
Cybersecurity in 2025: A Look Back at 2024’s Biggest Cyber Attacks & Lessons for the Future
The year 2024 saw a surge in high-profile cyber attacks across various industries, exposing the vulnerabilities that businesses and governments face in our increasingly interconnected world. From devastating ransomware incidents to sophisticated supply chain attacks, the cyber threats are dynamic.
Industries such as healthcare, telecommunications, finance, and government services bore the brunt of major cyber attacks, with critical infrastructure and sensitive data at risk. In fact, global cybercrime damage costs are expected to grow, reaching $10.5 trillion USD annually in this year, according to Cybersecurity Ventures.

Trends and strategies for cybersecurity in 2025 (Image illustrated by DALL-E)
One significant trend that dominated in 2024 was the targeting of supply chains, with attackers leveraging third-party vulnerabilities to breach multiple organizations at once. Ransomware groups like Termite and Salt Typhoon, along with vulnerabilities in services like Snowflake and Ivanti, made headlines, resulting in data theft, service disruptions, and financial losses. Even major government agencies, including the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), fell victim to SIM-swapping and credential theft attacks, highlighting that no organization is immune to threat actors’ tricks.
To mitigate these rising risks, it is critical for businesses to integrate advanced threat intelligence solutions into their cybersecurity strategies. SOCRadar’s Extended Threat Intelligence (XTI) platform offers real-time monitoring of potential threats across your supply chain, internal systems, and cloud environments, enhancing your ability to respond to and prevent breaches.
In this article, we will look into the most significant cyber attacks of 2024, break down the lessons learned, and offer key recommendations on how to better prepare your strategy for cybersecurity in 2025. From incident overviews to actionable takeaways, we’ll help you learn from 2024 navigate the new year of 2025.
Breach of CISA Highlighted the Risks in Third-Party Vulnerabilities
In early 2024, the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) became the victim of a security breach linked to vulnerabilities within Ivanti VPN products. This breach was driven by multiple flaws, namely CVE-2023-46805, CVE-2024-21887, and CVE-2024-21893, that allowed attackers to remotely infiltrate and control two of CISA’s key systems. The targeted systems, including the Infrastructure Protection (IP) Gateway and the Chemical Security Assessment Tool (CSAT), are essential for monitoring U.S. critical infrastructure and chemical safety.
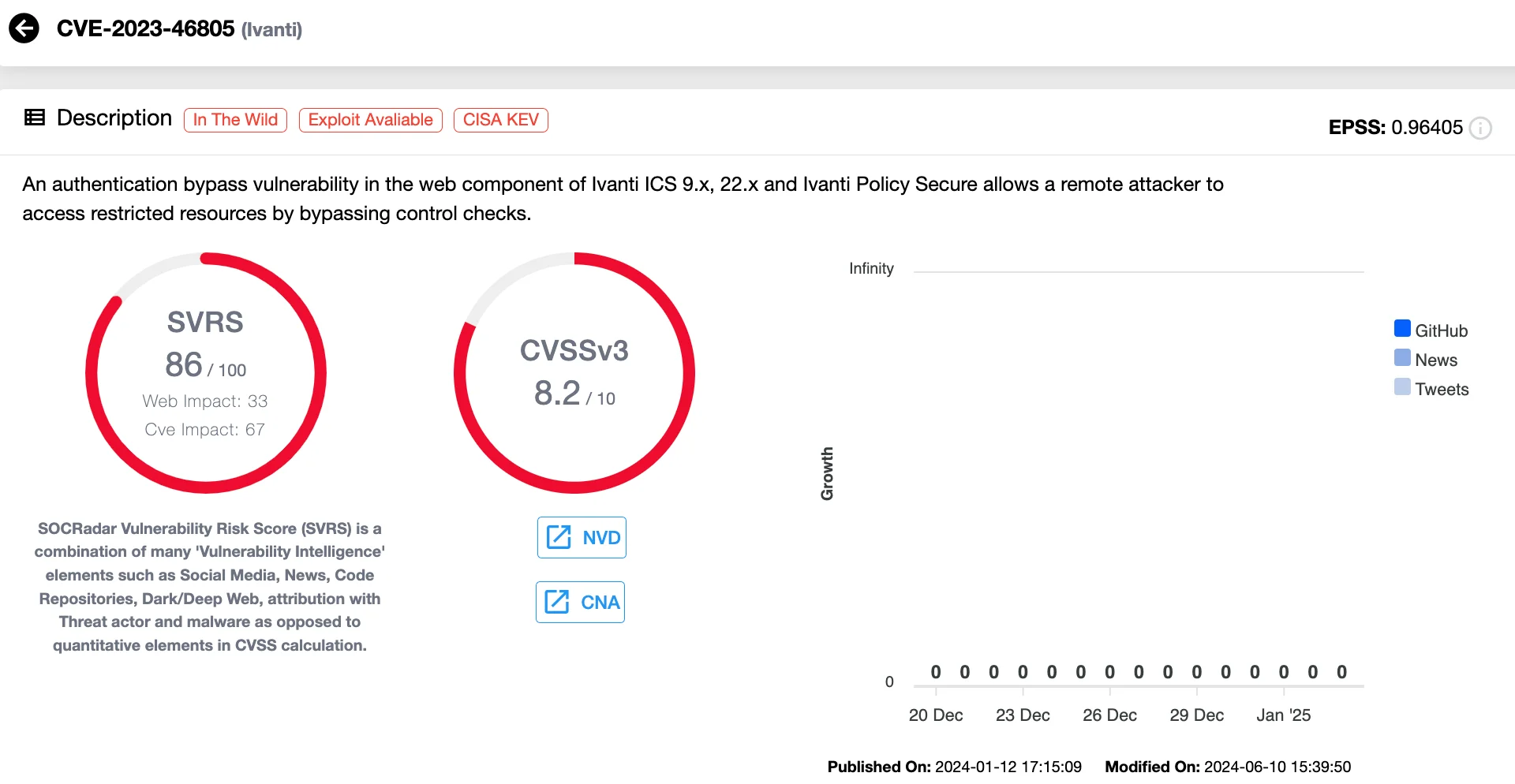
Vulnerability card of CVE-2023-46805 (SOCRadar Vulnerability Intelligence)
CISA’s breach came to light after a month-long delay, with the agency only confirming the incident in March 2024. Upon detecting suspicious activities, CISA acted swiftly to disconnect affected systems and prevent further damage.
