
What is Endpoint Security Management
Endpoint Security Management refers to the processes, tools, and strategies used to secure endpoints or entry points on end-user devices such as computers, mobile devices, and servers. These endpoints act as gateways into a network, making them prime targets for cyber attacks. The goal of Endpoint Security Management is to keep these devices safe from unauthorized access, malware, and other security threats that could jeopardize the entire network.
In today’s digital landscape, the number of endpoints connected to corporate networks has increased dramatically. Each connected device represents a potential vulnerability that threat actors can exploit. Effective endpoint security management is critical for protecting sensitive data, maintaining regulatory compliance, and ensuring business continuity.
Endpoint Security Management typically consists of antivirus software, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, data encryption, and access control mechanisms. Advanced solutions may also include Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) tools, which provide real-time monitoring and analytics in order to detect and respond to security incidents quickly.
Endpoint Management Explained
Endpoint Management is a broad term that includes not only security, but also the deployment, monitoring, and maintenance of endpoint devices throughout an organization. Given the growing number of such devices in modern organizations, managing and securing these endpoints is critical to ensuring overall network security.
Endpoint Security, a critical component of Endpoint Management, works by continuously monitoring all connected devices’ attack surfaces in order to detect and prevent potential threats. Endpoint Security, like traditional security systems, focuses on analyzing incoming data from each device to ensure that only secure and verified files enter the network. This proactive approach enables security systems to detect malware and other threats before they spread throughout the network.
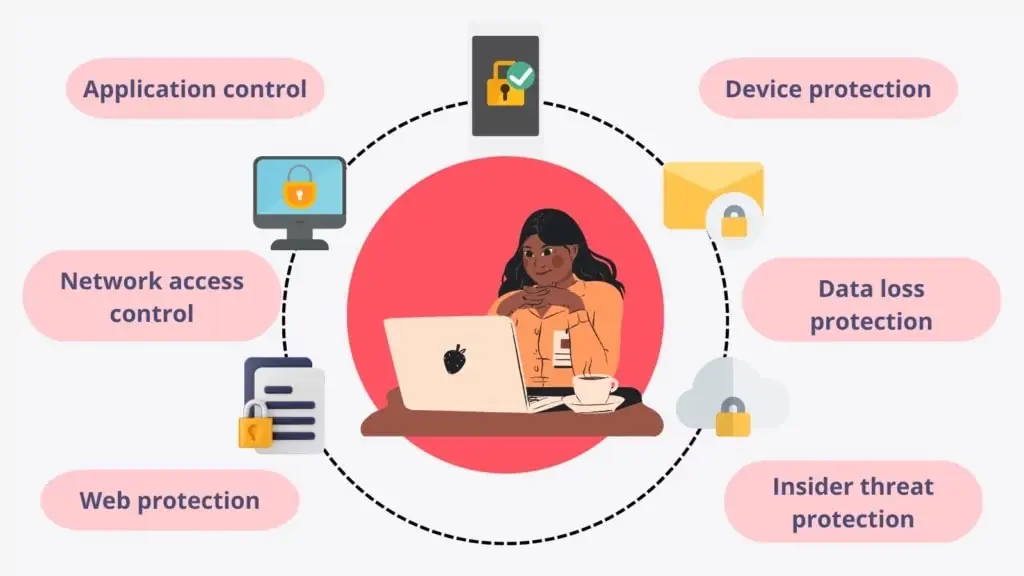
A diagram that shows how does endpoint security works, you can know more about it through our blog post “All You Need to Know About Endpoint Security”
Endpoint Security Management includes a control panel for security administrators. This centralized dashboard enables them to monitor the status of all endpoint devices in real time, respond quickly to potential threats, and take appropriate actions, such as isolating or remotely wiping data from compromised devices. This level of control is critical for preventing the spread of malware and mitigating the impact of a breach.
Organizations that integrate both security and management functions can reduce the complexity of managing multiple devices, ensure network-wide security, and improve overall operational efficiency. This approach not only protects against security threats, but it also increases productivity by ensuring that all devices function properly.
Identifying Typical Endpoint Security Threats
Common Endpoint Security Threats:
Malware
Malware is malicious software that infiltrates, damages, or steals data from endpoint devices. Malware can take many different forms in endpoint security, such as viruses, ransomware, spyware, and Trojans. These malicious programs can enter a system through a variety of channels, including email attachments, malicious downloads, and compromised websites. Once inside an endpoint, malware can disrupt operations, steal sensitive data, or even lock users out of their systems until a ransom is paid (as in ransomware attacks).
Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks are a type of social engineering in which attackers try to trick users into disclosing sensitive information or installing malicious software. In the context of endpoint security, phishing frequently targets employees via email, masquerading as legitimate communications from trusted sources such as colleagues, banks, or government agencies. When a victim clicks on a malicious link or opens a harmful attachment, the endpoint can be compromised, allowing attackers access to the network. Endpoint security management solutions must include advanced email filtering, user training, and real-time threat detection to prevent these attacks from succeeding.
Insider Threats
Insider threats are security risks that come from within an organization. These threats can originate from employees, contractors, or partners who, either intentionally or unintentionally, jeopardize endpoint security. For example, an employee may inadvertently download malware onto a company laptop, or a disgruntled employee may intentionally leak sensitive information. Endpoint security management must address these risks by implementing strong access controls, continuous monitoring of user activities, and clear policies that reduce the possibility of accidental or malicious actions by insiders.
Zero-Day Exploits
Zero-day exploits are software or hardware vulnerabilities that are unknown to the vendor and have yet to be patched. Attackers can use these flaws to gain unauthorized access to endpoints before the vulnerability is publicly disclosed and patched. Zero-day exploits are especially dangerous in endpoint security because they can get around traditional security defenses. To protect against these threats, endpoint security management uses advanced detection techniques like behavior analysis and machine learning to detect and mitigate zero-day attacks in real time.
Unpatched Software
Unpatched software is defined as applications or operating systems that contain known vulnerabilities but have not been updated with the most recent security patches. Attackers can easily exploit these vulnerabilities to take control of an endpoint, steal data, or spread malware. Endpoint security relies heavily on keeping all devices’ software up to date. Automated patch management systems are critical components of endpoint security management, ensuring that all software is regularly updated to protect against known vulnerabilities.
Unauthorized Access
Unauthorized access occurs when people gain access to endpoints or networks without proper authorization, usually by exploiting weak authentication mechanisms. This can result in data breaches, the loss of sensitive information, and further network vulnerabilities. In an endpoint security context, preventing unauthorized access entails implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), using strong passwords, and using encryption to protect data. Additionally, endpoint security management solutions should monitor access attempts and notify administrators of any suspicious activity.
DDoS Attacks
Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks overwhelm endpoint devices and networks by flooding them with too much traffic, causing them to slow down or crash. While DDoS attacks are most commonly associated with network infrastructure, they can also target endpoints, particularly if they are part of a larger botnet used to carry out the attack. In the context of endpoint security, protecting against DDoS attacks entails ensuring that endpoints are not vulnerable to hijacking into botnets, as well as implementing measures to detect and mitigate unusual traffic patterns that could indicate a DDoS attempt.
Mitigating Endpoint Security Threats
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): EDR solutions provide real-time monitoring and automated responses to potential threats across all endpoint devices. They detect suspicious activities, isolate compromised endpoints, and initiate remediation efforts to prevent the spread of threats within the network.
Employee Education and Training: Educating employees about common cyber threats, such as phishing and social engineering, is crucial. Regular training helps users recognize and avoid risky behaviors, ensuring that they serve as a strong first line of defense against security threats.
Data Encryption: Data encryption protects sensitive information on endpoint devices by converting it into an unreadable format that can only be decrypted with the correct key. This ensures that even if an endpoint is compromised, the data remains secure and inaccessible to unauthorized users.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access to endpoint devices or sensitive data. This reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if login credentials are compromised.
Regular Software Updates and Patching: Regularly updating software and applying security patches is essential to protect endpoints from known vulnerabilities. Automated patch management systems ensure that all devices are kept up-to-date, reducing the risk of exploitation by attackers.
Cloud-Based Security Solutions:Cloud-based security solutions offer scalable and centralized protection for endpoint devices, providing real-time threat intelligence and automated updates. These solutions are especially effective in environments with a diverse range of endpoints, such as remote workforces.
Continuous Monitoring and Scanning: Continuous monitoring and scanning of endpoint devices help identify vulnerabilities and suspicious activities before they can be exploited. Proactive scanning ensures that potential threats are detected early, allowing for swift response and mitigation.
