How SOCRadar Can Help You with Threat Hunting?
This article briefly explains threat hunting and SOCRadar’s ability to use the feature. If you are still reading this, we invite you to try SOCRadar XTI Free Edition, which has the full capabilities of the SOCRadar Threat Hunting module. Register now and be aware of the threats of the dark web.

What is Cyber Threat Hunting?
Cyber threat hunting is an enormous task that is a foundational stone to Threat Intelligence. The significance of threat hunting is discerned when proactive solutions are ineffective in securing cyberspace.
From time to time, a security researcher or analyst has to research the latest threats that could harm the subject of the analysis. As the OSINT techniques suggest, security researchers start a hunt based on the type of information in hand. The quality and result of the search depend on the information in writing.
Why Is Threat Hunting Important?
As the pool of information enlarges, the development diversifies. Therefore, in every threat hunt, the researcher follows a diagram referred to by authorities such as intel technologies. Furthermore, even though open-source tools, websites, and databases help the security researcher, the task is not easy to handle with a human force.
Nonetheless, the precision of the research is more dependent on the area in which it was conducted than on the process itself. For example, hacker groups organize a new dark web market, a new telegram group, or an IAM group daily.
It’s nearly impossible to track each new source of intelligence that has been born. As a result, threat hunting cannot be limited to keyword searches on the web surface based on user or company information. The hunt must include an Indicator of Compromise (IoC), the latest vulnerabilities of various software or hardware, etc., to fully comprehend the threat that could be faced. Therefore, traditional threat-hunting research is inefficient enough to execute successful and responsive threat intelligence.
Threat hunting is important for several reasons:
- Proactive Security: Threat hunting is a proactive approach to security that involves actively searching for threats lurking in an organization’s network and systems. This approach can help to detect an infiltrated asset that could be activated within a timeline or at the intended destination.
- Advanced Persistent Threats (APT): Advanced and persistent threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated, and traditional security measures may not be enough to detect and prevent them. Threat hunting enables organizations to avoid emerging threats by identifying unusual activity that may indicate a threat.
- Incident Response: Threat Hunting must be an operational, daily task to be made by SOC teams in order to recognize and understand the latest trends in threats. With this knowledge, teams can implement the best practices in their incident response procedures to prevent and respond to the latest threats.
- Compliance: Threat hunting can also help organizations comply with regulatory requirements by providing additional layers of security and demonstrating due diligence in identifying and mitigating threats.
- Improved Security Posture: Threat hunting can help to improve an organization’s security posture by identifying and addressing weaknesses in security controls and processes.
- Indicator of Compromise: Advanced Persistent Threats and Zero-day vulnerabilities are difficult to detect with YARA rules, signature, or anti-virus database checks. APT and Zero-day attacks can evade these securities. However, an anomaly of behavior could hint at a compromise caused by the undetected attack. For example, a request triggered from an unknown location or consecutive bids from an unauthorized or recognized IP could indicate compromised security.
Overall, threat hunting is an essential component of an effective cybersecurity strategy. It can help organizations avoid emerging threats and improve their overall security posture. By proactively searching for threats, organizations can detect and eliminate them before they can cause damage and improve their incident response capabilities.
How To Do Threat Hunting?
Threat hunting is a proactive approach to cybersecurity that involves actively searching for threats lurking in an organization’s network and systems. Even though there are no certain rules on how to conduct a hunt, there are predefined characteristics. Here are the general characteristics that can guide to build a threat-hunting process:
- Define the Objectives: Identify the objective of the threat-hunting operation. This can include identifying previously undetected threats or validating the effectiveness of your existing security controls.
- Identify the Scope: Define the scope of the operation, including the systems, applications, and data that will be analyzed. This will help focus the hunt and ensure the resources are used efficiently.
- Develop Hypotheses: Develop hypotheses about the types of threats that may be present. These hypotheses can be informed by threat intelligence feeds, previous incidents, and other sources of information.
- Gather Data: Collect data from various sources, including network traffic, system logs, and endpoint data. This data can be used to identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate the presence of a threat. There are prebuilt data gathering patterns by intel technologies that can help you to speed up your process.
- Analyze the Data: Analyze the collected data using advanced analytical techniques, such as machine learning algorithms, behavioral analytics, and statistical analysis, to identify any unusual activity.
- Investigate the Findings: Investigate the unusual activity identified during the data analysis phase to determine its nature, scope, and severity. This may involve collecting additional data, conducting interviews with employees, or using other investigative techniques.
- Mitigate and Remediate: Take appropriate actions to mitigate any identified threats. This may involve isolating systems, blocking traffic, or implementing other security measures. Remediation should be done with a focus on long-term prevention rather than just immediate reaction.
- Document and Report: Document the entire threat-hunting process, including the hypotheses, data sources, analysis techniques, investigative steps taken, and remediation actions. The report can be used to inform future threat hunting activities and to provide a record of the organization’s security posture.
- Continuously Improve: Use the findings from the threat-hunting operation to improve your security controls and processes continually.
Threat hunting is an iterative process that requires regular review and update of hypotheses and data sources to stay ahead of emerging threats. It is a proactive approach to security that can complement traditional security measures and provide an added layer of defense against advanced threats.
What Are the SOC Team Challenges for Threat Hunting?
SOC teams face several challenges when it comes to threat hunting. Some of the key challenges include:
- Limited Resources: SOC teams may have limited resources, including time, budget, solutions, and staff, making it challenging to allocate the resources needed for threat-hunting activities.