While it was not revealed if data had been stolen, the breach demonstrated the vulnerability of even government entities to third-party software weaknesses. In response, CISA temporarily disconnected all federal agencies from Ivanti’s systems to mitigate the risk until patches were applied.
Important lessons from this breach include:
- Vulnerability management is critical. Regularly patching and securing third-party software, on a schedule, is vital in preventing attacks.
- Monitor all your digital assets, always. Continuous monitoring of systems helps to quickly detect suspicious activities before they can escalate.
- Have strong incident response plans in place. Even with quick detection, organizations must be prepared with effective plans to contain breaches swiftly and minimize their impact. Ensure your incident response plans are well-practiced and tested.
To enhance your organization’s defenses, SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence module helps identify and prioritize vulnerabilities affecting your systems, offering real-time alerts and guidance to reduce exposure and strengthen your security posture.
SOCRadar’s Vulnerability Intelligence
The SEC Breach Exemplified How SIM Swapping Is a Growing Threat
Another breach, this time at a social platform account of an independent agency of the U.S. federal government, highlighted the growing danger of SIM swapping attacks. In January 2024, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) became a victim of this increasingly common threat.
In this incident, an attacker managed to hijack the SEC’s phone number, bypassing its Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) system, which had been disabled months earlier. Despite having MFA in place, the SEC was compromised because the critical authentication method had been disabled.
Once in control of the SEC’s phone number, the attacker posted false information on the SEC’s X (formerly Twitter) account, claiming approval of Bitcoin Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs). This led to a temporary spike in Bitcoin prices, altering the cryptocurrency market values, before the SEC clarified the misinformation.

The fraudulent tweet sent by the threat actors on SEC’s account
Importantly, SIM swapping attacks have been rising in frequency. In 2023, the FBI reported losses exceeding $48 million from SIM swapping, and by the end of 2024, more than 800 cases were recorded for the year. This incident at the SEC underscores the growing vulnerability of not just individuals but also institutions, including government agencies, to these types of attacks.
Here are the key lessons from this attack:
- Don’t rely solely on SMS-based MFA. While MFA adds an extra layer of security, it can be bypassed if phone numbers are not properly secured.
- Ensure persistent authentication protection. MFA should remain consistently enabled, especially for sensitive accounts, to prevent unauthorized access. Employ secure alternatives, such as app-based or hardware token authentication, to mitigate the risk of SIM swapping.
