
What You Need to Know About the CTI Capability Maturity Model (CTI-CMM)
As cyber threats grow in complexity and frequency, organizations are left grappling with how to respond effectively. Many struggle to keep pace due to a staggering shortfall of 3.12 million cybersecurity professionals worldwide. Enter the Cyber Threat Intelligence Capability Maturity Model (CTI-CMM) – a framework designed to empower organizations to build and enhance their cyber threat intelligence (CTI) programs, regardless of size or industry.
Introduced in August 2024 by a diverse coalition of industry leaders, CTI-CMM provides a roadmap for continuous improvement. It helps align CTI efforts with business goals, ensuring that intelligence protects and drives strategic decisions.

Cyber Threat Intelligence Capability Maturity Model (cti-cmm.org)
In an era where global cybercrime damages are expected to reach $9.5 trillion, adopting frameworks such as the CTI-CMM could be the key to staying ahead of evolving threats. In this article, we’ll explore the critical aspects of CTI-CMM, why it matters, and how it can transform your organization’s approach to cybersecurity.
What is CTI Capability Maturity Model?
The CTI Capability Maturity Model is a framework for organizations to develop, evaluate, and improve their Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) programs. It serves as a road map for coordinating CTI efforts with organizational goals, ensuring that intelligence is collected, actionable, and valuable for decision-makers.
Ultimately, the purpose of CTI-CMM is to integrate CTI initiatives with stakeholder needs and organizational priorities, enabling organizations to transform raw intelligence into actionable insights that directly support cybersecurity strategies.
Why Does CTI-CMM Matter?
Threats are more frequent and sophisticated in today’s complex cyber environment. A well-developed CTI program enables organizations to proactively identify, analyze, and respond to these threats before damage occurs.
In alignment, the CTI Capability Maturity Model helps organizations assess their CTI efforts, ensuring they are both reactive and proactive in defending against emerging threats. A mature CTI program provides deeper insights into adversaries’ tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs), reducing risk exposure.
Using CTI-CMM, organizations can measure current capabilities, identify gaps, and refine their approach to align with cybersecurity objectives. Therefore, for any organization aiming to protect its assets, a mature CTI program is crucial in defending against data breaches, operational disruptions, and other security incidents.
To align your CTI efforts with organizational goals, check out SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management (ASM) module. With ASM, you can actively monitor organizational digital assets and receive real-time alerts, staying ahead of potential threats and maintaining alignment with your cybersecurity objectives.
Key Features and Principles of CTI-CMM
Now that we understand the importance of CTI-CMM, let’s explore the key features and principles that guide this model.
The CTI Capability Maturity Model was designed to provide organizations with a structured approach to enhancing their CTI programs, ensuring they remain effective and aligned with stakeholder needs. Several key features and principles set CTI-CMM apart as a valuable tool for organizations of all sizes.
Collaborative Development
CTI-CMM was created through the combined efforts of industry experts across various sectors, geographies, and disciplines. This collaborative approach ensures the model is grounded in real-world experiences and best practices. By leveraging diverse expertise, CTI-CMM fosters a community-driven approach to cyber threat intelligence. This collaboration is vital, reflecting the complex and interconnected nature of cybersecurity and ensuring the model remains effective across industries.
Vendor-Neutral Approach
CTI-CMM is independent of specific vendors, making it adaptable for any organization, regardless of the technologies they use. This neutrality allows businesses to adopt the model without being restricted by proprietary systems. It promotes continuous improvement by focusing on CTI capabilities that align with unique organizational needs rather than product limitations.
CTI-CMM is guided by several principles:
- Collaboration: Emphasizing close work with stakeholders to ensure CTI delivers actionable insights that support decision-making.
- Stakeholder Focus: Ensuring CTI aligns with stakeholder needs to provide real organizational value.
- Iterative Processes: Recognizing that intelligence is dynamic, CTI-CMM encourages continuous improvement through self-assessment and adaptation.
With these principles in place, CTI-CMM is structured around 10 domains, each designed to enhance different areas of cyber threat intelligence, from risk management to situational awareness.
