
The Rise of Initial Access Brokers on the Dark Web
In recent years, the rise in cyber attacks has been directly linked to a growing network of Initial Access Brokers (IABs). These cybercriminals specialize in selling access to compromised networks, significantly lowering the entry barrier for cyber criminals and enabling faster, more widespread attacks. Our blog post from 2023 “Growing Cybercrime Outsourcing Model: Initial Access Brokers” examined the role of Initial Access Brokers (IABs) in the cybercrime ecosystem during 2022. Although their rise faced a slowdown last year, their growth has evidently rebounded this year.
Initial Access Brokers serve as intermediaries in the cybercrime supply chain. By gaining unauthorized access to corporate networks, often through phishing or exploiting vulnerabilities, they sell access to the highest bidder on underground forums. Especially, these brokers have become critical enablers for ransomware groups, another still rising, facilitating a drastic rise in successful attacks. SOCRadar data shows that ransomware victim listings rose from 2,598 in the first half of last year to 4,318 in the first half of 2024.
In the first half of 2023, SOCRadar monitored 785 unique incidents of initial access sales on hacker forums. By the first half of 2024, that number had surged to 965—a 22.9% increase. Notably, the total incidents in 2023 amounted to 1,812, a figure that will probably surpass soon in 2024, highlighting a significant growth in the market for initial access brokers. Therefore, the parallel rising indicates that the ransomware groups are frequently using IABs.
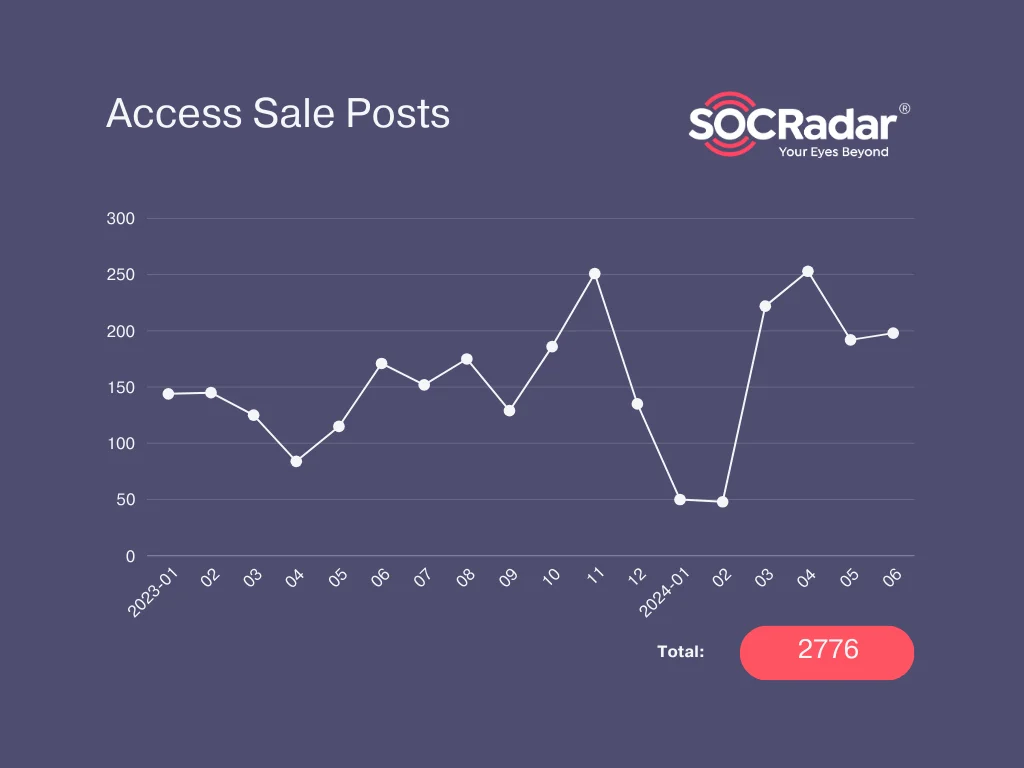
Unique access sale posts in hacker forums between 2023 and first half of 2024
The year began at a slower pace compared to the previous one, but the growth rate quickly surged and continues to rise. Successful law enforcement operations against ALPHV and LockBit, particularly in the early part of the year, likely contributed to the initial decline. During this period, forums like BreachForums did not tolerate ransomware-related posts, and the Initial Access Broker (IAB) landscape, having lost one of its biggest clients, likely faced setbacks. However, this data reflects only the publicly shared posts on hacker forums.
