
How to Monitor Your Supply Chain’s Dark Web Activities?
As organizations rely on complex networks of suppliers and vendors to deliver goods and services, ensuring the integrity and resilience of these supply chains is vital. However, with a rising tide of cyber threats, including those originating from the dark web, safeguarding supply chains has become an ongoing challenge.
Supply chain threats pose challenges to the security of interconnected companies and the delivery of their products or services. Each phase, from manufacturing, or development, to distribution, faces the risk of cyber attacks. Threat actors exploit supply chain vulnerabilities to steal data, disrupt operations, or gain access to valuable assets.

Illustration of supply chain security by Bing
One of the most significant threats to supply chain security comes from the dark web, a hidden corner of the internet where illicit activities flourish. On the dark web, threat actors openly trade stolen data, hacking tools, and other malicious services, posing a significant risk to organizations’ supply chains. From stolen credentials to insider information, the dark web provides a space for cybercriminals to exploit vulnerabilities and launch targeted attacks against supply chain partners.
Given the rise of threats, organizations must prioritize monitoring dark web activities in order to prevent harm to their supply chains. Using dark web intelligence and proactive monitoring tools, businesses can detect and mitigate potential threats before they turn into full-blown security breaches.
What Are the Common Dark Web Threats That Affect Supply Chain Security?
The dark web contains an overwhelming number of cyber threats that pose significant risks to supply chain security. Among the most common threats are:
- Data Breaches: Breached data, including sensitive customer information and proprietary business data, is frequently traded on the dark web, exposing organizations to reputational damage and regulatory scrutiny.
- Stolen Credentials: Cybercriminals sell stolen login credentials obtained through phishing attacks, data breaches, or malware infections, granting unauthorized access to critical systems and accounts within the supply chain.
- Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS): Many ransomware variants and RaaS offerings are available on the dark web, allowing cybercriminals to launch ransomware attacks against businesses, potentially disrupting supply chain operations.
- Malware and Exploits: Malicious software and exploit kits are readily available on the dark web, allowing threat actors to launch cyber attacks against supply chain partners, disrupt operations, and exfiltrate sensitive data.
- Fraudulent Activities:Dark web forums facilitate fraudulent activities such as identity theft, financial fraud, and counterfeit transactions, undermining trust and transparency across the supply chain ecosystem.
The Spreading Impact of Supply Chain Breaches
These threats can lead to severe reputational damage, substantial financial losses, and potential regulatory penalties for affected companies. The compromised data from such breaches not only disrupts the operations of a single company; the damage tends to propagate throughout the supply chain, affecting interconnected partners and amplifying the overall impact of the disruption.
In 2022, supply chain attacks emerged as a dominant threat, surpassing malware-based attacks by 40%, according to a report by the Identity Theft Resource Center. These attacks affected over 10 million individuals across 1,743 entities.
Moreover, a 2023 survey by BlueVoyant revealed a troubling trend: the average number of supply chain breaches rose by 26%, with the mean number of incidents per organization increasing from 3.29 in 2022 to 4.16 in 2023.
Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) helps organizations avoid such incidents by providing proactive insights into potential threats. Companies that use CTI solutions, such as SOCRadar, can anticipate and mitigate cyber risks before they escalate. These solutions improve supply chain visibility by mapping the attack surface, providing early vulnerability detection, and assisting in implementing appropriate cybersecurity measures.
SOCRadar’s Supply Chain Intelligence module provides users with access to real-time cybersecurity updates, reports, and alarms, allowing them to stay informed about emerging threats targeting their supply chain. By monitoring incidents such as ransomware attacks, defacements, and breaches through a timeline, SOCRadar equips organizations with the tools needed to detect and respond swiftly to cyber threats originating from the dark web.
