
What is Data Loss Prevention (DLP)?
Whether you’re dealing with private customer data, proprietary business information, or compliance-sensitive records, Data Loss Prevention (DLP) systems are essential for keeping your data secure.
Data Loss Prevention is a critical security measure that prevents unauthorized users from transferring sensitive data outside a business network. By implementing DLP systems, network administrators can regulate data flow, enforce stringent controls, and ensure the protection of private, sensitive, or otherwise valuable data across the organization.

An AI illustration for “Data Loss Prevention (DLP)”, by DALL-E
At its core, Data Loss Prevention allows network administrators to monitor, regulate, and control the flow of data within an organization. By categorizing data based on business rules, DLP ensures that sensitive information is protected from being accidentally or intentionally shared outside the network. For instance, DLP can monitor and control endpoint behavior and filter data streams within corporate networks to protect data in motion.
A common application of Data Loss Prevention is in email security. DLP systems can monitor emails sent by employees, and if an attempt is made to send or forward an email containing sensitive attachments, the system can block the email before it reaches the corporate email server.
Data Loss Prevention is not just about stopping data breaches; it’s also about compliance. With the rise of data privacy regulations, businesses are required to implement stringent data protection measures. DLP systems help organizations meet these legal obligations, reducing the risk of costly data breaches and ensuring that sensitive information remains secure.
Difference Between Data Loss and Data Leak
The terms “data leak” and “data loss” are often used interchangeably, but they refer to distinctly different events.
Data leaks involve the unauthorized exposure of sensitive information, often through vulnerabilities within digital systems. These incidents typically occur when sensitive data is unintentionally made accessible, whether at rest or in transit.
Conversely, data loss refers to the unintended removal or destruction of sensitive information. This can result from system errors, cyberattacks, or even insider threats.

What is the difference between data leak and data loss?
In data loss incidents, the data becomes irretrievable, either due to accidental deletion, system malfunctions, or theft by cybercriminals. The impact of data loss is often severe, as it may include both the loss of data and the associated legal and financial consequences.
How Much Critical Information Do You Manage?
In any organization, various teams handle different types of critical information. For example, your Sales team might manage client names and email addresses, while the Finance department oversees payroll details. The product and development teams could be working with sensitive Intellectual Property (IP), and roles like sales engineers or technical operations staff may have access to customer data.
All this information is vital – not just to your business operations but also to potential malicious actors, and it may all be lost with one incident.
Consider whether your company regularly handles any of the following types of sensitive information:
- Corporate trade secrets
- Credit card details
- Medical records
- Insurance information
- Legal case files
- Financial data
- Personally identifiable information (PII)
If your business deals with customers or clients, it’s highly likely you’re managing sensitive, business-critical data that needs protection.
The Cost of Data Loss
Data breaches that involve the theft, deletion, or unauthorized access to sensitive information – such as Personally Identifiable Information (PII), regulated data, or proprietary business information – can be extremely costly, resulting in financial costs in the millions of dollars for every occurrence and long-term financial harm that can last for years.
While the financial impact of data loss varies, there are additional risks too, such as:
- Significant downtime caused by the loss and subsequent recovery of critical data
- Legal liabilities stemming from the exposure of regulated data
- Loss of trust among clients, consumers, and stakeholders
How Does Data Loss Prevention Work?
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) software is designed to monitor, identify, and prevent the leakage of sensitive data within an organization. By monitoring both incoming and outgoing network traffic, DLP systems serve as a critical line of defense against unauthorized data access and transmission.
Most DLP software primarily focus on preventing suspicious activities. For example, if an employee attempts to send a business email with sensitive information, upload corporate files to a personal cloud storage account, or save data onto a USB device, the DLP system can automatically block these actions. This helps safeguard sensitive information from being accidentally or maliciously shared outside the organization.
Example cases where Data Loss Prevention (DLP) is useful
Beyond monitoring outgoing data, DLP also identifies threats within incoming communications. It scans emails for suspicious attachments and URLs, which may indicate a phishing attack. By flagging or quarantining such emails, DLP systems allow administrators to review and take appropriate action before any potential harm is done.
