Top 10 Cyber Incidents in 2022
2022 was a year in which everyone worked to overcome the COVID-19 pandemic and a year in which threat actors simply tried to profit more from it. Threat actors have also been encouraged by national crises like the Ukraine war and the Taiwan conflict.
Keep in mind that the attackers are increasing the frequency of their attacks with each passing year. IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach report proves it by showing how financial losses incurred by organizations participating in data breach research reached a peak of $4.35M in 2022.
Let us take a look back at the top cyber incidents of 2022.
Download SOCRadar’s End-of-Year Report to get more insights.
BlueBleed Data Leak

On September 24, 2022, SOCRadar’s integrated Cloud Security Module discovered that 65,000 entities’ sensitive data became public due to a server configuration error at Microsoft’s Azure Blob Storage.
PII (Personally Identifiable Information) data, documents that may contain intellectual property, Proof-of-Execution (PoE) and Statement of Work (SoW) documents, user information, product orders and offers, project information, and other information are all part of the leak.
Six significant public buckets of the many found contained data on more than 150,000 companies across 123 nations. With sensitive data contained in a single Bucket and affecting more than 65,000 entities across 111 countries, it can be considered one of the biggest B2B leaks.
Russian Invasion of Ukraine

The Russian invasion of Ukraine has significantly increased cyberattacks in the nation, and became a major topic in 2022.
As a beginning, several Ukrainian companies were infected with malware in January 2022. DDoS attacks began soon after, targeting government agencies in Ukraine, such as the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and the Security and Defense Council. The second wave of DDoS attacks hit both the government and two of the state’s largest banks.
Some known hacker groups also participated in the conflict. Anonymous, the world’s largest hacktivist organization, has declared cyber war on Russia; and the ransomware gang Conti sided with Russia.
Refer to our blog “Russian Cyber Escalation in Ukraine” for a detailed timeline of incidents.
China-Taiwan Conflict

Nancy Pelosi was the first US representative to visit Taiwan in the last 25 years, and her visit in August 2022 sparked some diplomatic events as well as cyberattacks. China did not want the visit to happen and started to pressure Taiwan in response to its recent political recognition.
Before Pelosi arrived, attackers hacked billboards in shops and train stations. The hacked billboards showed Chinese messages that were urging Pelosi to leave Taiwan.
Threat actors launched strong DDoS attacks against Taiwan’s presidential office and other official government agencies’ websites, including the Ministries of Foreign Affairs and National Defense; as a result, the websites went offline.
Around the time of the visit, many threat actors began selling and leaking company and citizen data related to both Taiwan and China on underground forums.
Hackers Released 10 Terabytes of Military Emails and Files

Approximately 10 terabytes of emails and other documents from military and police organizations in Chile, Mexico, El Salvador, Colombia, and Peru were released by the hacking group Guacamaya, which has mainly aimed Central American targets.
The data dump is the group’s most recent offering, concentrating on infiltrating police, several regulatory agencies in Latin America, mining and oil companies, and other organizations since March 2022.
$529M is Stolen from Indian Citizens by Chinese-linked Hackers

According to the cybercrime unit in the state of Uttar Pradesh, Chinese scammers have allegedly stolen $529 million from Indian citizens using instant lending apps, part-time job lures, and fake cryptocurrency trading schemes.
The police were able to trace the bulk TXT messages used by the scammers to the Middle Kingdom, with some of their operators being based in Nepal and acting on orders from Chinese threat actors, according to local media reports. To entice investors, threat actors created fake websites and cryptocurrency apps.
$570M Stolen from Binance Blockchain

Due to a cyberattack that happened on October 4, 2022, led to the theft of about two million BNB (Binance Coin) tokens, which could have been exchanged for more than $570 million in fiat currency.
The hacker began distributing some of the funds to other liquidity pools as soon as they become available to convert the BNB into other assets. Following the breach, the price of BNB decreased by about 3.7%.
In recent years, cross-chain bridges have become the most popular target of hacks because they consistently hold massive quantities of cryptocurrency tokens.
Ronin Bridge Hacked: $625M Has Been Stolen

In one of the largest crypto attacks to date, hackers stole about $600 million from a blockchain network linked to the well-known online game Axie Infinity. Players can earn virtual money and non-fungible tokens (NFTs), a type of financial security made up of digital data stored in a blockchain, by playing Ronin’s Axie Infinity game.
According to the company’s official report, the hackers compromised five validator nodes—the minimum number needed to approve a transaction—by gaining access to their private keys, which is how they were able to compromise validator nodes.
Cisco Confirms Hacking by the Yanluowang Ransomware Gang
Cisco has confirmed that the Yanluowang ransomware group has compromised their local network and that the actor attempted to extort them by threatening to publish stolen data online.
Investigation results showed a Cisco employee’s credentials were compromised after a hacker took over a personal Google account where the victim’s browser was synchronizing credentials.
To convince the victim to accept push notifications for multi-factor authentication (MFA), the attacker used a series of sophisticated voice phishing attacks by impersonating various reliable organizations.
Ultimately, the attacker was able to push MFA acceptance, giving them access to VPN in the context of the intended user.
The threat actor carried out a variety of activities to maintain access after gaining it initially, reduce forensic evidence, and broaden their level of access to the environment’s systems.
Nearly the Entire Uber IT System Was Breached

