
Dark Web Profile: Qilin (Agenda) Ransomware
[June 21, 2024] “Qilin Started Leaking Synnovis Data”
Qilin, also known as Agenda ransomware, represents a formidable threat in cybercrime. This ransomware, one of the known Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) groups, is designed with adaptability in mind, allowing it to customize attacks based on its victims’ specific environments. Originating from a sophisticated background, Qilin leverages advanced tactics to extort organizations. Recently, they have been on the news with their devastating ransomware attacks on Healthcare.

Threat Actor Card for Qilin Ransomware
Who is Qilin Ransomware
Qilin ransomware is a sophisticated cyber threat group that has emerged as a significant player in the ransomware landscape. Its name might be derived from the mythical Chinese creature Qilin, which symbolizes its strong and adaptable nature. However, the group is believed to be of Russian origin. This ransomware is distinguished by its advanced techniques, cross-platform capabilities, and targeted attacks, making it a formidable adversary for organizations worldwide.

Depiction of Qilin, Image created by Bing AI
Qilin ransomware first appeared on the cybercrime scene with a distinct approach and high level of sophistication. It has samples written in Go (Golang) and Rust, which are programming languages known for their efficiency and cross-platform compatibility. This allows Qilin to be easily compiled for various operating systems, including Windows and Linux, enhancing its versatility and reach.
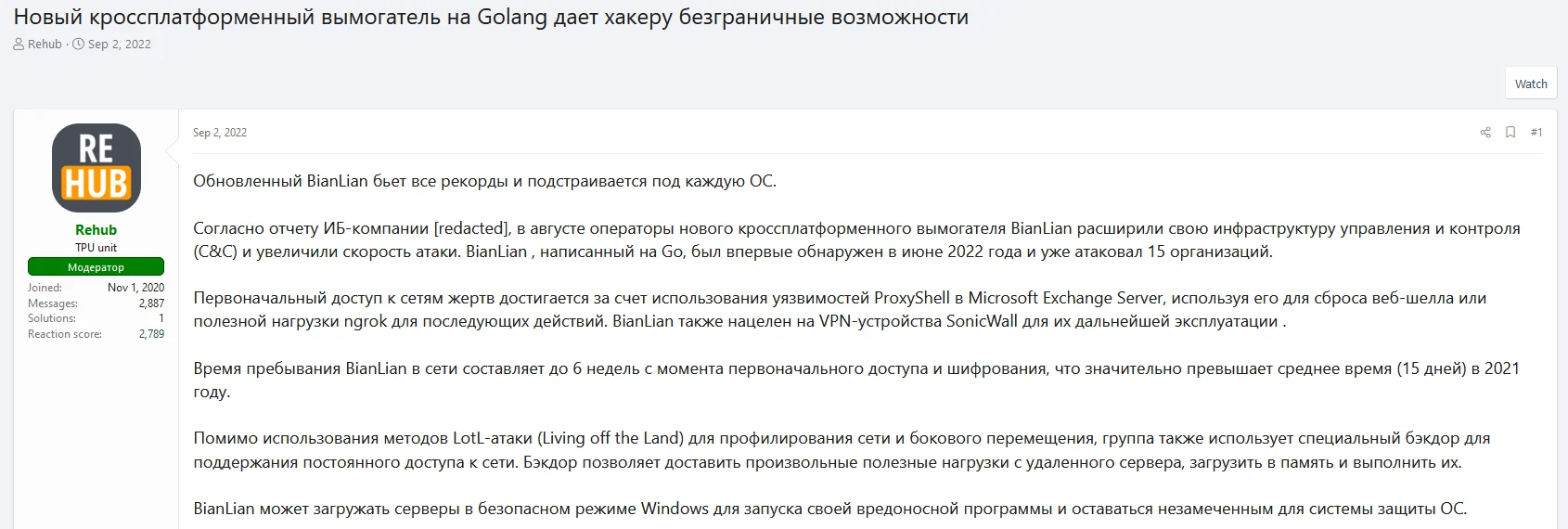
In 2022, ransomware variants written in Golang began to stand out in hacker forums. In addition to BianLian, Qilin (Agenda) Ransomware is one of the mentioned variants. As translated from Google Translate: “New cross-platform ransomware on Golang gives hackers unlimited possibilities”
The primary objective of Qilin ransomware is financial gain through extortion. It targets organizations across various sectors, with a particular focus on healthcare and education. These sectors are often chosen due to their reliance on critical data and the generally lower levels of cybersecurity compared to more financially-focused industries. By encrypting essential files and demanding a ransom for their decryption, Qilin aims to create significant operational disruptions, compelling victims to pay the demanded ransom to restore their systems.