Structure of CTI-CMM – The 10 Domains
The CTI Capability Maturity Model is organized into 10 domains, each focusing on a specific aspect of cyber threat intelligence (CTI). Together, these domains provide a comprehensive framework that helps organizations assess and improve their CTI programs. Here’s a concise look at each domain and how it contributes to enhancing CTI capabilities:
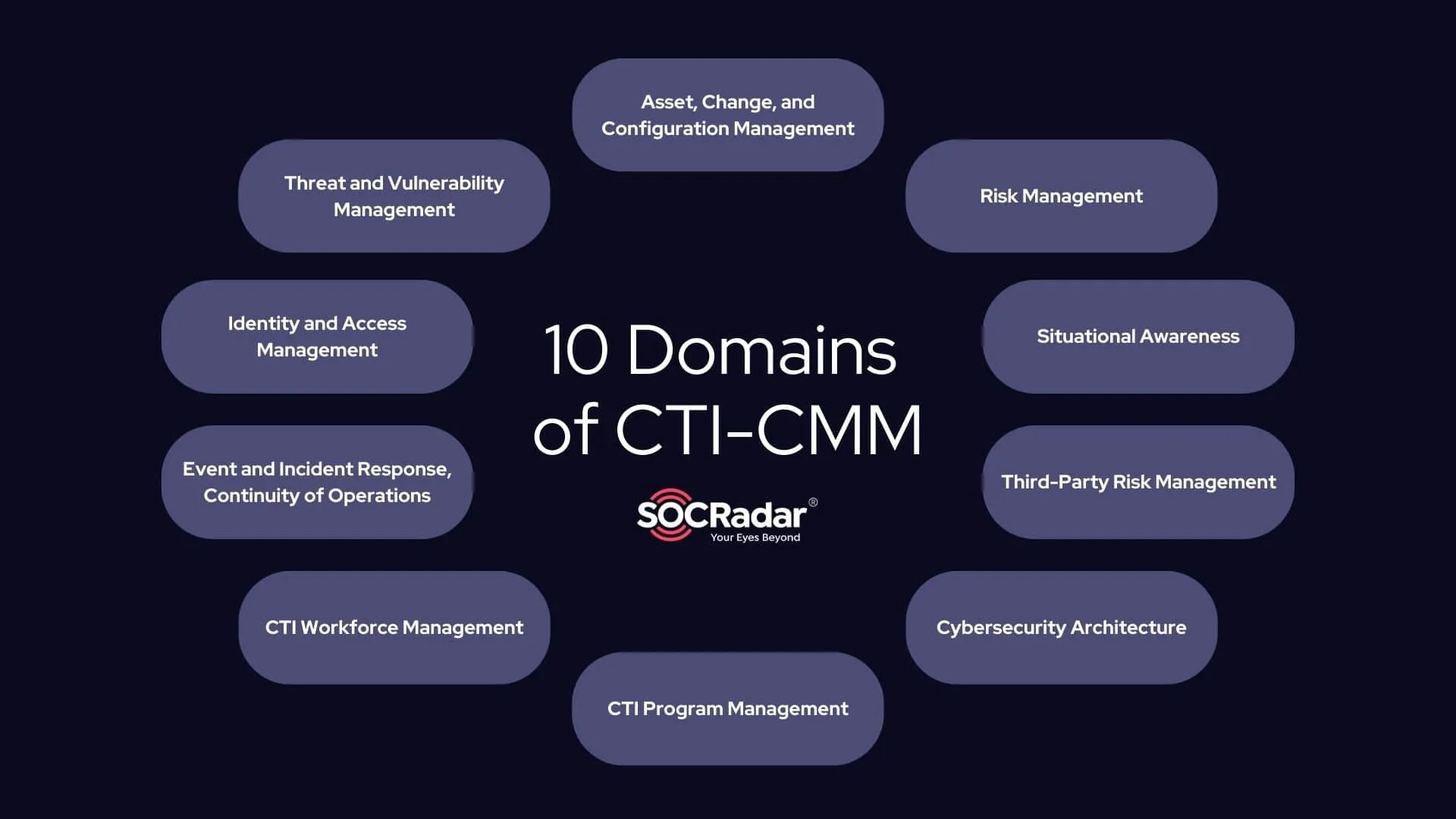
Ten domains of the CTI Capability Maturity Model
- Asset, Change, and Configuration Management manages IT and operational assets to minimize exposure to cyber threats.