Growth in IAB Market
The demand for initial access has surged in line with cybercrime and ransomware indicating a significant increase in listings for compromised networks. The variety of sectors targeted has also widened, affecting industries such as healthcare, finance, and manufacturing. The growing sophistication of IABs, combined with the sheer volume of networks they offer, has transformed ransomware operations into a more efficient and scalable business model.
The parallel rising indicates that the ransomware groups are frequently using IABs, diversifying their attack vectors and increasing their success rates. Most initial access sales occur on dark web forums and marketplaces, typically involving VPN or RDP credentials. Let’s consider how these accesses are initially obtained. The most common methods remain unsecured credentials, such as weak or default passwords, stealer logs, brute force attacks due to the absence of 2FA, and more advanced techniques like vulnerability exploitation and phishing attacks.
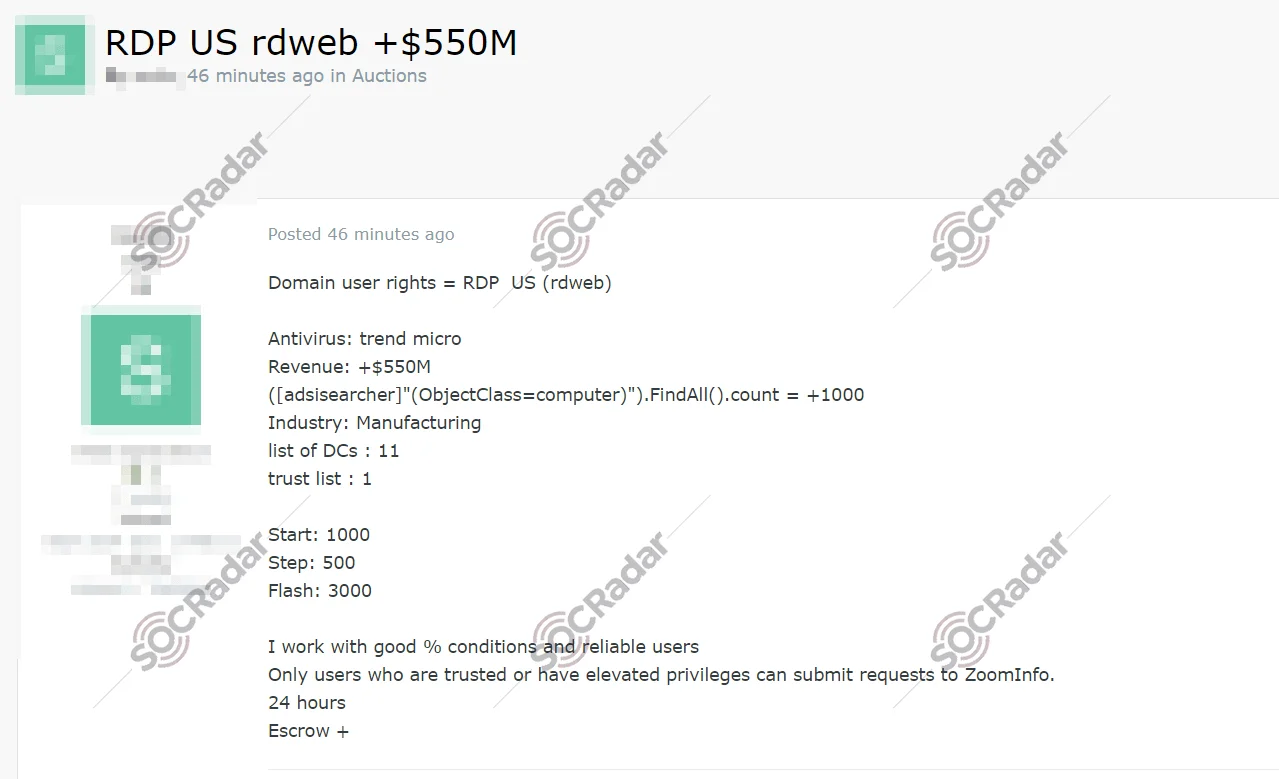
RDP access sale for a U.S based company
Lowering the Barriers for Ransomware Operators
Many ransomware actors tend to focus on collaboration with IABs rather than conducting their own reconnaissance and infiltration. This allows ransomware operators to concentrate on the payload delivery and extortion phases, leaving the initial access phase to specialized brokers.
