
Veeam Service Provider Console (VSPC) Users Urged to Patch CVE-2024-42448 and CVE-2024-42449
Veeam has recently released patches addressing two serious security vulnerabilities in its Service Provider Console (VSPC), a critical tool for monitoring and management of backup and replication workloads. One of these vulnerabilities stands out with a critical CVSS score of 9.9, highlighting the severe risk of Remote Code Execution (RCE) attacks.
VSPC plays a vital role in enabling service providers to proactively monitor customer backups, manage recovery operations, and centralize backup management. The prominence of Veeam products in the backup and disaster recovery space makes them attractive targets for attackers. As such, the newly issued patches demand immediate attention from users to mitigate potential risks and secure their environments against exploitation.
What Are the Recent VSPC Vulnerabilities?
The recent vulnerabilities in Veeam Service Provider Console, identified as CVE-2024-42448 and CVE-2024-42449, are classified as critical and high-severity, respectively. If exploited, these flaws could significantly compromise system integrity and operational security, putting sensitive data and backup processes at risk.
CVE-2024-42448 (Critical, CVSS 9.9):
According to Veeam’s advisory, this critical vulnerability enables Remote Code Execution (RCE) from the VSPC management agent machine to the VSPC server. This means attackers can execute arbitrary code remotely, effectively taking control of the server. With such access, they could carry out further attacks, exfiltrate sensitive data, or entirely disrupt the backup and recovery processes critical to business continuity.
This vulnerability underscores the importance of securing systems that handle backup operations, as these serve as the last line of defense in many disaster recovery scenarios.
CVE-2024-42449 (High Severity, CVSS 7.1):
The second vulnerability, CVE-2024-42449, is a high-severity flaw that permits attackers to extract NTLM hashes of the VSPC server service account and delete files on the server. These hashes could be used to escalate privileges within the system, granting attackers unauthorized access to critical resources.
Additionally, the ability to delete files could disrupt operations and create opportunities for further malicious activities when combined with other vulnerabilities, such as deploying ransomware or erasing logs to cover tracks. Though less severe than CVE-2024-42448, this vulnerability still poses a substantial risk to operational security and data integrity.
Exploitation Conditions and the Importance of Immediate Action