The internal systems of Uber were compromised on September 15. The hacker was able to access the company’s Slack account, HackerOne account, and full admin access to their AWS Web Services and GCP accounts.
The entry attack used a social engineering campaign to target Uber’s employees. An Uber employee received a text message from the hacker, which appeared to be from the company’s IT department. Believing it to be a legitimate message from their department, the employee shared their password. When the password was disclosed, the hacker gained access.
According to Uber, the Lapsus$ group, which has previously carried out similar hacks against Microsoft, Okta, and Nvidia, is responsible for the attack.
According to information coming from various sources, the hacker had access to Uber’s HackerOne account and probably all of their reports.
In addition, Bug Bounty Hunter Sam Curry tweeted that the hacker had claimed to have full administrative rights on the Google Cloud Platform and AWS.
Twilio, Cloudflare, and MailChimp Attackers Targeted Over 130 Organizations

The hackers responsible for some hacks, including those on Twilio, MailChimp, and Cloudflare, have been linked to a larger phishing campaign that targeted 136 organizations and resulted in the theft of 9,931 account login credentials.
This login information was gathered using the phishing tool known as 0ktapus. Most of the victim organizations are based in the US (114), India (4), Canada (3), France (2), Sweden (2), and Australia (1). There have reportedly been at least 169 different phishing domains made for this purpose. These websites had one thing in common: they made use of an undocumented phishing kit.
Software companies are the most affected, followed by those in telecommunications, business services, banking, education, retail, and logistics.
Verizon Wireless, AT&T, Binance, KuCoin, CoinBase, Microsoft, Epic Games, Riot Games, T-Mobile, MetroPCS, Evernote, AT&T, HubSpot, TTEC, Slack, Twitter, and Best Buy are a few of the companies that have been targeted.
Check out our blog post for more details.
The Largest DDoS Attack by Mirai Botnet on Wynncraft Minecraft Server

Cloudflare, a web infrastructure and security provider, announced this week that it had successfully stopped a 2.5 Tbps distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack carried out by a Mirai botnet.
Researcher Omer Yoachimik described the attack as a multi-vector attack consisting of UDP and TCP floods. It was targeted at the Wynncraft Minecraft server.
According to Yoachimik, the peak of the 26 million rps attack was only 15 seconds, and the entire 2.5 Tbps attack lasted about 2 minutes. From a bitrate perspective, this is the biggest attack that has ever been observed.
Stay Secure and Get Alerts with SOCRadar
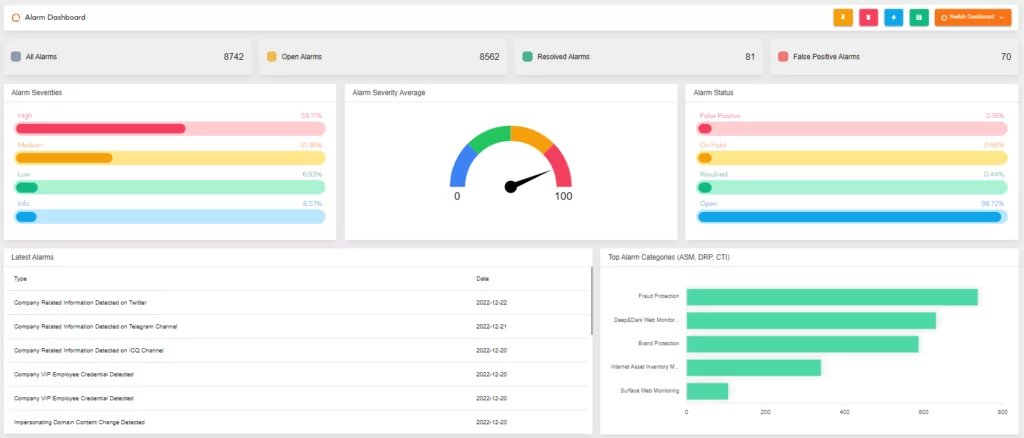
Incident Response Teams become more critical in achieving digital resilience as the frequency and scope of cyberattacks increase. Rapid access to incident-specific information is required for both effective incident response and general threat awareness.
Our platform’s radar pages are constantly updated with the most recent major incidents, vulnerabilities, leaked databases, and other information that will help keep track of cyber trends.
SOCRadar acts as an extension of your team, empowering you to be more proactive by providing background on TTPs and threat actors’ motivations.