This collaboration between IABs and ransomware groups has significantly lowered the skill level required to launch a ransomware attack. Even novice threat actors can now purchase access to a network and deploy ransomware with minimal effort, exacerbating the ransomware threat landscape.
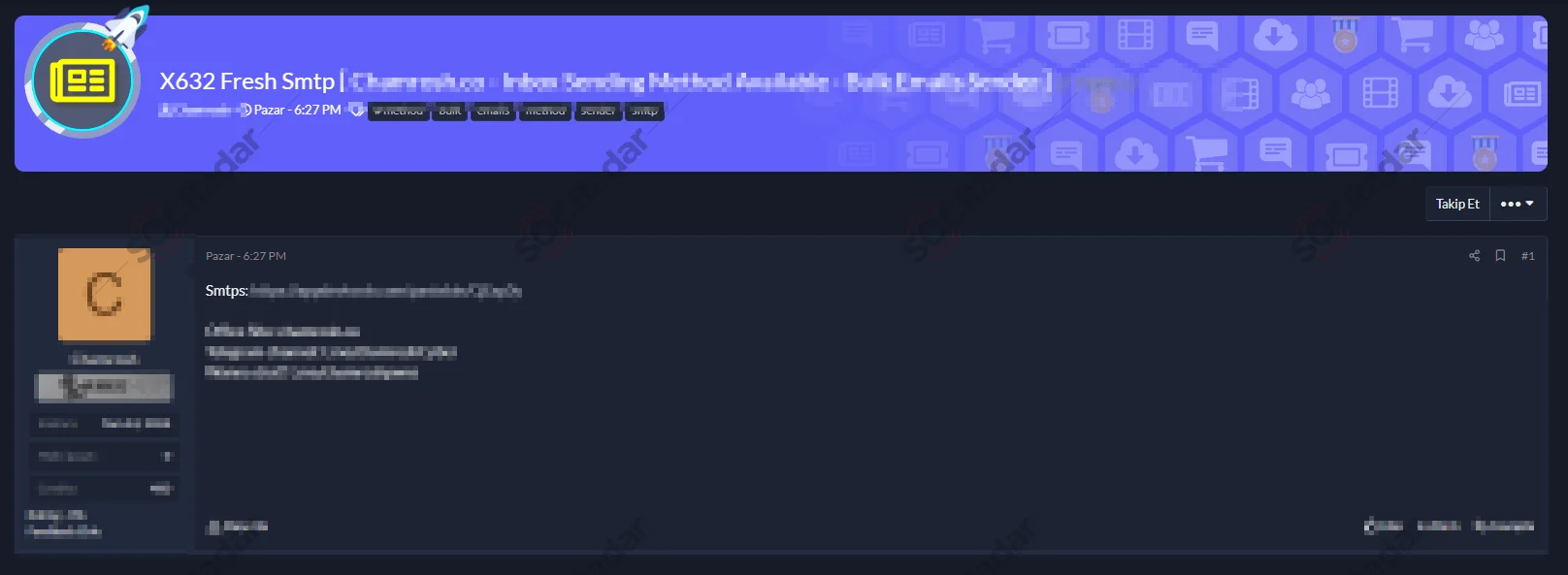
Access sales of relatively less important protocols could also be sold in huge numbers
So, the increase in the volume of ransomware incidents globally, despite many setbacks by law enforcement agencies and cyber defenses, is likely due to this low barrier. Moreover, leaked builders of ransomware and RaaS models further lower the barrier, and the combination with the access brokers, even very novice threat actors, could inflict heavy damage.
