
Top 10 Metrics Every CISO Should Track for Better Security
Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) must navigate a wide range of threats and vulnerabilities in order to effectively protect their organizations. As attacks become more complex and frequent, it is critical to monitor key metrics.
For CISOs, tracking specific cybersecurity metrics is about more than just evaluating technical defenses; it’s about building a resilient organization that can anticipate, withstand, and adapt to the changing threat landscape. Focusing on key metrics provides CISOs with visibility into both immediate vulnerabilities and long-term risks, allowing them to develop a proactive security strategy. Metrics provide a reliable way of measuring the impact of security investments, justifying resource allocation, and communicating security effectiveness with stakeholders.

DALL-E generated AI image for CISO
Metrics such as phishing attack frequency, endpoint protection coverage, and breach costs help CISOs evaluate the efficacy of their security initiatives, identify flaws, and make sound decisions. These metrics guide a proactive cybersecurity strategy, aligning the security team’s efforts with the organization’s goals and compliance requirements.
1. Cybersecurity Awareness Training
Building a strong cybersecurity awareness culture is critical for reducing human errors, which account for a significant portion of security breaches. According to Verizon’s 2024 report, 74% of cyber incidents are the result of human error, most commonly through phishing or social engineering attacks. By monitoring the effectiveness of awareness programs, CISOs can ensure that employees are well-prepared to identify and mitigate common threats.
Metrics like training completion rates, phishing simulation results, and reported incidents provide information about employee readiness. Continuous updates to these training programs are critical, especially as attackers adapt tactics such as Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) fatigue or increasingly sophisticated phishing techniques.
Incorporating cybersecurity awareness into corporate culture requires more than just regular training; it also necessitates making security a shared responsibility. Simulated attack scenarios, interactive workshops, and even gamification can help improve engagement and knowledge retention.
CISOs should track metrics such as the speed and accuracy with which employees report potential threats, as this reflects the practical effectiveness of awareness training.
2. Phishing Attacks
Tracking phishing attacks is critical because they are among the most common initial access vectors for cyberattacks. By tracking metrics such as the volume of phishing emails detected, the click-through rate on phishing simulations, and the percentage of employees who report phishing attempts, CISOs can assess both the prevalence of phishing threats and employee resilience. Monitoring these metrics helps to improve security training, identify high-risk departments, and adapt defenses to new phishing tactics, lowering the likelihood of successful attacks.
To strengthen your defenses, SOCRadar Labs provides the Phishing Radar service, which actively monitors for potential phishing domains targeting your organization. Phishing Radar detects spoofed domains by generating possible domain variations and searching domain databases.
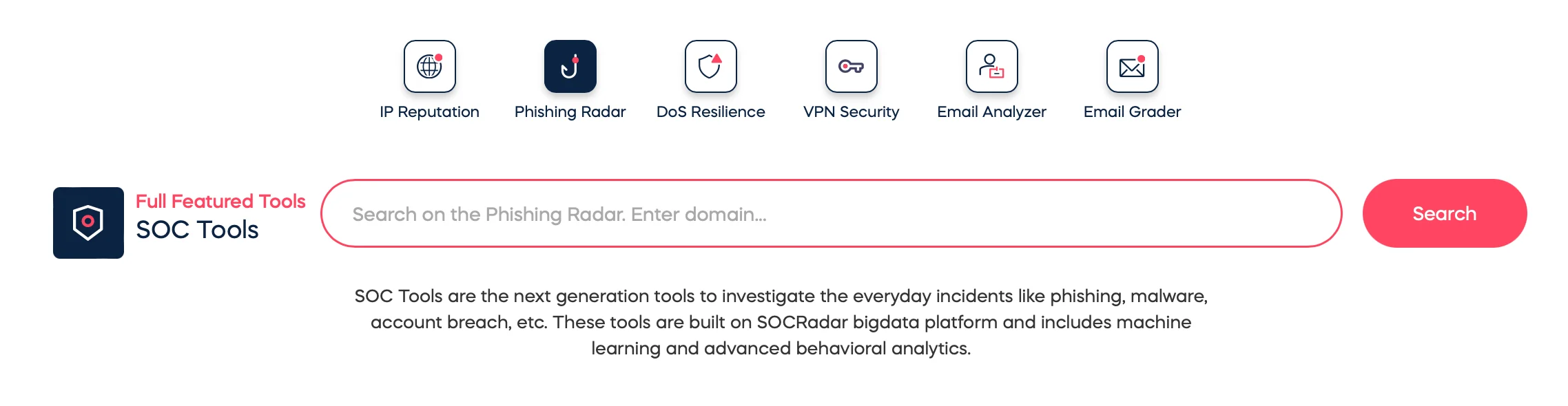
SOCRadar Labs Phishing Radar tool
This proactive tool enables CISOs to quickly identify and address phishing risks, thereby strengthening your organization’s overall security posture against increasingly sophisticated threats.