In the past, traditional DLP solutions relied heavily on static rules set by the security team – an approach that was often labor-intensive and could be easily bypassed.
However, modern DLP software has evolved, utilizing machine learning algorithms to establish a baseline of typical activity. This advancement allows data loss prevention systems to detect unusual or “strange” activities, such as atypical email patterns or data transfers, which may warrant further investigation.
To enhance your Data Loss Prevention (DLP) efforts, you can integrate an advanced Digital Risk Protection (DRP) solution like SOCRadar. SOCRadar’s DRP helps organizations detect and mitigate data leaks across the open web, deep web, and dark web, providing real-time alerts on potential threats to your sensitive information.
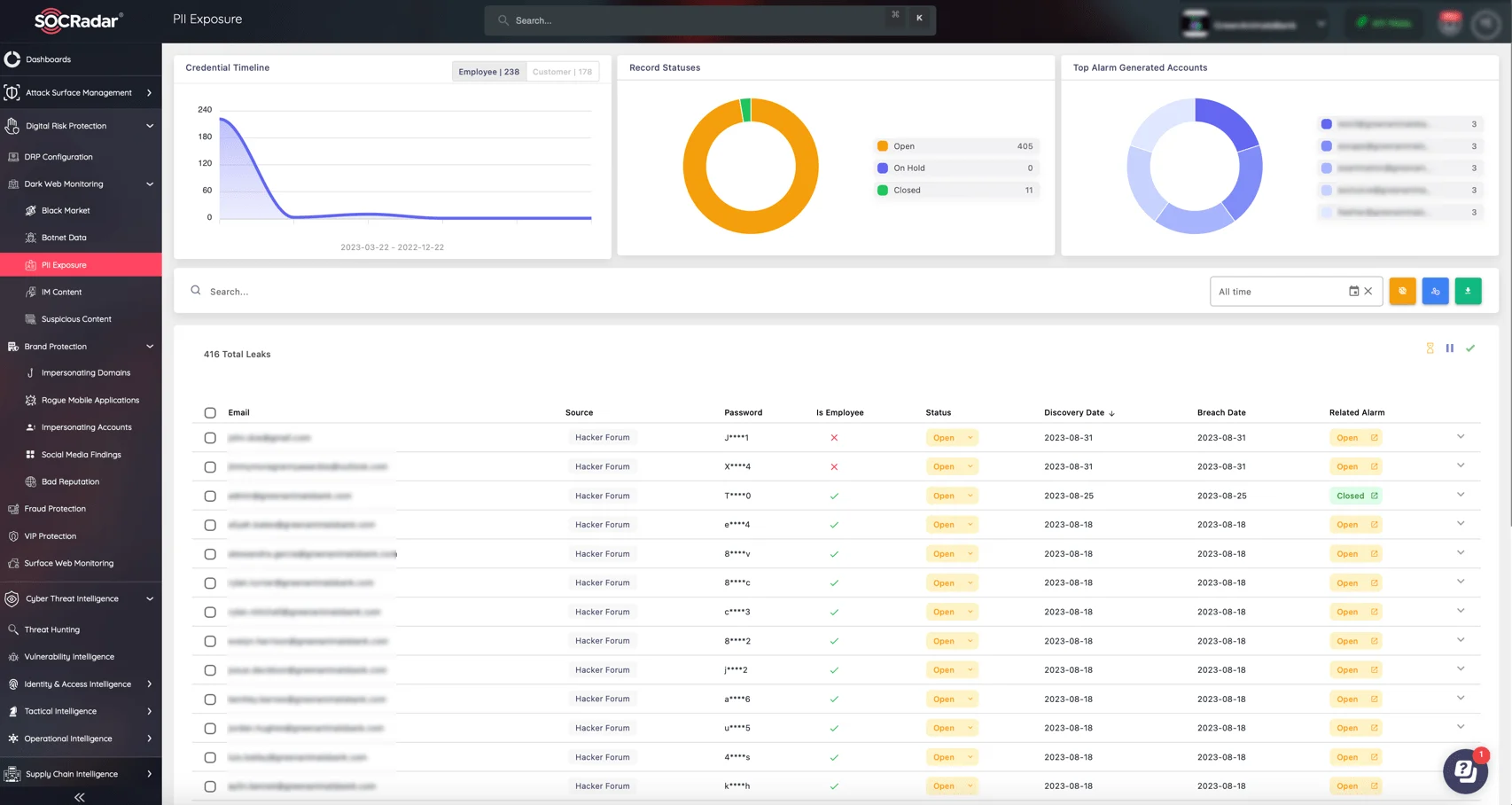
Monitor PII exposure and more with SOCRadar’s DRP module
Key Objectives of an Effective Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Solution
The following are the primary objectives of an efficient Data Loss Prevention (DLP) solution:
1. Protect Data at Rest
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) systems enforce access controls, encryption, and data retention policies for data at rest, which includes archived or stored data.