- Threat and Vulnerability Managementdetects and responds to emerging threats, helping organizations stay aware of the evolving threat landscape and mitigate vulnerabilities.
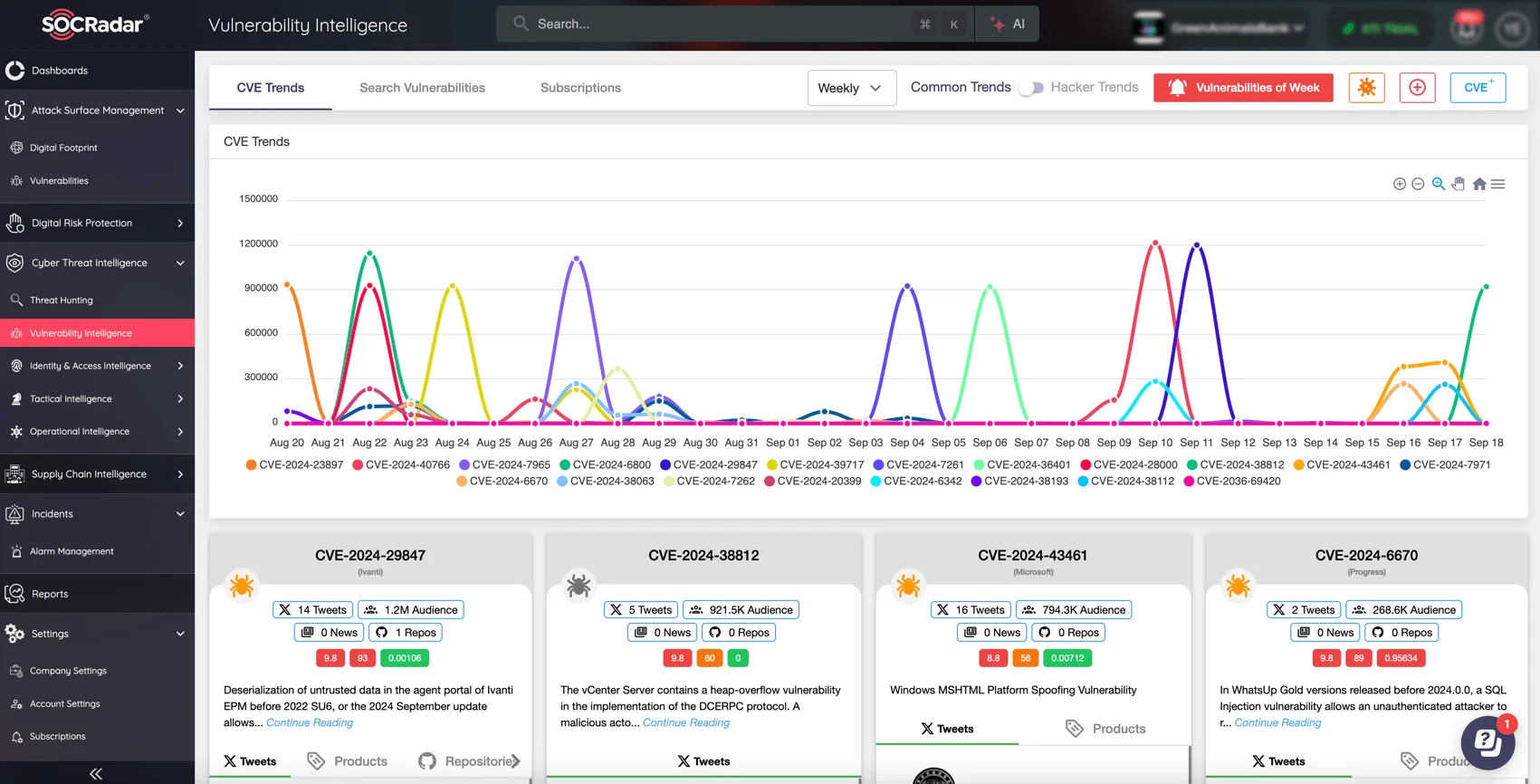
For example, SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence provides real-time updates on emerging vulnerabilities, enabling organizations to respond swiftly.
