
How to Use SOCMINT for Better Cause?
With the increasing use of social media by private and public practitioners, advanced methods of collecting and analyzing social media data, known as Social Media Intelligence (SOCMINT) have become an important means of gathering information. Social Media Intelligence (SMI) and SOCMINT make it possible to use information collection on social media sites by both intrusive and non-intrusive means, both in open and closed social networks. Although they do not directly use social media, social media users are integrated into the community and share information about criminal activity that can be captured, analyzed and transformed into actionable intelligence.
SOCMINT is the process of collecting and analyzing collected data from different social media sites and channels in order to understand users, determine influencers, monitor online conversations, gauge customer sentiment and predict consumer behavior. It includes monitoring content such as news, images, posts and other data generated through social networks and websites. Beyond listening, SOCMINT has a variety of tools at its disposal on social media platforms and channels, each of which has unique functions that can be used in the intelligence and analysis process.
Social Media Intelligence (SOCMINT) refers to a technology and technique that allows companies and governments to monitor social media networks such as Facebook and Twitter. Content such as messages, posted images and other data generated when someone uses a social media networking site affects person-to-person, group-to-group and group-to-group interactions, including private and public interactions. OSINT experts consider that information shared on social media sites to be part of the OSINT domain because it is public, shared on an online public platform and can be used for intelligence purposes.
SOCMINT is the process of identifying, gathering, validating and analyzing data from social media sites and accounts using non-intrusive and intrusive methods to develop intelligence and reduce unknowns in the decision-making process. Social Media Intelligence (SMI) and SOCMINT refer to collective tools and solutions that enable companies to analyse conversations, respond to social signals, synthesize social data points into meaningful trends and perform analyses based on user needs.
The randomness of people’s social profiles has increased the possibility of information leakage and made social networks a new communication point for fraudsters to carry out scams. Social networks allow their users to enforce their privacy policies to prevent others from seeing posts and content that few people care about, such as topics, activities, text messages, check-ins and public status messages posted by many of them.
Social media intelligence plays a major role in feeding data into algorithms that are used to make important decisions about people’s lives, including decisions such as a person’s access to credit, jobs, and renting an apartment. Information about certain users is available to the public through pictures and videos posted, and law enforcement authorities can obtain this information if allowed, which is the essence of the OSINT collection concept. For example, a single image posted on a social network may contain geolocation metadata and camera serial numbers.
According to a procurement request to obtain a tool that will allow agencies to search social media platforms for evidence of tax evasion, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) plans to use the tool for activities such as identifying cases of tax returns and thefts. Obtain the consent of potential tenants or employees before they feel forced to give up what they want – an apartment, job or startup – to collect information from their social media profiles to make an assessment of the person’s reliability.
Classifications of Social Media Platforms[1]
Many people use the terms social media and social networking interchangeably to refer to Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, and related social platforms. This is not absolutely wrong, but it is not accurate because social media is the main umbrella that contains other categories like “social networking” that holds sites like Facebook.
The following are the main social media types classified according to function:
- Social networking: This allows people to connect with other people and businesses (brands) online to share information and ideas. Examples include Facebook and LinkedIn.
- Photo sharing: Such websites are dedicated to sharing photos between users online. Examples include: Instagram & Flicker.
- Video sharing: Such websites are dedicated to sharing videos, including live video broadcasts. The most popular one is YouTube. Please note that Facebook and Twitter also offer live video broadcast service.
- Blogs: This is a type of informational website containing a set of posts—belonging to one topic or subject—organized in descending order according to the publish date. The most popular blogging platforms are WordPress and Blogger, which is powered by Google.
- Microblog: This allows users to publish a short text paragraph (which can be associated with an image or video) or a link (URL) to be shared with other audiences online. Twitter is the most popular example.
- Forums (message board): This is one of the oldest types of social media. Users exchange ideas and discussions in the form of posted messages and replies. Reddit is an example.
- Social gaming: This refers to playing games online with other players in different locations. It has gained more popularity recently. KAMAGAMES and Zynga are examples of this type.