Modus Operandi
Qilin ransomware has samples written in Go (Golang) and Rust, as we mentioned before these programming languages are known for their cross-platform capabilities and efficiency. This choice of language allows Qilin to be easily compiled for various operating systems, including Windows and Linux. The ransomware’s ability to customize attacks to individual victims’ environments makes it particularly dangerous.
Check out our blog post, “Why Ransomware Groups Switch to Rust Programming Language?”
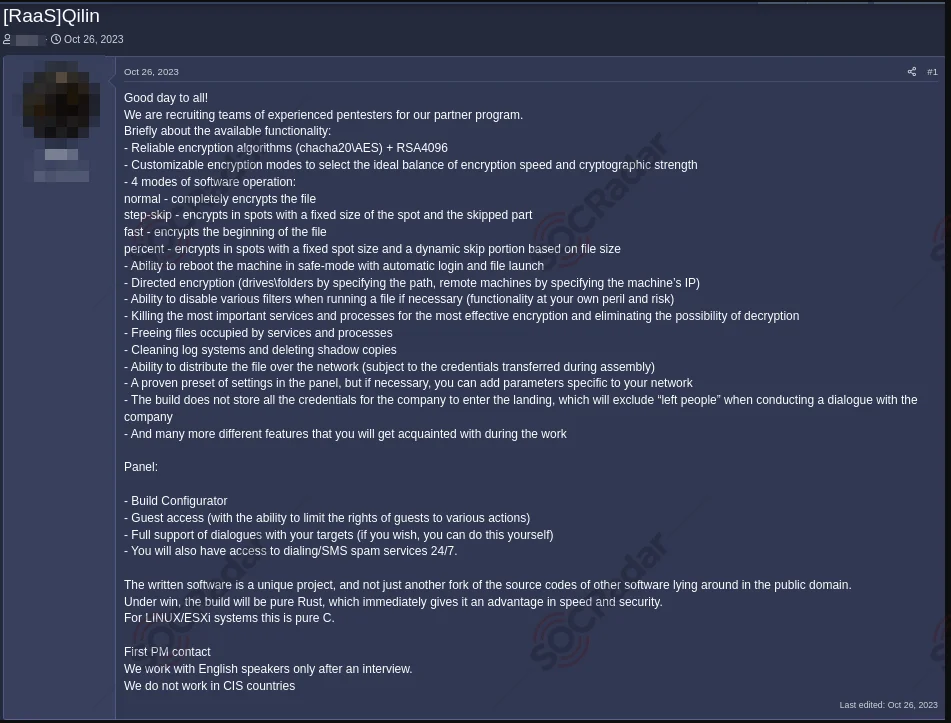
A recruitment post for Qilin in October 2023
The group showed that it was working like a classic Russian ransomware operator by excluding CIS countries from its targets and shared recruitment posts on hacker forums for affiliates.
Initial Infection
Qilin ransomware typically initiates its attack through several primary vectors. One of the most common methods is via phishing emails, which often contain malicious attachments or links. When these are opened by unsuspecting users, they download and execute the ransomware payload. Additionally, Qilin exploits known vulnerabilities in software or operating systems to gain entry. Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) attacks are another favored tactic, targeting weak or exposed RDP configurations to infiltrate systems.
Payload Delivery
Once Qilin has gained initial access, it employs advanced obfuscation techniques to evade detection. The ransomware code is packed, disguising its true nature to avoid static analysis. Further, Qilin uses various code obfuscation methods, such as renaming functions, altering control flows, and encrypting strings, to complicate reverse engineering efforts. This also makes Qilin difficult to detect with IoCs located lower on the pyramid of pain.
Qilin incorporates anti-analysis techniques, such as detecting and disabling debugging and sandbox environments, making it difficult for security researchers to analyze its behavior. This includes checks for virtual machines and other common sandbox artifacts to prevent dynamic analysis. So, we are actually faced with a typical ransomware attack chain, but they are successful in putting it into practice.