- Risk Management integrates cyber risk into enterprise risk management, aligning CTI efforts with organizational goals to inform risk reduction strategies.
- Identity and Access Management manages identities and system access based on risk assessments, controlling how users and systems interact to reduce unauthorized access risks.
SOCRadar’s Identity & Access Intelligence module focuses on detecting leaked credentials and other sensitive access information before they can be exploited. By monitoring data from stealer logs and other underground sources, SOCRadar helps organizations mitigate the risk of credential theft.
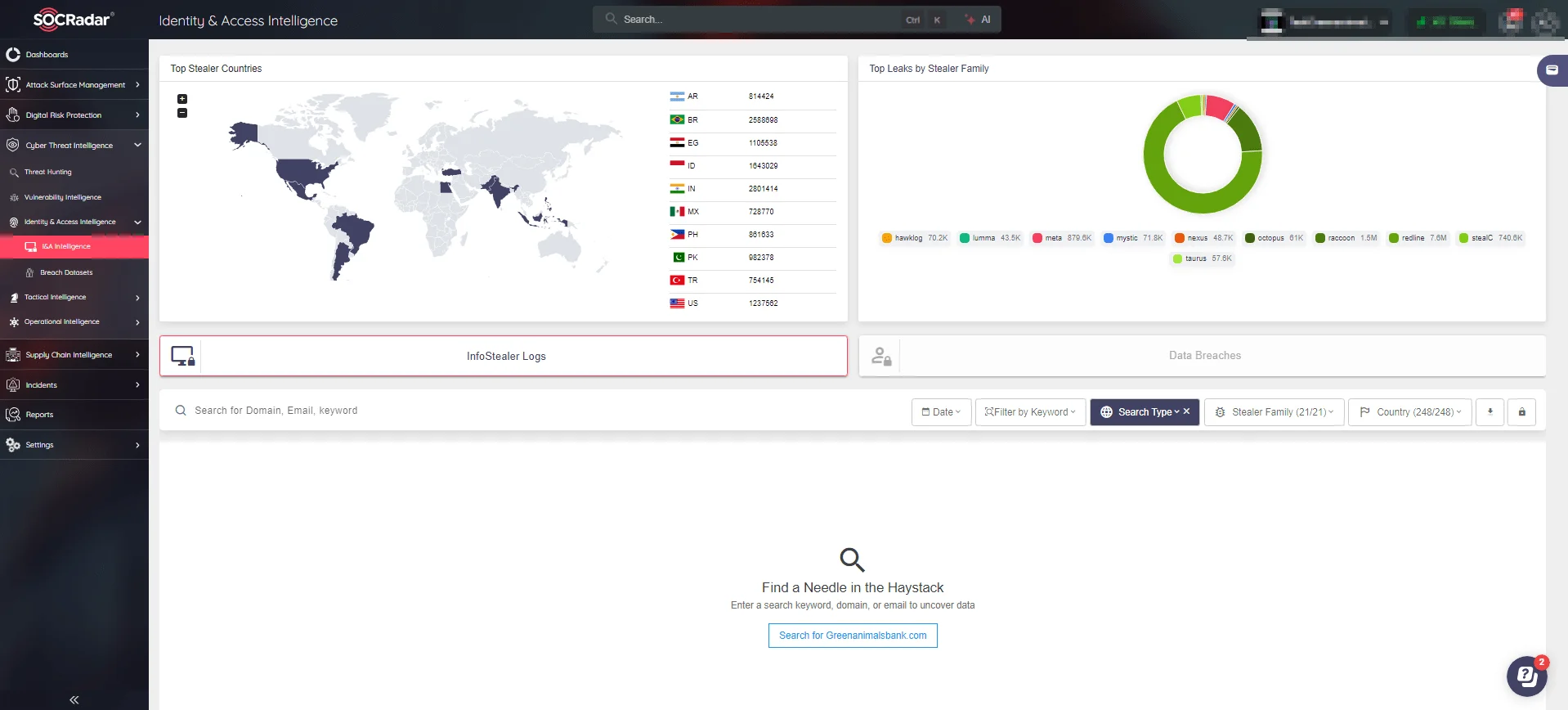
SOCRadar’s Identity & Access Intelligence module page
Rather than just identifying compromised accounts, this module offers insights into how access data was stolen, allowing organizations to address the root causes of exposure and strengthen their defenses. By taking proactive action, organizations can protect themselves from potential unauthorized access, especially when credentials are leaked on underground markets.
