
How Easy Is It to Guess Fortune 500 Executives’ Passwords?
Recently, many cyberattacks on large corporations have begun with acquiring credentials via multiple methods, particularly social engineering and stealer malware. Obtaining the passwords of a senior executive rather than an ordinary employee is the cherry on the cake for attackers.
Attacks targeting C-suite executives need more effort and planning. Meanwhile, it provides access to sensitive data if successful. When a senior executive is targeted, they may not be the only victim. Threat actors can harm companies, and data leaks that affect employees or consumers can occur due to executives’ high-level access privileges.
It is possible to gain unauthorized access to administrator accounts, access internal databases, steal confidential data, and carry out social engineering attacks using compromised passwords. Threat actors could use the acquired administrator passwords for CEO fraud, a business email compromise (BEC) scam. Cybercriminals can impersonate managers and launch attacks against supply chain partners or employees.
SOCRadar researchers conducted a study on a sample group of C-level executives from the top 50 companies on the Fortune 500 list to analyze the cybersecurity awareness of executives. SOCRadar analysts researched public data breaches and discovered passwords belonging to the executives of the first Fortune 500 firms among the exposed credentials.
Top Leaked Passwords Belong to CEOs and VPs
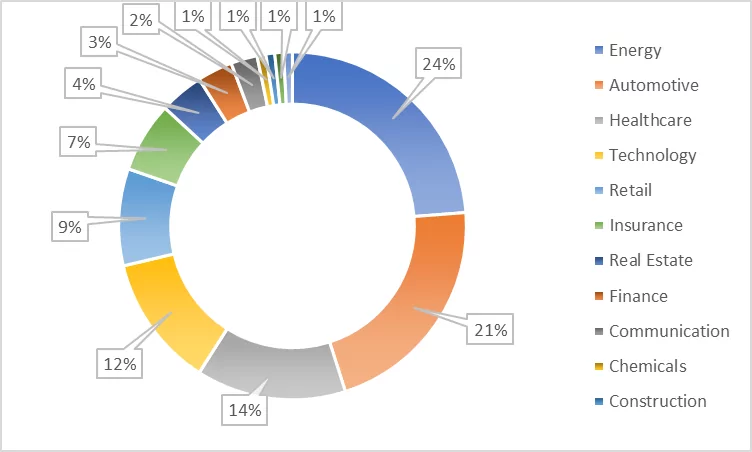
The three industries that have the highest exposure are energy (24%), automotive (21%), and healthcare (14%). The fact that two of the three most exposed industries (energy and healthcare) are critical infrastructure industries highlights the importance of breaches.
The analysis showed that the top three titles of the leaked password owners are; 24% Chief Executive Officer (CEO), 19% Vice President (VP), and 11% Chief Financial Officer (CFO).
The identified passwords were evaluated according to the following criteria determined by the National Institute for Standards and Technology (NIST) 800-53:
- A strong password should be a minimum length of eight characters for user-generated passwords and six characters for those created by a generator (maximum length of at least 64 characters).
- It may include special characters, even emojis and spaces. It should restrict sequential (ex: 1234) or repeating (ex: aaaa) characters and dictionary words.
- Users should avoid choosing context-specific passwords (ex: such as the name of the service) and commonly used passwords.
As a result of the evaluation, the below outputs are obtained:
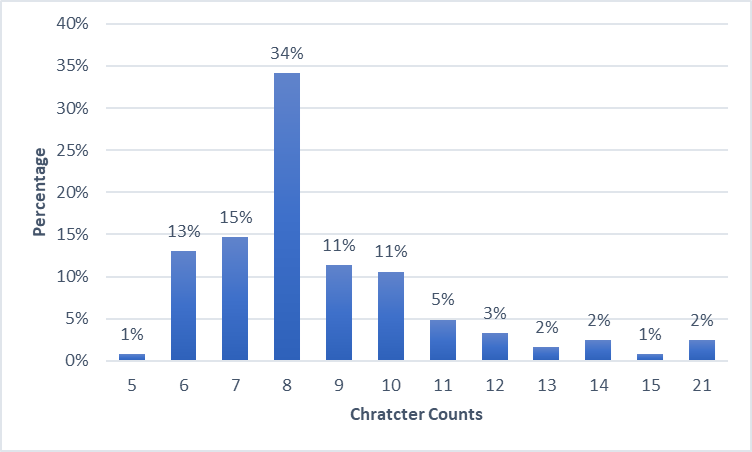
- The lengths of the passwords obtained range from 5 to 21 characters. The most often used password length is 8 characters (34%). The main reason for this output can be policies forcing users to create passwords of at least 8 characters.