Execution and Persistence
Upon successful deployment, Qilin seeks to escalate its privileges to gain administrative control over the infected system. This can involve exploiting system vulnerabilities or using legitimate tools like PowerShell or PsExec to achieve higher-level access. With elevated privileges, Qilin then scans the network for additional targets. It uses network enumeration to identify other systems, shares, and services within the network and employs credential dumping to extract passwords and other authentication details. This enables the ransomware to move laterally across systems, using compromised credentials to infect other machines within the network.

A sample written in Golang uses PsExec for remote execution (JoeSanbox)
Data Encryption
Qilin ransomware employs a robust encryption mechanism that combines symmetric and asymmetric encryption to lock files. Initially, it uses symmetric encryption to encrypt files with a randomly generated key. This symmetric key is then encrypted with a public RSA key, ensuring that only the attackers, who hold the corresponding private RSA key, can decrypt it. Qilin targets a wide range of file types to maximize impact, including documents, databases, and backups, while avoiding critical system files to keep the system operational enough to display the ransom note.

Qilin’s recruitment post includes details about its functionalities, the mentioned encryption algorithms are ChaCha20, AES, and RSA4096
Ransom Note and Extortion
After encryption, Qilin drops a customized ransom note on the infected systems. This note typically includes the demanded payment amount, usually in cryptocurrency, and instructions on how to contact the attackers for payment and decryption. The note often contains threats of data leakage or permanent data loss if the ransom is not paid within a specified timeframe.
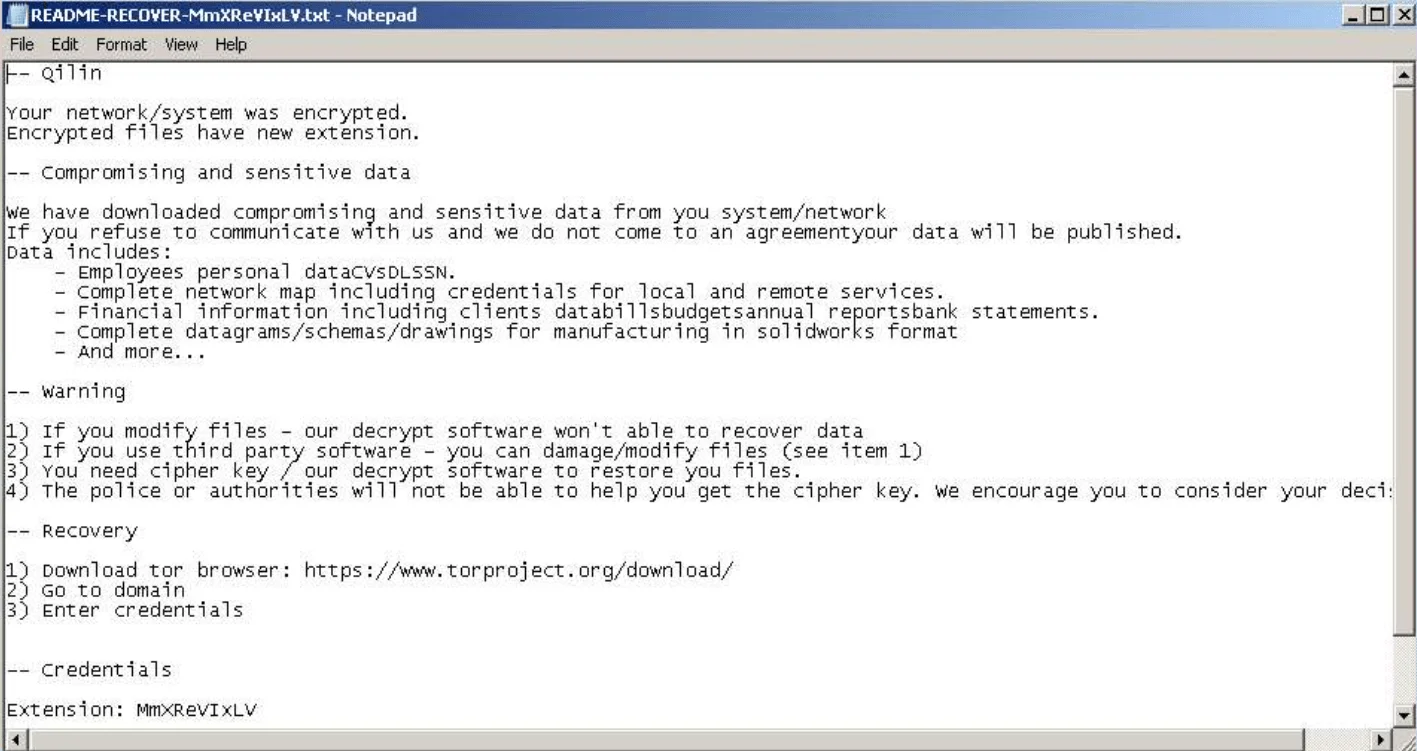
Ransomware note from a recently uploaded sample (Any.run)
Communication and Payment
Victims are directed to communicate with the attackers via Dark Web portals or encrypted messaging services, ensuring the attackers’ anonymity and complicating law enforcement efforts to track interactions. Payments are demanded in cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin or Monero, to maintain anonymity and complicate traceability. Even after payment, there is no guarantee that victims will receive the decryption tools required to recover their data.