- Situational Awareness helps collect and analyze security data to provide a clearer view of the threat environment, enabling real-time decision-making.
- Event and Incident Response, Continuity of Operations develops response plans to handle incidents and ensures that operations continue during cyberattacks or security events.
- Third-Party Risk Management helps assess and manage cyber risks from third-party vendors. Continuous monitoring mitigates supply chain vulnerabilities.
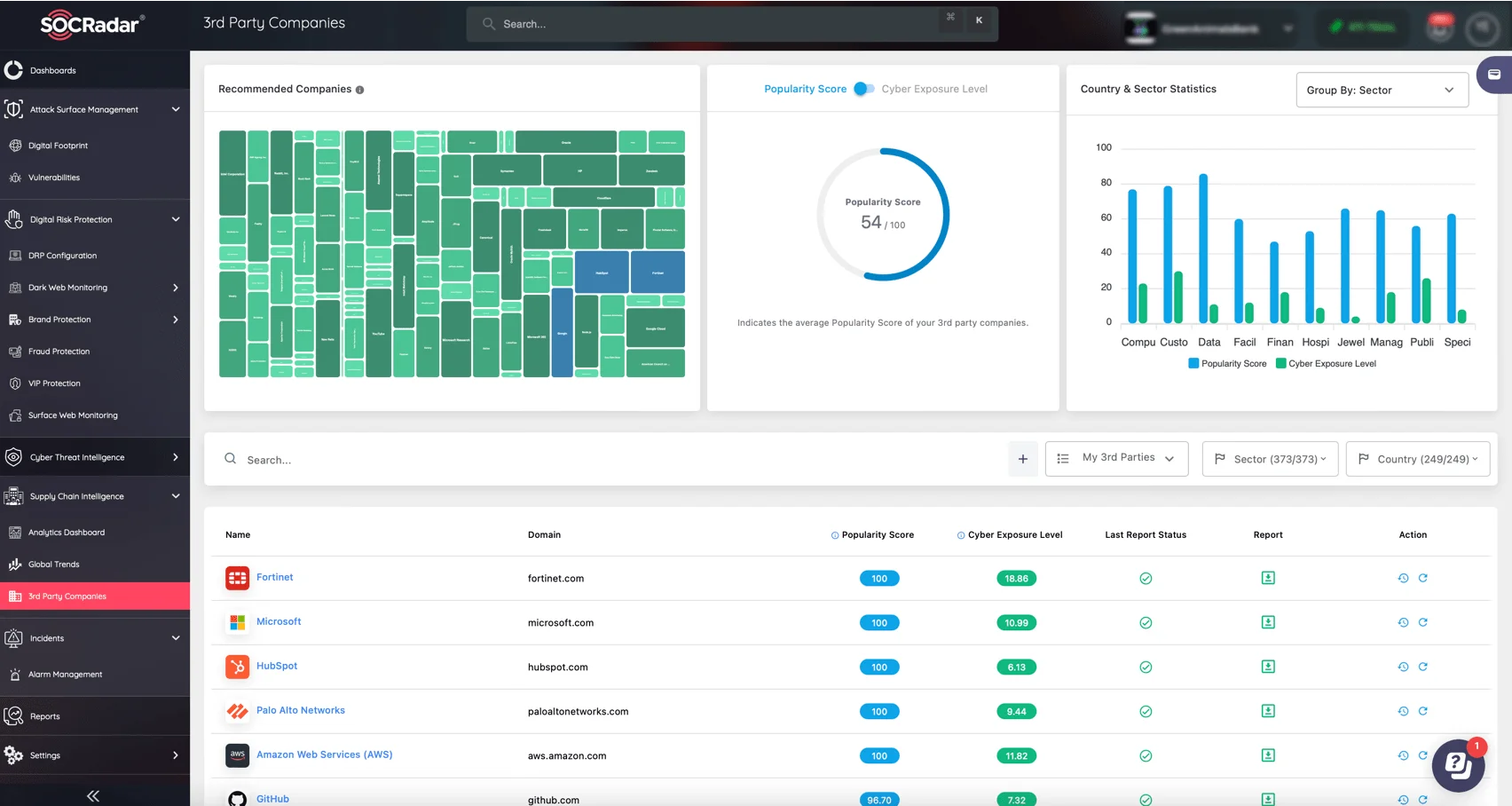
Similarly, SOCRadar’s Supply Chain Intelligence helps identify risks introduced by third-party vendors, keeping critical supply chains secure.