Both vulnerabilities were discovered during internal testing by Veeam and are only exploitable if the Veeam Service Provider Console management agent is authorized on the server. This specific condition highlights the importance of proper access controls and vigilant system monitoring to prevent exploitation.
Given the potential impact of these flaws, organizations relying on VSPC for backup and disaster recovery should prioritize applying the available patches.
Vulnerabilities like CVE-2024-42448 and CVE-2024-42449 demonstrate the growing risk of unpatched software. SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence keeps you informed of newly discovered CVEs and emerging exploit trends, enabling you to take timely action.
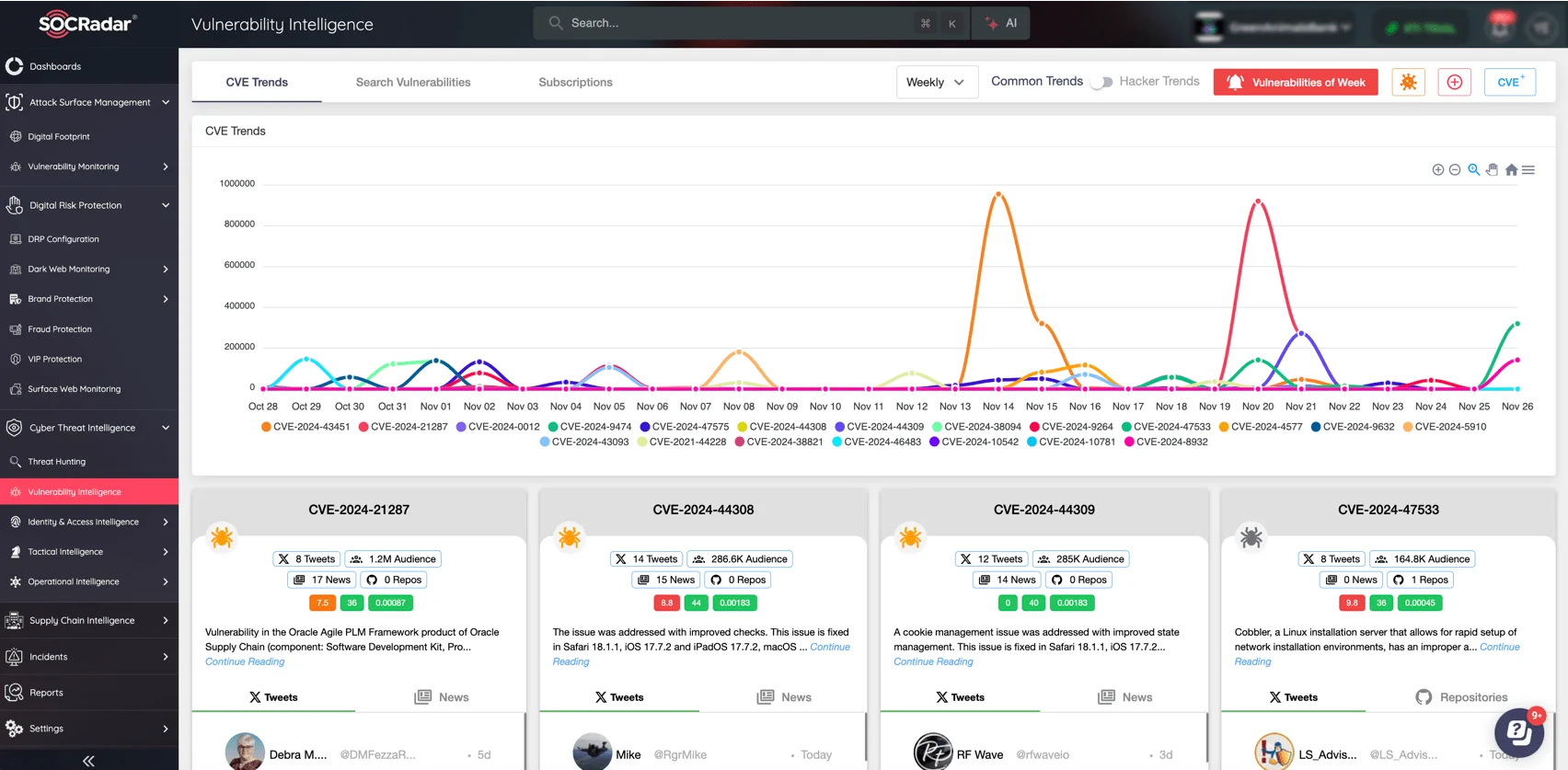
Stay updated on newest CVEs and monitor threat actor activity associated with specific vulnerabilities (SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence)
Which Versions Are Affected?
The vulnerabilities, CVE-2024-42448 and CVE-2024-42449, impact Veeam Service Provider Console (VSPC) versions 8.1.0.21377 and all earlier builds, including versions 8 and 7.
Veeam has noted that unsupported product versions, while not tested, are also likely affected and should be considered vulnerable. Maintaining outdated or unpatched software could leave your systems exposed to malicious activity.
Ensure Your Systems Are Patched with VSPC Version 8.1.0.21999
Veeam has released VSPC version 8.1.0.21999, which addresses the recent vulnerabilities CVE-2024-42448 and CVE-2024-42449. Organizations using supported versions are strongly encouraged to apply this cumulative patch immediately. The update mitigates the risk of Remote Code Execution (RCE), privilege escalation, and data compromise.
For users of unsupported versions, Veeam advises upgrading to a supported release. Unsupported versions remain susceptible to these and potentially other vulnerabilities, leaving systems exposed to cyber threats. Proactively upgrading ensures the safety and integrity of your backup and disaster recovery operations.
Detailed information on these vulnerabilities and patch instructions can be found in Veeam’s official advisory: KB4679.
The recent vulnerabilities in Veeam Service Provider Console highlight the need for a proactive approach to managing your organization’s digital risks. SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) helps you identify and secure exposed assets before attackers can exploit them.
With ASM, you can:
- Detect misconfigurations, shadow IT, and exposed services.
- Continuously monitor for vulnerabilities and changes in your environment.
- Receive actionable insights to prioritize security efforts and mitigate risks before they escalate into major incidents.