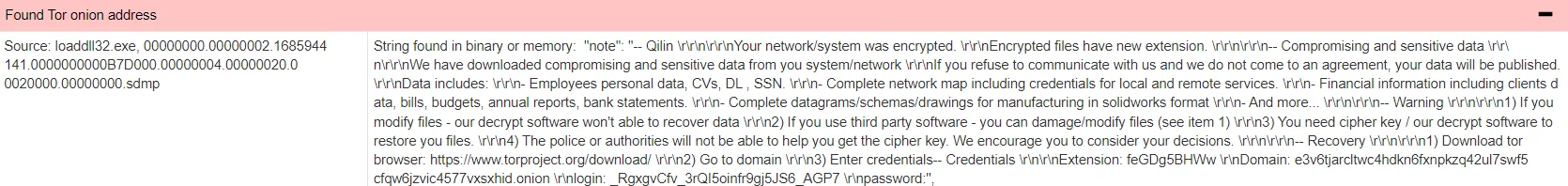
Victims are instructed to download the TOR Browser and redirected to their dark web portals (JoeSandbox)
Clean-Up and Cover-Up
To cover their tracks, Qilin ransomware deletes logs and other artifacts that could aid forensic investigations. This includes clearing event logs and removing any temporary files created during the attack. In some instances, Qilin may also include functionality to remove itself from the system after completing its objectives, further complicating post-incident analysis and response.
Victimology
Qilin has shown a particular focus on the Healthcare, Education, and Public Administration industries, although it is not limited to these industries. These sectors are often targeted due to their reliance on critical data and their tendency to have weaker cybersecurity measures compared to financial or governmental institutions.
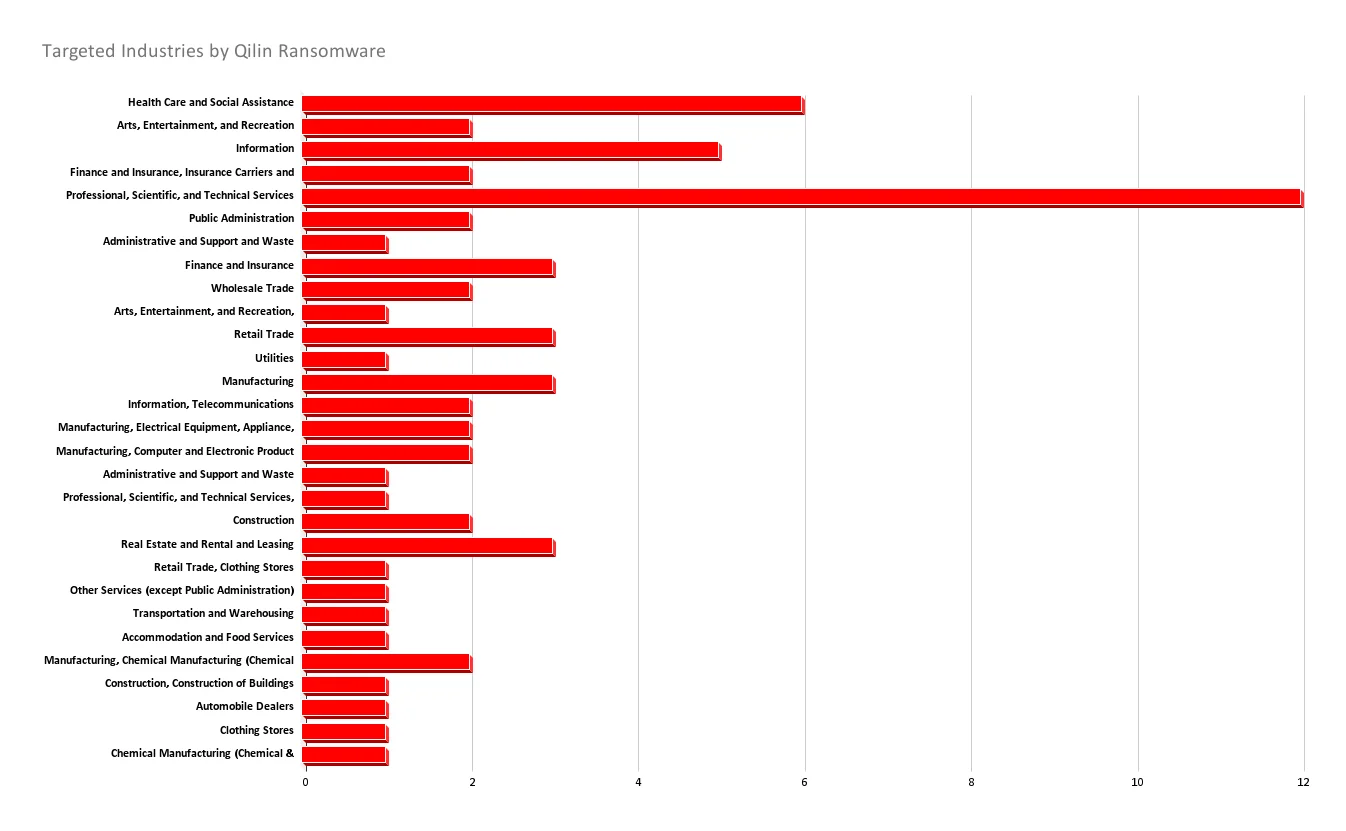