- CTI Workforce Management emphasizes building a skilled workforce knowledgeable about organizational risks, which is critical to a successful CTI program.
- Cybersecurity Architecture aligns security controls with potential threats, focusing on building a solid infrastructure to withstand evolving cyberattacks.
- CTI Program Management governs the CTI program to align with organizational objectives, ensuring resilience and continuous improvement against cyber threats.
How These Domains Support CTI
The ten domains of the CTI Capability Maturity Model work together to create a well-rounded approach to cyber threat intelligence. Each domain addresses a different aspect of cybersecurity, from managing assets and vulnerabilities to ensuring an organization’s workforce is prepared for emerging threats.
For example, Situational Awareness helps organizations understand their current threat landscape, while Risk Management ensures that identified risks are mitigated in line with the company’s overall strategy.
By integrating these domains, CTI-CMM enables organizations to strengthen various aspects of their CTI program, ensuring they remain adaptive and resilient in an ever-evolving cyber threat environment. Each domain provides a piece of the puzzle, forming a holistic approach to cybersecurity that goes beyond individual silos.
Next, let’s look at the maturity levels organizations can achieve as they implement the CTI-CMM framework.
Cyber Threat Intelligence Maturity Levels in CTI-CMM
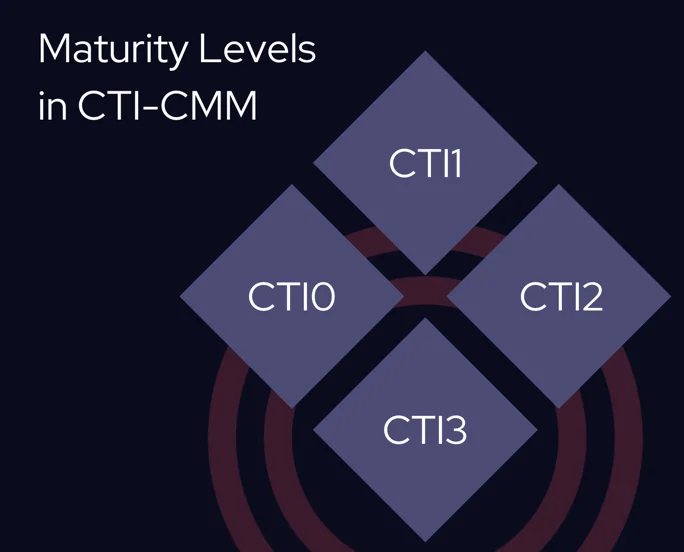
The CTI Capability Maturity Model defines four distinct maturity levels that help organizations evaluate the progress and effectiveness of their cyber threat intelligence (CTI) programs. Each level represents a step in developing CTI capabilities, from the absence of structured processes to a fully mature, integrated intelligence function.
What are the CTI maturity levels covered in this model?
- CTI0 (Pre-Foundational): Organizations at this level lack formal CTI processes and established practices for handling cyber threat intelligence, leaving them highly vulnerable to cyber risks. This stage represents a significant gap in their ability to address evolving threats.
- CTI1 (Foundational): CTI efforts are reactive at this stage, with intelligence gathered on each new case. While some initial capabilities exist, there’s no cohesive strategy, and the focus is on short-term problem-solving rather than proactive threat management.
- CTI2 (Advanced): Organizations at the advanced level have structured CTI practices, moving toward proactive intelligence gathering. They use predictive intelligence to anticipate threats and integrate CTI more fully into their cybersecurity framework, delivering medium-term results.
- CTI3 (Leading): At the highest maturity level, organizations use prescriptive intelligence to predict threats and offer actionable recommendations aligned with business goals. CTI practices are measurable, integrated into the business, and contribute to long-term strategic outcomes.