3. Intrusion Attempts
Intrusion attempts provide valuable information about the severity and persistence of threats to an organization’s infrastructure. CISOs should monitor metrics such as the frequency of detected intrusion attempts, attack source, and attack type (e.g., brute force, SQL injection).
Analyzing trends over time in intrusion attempts enables security teams to identify recurring patterns or persistent threat actors, allowing them to anticipate and mitigate attacks. These insights can reveal gaps in the organization’s defenses, such as unprotected endpoints or unpatched vulnerabilities, requiring timely upgrades and fortifications.
Furthermore, regularly reviewing this data allows security teams to fine-tune Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and automated response protocols, ensuring that they are ready to block increasingly sophisticated intrusion tactics. By transforming these metrics into actionable insights, CISOs can improve their organization’s resilience in the face of a rapidly changing threat landscape.
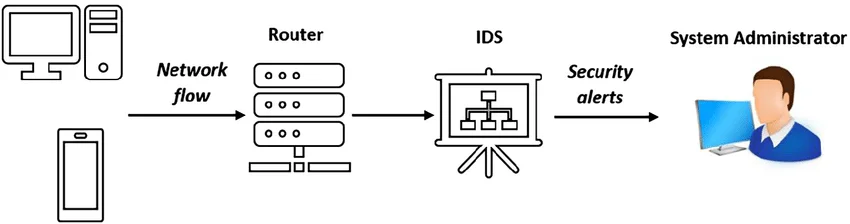
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) flow (source: ResearchGate)
4. Endpoint Protection Coverage
As remote work and mobile device usage increase, endpoint protection has become critical for securing an organization’s growing attack surface. Comprehensive endpoint security management entails ensuring that all user devices, such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets, are equipped with up-to-date protection software capable of detecting and responding to threats. Key metrics include the percentage of devices covered, update frequency, and endpoint threat detection rate, all of which provide critical insights into the organization’s endpoint security effectiveness.
EDR workflow
To maintain a strong security posture, CISOs should prioritize complete coverage of all endpoints, regular software updates, and strict security policies. Furthermore, centralized management tools are extremely useful for monitoring and enforcing consistent endpoint protection standards across multiple device types and operating systems. Strong endpoint protection prevents unauthorized access, detects malicious activity early, and protects sensitive data throughout the network.
SOCRadar’s insights into endpoint security trends and threat detection enable CISOs to make informed decisions about endpoint protection and response strategies, thereby increasing overall resilience to endpoint-driven cyberattacks.
5. Mean Time to Detect (MTTD)
The MTTD is an important metric for determining the effectiveness of an organization’s threat detection capabilities. It calculates the average time required to identify a security incident from its initial occurrence. A lower MTTD indicates more effective monitoring tools and processes, whereas a higher MTTD may reveal detection gaps. By monitoring this metric, CISOs can assess the effectiveness of their detection systems and ensure that their security teams are prepared to identify threats before they escalate.
6. Mean Time to Respond, Recover, and Resolve (MTTRs)
The MTTR includes the time required to respond to, recover from, and resolve a security incident. This metric helps CISOs understand the effectiveness and agility of their incident response team. A faster MTTR indicates a well-coordinated response plan and reduces the impact of an incident on the organization. CISOs benefit from regular MTTR analysis because it streamlines response processes, improves department collaboration, and reduces operational disruption caused by security incidents.
7. Third-Party Risk Management
As supply chain attacks become more sophisticated, managing third-party risks has become critical to a robust cybersecurity strategy. Attackers frequently use vulnerabilities in vendor systems to gain indirect access to their target organization. To prevent such breaches, CISOs must closely monitor and assess third-party vendors’ security practices.