Most Targeted Industries by Qilin according to the SOCRadar data
When we look at the target countries chart, it seems that the US is the most targeted country as usual, followed by mostly EU countries. In Latin America and Asia, educational institutions are the main targets.
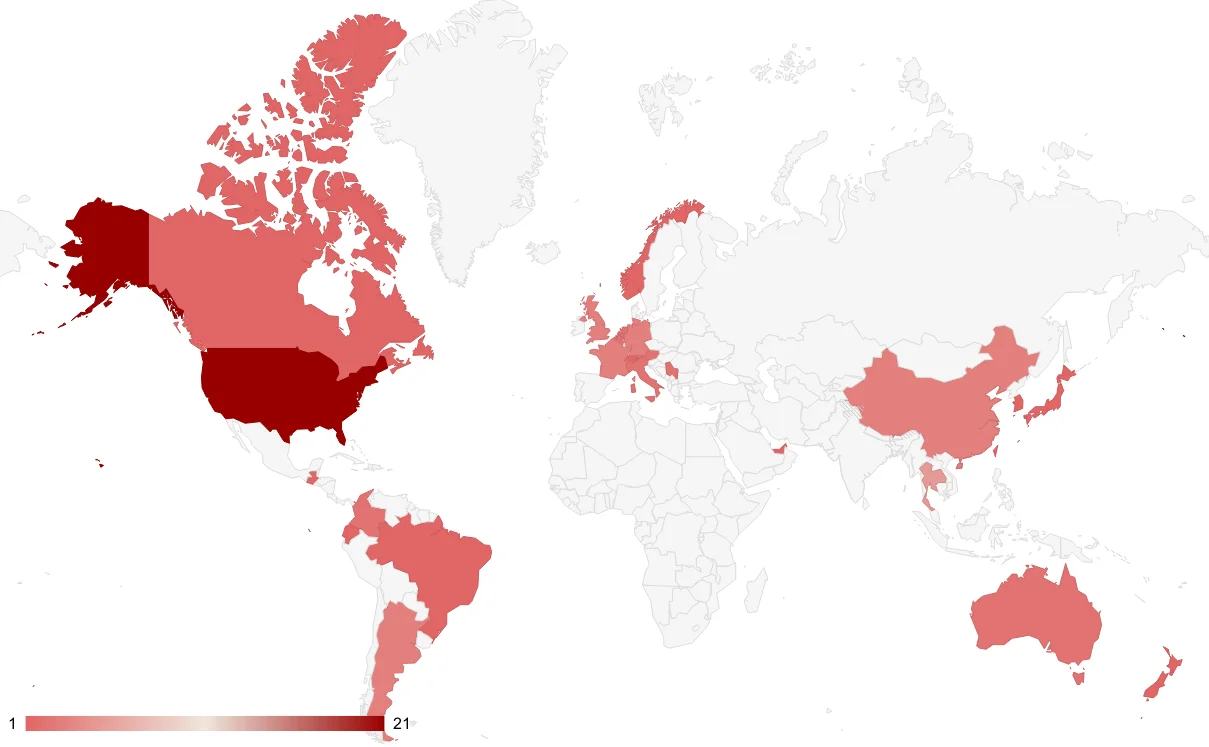
Most Targeted Countries by Qilin according to the SOCRadar data
One of the Biggest Threats to the Healthcare Industry
In a recent incident, UK healthcare providers fell victim to Qilin, resulting in catastrophic following events. According to Ciaran Martin, the former chief executive of the National Cyber Security Centre, a Russian cyber hacking group is responsible for a ransomware attack that severely disrupted operations at three London hospitals. The attack targeted pathology services firm Synnovis, leading to a significant reduction in hospital capacity. Hospitals declared a critical incident, resulting in canceled operations, tests, and blood transfusions.