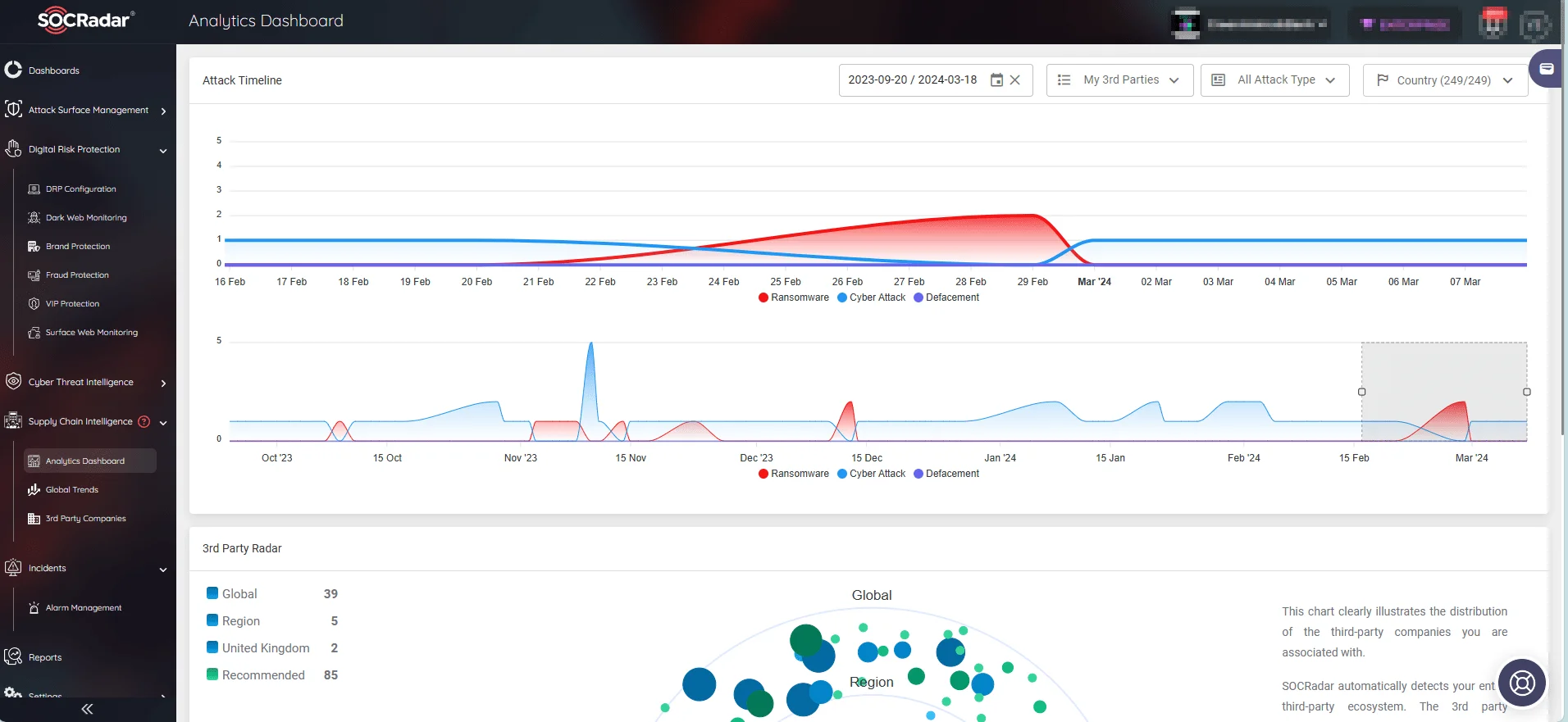
SOCRadar’s Supply Chain Intelligence, Analytics Dashboard
Furthermore, the platform provides insights into global trends for country and sector-specific attacks, allowing organizations to forecast and defend against dark web threats.
