Malicious Actors in Dark Web: December 2022 Ransomware Landscape
Ransomware is one of the more common cyberattack types in the news. Behind the scenes of ransomware, there are numerous threat actors, each with a motive. Although the motive usually includes financial gain, the threat actors may also be driven by other causes.
A ransomware attack typically infects one device before spreading to others. Phishing or drive-by installations of related malware from suspicious websites are most likely to initiate ransomware attacks.
Ransomware operations often target businesses and organizations with valuable data, knowing they are more likely to pay the ransom to regain access to their crucial information. Some threat actors also demand additional payments for not leaking the victim’s data or threatening to cause damage to the infected system.
If a victim’s data is leaked, other threat actors will make use of it too. In this regard, the use of the dark web and leak channels by ransomware actors also poses a risk.
What are the Motives of Ransomware Operations?
All ransomware operations cause disruption, even if minor, and all are detrimental to a company’s reputation. There could be many motives, but the common motives we see are:
- Financial gain: Most ransomware threat actors are motivated primarily by monetary gain, by demanding a ransom payment in exchange for the decryption key.
- Extortion: Ransomware threat actors may also use extortion tactics, threatening to damage the infected system or publish private information unless their ransom demand is met.
- Disruption: Some ransomware threat actors may be motivated by disruption; they might look to sabotage the operations of specific organizations or governments.
- State-sponsored: Some ransomware attacks have been linked to state-backed groups with political or geopolitical motivations.
- Ideological: In rare cases, ransomware attacks have been motivated by ideological or personal beliefs, like hacktivism.
All possible motives cannot be listed, as there could be other motives specific to threat actors or groups associated with ransomware operations.
New Ransomware Variants in December
In December, the researchers at SOCRadar found 34 newly emerged ransomware infections. The following is a list of them:

Top 10 Ransomware Groups in December
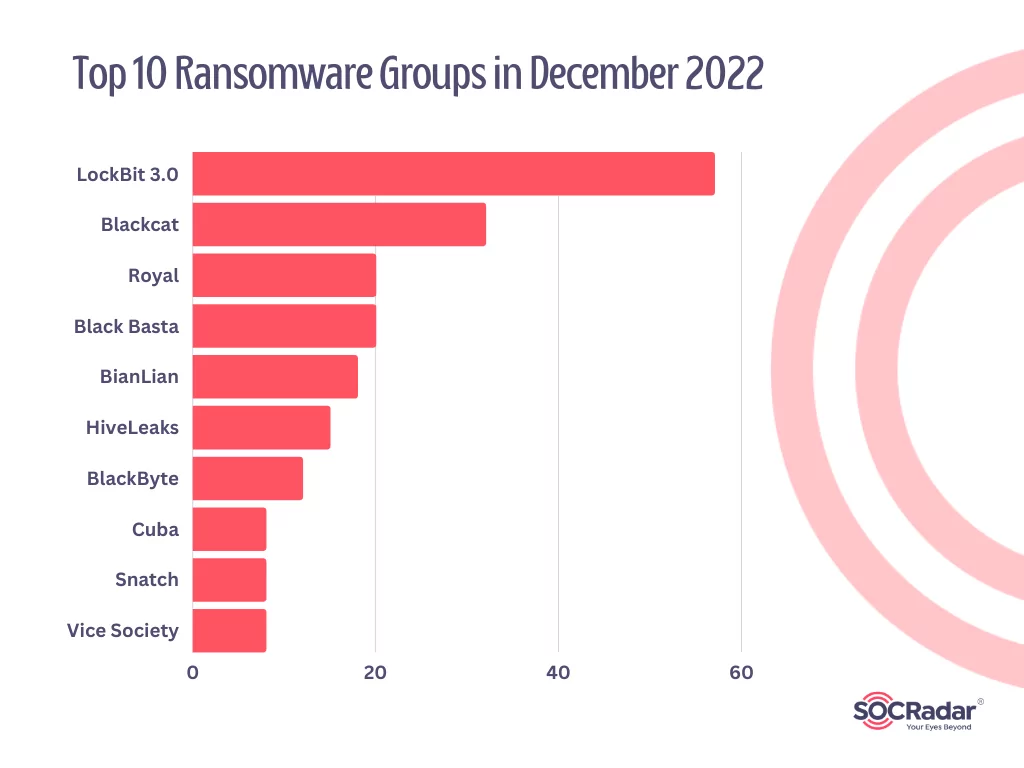
LockBit 3.0, AlphVM BlackCat, and Royal were the most impactful ransomware groups of December 2022.