Key Metrics for Effective Third-Party Risk Management:
- Percentage of Vendors with Up-to-Date Security Assessments: Regularly assessing vendors’ security practices ensures that each third-party meets the organization’s security requirements. This includes reviewing recent audits, certifications (such as SOC 2, ISO 27001), and penetration testing results.
- Frequency of Third-Party Security Incidents: Tracking incidents that originate with third-party vendors provides insight into the supply chain’s vulnerability level. Monitoring these incidents allows CISOs to better identify at-risk vendors and prioritize additional security assessments or mitigation strategies.
- Vendor Compliance with Security Standards: Vendors that follow recognized security standards, such as NIST, PCI-DSS, or GDPR, demonstrate a commitment to strong security. This compliance metric ensures that vendors maintain a standard level of security, lowering the likelihood of supply chain attacks affecting your organization.
- Risk Scores from Continuous Monitoring: CISOs can prioritize high-risk vendors by assigning them a risk score based on ongoing assessments and threat intelligence. Regular monitoring provides real-time updates on vendors’ security statuses, ensuring timely response to emerging threats.
Improving Third-Party Security with SOCRadar’s Supply Chain Intelligence
SOCRadar’s Supply Chain Intelligence gives CISOs complete visibility into their third-party ecosystem, allowing them to address supply chain threats more proactively. The 3rd Party Companies feature allows security teams to monitor high-priority vendors, receive risk scores, and access up-to-date assessments from an extensive database.
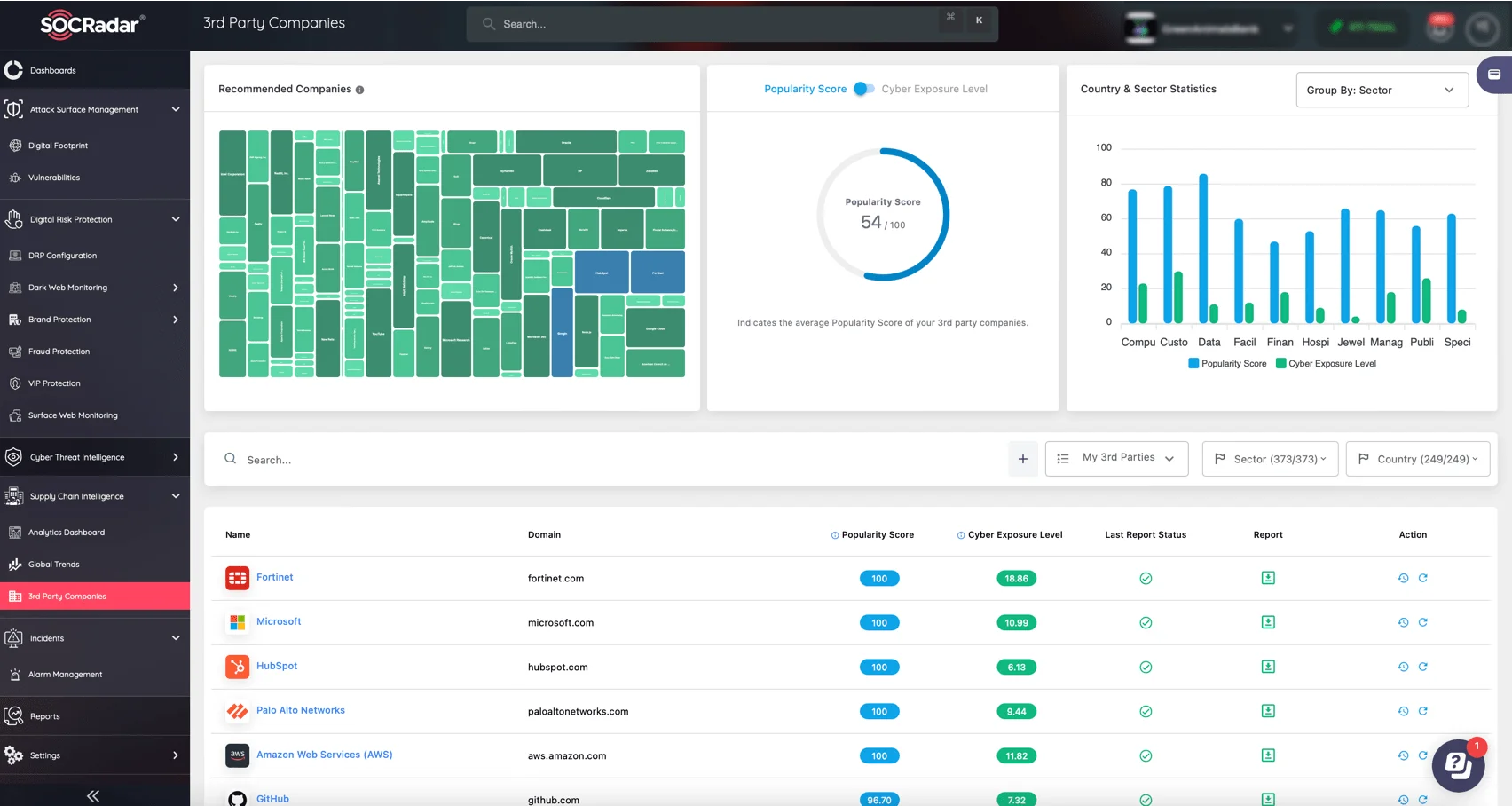
SOCRadar’s Supply Chain Intelligence 3rd Party Companies feature