Moving from Foundational to Leading
Progressing from CTI1 (Foundational) to CTI3 (Leading) requires organizations to transition from reactive, unstructured intelligence efforts to proactive and predictive strategies deeply embedded within the business.
The shift from CTI1 to CTI2 involves:
- Formalizing CTI processes.
- Ensuring regular intelligence collection.
- Moving from short-term responses to more strategic, medium-term planning.
Organizations must invest in resources, tools, and training to build a more structured CTI function that anticipates and mitigates emerging threats.
To reach CTI3, organizations need to elevate their practices further, focusing on prescriptive intelligence aligned with long-term business goals. This level of maturity requires close collaboration between CTI teams and other business units to ensure intelligence is actionable and directly contributes to strategic outcomes.
By measuring the effectiveness of their intelligence activities and continuously refining their processes, organizations can create a CTI program that shapes their cybersecurity posture in anticipation of future challenges.
Driving Organizational Success with CTI
Understanding the maturity levels helps organizations assess their current standing, but how do you implement the CTI Capability Maturity Model to improve your capabilities? While the CTI-CMM provides a roadmap for developing your Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) program, it aligns those efforts with your business objectives, ensuring your security initiatives deliver tangible value. By adopting this model, organizations can better manage and mitigate threats while simultaneously meeting the needs of stakeholders.
CTI Capability Maturity Model fosters a continuous improvement approach, promoting regular self-assessment and refinement to stay ahead of evolving cyber threats. This ongoing adjustment keeps CTI programs agile and responsive, ensuring they provide actionable intelligence that helps decision-makers mitigate risks effectively. The maturity roadmap offered by CTI-CMM further supports growth, guiding organizations to enhance their CTI capabilities over time in a structured, measurable way.
Building a Future-Ready CTI Program
Implementing the CTI Capability Maturity Model enables organizations to strengthen their CTI programs and build a more resilient, future-proof cybersecurity approach. The following steps offer a guide to adopting the CTI-CMM framework.

Steps to implement the CTI-CMM model
The process begins by engaging key stakeholders and setting clear objectives (Step 0: Prepare), ensuring the CTI program is aligned with broader organizational goals. A self-assessment follows (Step 1: Assess), allowing organizations to evaluate their capabilities across the 10 CTI domains, identify gaps, and establish priorities.
Based on the gathered insights, organizations can then plan (Step 2: Plan) and deploy (Step 3: Deploy) the necessary resources, focusing on the areas that will deliver the most impact.
Finally, continuous monitoring (Step 4: Measure) ensures that CTI efforts align with organizational objectives and the ever-changing threat landscape, promoting constant improvement and long-term security resilience.
Conclusion
The CTI Capability Maturity Model (CTI-CMM) provides a structured, clear path for organizations to improve their cyber threat intelligence (CTI) programs, ensuring their responsiveness to the changing cyber threat landscape. By aligning CTI initiatives with stakeholder needs, promoting continuous self-assessment, and providing a roadmap for maturity, the model equips organizations with the tools to protect their digital assets more effectively.
As organizations progress through CTI maturity levels, leveraging all-in-one tools like SOCRadar’s Extended Threat Intelligence (XTI) becomes essential for proactive security management. With its many modules, such as Dark Web Monitoring, Threat Actor Intelligence, Vulnerability Intelligence, and Identity & Access Intelligence, SOCRadar helps organizations detect and respond to threats before they can escalate into serious breaches. Such tools empower security teams to anticipate risks, make informed decisions, and take action swiftly, aligning intelligence with strategic business goals in the easiest way.
Whether you’re in the early stages of building a CTI program or looking to take your efforts to the next level, the CTI Capability Maturity Model enables continuous growth, strategic alignment, and meaningful stakeholder engagement. It strengthens your security posture and ensures your CTI efforts deliver value where it matters most across the organization.
Adopting CTI-CMM is a proactive step toward achieving cybersecurity maturity, empowering your organization to anticipate threats, respond swiftly, and stay ahead of potential risks. As cyber threats become more sophisticated, investing in a robust, mature CTI program and leveraging tools like SOCRadar’s XTI modules helps maintain resilience and long-term security success.




