As the top ransomware in December 2022, the LockBit gang has targeted well-known organizations in multiple countries since 2019. According to US prosecutors, the ransomware has been used against over 1,000 organizations, with the gang collecting tens of millions of dollars in ransom payments.
The top 10 ransomware groups of December are listed below:
Darkline of December 2022
Looking back on 2022, we know the cyber world will never be completely free of cybercriminals. As the demand for digital solutions grew, so did the cost of security implementation. The overall attack surface is constantly increasing, and organizations are trying to maintain the growth rate as minimal as possible, as a smaller attack surface is less risky.
Ransomware is not the only threat to an organization’s security and integrity; however, it plays a significant role as a more common threat. We can see that ransomware activity was high even in a single month in 2022.
Our research team has compiled a list of all significant ransomware-related events from December 2022. Here is the timeline of those events:
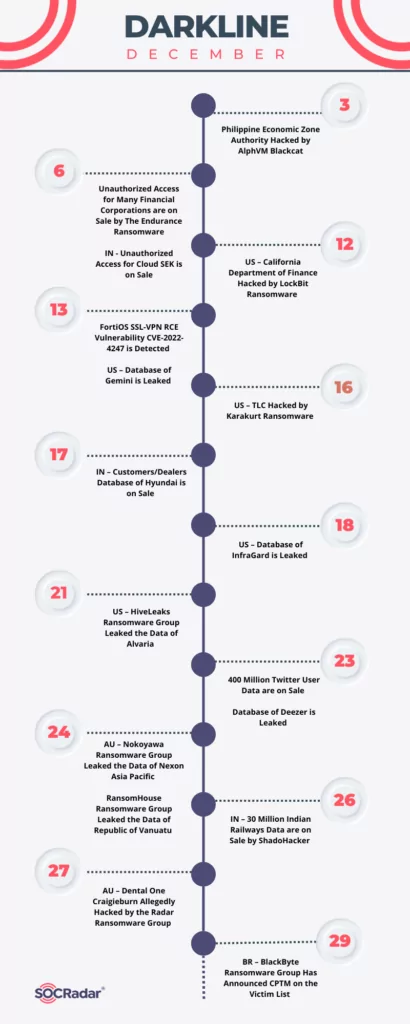
The ransomware groups targeted well-known companies in some of the incidents listed on the timeline. Some of the incidents ultimately resulted in the leak of private information due to refusal of payment. We can see that the threat actors had diverse motives in different events. Certain incidents are described in the following part.
California Department of Finance Hacked by LockBit Ransomware
The California Department of Finance has confirmed a cyber incident after the LockBit ransomware group claimed to have stolen sensitive data from the agency.
While the agency did not provide any information about the incident, the LockBit ransomware gang claimed responsibility by listing the agency as a victim on their leak site and setting the ransom payment deadline for December 24. The threat actor allegedly stole databases, confidential data, financial documents, certification, IT documents, and other information totaling 76GB.
FortiOS SSL-VPN RCE Vulnerability CVE-2022-4247 is Detected
Governments are now being targeted by a vulnerability in Fortinet’s FortiOS SSL-VPN feature that was recently patched. The vulnerability has the tracking number CVE-2022-4247 and a 9.3 severity rating.
A remote attacker may use specially crafted web requests to execute malicious code or commands remotely due to this heap-based buffer overflow vulnerability. The exploit was accessible in the wild. According to further investigation, a state-sponsored actor posing as a ransomware group was probably behind the exploits.
Additionally, researchers have found a new sophisticated BoldMove malware explicitly designed to operate on Fortinet’s FortiGate firewalls after gathering information regarding the vulnerability.
Database of Gemini Cryptocurrency Exchange is Leaked
The Gemini cryptocurrency exchange revealed that users had been the target of phishing campaigns after a threat actor obtained the customers’ personal information from a third-party vendor.