The group behind the attack was Qilin. The attack impacted various hospitals, including King’s College Hospital, Guy’s and St Thomas’, Royal Brompton, Evelina London Children’s Hospital, and primary care services in the capital. Thus, it should be noted that Qilin’s DLS website has not been accessible for a long time and there is no statement from the group.
This section will be updated as more information about the incident is revealed. A counter-operation move or an advisory can be expected from the security forces regarding this incident in the near future.
Qilin Started Leaking Synnovis Data
Qilin was aiming to extort a substantial ransom from the company. Reports indicate that Qilin is demanding a staggering $50 million from Synnovis for decryption tools and a promise not to publish the data. However, in a series of media interviews, the Qilin ransomware gang has claimed that their attack on the hospitals was not financially motivated but rather a protest against the British government’s involvement in an unspecified war.

Qilin’s victim listing of Synnovis
Unable to reach an agreement, the Qilin group initiated a massive leak on their Telegram channels. After the June 20 deadline passed, Qilin began sharing nearly 400GB of purported Synnovis data, divided into more than 100 parts, on their Telegram channel.
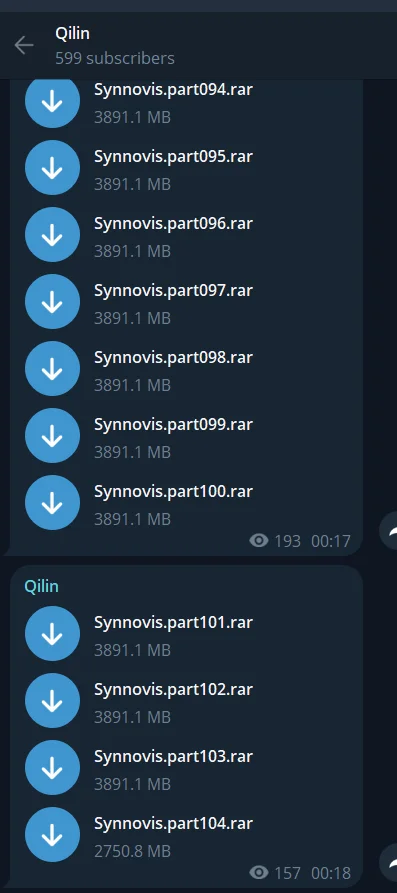
104 parts of alleged Synnovis data has been shared on Qilin’s Telegram channel
Mitigation and Protection
As cyber threats continue to evolve, organizations must adopt a multifaceted approach to cybersecurity, especially in defending against ransomware attacks like Qilin. Leveraging advanced security tools and implementing proactive strategies are imperative in fortifying digital defenses.
- Robust Anti-Malware Solutions: Implementing advanced anti-malware software is essential in combating Qilin ransomware. These tools use signature-based detection, heuristic analysis, and machine learning algorithms to identify and block known and emerging ransomware variants. Coupled with endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions, organizations can enhance real-time threat detection and response capabilities.
SOCRadar Attack Surface Management has Ransomware Check function
- Regular Security Audits and Vulnerability Management: Conducting routine security audits and vulnerability assessments is critical to identifying and addressing potential security gaps within an organization’s infrastructure. By systematically evaluating network configurations, system settings, and application vulnerabilities, organizations can proactively remediate weaknesses exploited by Qilin ransomware attackers.