Passwords that contain only one type of character are 31.45% (loweralpha: 20.16%; numeric: 9.68%; upper alpha1.61%). Passwords that contain all types of characters (lower alpha, upper alpha, numeric, special characters) are just 2.42%. All the character sets are as follows:
- Loweralphanumeric: 46.77%
- loweralpha: 20.16%
- loweralphaspecial: 10.48%
- numeric: 9.68%
- mixedalphanumeric: 7.26%
- mixedalphaspecialnumeric: 2.42%
- upperalpha: 1.61%
- mixedalpha: 0.81%
- loweralphaspecialnumeric: 0.81%
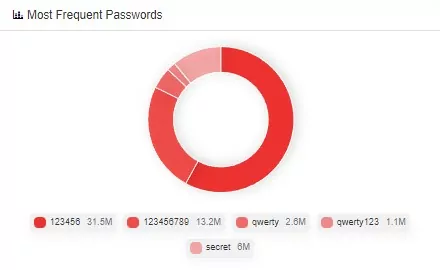
Among these passwords, there are numerous meaningful strings just as names, names of cities, animals, and heroes. Inevitably, two of the most often used passwords of all time, ‘password‘ and ‘1234567890‘, are also on the list. Usage of ‘1234567890‘ as a password is a common habit for all users. In SOCRadar XTI Platform Breach Database, 123456 and 123456789 are at the top of the most frequent passwords list.
35% of the passwords contain a meaningful dictionary word. Dictionary attacks can reveal such passwords.
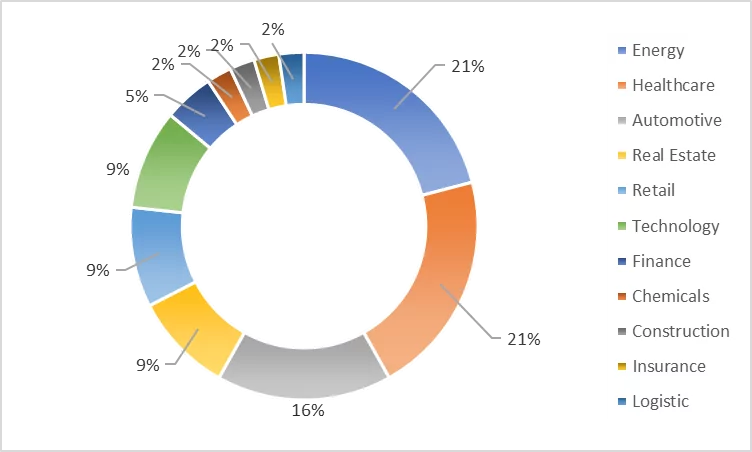
- The industrial distribution of usage of meaningful strings in the password shows that energy (21%), healthcare (21%), and automotive (16%) are on the top of the list.
- 11% of the passwords contain company-related strings. The industries that most commonly use company-related strings in passwords are automation, technology, and energy. Furthermore, the two titles most frequently use the business name as passwords are CEO and VP.
- 11% of the passwords contain the owner’s name. Account holders, mostly in the energy and automobile industries, prefer strings related to their name/surname in their passwords. Individuals with the titles of CEO and CFO generally prefer these credentials.
More Cybersecurity Awareness Needed
While the length of the passwords is fair, passwords consisting of predictable personal information and a few character groups are in the majority. As a result, many passwords can be classified as weak under the NIST criteria. This analysis reveals that sample C-level executives have similar cybersecurity awareness and knowledge levels compared to ordinary internet users.
Under these circumstances, organizations responsible for ensuring the cybersecurity of themselves, their workers, and their customers should utilize additional solutions to keep senior executives out of cyber attackers’ scope and protect sensitive data.
Prevent Attacks Targeting Your C-levels
Organizations should implement a system for proactively monitoring the dark web so that they can be notified immediately when administrative credentials are leaked to underground platforms. Rapid detection and investigation of the leak will allow organizations to handle the situation quickly and help protect the organization’s and executives’ security and reputation.