Examples of data at rest include sensitive information kept for legal compliance, intellectual property, and confidential business secrets. DLP adds an essential layer of security to prevent and detect unauthorized access to this critical information.
2. Detect Data Leaks
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) solutions provide real-time monitoring of data usage, enabling them to detect and prevent data leaks as they occur.
When a potential data breach is identified, the DLP system can halt the leak and alert IT security teams for immediate action. This proactive approach helps mitigate the impact of data breaches by addressing them in real time.
3. Identify Data
Another of the core functions of Data Loss Prevention (DLP) solutions is to identify and classify an organization’s data, especially sensitive data at rest or in use.
By accurately locating and isolating critical information, DLP systems can deploy appropriate safeguards where they are most needed. Data identification can be performed manually by the organization or automatically by the advanced tools within the DLP solution.
How to Prevent Data Loss?
Effectively preventing data loss requires a comprehensive approach that combines industry compliance, strategic planning, and the right technologies. Here are some best practices for Data Loss Prevention (DLP) efforts:
Ensure Compliance First
For regulated industries, compliance with industry standards like HIPAA for healthcare or PCI-DSS for credit card transactions is essential. Begin by aligning your DLP strategy with these regulations to avoid legal conflicts and ensure your organization is protected from compliance-related risks.
Prioritize Data Based on Risk
Identify and classify your data according to its level of risk. Focus on safeguarding the most vulnerable and high-risk information first, deploying appropriate technologies and safeguards to protect critical assets.