- Social bookmarking: These websites offer a similar function to your web browser’s typical bookmark. However, they allow you to do this online and share your Internet bookmarks among your friends in addition to adding annotations and tags to your saved bookmarks. Example include: Atavi and Pinterest
- Product/service review: These websites allow their users to review—give feedback—about any product or service they have used. Yelp and Angie’s Listare examples of this type.
The two most popular social media sites are: Facebook and Twitter.
Online Facebook Search Tools/Services
There are many online services that simplify the process of acquiring/analyzing information from Facebook accounts. The following are the most useful ones:
- Lookup ID (https://lookup-id.com): This site helps you to find Facebook personal IDs. This ID is necessary when using any of the previous online services –mentioned previously- used to compliment Facebook standard keyword search.
- Facebook Page Barometer (http://barometer.agorapulse.com): This site gives statistics and insight about specific Facebook profiles or pages.
- Information for Law Enforcement Authorities (https://www.facebook.com/safety/groups/law/guidelines): Offers information and legal guidelines for law enforcement/authorities when seeking information from Facebook and Instagram.
- A directory of free tools and online services for searching within Facebook can be found at: https://osint.link/osint-part2/#facebook
Twitter Advanced Search Operators
Similar to Google, Twitter allows you to use specialized operators to find related tweets more precisely. Twitter search operators are already available in the Twitter developer site, go to https://developer.twitter.com/en/docs/tweets/rules-and-filtering/overview/standard-operators to view them (see Figure 4).
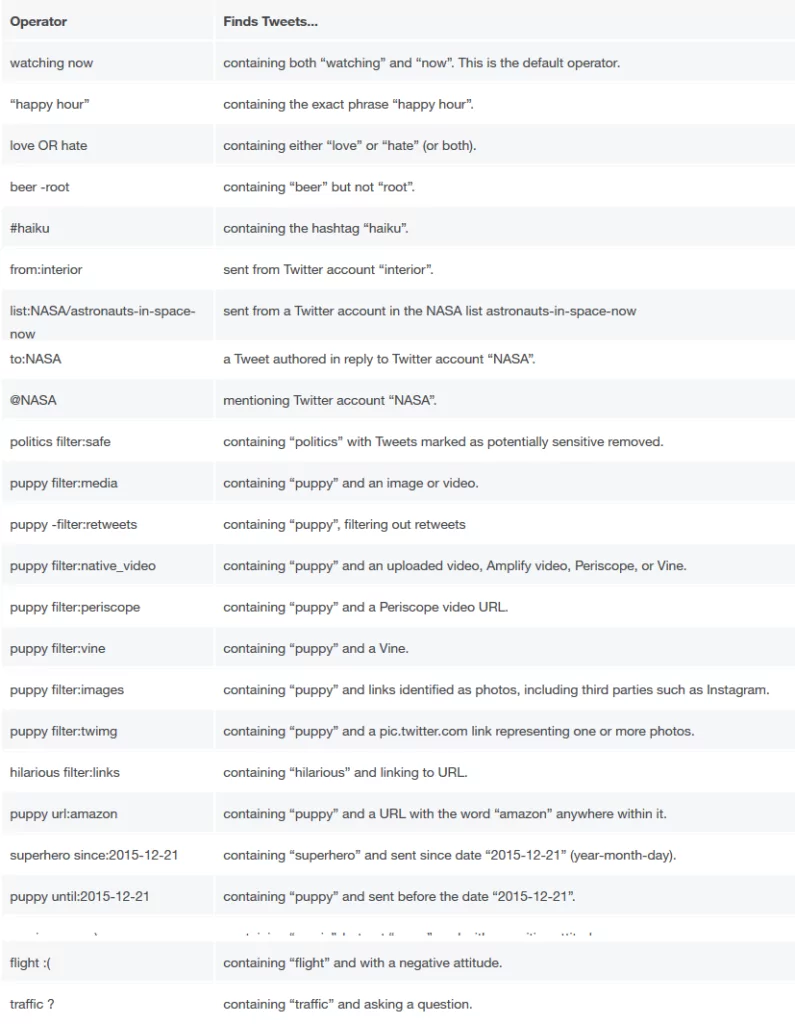
Twitter search operators can be incorporated with other criteria to create more advanced search queries to find related tweets more precisely, the following are some advanced Twitter search queries to start your search with.
