Secure Your Cloud Environment: 5 Best Practices
With the increasing adoption of cloud computing, cloud security has become a major concern for businesses that rely on cloud-based services to store, process, and manage their data.
Cloud computing is a model for delivering computing services over the internet, such as servers, storage, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence. Instead of building and maintaining their own infrastructure, users can access and use resources on demand, anywhere, and at any time.
Commonly used cloud computing services are:
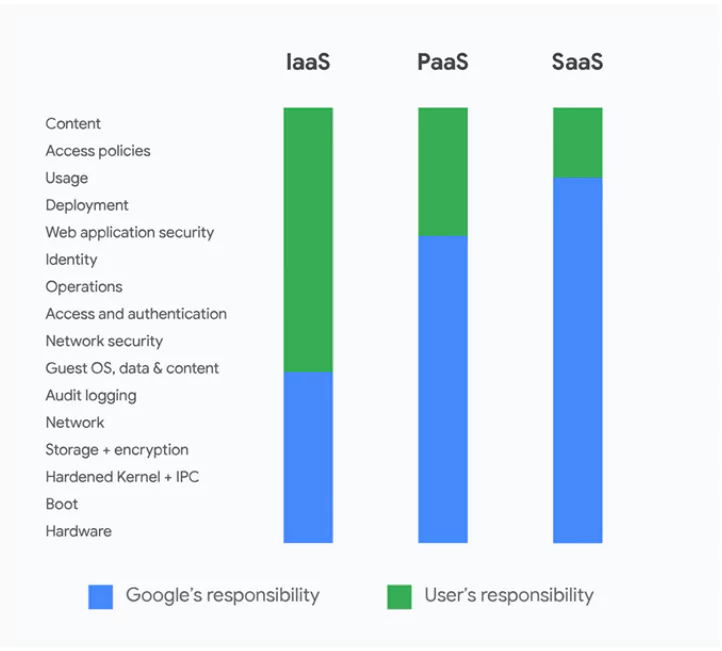
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS provides users access to a range of computing resources, including servers, storage, and networking, over the internet. These resources can be accessed and used on demand, and users only pay for what they use.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS provides users access to a development platform over the internet, including tools for building, testing, and deploying applications. PaaS enables developers to focus on developing the applications rather than worrying about infrastructure.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS, also called cloud application services, delivers software applications over the internet, allowing users to access and use them on demand. SaaS applications are typically accessed through a web browser and are frequently subscription-based.
Users can take advantage of the cloud’s scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency, paying only for the resources they consume.
It is important to ensure that cloud-based data and systems are protected against unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security threats. Cloud security, in this context, refers to the set of policies, technologies, and controls aimed to protect data and systems in the cloud environment, as well as the practices that organizations use to ensure the security of their cloud assets.
Why Is It Important for Organizations to Secure Their Cloud Environment?
Organizations using cloud computing services have less control over their data and infrastructure than if they manage it internally. Despite its benefits, implementing specific security measures and responding to security incidents may become more difficult with cloud.
One of the main concerns with cloud computing is the risk of data breaches. Storing data in the cloud means that it is stored on servers owned and managed by a third party, which can make it more vulnerable to attacks.
Furthermore, organizations that rely heavily on cloud computing services may be at risk if the cloud provider experiences a disruption or a cyberattack. This can also disrupt operations in your organization and potentially lead to financial losses.
What are the Threats?
Listed below are common threats that can compromise the security of cloud-based systems and data:
- Data Breaches: Data breaches can occur when unauthorized individuals or organizations gain access to sensitive data stored in the cloud. The point of entry for a data breach can vary; vulnerabilities in the cloud infrastructure, insider threats, and cyberattacks. Typically, attackers steal credentials or use weak passwords to gain access to corporate networks and cloud-based applications.
- Misconfigurations: Weak privacy settings and default administrative passwords are frequent examples of misconfiguration that can result in the data being deleted or made publicly available.
- Malware: Attackers can use malware, such as ransomware, to infect cloud-based systems. It can spread to other systems or devices, causing bigger damage.
- Insider threats:Insider threats refer to individuals who have authorized access to cloud systems and data but use that access for malicious purposes. This can include employees, contractors, or partners who misuse their access privileges or steal sensitive data.
- Denial of Service:DoS attacks can prevent access to cloud-based systems and data, resulting in downtime and possibly harming business operations.
To protect against these threats, you must implement strong security measures such as encryption, access controls, firewalls, and security monitoring. Educating employees and other users on recognizing and preventing security threats is also critical.
What Can Be Done for Cloud Security?
Here are the top five best practices for cloud security:
Choose the right cloud service provider for your organization:
Select a cloud service provider that offers the security features you need. Take compliance into account, and ensure your cloud provider complies with your legal requirements for processing and storing data.
Understand your shared responsibility with the provider as well. Shared responsibilities differ with which kind of cloud service you choose and determine which security-related tasks you are still responsible for and which are handled by the provider.

Encrypt data at rest and in transit to prevent unauthorized access:
Cloud providers could provide internal encryption services to safeguard your data from other parties. You could also use your encryption methods and keys to maintain total control.
Implement access controls to prevent unauthorized access:
Consider implementing an Identity and Access Management (IAM) system. The IAM system combines user access policies and authentication methods and is essential for managing access to information. Cloud service providers may integrate with clients’ IAM systems or offer an internal one.
Ensure that administrator and user accounts have the proper privileges. Do not grant employees any privileges that are not necessary, as they have the risk of being compromised by an attacker.
Keep a backup to prevent losing your data:
Data backups and offline storage should be part of a sensible cloud security strategy. This will prevent disruption in workflow if a security incident renders cloud services unavailable.
Maintain constant asset monitoring and auditing:
Monitor for unusual activity in cloud-based systems and applications and audit their security posture regularly to address any vulnerabilities that may affect them. Keep systems and applications updated with the most recent patches and updates to avoid emerging vulnerabilities.
By following these best practices, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and other security threats in the cloud.
How Can SOCRadar Help?
SOCRadar’s platform excels in security monitoring and management of all digital assets related to your organization, including cloud-based assets.
SOCRadar can assist with cloud security in many ways, including:
- Monitoring: Our platform provides real-time monitoring, which can help alert organizations to unusual activity and potential security threats in cloud-based systems and applications.
- Compliance: SOCRadar helps organizations ensure compliance with various regulations and industry standards by providing visibility into their security posture and identifying potential vulnerabilities.
- Threat intelligence: SOCRadar’s Cyber Threat Intelligence provides actionable insights into emerging security threats and aids in determining the priority of updates, helping organizations stay ahead of potential attacks.
- Cloud Security Module: The module can notify you when new cloud buckets connected to your organization are discovered and update you on their status. SOCRadar CSM constantly monitors the status of your buckets and sends a “Cloud Bucket Status Change” alert if there is a situation.