To effectively manage and protect your organization’s most critical assets, SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) module provides continuous visibility into your digital footprint. This allows you to prioritize and safeguard high-risk data by identifying vulnerabilities and potential points of exposure.
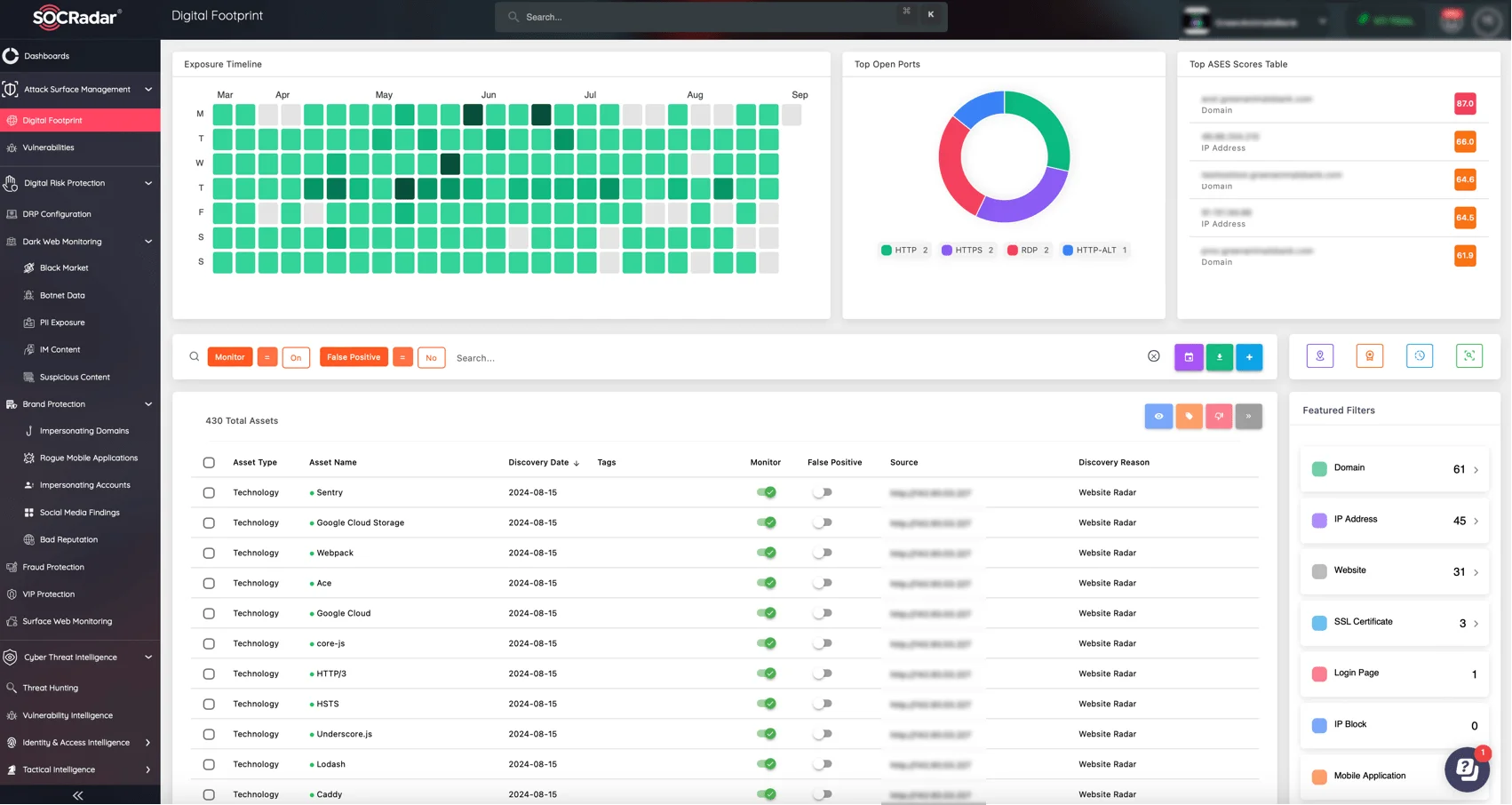
Track your organization’s Digital Footprint with SOCRadar’s ASM module
Define and Limit User Access
Clearly define user roles and limit access to only the data necessary for each role. For instance, while a sales agent may require access to credit card information, technical support personnel do not. Tailor access levels to minimize exposure and reduce the risk of data breaches.
Engage Key Stakeholders
Involve leaders from various departments in your DLP planning to gain insights and identify potential vulnerabilities. Their involvement not only enhances the strategy but also fosters buy-in and collaboration across the organization.
Implement Policies and Technology
Translate your DLP strategy into actionable steps by assigning specific tasks, reviewing firewall settings, and scheduling regular software updates. Ensure that everyone involved understands their responsibilities and deadlines to maintain a robust data protection environment.
Automate Where Possible
Automation reduces human error and strengthens your defenses. For example, implementing automated spam filters can block phishing attempts before they reach your employees, adding an essential layer of protection against data loss.
For proactive protection against phishing and other malicious activities, SOCRadar’s Extended Threat Intelligence (XTI) platform offers real-time monitoring and automated alerts on emerging threats. This enables organizations to stay ahead of cybercriminals and prevent data loss before it occurs.