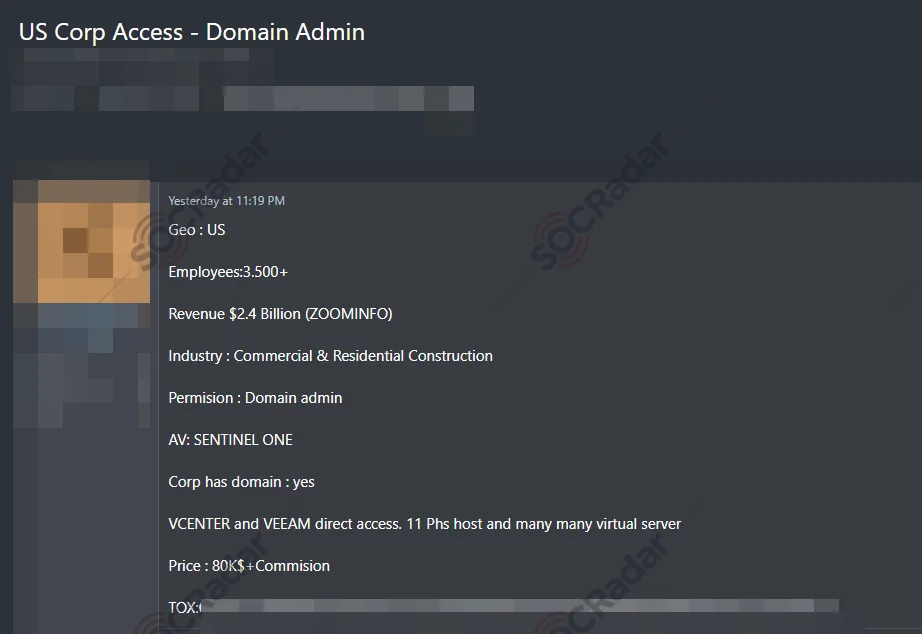
The broker also wants a share from the profit, likely indicating a habit of working with ransomware operators
The availability of network access on underground markets means that any organization, regardless of its size or sector, is a potential target. This growing ecosystem of IABs is proving to be a major factor in the surge of cyberattacks witnessed over the past few years.
Mitigating the IAB Threat
Fighting against Initial Access Brokers (IABs) is a complex challenge. The decentralized and elusive nature of these brokers makes it difficult to track them and shut down their operations. This raises a key question: how can organizations effectively monitor these channels and stay ahead of the threat?
The first step is understanding where to look. While credential markets and initial access markets differ, they are closely linked since IABs frequently rely on stolen credentials to gain access. Dedicated markets for selling these credentials exist on the dark web, but they are also frequently traded on hacker forums and general dark web marketplaces. Some IABs obtain credentials from these public sources, while others receive them from affiliates, creating a layered ecosystem that is difficult to navigate.
Researchers have reported tens of millions of credentials being sold on the dark web, with many of these being repackaged and resold multiple times. VIP-level credentials, which provide access to more valuable targets, are often sold individually or bundled into larger datasets. Popular forums, such as BreachForums, have become hot spots for many IABs to conduct these transactions, making it essential for cybersecurity teams to know where these threats are originating.