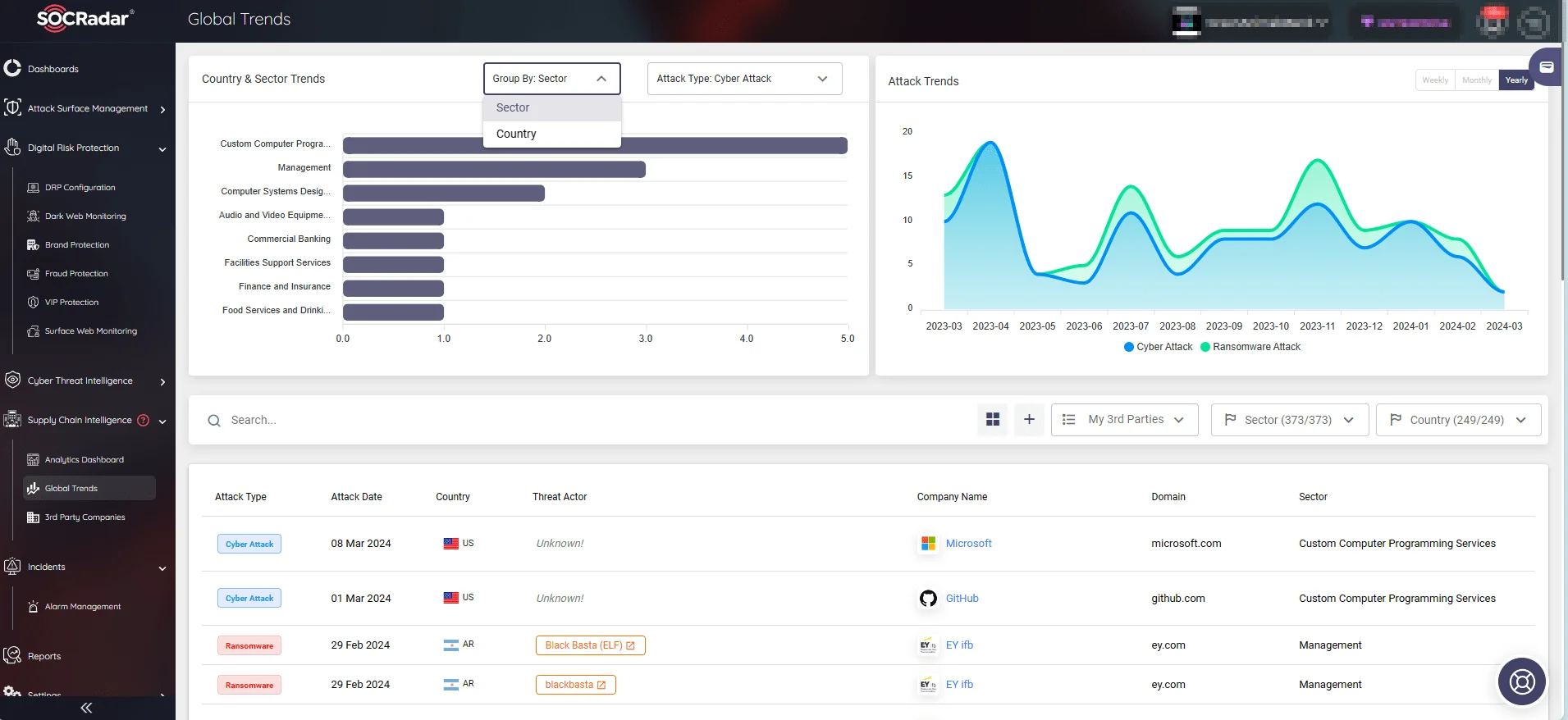
SOCRadar’s Supply Chain Intelligence, Global Trends
What Happens When Organizations Fail to Monitor Breached Data and Supply Chain Activities?
The dark web is a thriving hub for the activities of threat actors, including the trade of stolen data obtained through high-profile breaches. Failure to diligently monitor the aftermath of such breaches can have serious consequences for businesses and supply chains.
Let’s take a moment to go over previous incidents where breaches caused widespread effects throughout supply chains:
- Target Data Breach (2013): In 2013, a breach at Target, stemming from the compromised credentials of a third-party contractor, resulted in the theft of millions of credit card numbers and customer details. The financial effects, which included a $18 million settlement and estimated losses of more than $200 million, severely disrupted Target’s supply chain operations and weakened customer trust.
- Maersk Cyber Attack (2017): The NotPetya ransomware attack on Maersk in 2017 caused losses of up to $300 million and disrupted critical shipping operations for weeks. This cyberattack highlighted the vulnerability of supply chains to sophisticated attacks, stressing the serious financial and operational consequences of cyber threats.
- SolarWinds Hack (2020): The infamous SolarWinds supply chain attack of 2020 compromised systems across numerous organizations, including government agencies and multinational corporations. The injection of malicious code into SolarWinds’ software updates enabled widespread infiltration and unauthorized access to sensitive data, severely impacting affected organizations’ operations and reputations.