- The negation operator (-) is used to exclude specific keywords or phrases from search results. Example: virus –computer
- To search for hashtags, use the (#) operator followed by the search keyword. For example: #OSINT
- To search for tweets sent up to a specific date, use the (until) operator. Here’s an example: OSINT until:2019-11-30(this will return all tweets containing OSINT and sent until November 30, 2019).
- To search for tweets sent since a specific date, use the (since) operator followed by the date. Here’s an example: OSINT since:2019-11-30 (this will return all tweets containing OSINT and sent since November 11, 2019).
- Use the (images) keyword to return tweets that contain an image within it. Here’s an example: OSINT Filter:images(this will return all tweets that contain the keyword OSINT and have an image embedded within them).
- To return tweets with video embedded with them, use the (videos) keyword (similar to the images filter). Here’s an example: OSINT Filter:videos
- To search for videos uploaded using the Twitter Periscope service, use the (Periscope) filter. Here’s an example: OSINT filter:periscope (this will search for all tweets containing the OSINT keyword with a Periscope video URL).
- To return tweets with either image or video, use the (media) operator. Here’s an example: OSINT Filter:media
- To return tweets that contain a link (URL) within them, use the (links) keyword. Here’s an example: OSINT Filter:links
- To return tweets that contain a link (URL) and hold a specific word within that URL, use the URL keyword. Here is an example: OSINT url:amazon this will return all tweets that contain OSINT and a URL with the word “amazon” anywhere within it.
- To return tweets from verified users only (verified accounts have a blue check mark near their names), use the (Verified) operator.
- Use the (min_retweets) operator followed by a number. Here’s an example: OSINT min_retweets:50 (this will return all tweets containing the OSINT search keyword that have been retweeted at least 50 times)
- Use (min_faves) followed by a number to return all tweets with NUMBER or more likes. Here’s an example: OSINT min_faves:11 (this will return all tweets that have at least 11 or more likes and that contain the OSINT search keyword)
- To limit Twitter returned results to a specific language, use the (lang) operator. Here’s an example: OSINT lang:en (this will return all tweets containing OSINT in the English language only). To see a list of Twitter-supported language codes, go to https://developer.twitter.com/en/docs/twitter-for-websites/twitter-for-websites-supported-languages/overview.
- To search for tweets with a negative attitude use the following symbol 🙁 For example: OSINT 🙁 will return all tweets containing the keyword OSINT written in a negative attitude.
Online Twitter Analysis Services
The following are online services to help you find information on Twitter:
- All My Tweets (https://www.allmytweets.net): View all public tweets posted by any Twitter account on one page.
- Trendsmap (https://www.trendsmap.com): This shows you the most popular trends, hashtags, and keywords on Twitter from anywhere around the world.
- First Tweet (http://ctrlq.org/first): Find the first tweet of any search keyword or link.
- Social Bearing (https://socialbearing.com/search/followers): Analyze Twitter followers of any particular account (a maximum of 10,000 followers can be loaded).
- Spoonbill (https://spoonbill.io): Monitor profile changes from the people you follow on Twitter (see Figure 7).
Discover SOCRadar® Free Edition
With SOCRadar® Free Edition, you’ll be able to:
- Discover your unknown hacker-exposed assets
- Check if your IP addresses tagged as malicious
- Monitor your domain name on hacked websites and phishing databases
- Get notified when a critical zero-day vulnerability is disclosed
Free for 12 months for 1 corporate domain and 100 auto-discovered digital assets.
Try for free

