Several posts on a hacker forum offering to sell a database purportedly belonging to Gemini and containing contact information for 5.7 million users prompted the alert. The cryptocurrency exchange’s customers received phishing emails because of the breach.
TLC Hacked by Karakurt Ransomware

The Learning Channel (TLC) has been added by the cyber extortion group Karakurt to its list of alleged victims. The group threatens to release 931 GB of the company’s scripts, videos, internal documentation, and employee information if the company doesn’t pay up.
Neither the ransom demands nor the claims made by Karakurt that it has infiltrated the network have been verified.
Database of Hyundai is on Sale
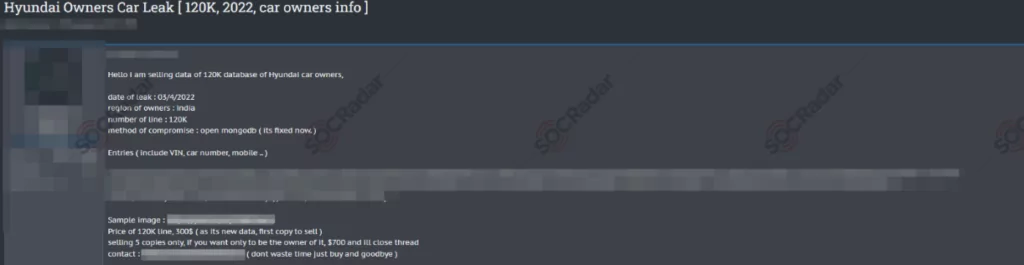
A threat group claimed to have access to the records of 120,000 Hyundai car owners when it posted information about the incident on well-known underground hacking forums, Breach Forums.
According to another post shared by the threat group, the data is for sale and costs $120. The information, which includes user names, reveals that the car owners are of Indian descent and that several important pieces of information, including their insurance number and registered mobile number, are for sale.
400 Million Twitter User Data are on Sale
In a post shared on a dark web forum monitored by SOCRadar, a threat actor claimed to have 400 million Twitter user records by exploiting a vulnerability. The sample shared in the post included the personal information of 37 people who are allegedly celebrities. The threat actor also shared a link to the data of another 1,000 users.
SOCRadar analysts examined the sample data and found that some information, such as name, username, number of followers, and account creation date, is already public and can be scraped from Twitter by using automated tools.
Database of Deezer Leaked
A well-known music streaming service, Deezer, has acknowledged a data breach affecting over 250 million users.
Deezer clarified the situation in an advisory posted on its platform, noting that threat actors had acquired the data from a third party that had suffered a data breach incident in 2019. The business added that starting in 2020, they have collaborated with a different third party.
There are full names, genders, birthdates, email and IP addresses, locations, user IDs, and join dates among the stolen data. According to Deezer, attackers stole no payment or password information.
30 Million Indian Railways Data are on Sale by ShadoHacker
A data breach at the Indian Railways led to the theft of about 30 million people’s personal information. The information was later put on sale on a dark web forum by ShadoHacker.
Username, email, mobile numbers, gender, city ID, city name, state ID, and language preferences are among the stolen information and user invoices, some of which had due dates of December 31, 2022.
Safeguard Against Ransomware Threats with SOCRadar
There are daily attempts to breach the network of a company. Monitoring the dark web is essential for businesses because it enables you to find out whether sensitive information about your organization is accessible or not.
You can connect your devices to the web data API to receive a steady stream of data feeds using a dark web monitoring tool.
Your IP address, business email domains, employee login credentials, and customer information might already be on the dark web without your knowledge.
If the monitoring tool finds any information about your business, it alerts you to any past or present attacks so you can take steps to lessen the damage.
Select a dark web surveillance tool that uses artificial intelligence to track the websites, blogs, forums, chat rooms, and private networks of cybercriminals.
Organizations can recognize and mitigate threats on the surface, deep, and dark web with the help of SOCRadar’s comprehensive Dark & Deep Web Monitoring solution.