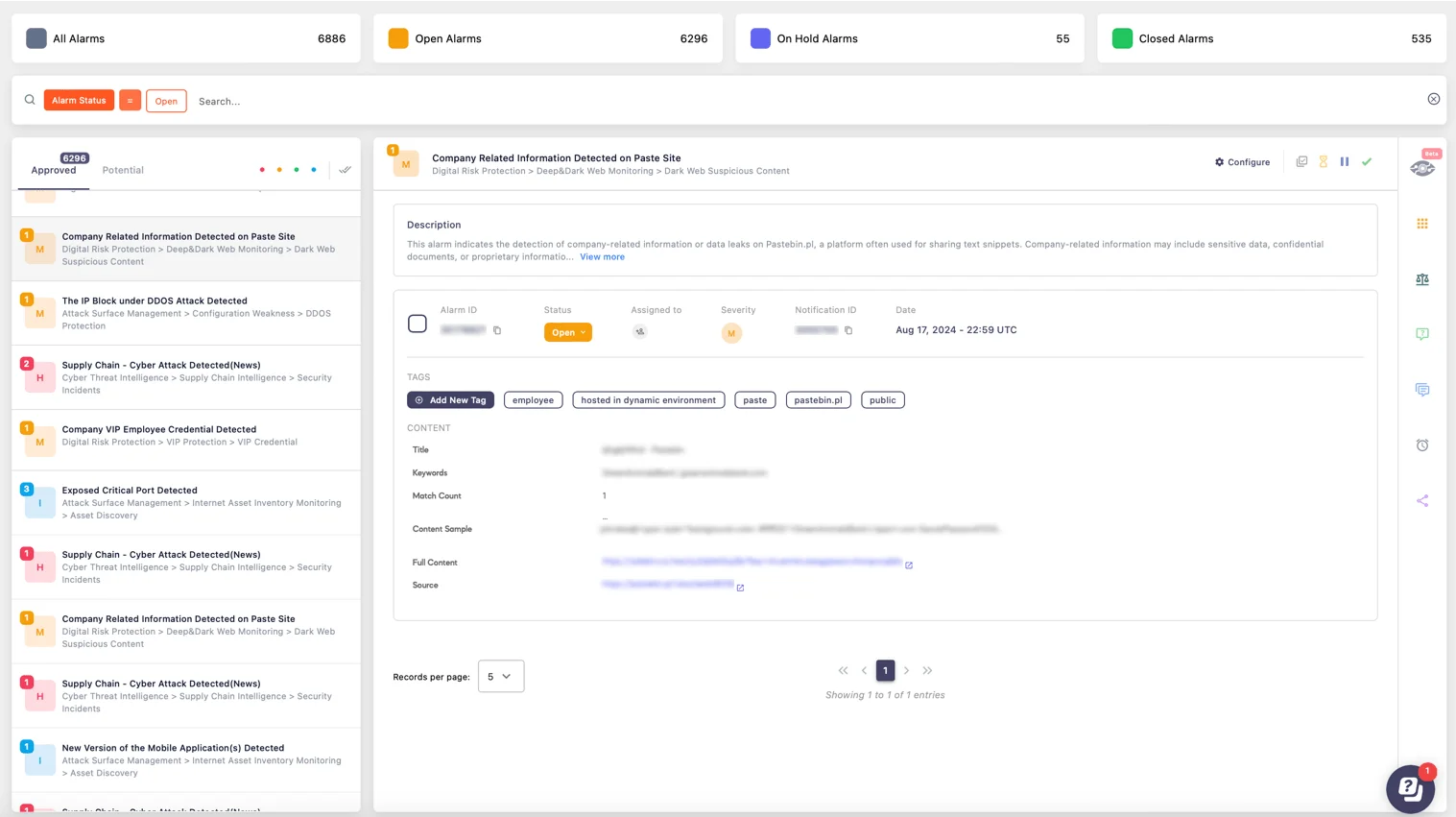
Alarm: Company Related Information Detected (SOCRadar Alarm Management)
Educate and Train Your Team
Educating your team on the importance of DLP systems is crucial. When employees understand the “why” behind data protection measures, they are more likely to adhere to policies and contribute to the overall security of the organization.
Document the Strategy
Keep detailed documentation of your DLP strategy, including the “how” and “why” behind each component. This documentation serves as a critical reference point and ensures consistency in the implementation and management of your data protection efforts.
Regularly Review and Measure
Continuous monitoring is key to a successful DLP strategy. Regularly review the effectiveness of your DLP measures, using metrics to track attempted breaches and refine your approach as necessary.
Delete Unnecessary Data
Holding onto outdated or unnecessary data can increase your risk of data loss. Regularly review your data holdings, securely deleting or archiving information that is no longer needed to reduce potential vulnerabilities.


