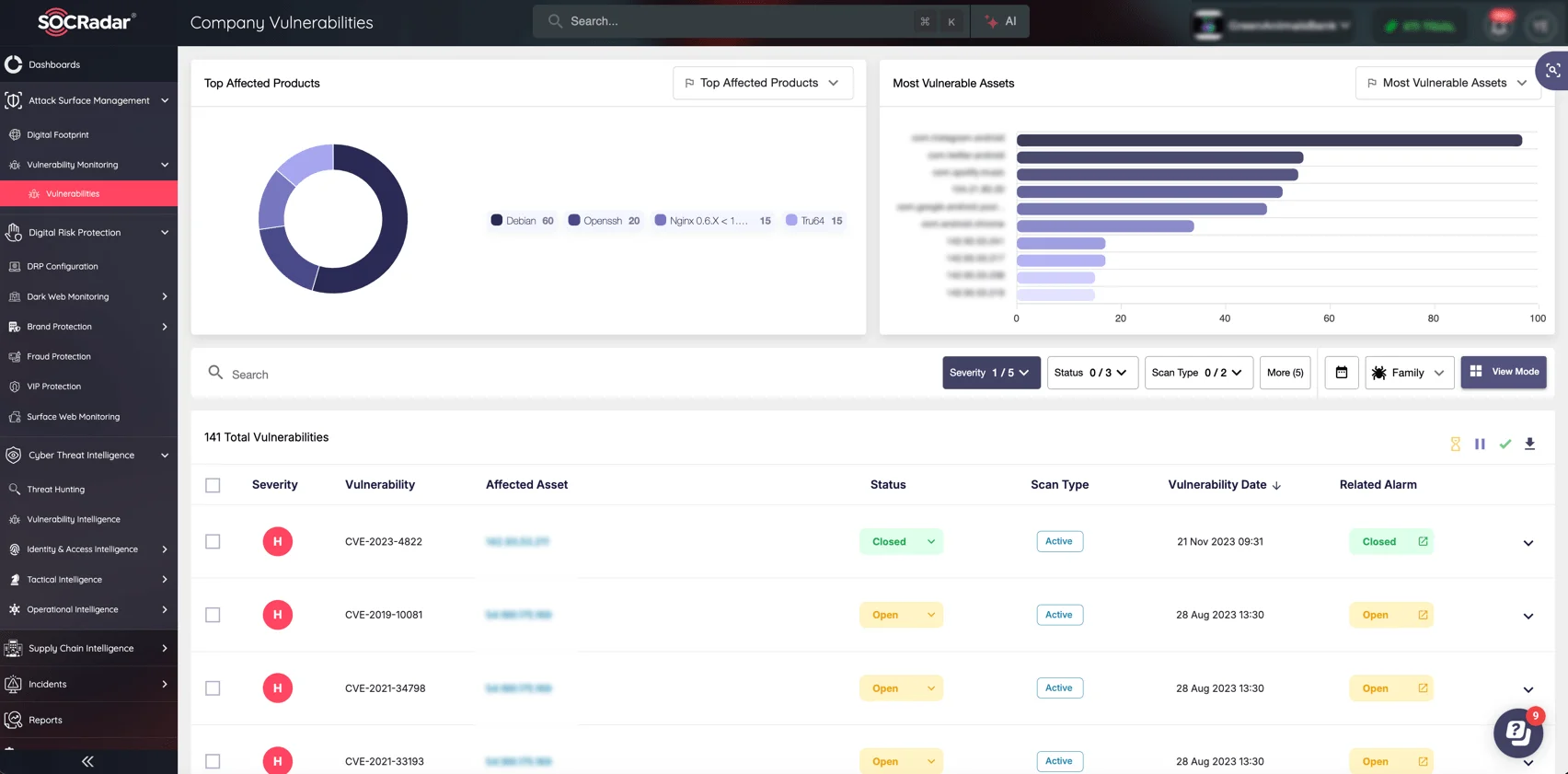
Stay one step ahead and defend your organization with a proactive approach to reducing attack vectors. (SOCRadar’s ASM module)
The Growing Threat Landscape of Vulnerabilities in Veeam and Beyond
Veeam’s track record with vulnerabilities emphasizes the continuous need for vigilance in backup and recovery security.
In October 2024, CVE-2024-40711 in Veeam Backup & Replication was added to CISA’s KEV Catalog. It was reported that the flaw was exploited by threat groups like Akira, Fog, and Frag in ransomware attacks to achieve code execution.
In September 2024, critical flaws in VSPC—CVE-2024-38650 and CVE-2024-39714—were revealed to enable Remote Code Execution (RCE) and expose sensitive data. Earlier in the year, Veeam addressed another critical vulnerability, CVE-2024-29212, mitigating further risks of code execution.
In more recent developments, Cisco, another well-known company, has issued a warning about exploitation attempts targeting a decade-old vulnerability, CVE-2014-2120, in its Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA). A November research report reveals that Androxgh0st exploited this and other vulnerabilities to spread botnet malware.




