- Monitor and secure mobile accounts. Mobile phone numbers are often the gateway to accessing other critical accounts and should be treated as an asset to protect. Monitor mobile accounts for signs of suspicious activity and implement protections like number portability locks with service providers.
For more information on SIM swapping and how to protect your organization, check out SOCRadar’s recent blog post: “The Threat of SIM Swapping Attacks on Financial Institutions”
Healthcare Organizations Were Among the Top Targets of Cybercrime in 2024
The healthcare industry faced several significant cyber attacks in 2024, underscoring vulnerabilities within this critical industry. These attacks, ranging from ransomware to data breaches, have exposed sensitive patient and organizational data, while also disrupting essential services. Notably, healthcare providers and their partners continue to grapple with the complexities of securing data in the face of these attacks.
Change Healthcare Attack
One of the most high-profile incidents occurred early in 2024 when Change Healthcare, a major provider of IT solutions for the healthcare industry, was targeted by a ransomware attack from the ALPHV/BlackCat group.
The attack disrupted prescription drug distribution for over ten days, affecting both patients and healthcare providers. Concerns about further data breaches were raised, as reports indicated that UnitedHealth Group, a key partner of Change Healthcare, may have paid a hefty ransom of $22 million to recover encrypted data. However, this claim has not been officially confirmed by either party, and even if the ransom was paid, the stolen data was not deleted, leaving the door open for further exploitation.

ALPHV’s victim listing of Change Healthcare in 2024 (Source: SOCRadar Dark Web News)
Cencora Healthcare Attack
Cencora Healthcare also fell victim to a significant breach in February 2024, which compromised data from top pharmaceutical companies such as Novartis, Bayer, and AbbVie.
The breach exposed sensitive patient data, including names, diagnoses, and prescriptions. Despite the widespread exposure, no fraudulent activities or public disclosures have been reported. The breach highlighted the ongoing threats to healthcare organizations and their partners, who store vast amounts of sensitive data.
HealthEquity Attack
Similarly, in March 2024, HealthEquity, a leading healthcare benefits administrator, reported a breach affecting 4.3 million individuals.
The breach, caused by unauthorized access to an unstructured data repository through a vendor’s compromised account, exposed critical data such as Social Security numbers and health diagnoses. This incident raised alarm over third-party vendor security, reinforcing the need for heightened vigilance when it comes to managing external relationships in the healthcare industry.
These were not the only well-known healthcare companies that experienced cyber attacks in 2024; names like HCA Healthcare, Rite Aid, and NHS were also targeted. In these cases, a prior HCA Healthcare data breach resurfaced on Dark Web forums, RansomHub hackers targeted Rite Aid, and Qilin targeted NHS.
To enhance cybersecurity in 2025, the healthcare industry must focus on:
- Ransomware preparedness: Strengthen defenses against ransomware with advanced threat detection and proactive mitigation strategies. Regularly update and patch critical systems to reduce the risk of exploitation.
- Third-party vendor security: Given the vulnerabilities introduced through vendors, healthcare organizations must enforce strict third-party risk management practices. This includes conducting regular security assessments and ensuring vendors comply with cybersecurity standards.
- Data encryption and backup: Encrypt sensitive data both in transit and at rest. Ensure that regular backups are maintained, enabling organizations to quickly recover in case of an attack.
Gaining intelligence about your adversaries will help you overcome the digital risks. SOCRadar’s Threat Actor Intelligence and Ransomware Intelligence modules offer detailed profiles of cybercriminals targeting the healthcare sector and beyond, providing real-time updates and actionable insights. By integrating this intelligence into your security strategy, you can stay steps ahead and enhance both your prevention and response to cybersecurity threats in 2025.