SOCRadar’s dynamic approach continuously scans for vulnerabilities associated with third parties, providing real-time intelligence on security alerts and trends. This proactive insight enables CISOs to make data-driven decisions while strengthening supply chain security against emerging threats.
8. Identity and Access Management (IAM) Metrics
Identity and Access Management (IAM) metrics are critical for CISOs in ensuring that sensitive resources are only accessible to authorized users, lowering the risk of insider threats and other access-related vulnerabilities. The number of privileged accounts, the frequency of access reviews, and the organization’s Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) adoption rate are all important IAM metrics to keep track of. By keeping track of the number of privileged accounts, CISOs can restrict access to critical systems, reducing the potential damage from an insider threat or account compromise.
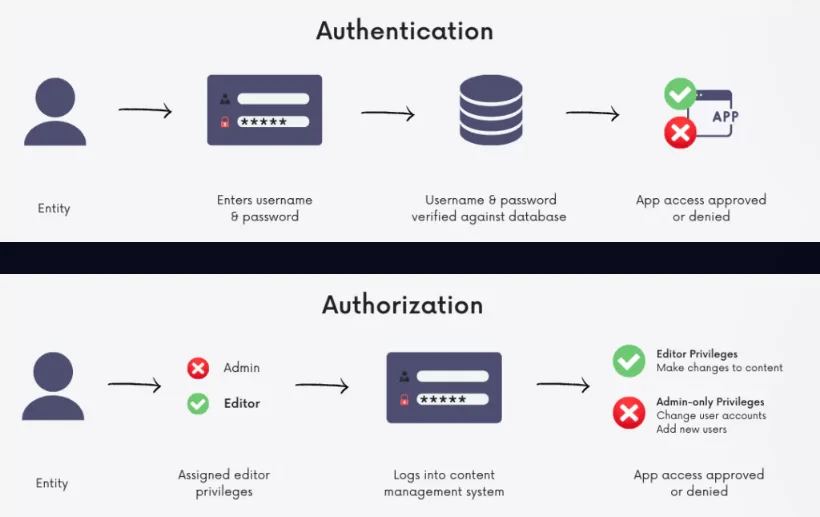
IAM solutions showcase
Regular access reviews are required to ensure that users have only the permissions they require for their roles, preventing privilege creep and ensuring alignment with job responsibilities. MFA adoption rate is also an important metric, as it significantly improves security by adding a second layer of authentication, lowering the risk of unauthorized access.
9. False Positive Rate
False positives, or incorrect threat detections, can consume resources and cause alert fatigue in security teams. Tracking the false positive rate enables CISOs to evaluate the accuracy of security tools and make adjustments to improve detection mechanisms. A high false positive rate can obscure real threats, so a balanced, low false positive rate ensures that security teams focus on legitimate incidents. Regularly reviewing and optimizing detection systems enables CISOs to strike a balance between robust detection and efficient response.