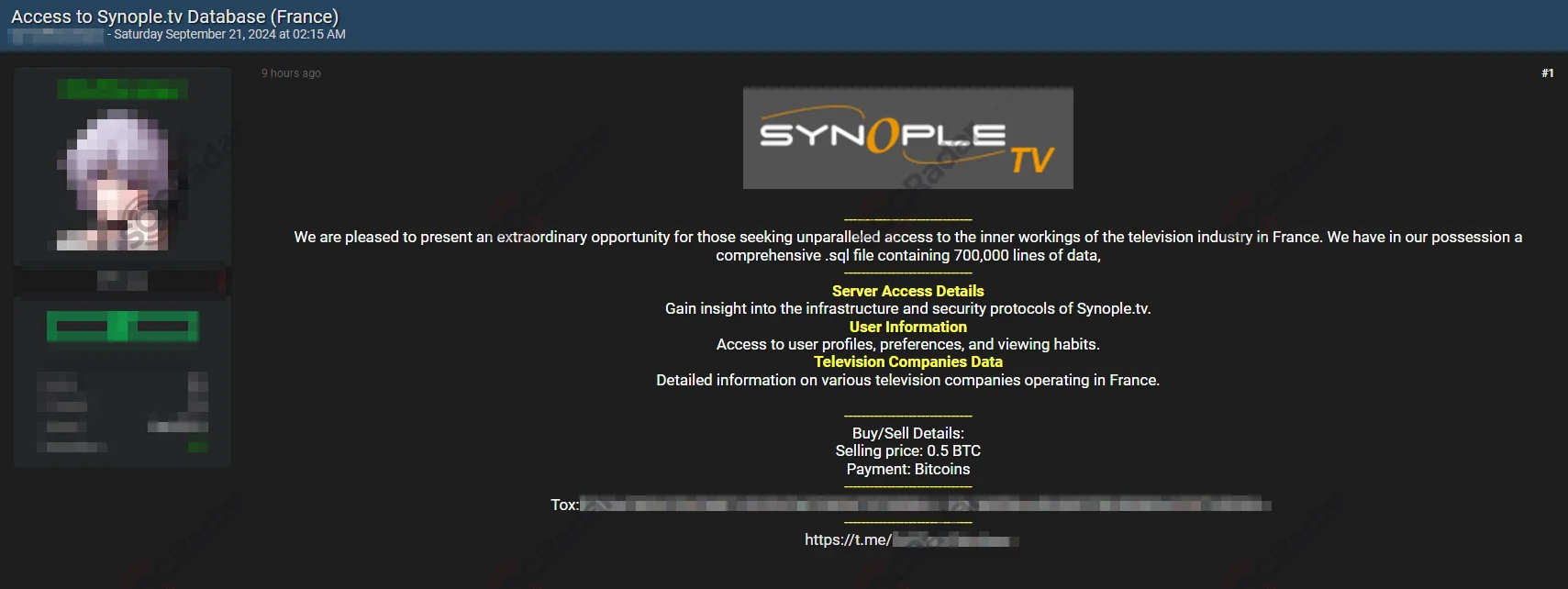
Hacker forums like BreachForums have been a popular sale spot for many IABs
Given this knowledge, how can organizations protect themselves? A reactive approach is no longer sufficient; organizations must adopt a proactive cybersecurity strategy. This starts with the continuous monitoring of dark web forums and marketplaces where access credentials are frequently traded.
Utilizing advanced threat intelligence tools, such as SOCRadar’s Dark Web Monitoring service, can significantly enhance an organization’s ability to identify and respond to compromised credentials in real-time. SOCRadar’s platform continuously scans dark web channels, hacker forums, and marketplaces for sensitive data, providing alerts on emerging threats and helping organizations detect potential breaches early on.
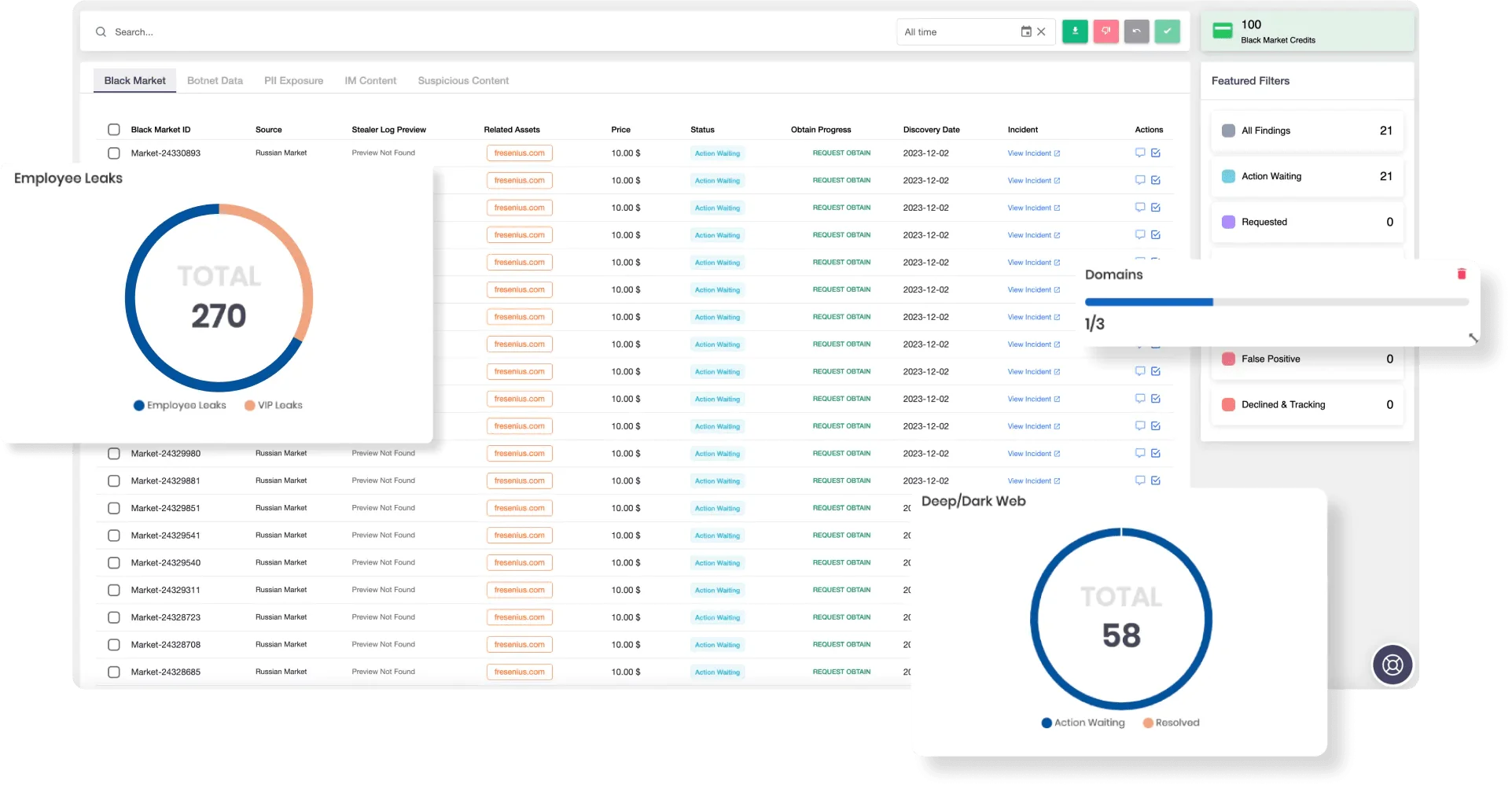
SOCRadar’s Advanced Dark Web Monitoring, powered by CTI
In addition to monitoring these dark web sources, organizations should focus on improving their detection capabilities for unusual network activities that might indicate an IAB-driven breach. This could include monitoring for suspicious logins, unusual access patterns, or signs of credential misuse. By combining dark web monitoring with enhanced internal threat detection, organizations can better safeguard against IABs and mitigate the risks posed by their operations.
In Summary
The rise of Initial Access Brokers (IABs) has dramatically reshaped the cybercrime landscape, enabling a surge in ransomware attacks and lowering the barriers for cybercriminals to infiltrate corporate networks. These brokers have become vital facilitators, offering easy access to compromised systems on dark web marketplaces and hacker forums. Despite efforts by law enforcement and cybersecurity advancements, IABs continue to thrive, contributing to the growing number of ransomware incidents globally.
To effectively combat this threat, organizations need more than just awareness—they require proactive strategies. Understanding where to monitor, utilizing advanced threat intelligence platforms like SOCRadar’s Dark Web Monitoring, and improving internal detection of suspicious activity are critical steps in mitigating the IAB threat. By staying ahead of these brokers and their activities, businesses can reduce the risk of becoming the next victim in this rapidly evolving cybercrime ecosystem.
While the task is challenging, it is not insurmountable. With the right tools and a vigilant approach, organizations can safeguard their networks and stay resilient against the ever-changing tactics of IABs.


