Leverage SOCRadar’s Operational Intelligence Trends
SOCRadar’s Operational Intelligence Trends offers real-time insights into emerging threats that have a direct impact on endpoint security. This powerful tool allows you to keep track of the most commonly exploited vulnerabilities by threat actors as well as the activities of ransomware groups. With SOCRadar, you can customize your threat landscape view to focus on what is most important to your organization, ensuring that your defenses are always in sync with the evolving threat environment.
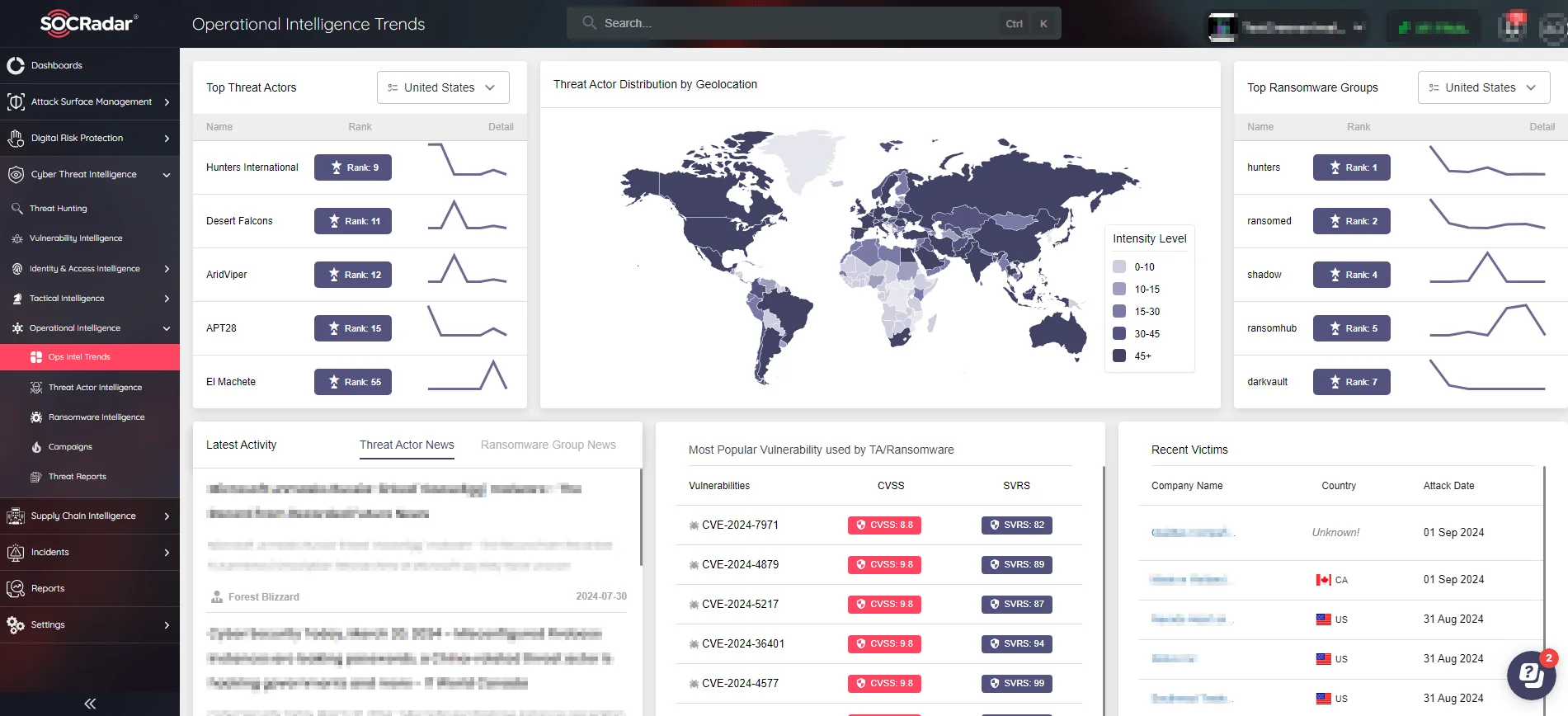
SOCRadar’s Operational Intelligence Trends real time monitoring of all kinds of possible threats
Conclusion
Effective endpoint security management is more important than ever in protecting an organization’s network from a variety of cyber threats. As the number of connected devices increases, so does the complexity of managing and securing these endpoints. Organizations can significantly reduce the risk of breaches and ensure network security by implementing comprehensive security measures such as Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR), regular software updates, and multi-factor authentication.
SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence increases your security vigilance by providing instant alerts and actionable insights, allowing you to protect against potential breaches. SOCRadar’s advanced alert system notifies you of these critical vulnerabilities as soon as they are discovered, allowing you to respond quickly and decisively.
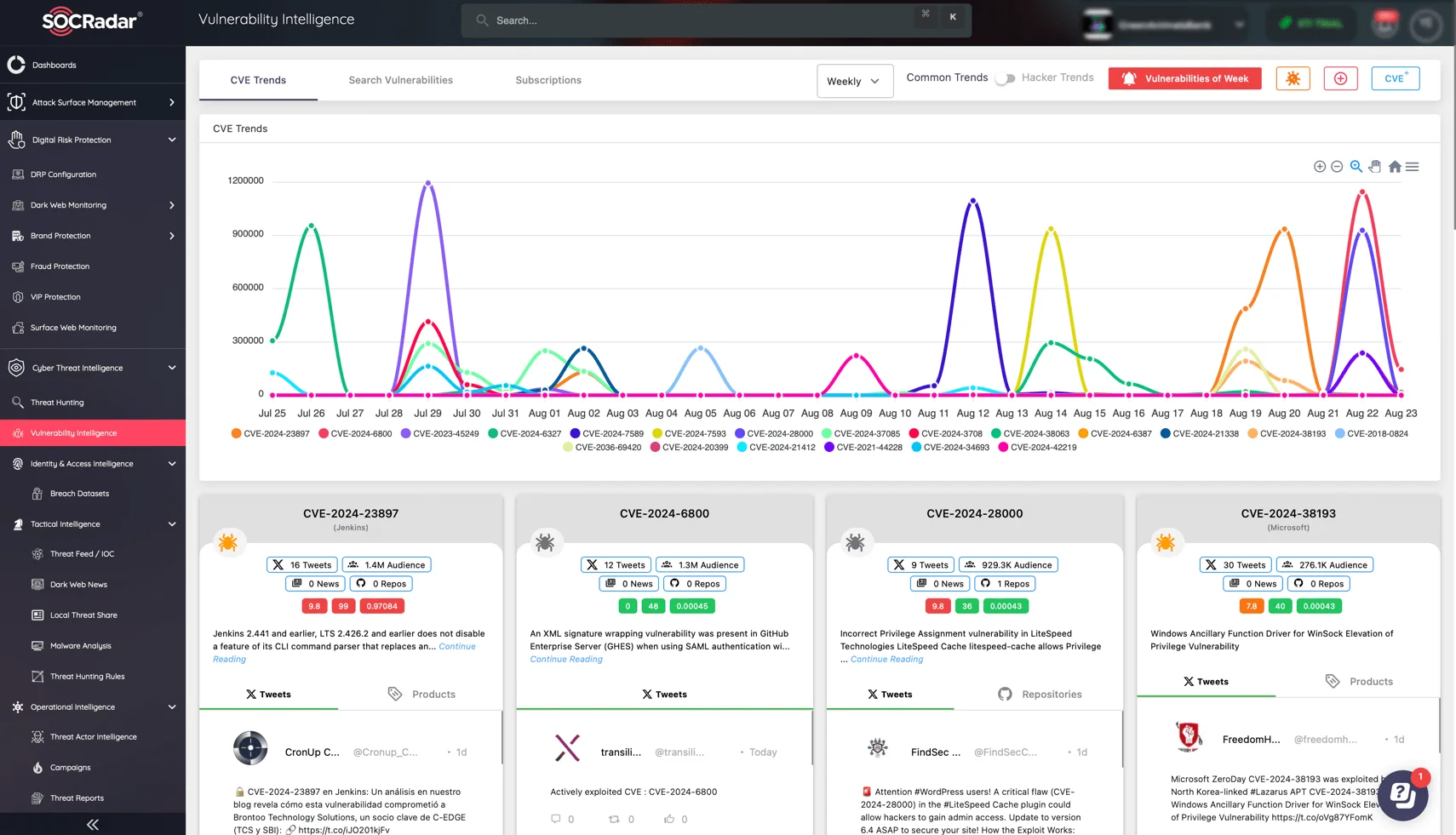
SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence Module
SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence enables your organization to close the door on cyber threats before they can be exploited by staying up to date on the latest threats, including Zero-Day Exploits, and utilizing tailored monitoring and efficient search capabilities.




