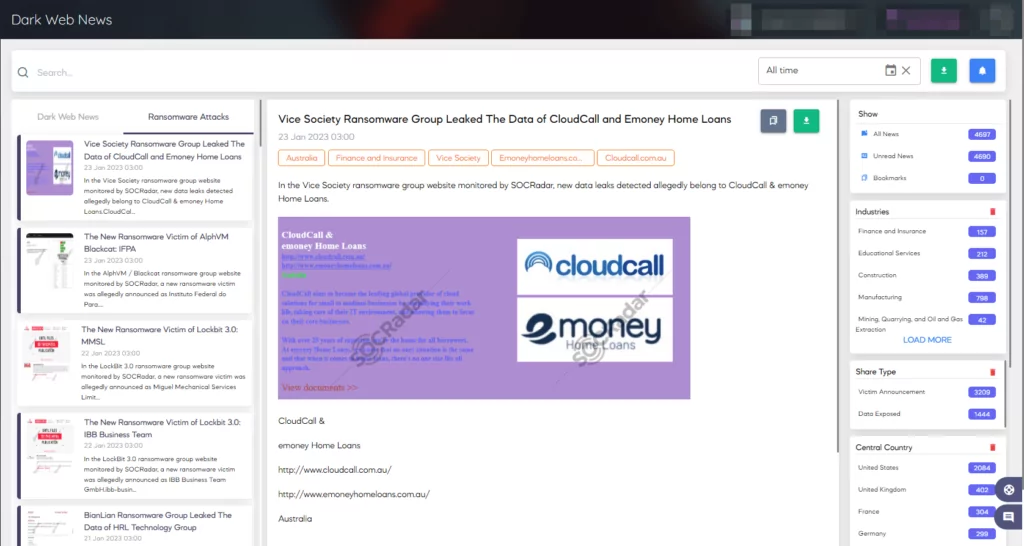
We provide actionable intelligence to assist your organization’s proactive security using our reconnaissance capabilities and threat analysis.
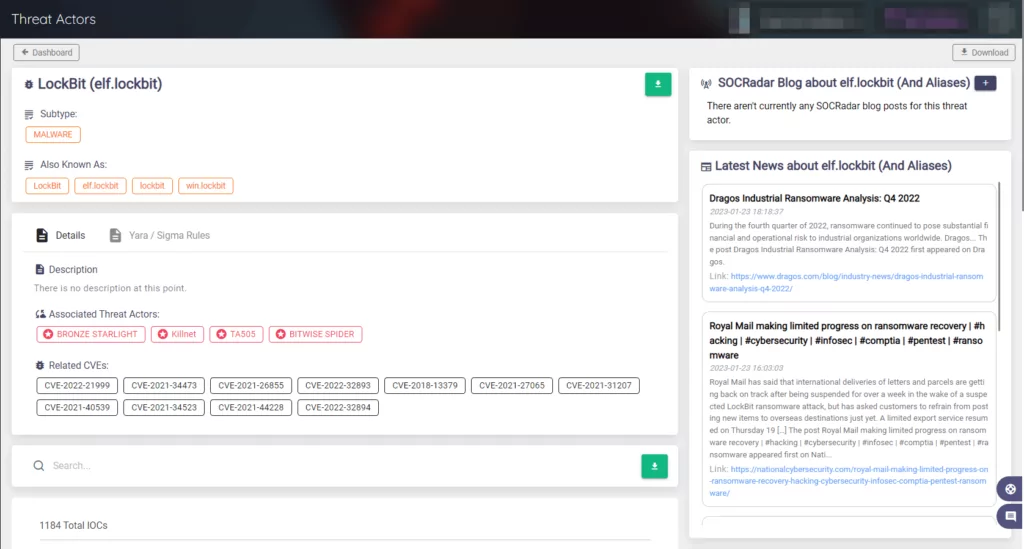
The Threat Actor panel on SOCRadar, which constantly updates its knowledge base, can help you stay informed about the most recent information about threat actors. Additionally, this panel allows for a detailed examination of threat actors.

Additionally, this panel allows for a detailed examination of threat actors.
Also, you can instantly determine if your data has been leaked on dark web forums, the black market, leak sites, or Telegram channels with the help of SOCRadar Labs’ free Dark Web Report.