- Lack of Skills: Threat hunting requires a combination of technical and analytical skills, which can be difficult to find in the current cybersecurity skills gap. SOC teams may need additional training or hiring specialized staff to conduct effective threat hunting.
- Complexity: Threat hunting can be a complex and time-consuming process that requires access to large amounts of data, including network traffic, system logs, and endpoint data. SOC teams may need advanced analytics and machine learning techniques to identify and analyze potential threats.
- Tool Overlap: SOC teams may have to use multiple tools to perform their duties, leading to tool overlap and duplication of efforts. This can be time-consuming and reduce efficiency.
- Integration: Threat hunting may require integrating various security tools and technologies, which can be challenging to manage and maintain.
- False Positives: False positives are alerts that are triggered by legitimate activities. They can be time-consuming to investigate and lead to alert fatigue among SOC analysts.
- Knowledge Gap: Threat hunting requires continuous learning and knowledge of the latest threats and techniques attackers use. SOC teams may need ongoing training and education to stay current on the latest threats.
- Communication: Effective threat hunting requires close collaboration between SOC team members and other departments and stakeholders within the organization. SOC teams may need to improve communication channels and processes to ensure effective cooperation and information sharing.
Overall, SOC teams face several challenges when it comes to threat hunting. However, by addressing these challenges and investing in the necessary resources, SOC teams can effectively detect and respond to security threats to protect their organization’s assets and data.
How to Use SOCRadar for ‘Threat Hunting’?
SOCRadar XTI is an Extended Threat Intelligence platform, and one of its main purposes is to give users the ability to hunt the latest threats with the Threat Hunting module. SOCRadar’s intelligence depends on the big data gathered by selected research analysts and automated tools configured by expert analysts.
With the Threat Hunting module, you can conduct a word-based search in the Threat Hunting module. The module will look into SOCRadar’s big data, which includes the latest vulnerabilities in various products and OS, IoC, botnet data, IAM data exposure, PII data exposure, and the black market.
These alarms run continuously in the product’s backend as long as you want. When the rule has been realized, the alarm is triggered, and a notification email is sent to alarm subscribers.
Furthermore, each alarm notification explains the threat, what could or has been compromised, the time detected, and a link to the platform to read more information on the alarm. In addition, these alarms can be fed to a SIEM or SOAR to take automated or orchestrated actions.
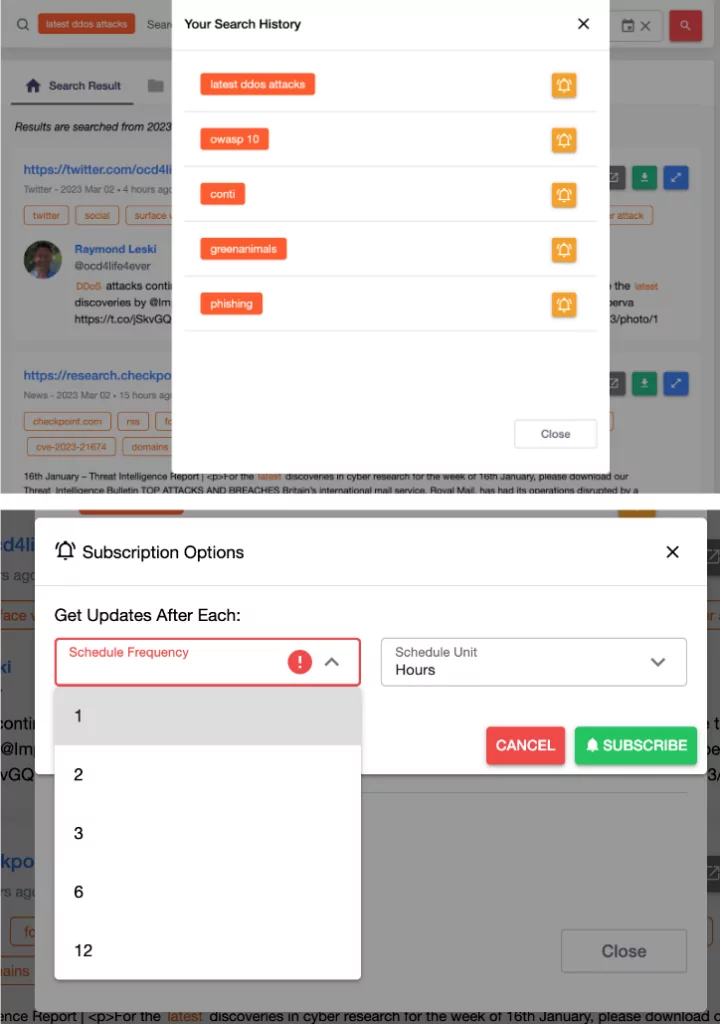
There is a great feature of SOCRadar in that a user can set up a customized subscription through the Threat Hunting Module. If a conducted search and its conditions are saved and set as a custom alert, a hunt will be conducted automatically by SOCRadar’s Threat Hunting module, and the result will be returned to the user if a threat is found by the rule set.
Furthermore, these results can be fed into a SIEM or SOAR solution to automate and orchestrate the organization’s security framework. As a result, the security solutions in your organization’s threat feed will always be up to date, strengthening your security and resilience posture.
Remediate and Mitigate Attacks with Threat Hunting Rules
Each threat hunt that succeeds in finding a threat needs to be completed with remediation and mitigation action. SOCRadar’s Threat Hunting Rules feature helps you find the right YARA rules that are actively used against the latest threats. Furthermore, as an iterative process, Threat Hunting rules are always up to date.