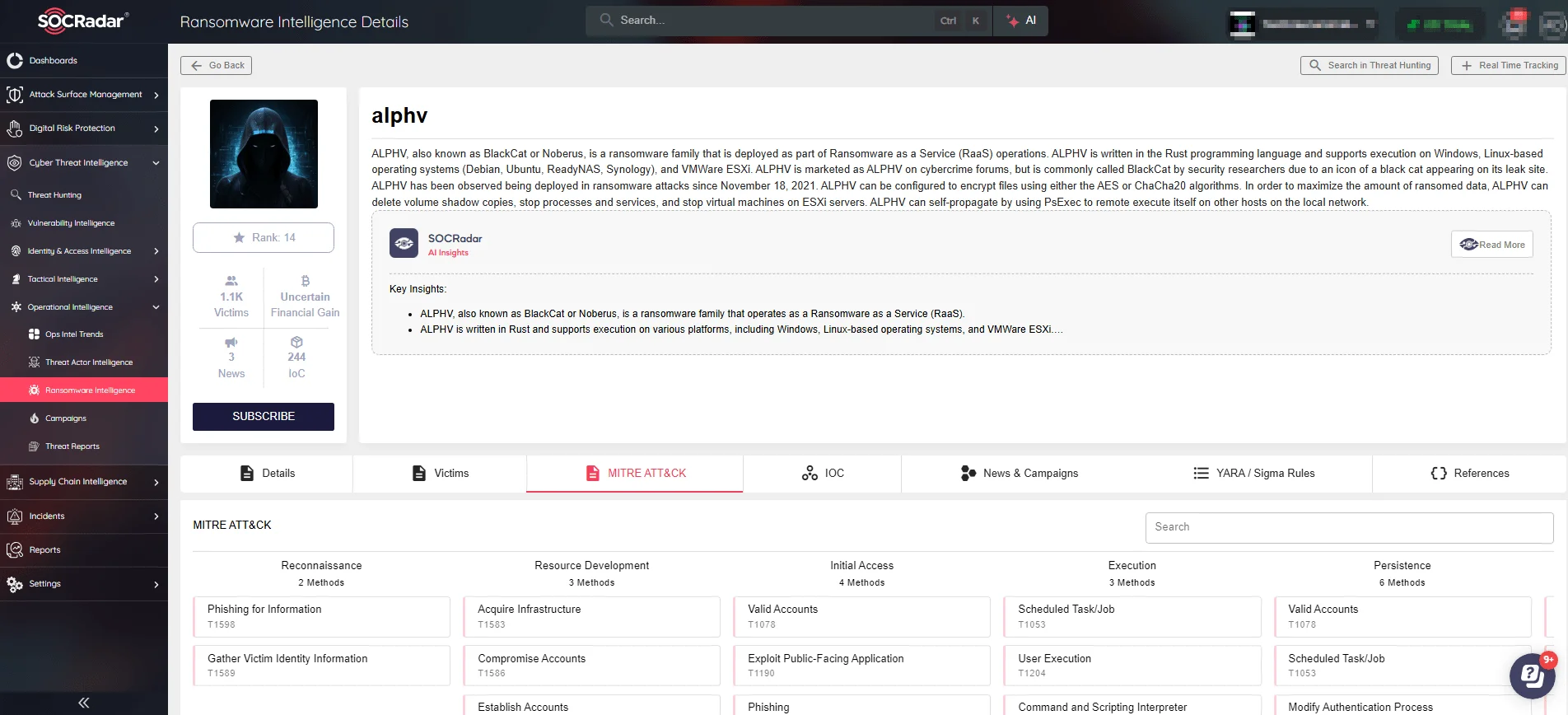
Details of ALPHV (BlackCat) on SOCRadar’s Ransomware Intelligence module
For a deeper dive into the cybersecurity landscape in healthcare, check out SOCRadar’s Healthcare Industry Threat Landscape Report.
The 2024 FBCS Hack, A Wake-Up Call for Third-Party Security
In February 2024, Financial Business and Consumer Solutions (FBCS), a U.S.-based debt collection agency, became the target of a significant ransomware attack that exposed sensitive data for over 4 million individuals.
Even without major players like LockBit and BlackCat (ALPHV) dominating the threat landscape, ransomware victims in Q1 2024 rose by nearly 20% – as 2025 is already here, the threat continues to escalate.
The FBCS breach lasted from February 14 to 26 and affected several high-profile clients, including Comcast and Truist Bank. The compromised data included names, Social Security numbers (SSNs), and medical information.
Despite an initial notification to Comcast in March, it wasn’t until July that over 273,000 customers were confirmed to have been impacted. Truist Bank similarly notified affected customers months later, in September.
This breach underscores the growing risks associated with third-party service providers. FBCS, despite its own security protocols, became a vector for data exposure affecting its clients and their customers. Notably, FBCS’s clients (including Comcast and Truist Bank) bore the responsibility for breach notifications and remediation efforts, highlighting a critical gap in security oversight for businesses relying on third-party vendors.
A few key takeaways from this incident include:
- Businesses must recognize the risks posed by third-party service providers and ensure they implement solid security measures across their vendor ecosystem.