10. Breach Costs
Understanding the financial impact of a security breach is critical for CISOs to justify cybersecurity investments and ensure sufficient budget allocation for future protections. Breach costs include direct expenses such as legal fees, system repairs, and notification of affected parties, as well as indirect costs like lost revenue, brand damage, and customer trust erosion. Tracking these expenses helps CISOs quantify the overall financial effect of breaches on the organization and allows them to measure the effectiveness of incident response strategies over time.
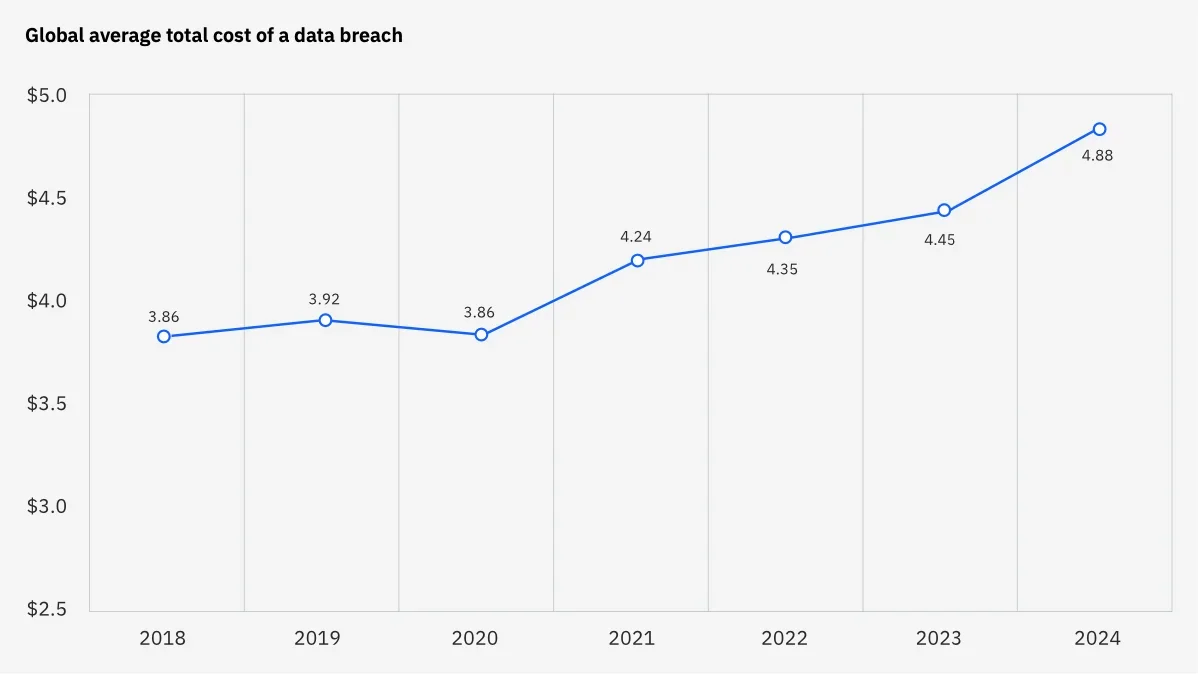
Global Average Total Cost of a Data Breach – Source: IBM Cost of a Data Breach 2024
A detailed analysis of breach costs can be found in IBM’s Cost of Data Breach Report 2024, which revealed that the global average cost of a data breach has risen to $4.88 million, with the healthcare sector seeing the highest impact at $9.77 million per breach. The report highlights key cost drivers, including operational downtime, customer loss, and regulatory penalties. For more insights, read the full report on the cost of data breaches here.
Conclusion
To effectively manage cybersecurity, CISOs must use metrics to identify vulnerabilities, allocate resources strategically, and adapt to emerging threats. These metrics provide CISOs with critical insights into their organization’s security posture. By closely monitoring and analyzing them, CISOs can create a security-conscious culture, increase resilience, and make data-driven risk-reduction decisions. As the threat landscape evolves, focusing on these metrics will help organizations remain prepared and secure in the face of future challenges.





































