
Insider Threats Rising: Average Cost of an Incident is $6.6M
The annual Cost of a Data Breach Report, featuring research by Ponemon Institute, offers insights from 550 actual breaches to help you understand cyber risk in a changing world. Research shows that insider threats cause most data breaches. Widespread usage of insider threat management (ITM) solutions are essential for these increasing threats.
The figures given in the report of the Ponemon Institute are pretty striking. Insider-related incidents take a long time to be noticed, and the damage is increasing daily. Let’s take a closer look at some critical issues in which both large and small companies have their share.
What are the Insider Threats?
Insider threats are defined as:
- A careless or negligent employee or contractor (most prevalent)
- A criminal or malicious insider
- A credential thief
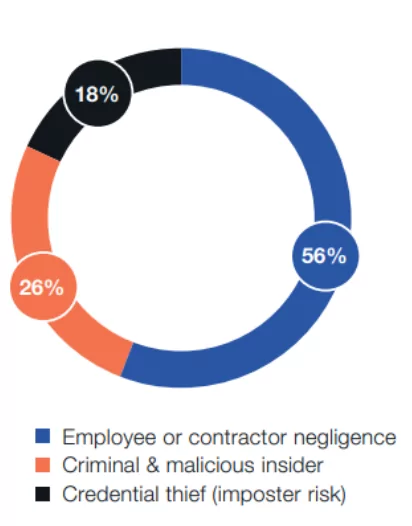
56% of incidents were due to negligence, and the average cost to remediate the incident was $6.6 million.
Malicious insiders caused 26% or 1,749 incidents at an average cost per incident of $648,062. Malicious insiders are harder to detect than external attackers or hackers.

At an average of $804,997 per incident, credential theft is the costliest to remediate. A favorite technique of credential thieves is primarily phishing. A total of 1,247 incidents, or 18%, involved stolen credentials in this year’s research.
67 percent of companies are experiencing between 21 and more than 40 incidents per year. This is an increase from 60 percent in 2020.
Disruption or downtime and technological investment represent the highest costs when dealing with insider threats.
An average of $184,548 is spent to contain the consequences of an insider threat.
The average activity cost for financial services is $21.25 million, and services are $18.65 million
55% of organizations say they are most concerned about a hacker stealing the valid credentials of an employee. Vulnerable IoT devices are the most significant risk of data loss. Most sensitive data is in employees’ emails. Malicious insiders use corporate email to steal sensitive data.
As the volume and time to contain insider threats increases, advanced technologies such as user behavior tools and automation are essential to helping reduce insider threats.
5 Signs that Your Organization is at Risk of Insider Threat
- Employees are not trained about things that affect the organization’s security.
- Employees are unaware of the steps they should take to ensure that their devices are always secured.
- Employees are sending confidential data to an unsecured location in the cloud.
- Employees break your organization’s security policies to simplify tasks.
- Employees that do not keep devices and services patched and upgraded to the latest versions.
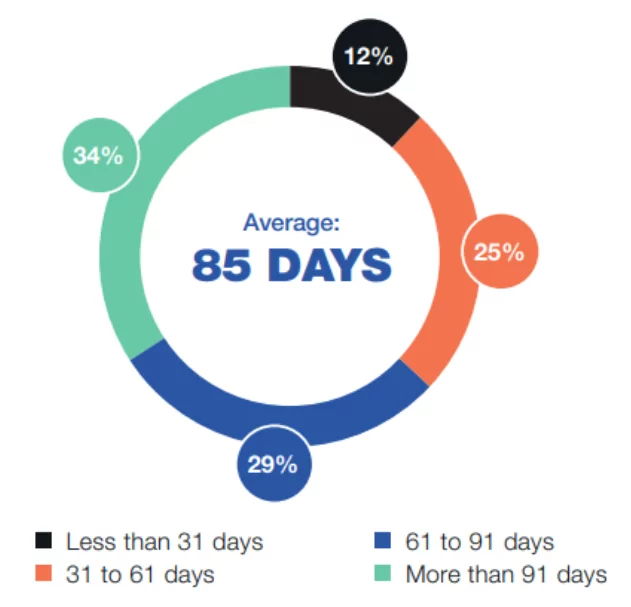
Percentage distribution of insider-related incidents based on the time to contain:
Cost Analysis
Insider threat cost is usually based on seven activities. These activities are also named internal costs:
- Monitoring and Surveillance
- Investigation
- Escalation
- Incident Response
- Containment
- Ex-post Response
- Remediation
There are external costs too, which are caused by business disruption, equipment damage, revenue, and data loss.
Containment activities are the most costly during an insider threat incident. According to research this year, the average time needed to contain an incident has increased from 77 to 85 days. The second most costly activity is investigation. Ex-post analysis and escalation are the least expensive.
Response to an insider threat incident has significantly increased in cost since 2016 (by about 80%). Monitoring, surveillance, and escalation have the most significant cost increases (114% and 113%).
Companies in North America spend more than the industry average on ITM (insider threat management), with the highest total cost being $17.53 million. The second-highest cost came from European businesses, at $15.44 million. Asia-Pacific had an average cost of $11.90 million, which is way less than the total for all other companies in research (278 companies).
Larger organizations with 25,000–75,000 employees have to spend more to resolve an insider threat incident, with an average cost of $23 million. Smaller-sized organizations with a headcount below 500 spent an average of $8.13 million.
The cost is directly proportional to the time it takes to contain the incident. The highest average cost per year for incidents that took more than 90 days to contain was $17.19 million. Incidents contained in less than 30 days had the lowest total cost of $11.22 million.
Insider Threat Management
Though both are root causes for most insider incidents, organizations are more concerned about a hacker stealing an employee’s credentials than a negligent insider because credential theft costs the most to remediate.
Data Loss
Unmanaged IoT devices are at the greatest risk of data loss and increase insider risk in organizations. Other prevalent factors that increase data loss risk are cloud and network.
Employee emails contain the most sensitive data, such as PII, intellectual property, and business information. Training and awareness programs are critical to reducing employees’ negligence with information handling.
Use of Advanced Technologies
Advanced technologies are crucial to reducing insider threats as the time needed to contain these incidents increases. Detection tools based on user behavior are thought necessary for lowering insider threats. AI and machine learning also provide insider incident prevention, investigation, escalation, containment, and remediation automation.
Organizations are trying to adopt an ITM program primarily because they’ve had past incidents or are seen at risk due to incidents directed at other companies. Industry regulations are another cause to start implementing an ITM.
Conclusions
Insider threats grow together with digital transformation. With the increased use of personal devices and the cloud, organizations are looking for more effective ways to secure their data. Organizations must implement an ITM program. With technical and non-technical representatives on the team, organizations can achieve the three successful elements of an ITM program: transparency, consistency, and visibility.
Implementing an ITM program to detect risky user behavior and data interaction and respond to the incident is vital in preventing data loss and mitigating insider risk.



