- Delayed breach notifications not only harm the reputation of the involved entities but can also exacerbate the long-term impact on affected individuals.
- Organizations need to have clear processes in place for identifying, containing, and notifying stakeholders when third-party breaches occur.
Major Breach Targeted Prominent Clients of Snowflake
In May 2024, one of the most significant data breaches of the year was uncovered, involving the cloud data platform Snowflake. This breach, which captured widespread attention, was linked to compromised user credentials, impacting several high-profile organizations, including Santander Bank, Ticketmaster, and AT&T. Attackers took advantage of this access to steal sensitive data, ranging from personal information to financial records, wreaking havoc for many businesses, and millions of individuals.
The breach was the result of compromised credentials circulating on the dark web, stemming from information stealer malware infections. These compromised accounts, which did not have Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) enabled, provided attackers with unauthorized access to organizations’ Snowflake systems. Furthermore, the affected Snowflake instances lacked network allow lists, which made it easier for the attackers to move freely within the network and exfiltrate sensitive data.
The stolen data was later sold on Dark Web forums, where it included a range of sensitive information, such as call logs, personal data, and financial records. The threat group ShinyHunters amplified these sales posts to a wider audience of threat actors, and the breach prompted investigations, ransom demands, and highlighted critical vulnerabilities in cloud-based services.
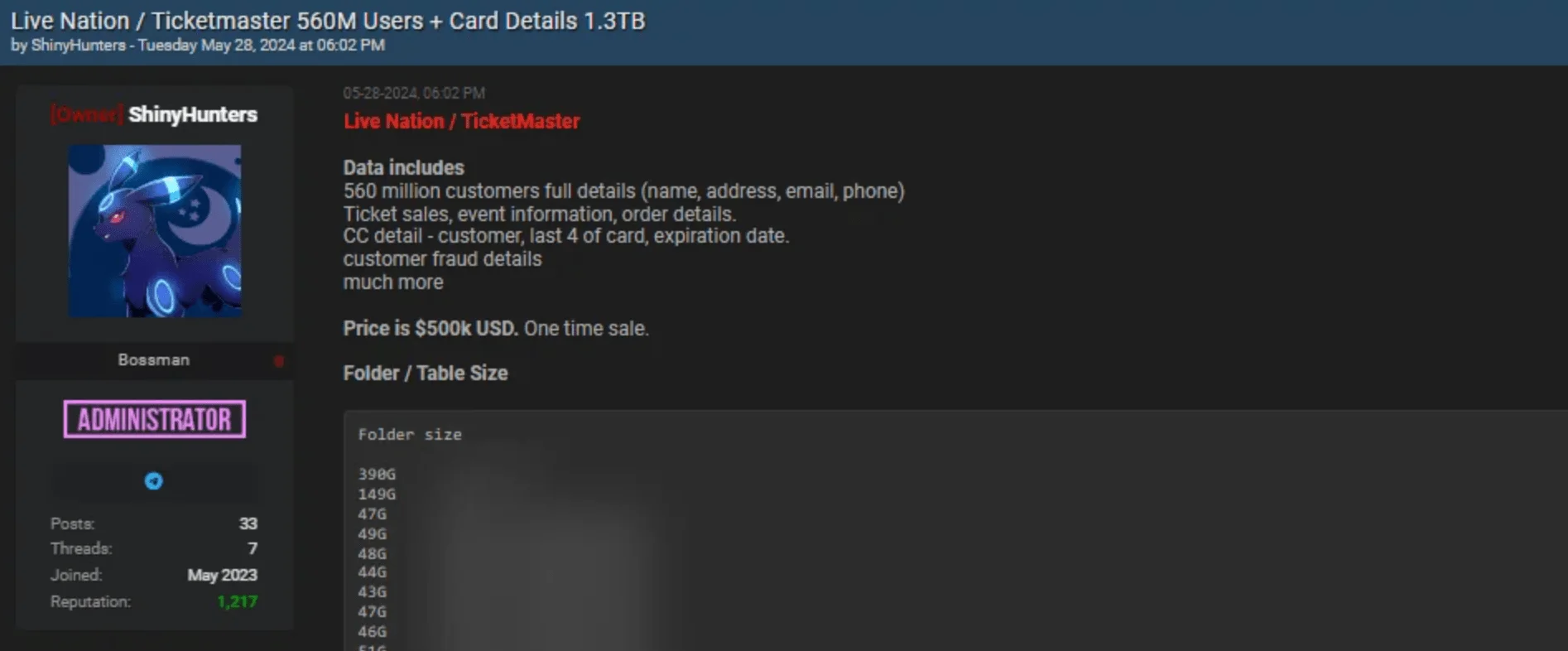
Ticketmaster breach post on the Dark Web forum
Ticketmaster
One of the most concerning impacts of the breach was on Ticketmaster, the renowned event ticketing company, affecting over 560 million users. The exposed information included email addresses, phone numbers, some financial details along with ticket sales and event information. Despite taking immediate action to contain the damage, Ticketmaster could not prevent the stolen data from being listed for sale on the dark web, resulting in significant financial and reputational damage, including a class action lawsuit.