SOCRadar Extended Threat Intelligence platform offers a VIP Protection solution for companies.
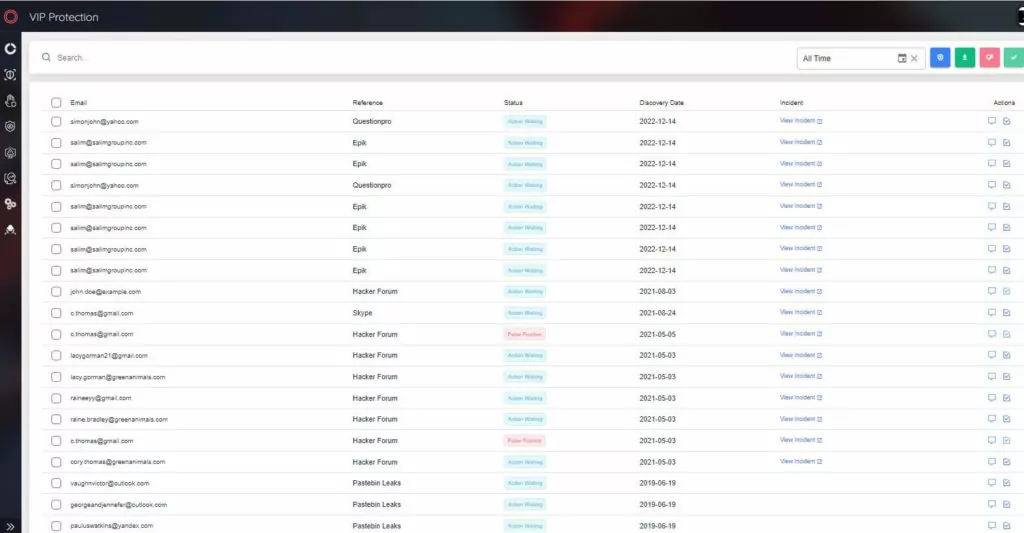
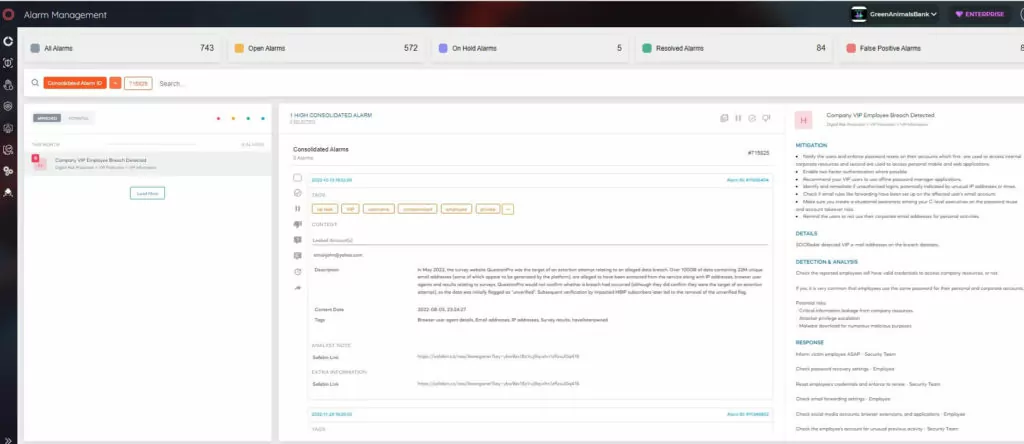
SOCRadar identifies threats for the key C-level executives with the VIP Protection solution. SOCRadar allows security teams to search and monitor critically important personal email addresses of C-suite people, whether it is indexed somewhere in the growing database of major worldwide breaches. With VIP Protection solution;
- Prevent CEO fraud by detecting compromised credentials, which threat actors can use for impersonation.
- Monitor PII (personally identifiable information) & credit card details of C-level people for any unwanted breach or underground trading on the dark web.
- Taking advantage of SOCRadar’s HUMINT services, where experienced analysts will handle risky situations which may have a significant impact on the brand reputation or result in financial loss, is possible.



