- Strong Authentication and Access Controls: Enforcing strong authentication mechanisms like Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and implementing stringent access controls significantly enhances user account security and mitigates the risk of unauthorized access. This adds an extra layer of protection against Qilin ransomware attacks targeting user credentials.
- Comprehensive Backup and Disaster Recovery Planning: Developing a robust Backup and Disaster Recovery (BDR) plan is essential in mitigating the impact of Qilin ransomware attacks and ensuring business continuity. Regular backup schedules for critical data, both onsite and offsite, along with backup testing and data recovery drills, validate the effectiveness of the BDR plan and ensure timely restoration of operations in case of an attack.
For further information about protection against ransomware also check out our blog post titled “How to Detect & Prevent Ransomware Attacks (2024 CISO Edition)”
By integrating these advanced security measures and proactive strategies into their cybersecurity framework, organizations can significantly enhance their resilience against ransomware threats and safeguard their sensitive data assets effectively. Adopting a proactive and holistic approach to cybersecurity is essential in mitigating the evolving threat landscape and maintaining a robust defense posture against ransomware attacks.
Conclusion
Qilin (Agenda) ransomware represents a significant threat due to its adaptability and sophisticated attack methods. Organizations must remain vigilant and proactive in their cybersecurity efforts to defend against such advanced threats. By understanding the tactics and techniques employed by Qilin, organizations can better prepare and protect themselves from this formidable ransomware.
MITRE ATT&CK TTP Table
| Tactic | Technique | ID |
| Initial Access | Valid Accounts | T1078 |
| Phishing | T1566 | |
| Exploit Public-Facing Application | T1190 | |
| Execution | Scheduled Task/Job | T1053 |
| Command and Scripting Interpreter | T1059.003 | |
| PowerShell | T1059.001 | |
| Persistence | Boot or Logon Initialization Scripts | T1037 |
| Privilege Escalation | Exploitation of Vulnerabilities | T1068 |
| Abuse Elevation Control Mechanism | T1548 | |
| Defense Evasion | Process Injection | T1055 |
| Rootkit | T1014 | |
| Exploitation for Defense Evasion | T1211 | |
| Execution Guardrails | T1480 | |
| Virtualization/Sandbox Evasion | T1497 | |
| Obfuscated Files or Information | T1027 | |
| Credential Access | OS Credential Dumping, LSASS Memory | T1003, T1003.001 |
| Discovery | System Information Discovery | T1082 |
| Application Window Discovery | T1010 | |
| Network Service Scanning | T1046 | |
| Remote System Discovery | T1018 | |
| Lateral Movement | Remote Services, Remote Desktop Protocol, SSH | T1021, T1021.001 |
| Lateral Tool Transfer | T1570 | |
| Execution | System Services: Service Execution | T1569.002 |
| Collection | Data from Local System | T1005 |
| Exfiltration | Exfiltration Over Other Network Medium, Exfiltration Over Bluetooth | T1011, T1011.001 |
| Command and Control | Data Obfuscation, Junk Data | T1001, T1001.001 |
| Impact | Data Encrypted for Impact | T1486 |
| Data Destruction | T1485 | |
| Inhibit System Recovery | T1490 | |
| Disk Wipe | T1561.001 |
How Can SOCRadar Help?
Understanding the tactics and strategies of ransomware groups like Qilin is crucial for organizations looking to bolster their cybersecurity defenses. Implementing robust mitigation measures and staying vigilant are key steps in combating these threats effectively.
SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management includes a specialized Ransomware Check function designed to help organizations protect against ransomware attacks, including those orchestrated by groups like Qilin. Our platform empowers you to proactively monitor potential attack vectors, detect suspicious activities, and take preemptive actions to safeguard your digital assets.
SOCRadar Attack Surface Management could give organizations an holistic overview
By leveraging SOCRadar’s intelligence-driven solutions, you can gain insights into threat actors’ methods and vulnerabilities, enabling you to fortify your cybersecurity posture. Our continuous monitoring and timely alerts ensure that you stay ahead of potential threats, allowing for swift responses and enhanced overall defense against ransomware and other cyber threats.
Integrating SOCRadar into your cybersecurity framework adds an additional layer of protection, helping you mitigate the risks posed by ransomware groups like Qilin and ensuring the resilience of your organization’s security defenses.

