Santander Bank
Santander Bank was another victim of the Snowflake breach and sensitive data from 30 million customers was exposed. The stolen data included account numbers, credit card information, and employee details. While Santander took swift action to mitigate the incident, this breach raised critical concerns about the security of financial data stored in third-party cloud environments.
AT&T
The breach also hit AT&T, exposing the phone records of 109 million customers. The attackers gained unauthorized access to call logs, phone numbers, and location data via a third-party cloud service. This breach further emphasized the vulnerability of telecom infrastructure in the cloud, resulting in concerns about the security of sensitive telecommunications data.
The Snowflake breach was one of the most talked-about incidents of 2024. From financial institutions to telecommunications and ticketing companies, its impact was felt throughout multiple industries. The breach remained a focal point for months, with data from compromised accounts circulating on the dark web and affecting numerous organizations. The ordeal lasted until October, when the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) released an indictment, marking a significant development in the investigation.
For organizations, the lesson is clear:
- Credential security: Implement strong access control policies and enforce MFA across all accounts to add an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access.
- Cloud configuration: Ensure that cloud environments are configured securely, with measures such as network allow lists to restrict access to trusted sources only.
- Continuous monitoring: Cloud-based services need to be monitored continuously for any unauthorized access or data exfiltration attempts, allowing for faster detection and mitigation.
The breach’s far-reaching impact, with sensitive data stolen from major organizations like Ticketmaster, Santander, AT&T, as well as other organizations like Advance Auto Parts and Neiman Marcus, highlights the growing threat to data in the cloud. The prolonged exposure of stolen data on the dark web, which continued to affect these companies well beyond the initial breach, further emphasizes the need for vigilant monitoring.
SOCRadar’s Advanced Dark Web Monitoring helps organizations track stolen credentials and sensitive data circulating on dark web forums. This real-time intelligence enables your business to act swiftly, providing you with the right toolset to prevent further exploitation of compromised information and ensure a stronger cybersecurity in 2025 and beyond.
SOCRadar’s Dark Web Monitoring module
Key capabilities of SOCRadar’s Advanced Dark Web Monitoring module involve:
- Credential and leaked data monitoring: Track compromised credentials and other leaked data to prevent unauthorized access.
- Real-time alerts: Get notified of exposed data instantly.
- Suspicious activity tracking: Monitor the dark web for emerging threats targeting your business.
Integrate SOCRadar’s Dark Web Monitoring into your security strategy to gain actionable insights and enhance both your prevention and response capabilities.
2024’s Opportunistic Cyber Threats, Supply Chain and Impersonation Targets
In 2024, a number of opportunistic cyber threats received attention. As evidenced by the Polyfill supply chain attack and the CrowdStrike phishing campaign, threat actors take advantage of disruptions and disguise themselves as other organizations to target unwary organizations and users.
Malicious Redirects by Polyfill
In June 2024, a supply chain attack compromised the Polyfill[.]io service, a widely used JavaScript library. A Chinese company, Funnull, acquired control of Polyfill’s domain and redirected users to fraudulent sites. By injecting malicious scripts into over 100,000 websites, Funnull redirected visitors to harmful destinations, delivering malware and scams. High-profile organizations, including Warner Bros and Hulu, were affected, with over 380,000 hosts reportedly compromised.
This opportunistic attack took advantage of the wide usage of a third-party service, targeting a large number of websites simultaneously.
CrowdStrike Blue Screen Phishing Campaign
In July 2024, CrowdStrike, a leading cybersecurity provider, inadvertently triggered widespread “Blue Screen of Death” (BSOD) issues due to a faulty software update. Cybercriminals seized this opportunity to create phishing domains that impersonated CrowdStrike’s official support channels, tricking users into revealing sensitive information. At the same time, the hacktivist group Handala launched phishing campaigns against Israeli organizations, distributing wiper malware.
