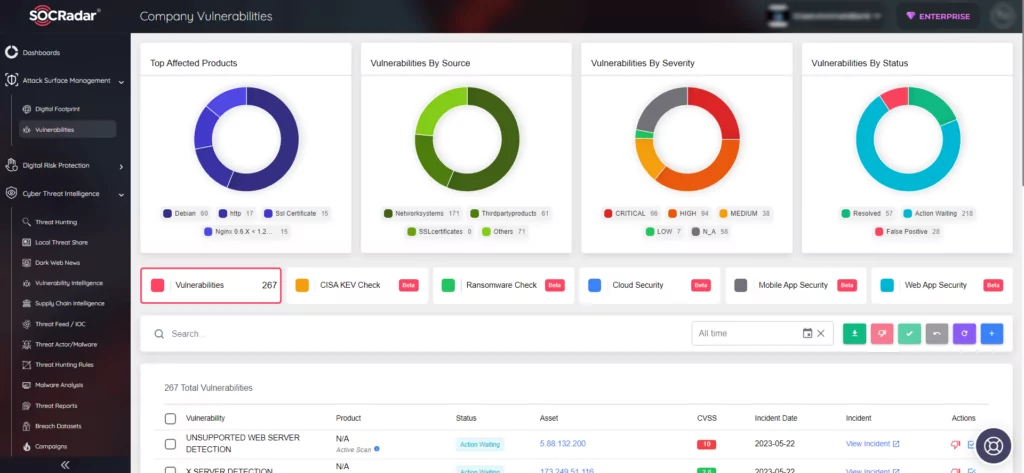
SOCRadar helps organizations for staying up-to-date on the latest security threats and vulnerabilities. It gathers information on all known vulnerabilities and presents it in a way that is easy to act upon, using alerts to help you prioritize your actions and stay informed about any potential threats to your organization.
You can utilize SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence module to access detailed information on vulnerabilities, allowing you to effectively manage any related issues and prioritize the necessary patches.

Additionally, with SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management, you have the capability to monitor vulnerabilities in automatically identified products within your organization’s digital footprint in real time. This empowers security teams to take a proactive approach toward prioritizing vulnerabilities by accessing contextual intelligence.