This attack showed how disruptions in trusted services can be exploited by threat actors to deliver malicious payloads.
The Polyfill and CrowdStrike incidents emphasize the risks posed by third-party services and the need for attentiveness in securing external relationships. Such incidents prove that threat actors are quick to exploit any moment of weakness. To combat such threats:
- Routinely evaluate the security of third-party services and maintain strong vendor management practices to reduce exposure to supply chain risks.
- Implement strong anti-phishing strategies, especially during system disruptions. Train staff to spot suspicious activity.
- In the case of Polyfill, warnings were issued by the service’s original developers and cybersecurity experts. It is essential to quickly notify customers/other users about security issues, like those seen with CrowdStrike and Polyfill, to minimize potential impacts.
You can track phishing threats with SOCRadar LABS’ Phishing Radar. This tool detects and analyzes phishing campaigns targeting your organization.

Example results from the free Phishing Radar service on SOCRadar LABS
Furthermore, with the Brand Protection module, you can protect your organization from phishing threats and brand impersonation, gaining access to real-time insights and actionable alerts. Defend your users from malicious sites and prevent data breaches with SOCRadar’s advanced phishing intelligence and Integrated Takedown service.
Takedown Activity Management tab, now available under the Digital Risk Protection module
A Resurgence of Cyber Espionage with the Ongoing Salt Typhoon Telecom Hacking Campaign
In late 2024, the Salt Typhoon hackers, a Chinese state-sponsored Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) group, made a return to the spotlight after a two-year hiatus. Their recent campaign targeted U.S. telecommunications companies, including major players such as Verizon, AT&T, T-Mobile, and Lumen Technologies.
Salt Typhoon, known for its cyber espionage tactics, exploited vulnerabilities within telecom networks to conduct intelligence gathering, data exfiltration, and espionage, with a particular focus on sensitive communication data. This surge in attacks highlighted the risk of supply chain vulnerabilities and data leaks within the telecommunications sector.
As telecom companies provide critical infrastructure and communication channels, their compromise can have great consequences. The attacks also affected political figures, emphasizing the strategic value of telecom infrastructure in cyber espionage campaigns.
Notably, by December 2024, the U.S. government confirmed the breach of a ninth telecom company, with officials noting the increasing complexity and sophistication of Salt Typhoon’s tactics.

Part of a one-pager by the U.S. Senator Ron Wyden of Oregon
As the U.S. government and its allies collaborate on defense strategies such as the Secure American Communications Act, organizations should incorporate cyber defense frameworks that are consistent with these efforts to strengthen critical infrastructure protection.
Moreover, given the strategic value of telecom companies, it is required to regularly assess the security of communication networks, applying the latest patches and monitoring for vulnerabilities.
Blue Yonder Attack Disrupted Critical Supply Chain Services
In November 2024, Blue Yonder, a major provider of AI-driven supply chain solutions, was targeted by the Termite ransomware group. The attack began on November 21 and quickly disrupted services for more than 3,000 high-profile clients, including Microsoft, Tesco, and Starbucks.
The Termite group, an evolution of the Babuk ransomware group, deployed a sophisticated double extortion tactic, encrypting Blue Yonder’s systems and demanding a ransom, while simultaneously threatening to leak 680GB of stolen data.
This attack points out the security risks inherent in supply chains, more so for companies providing fundamental services to high-profile clients. The breach also draws attention to the risks posed by providers whose downtime can affect multiple industries.
Here are some key takeaways and actions to consider for your supply chain security:
- Organizations relying on third-party service providers must conduct detailed, ongoing risk assessments to evaluate the security posture of all vendors. Strengthening third-party security should be a priority, with a focus on securing data access points.
- The sophistication of ransomware attacks requires multi-layered defenses, including strong encryption, regular system updates, and advanced monitoring systems to detect threats before they escalate.
- The ability to swiftly respond to supply chain cyber attacks is critical. Having real-time alerts and intelligence at your disposal allows for timely responses to potential risks, minimizing disruptions and protecting sensitive data.
SOCRadar’s Supply Chain Intelligence module offers advanced tools to protect your business against such attacks. By automatically mapping your third-party environments and identifying high-risk entities, you can streamline your risk assessment process.
Monitor third-party companies with SOCRadar’s Supply Chain Intelligence
SOCRadar’s database provides visibility into over 50 million companies across sectors and countries, enabling you to evaluate the security posture of your suppliers with real-time data and advanced scoring systems, including the Cyber Exposure Level and Popularity Score.
With continuous monitoring and real-time alerts, SOCRadar helps you stay ahead of emerging risks and make informed decisions to protect your supply chain network.
2024’s Latest Major Phishing Campaign: Chrome Extensions Compromised, Affecting Millions
In late 2024, a significant phishing campaign emerged, involving the compromise of popular Chrome extensions, including Cyberhaven‘s own security extension. This breach is part of a broader attack targeting multiple extensions, affecting thousands of users. The attackers injected malicious code into legitimate extensions, enabling them to steal sensitive data such as cookies and access tokens.
The campaign was initially investigated through the compromise of Cyberhaven’s extension, but later findings revealed that at least 36 other extensions were also affected. The attack, which began in early December 2024, impacted an estimated 2.6 million users, and early signs of malicious activity trace back to March 2024.
As the campaign unfolds, new compromised extensions continue to be found, highlighting its extensive scope.

Learn more about this ongoing campaign on SOCRadar’s blog post.
This breach underscores the dangerous potential of cybercriminals exploiting widely used tools. By targeting trusted extensions, they gain access to millions of users’ sensitive data, demonstrating how small vulnerabilities can lead to large-scale cyberattacks.
Recommendations to mitigate the risks of malicious extensions:
- For Extension Developers: Implement strong security measures, such as code signing and regular security audits, to ensure the integrity of your extensions. Regularly monitor for unusual behavior or vulnerabilities within your extensions, and promptly patch any security gaps. Educate users about the risks and encourage them to keep their extensions updated.
- For Users: Always verify the source and permissions of any extension before installation. Regularly update your extensions to ensure you are using the latest, secured versions. Enable security features like Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for added protection against unauthorized access to your accounts.
By addressing both developer responsibilities and user practices, we can collectively reduce the risks posed by such widespread phishing campaigns and strengthen security. SOCRadar’s Extended Threat Intelligence (XTI) platform provides the real-time insights needed to identify these risks and respond quickly. With continuous monitoring, it offers up-to-date information on potential threats, so you can take action before they escalate. By integrating XTI into your security strategy, you ensure that your business is protected with relevant, timely intelligence to address current and future risks.
Conclusion: Key Steps to Improve Cybersecurity in 2025
The year 2024 presented a range of significant cybersecurity challenges, with cybercriminals exploiting vulnerabilities across various industries. From high-profile ransomware attacks to the rise of sophisticated supply chain and phishing campaigns, the threat continues to grow more complex and interconnected.
As we look ahead to 2025, it is clear that cybersecurity must be a priority for all organizations. To navigate the increasingly hostile cyber landscape in 2025, businesses must take targeted action:
- Proactively patch high-risk systems. The Ivanti vulnerabilities exploited in the CISA breach was a prime example of how delayed patches can possibly lead to exposure in even the most trusted organizations. Identify and prioritize the patching of critical systems within your environment. Regularly audit your software for unpatched vulnerabilities and create a patch management schedule that minimizes risk exposure.
- Enhance visibility with real-time monitoring. The Snowflake breaches revealed the importance of continuous monitoring – compromised credentials went unnoticed for too long, impacting millions of users. Set up proactive monitoring for cloud systems, third-party integrations, and sensitive accounts to detect unauthorized access immediately. Automated real-time alerts should be implemented to prompt rapid responses when suspicious activity is detected.
- Take third-party risk management seriously. The Blue Yonder breach demonstrated how third-party vulnerabilities can cause cascading effects across multiple industries. Vet your suppliers and third-party partners rigorously. Ensure they meet cybersecurity standards and conduct regular audits to monitor their security posture.
With these lessons from 2024, businesses can make informed decisions and tighten their defenses. To ensure that your security team is always ready to respond to threats, SOCRadar’s Extended Threat Intelligence (XTI) platform offers real-time insights and automated alerts. Our precise monitoring of the Deep and Dark Web, Surface Web, hacker channels on apps like Telegram, and organizations’ supply chain and internal systems helps identify and mitigate risks before they escalate into major breaches.
For more coverage of 2024’s notable cyber incidents, be sure to explore SOCRadar’s Major Cyber Attacks in Review series, featuring monthly updates. For a quick overview of these, you may also visit SOCRadar’s dedicated Radar page.





