- SmoothOperator Supply Chain Attack (2022): In 2022, the cybersecurity landscape was shaken by the SmoothOperator supply chain attack, targeting the 3CX VOIP desktop client. Orchestrated by a North Korean hacker group UNC4736, possibly affiliated with Lazarus APT, this attack marked the unprecedented occurrence of a double supply chain attack, compromising both 3CX and X_TRADER, a defunct trading platform, to distribute malware.
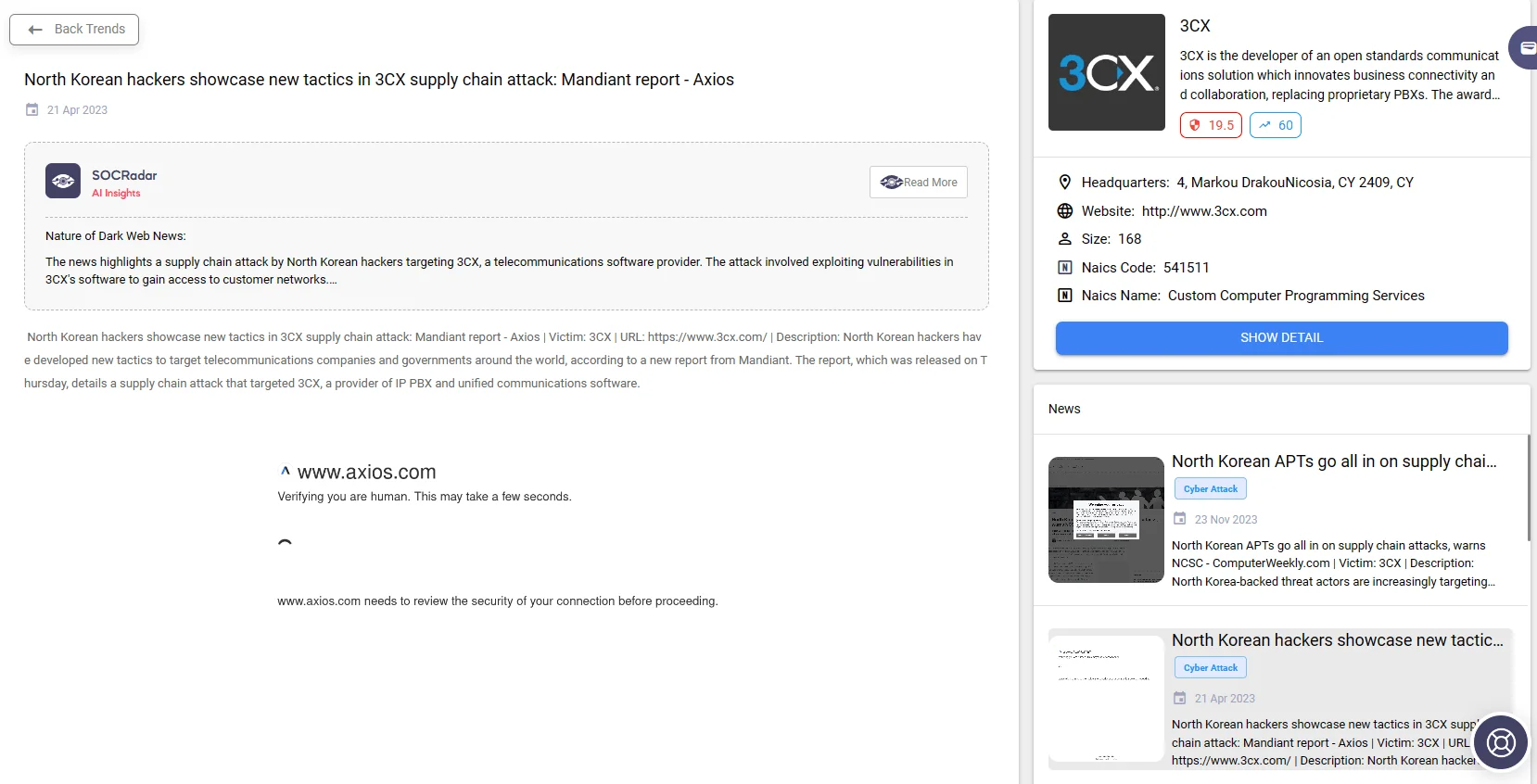
Details of a supply chain attack on 3CX; the page provides access to related news and reports(Source: SOCRadar Supply Chain Intelligence).
- MOVEit Ransomware Breaches (2023): In June 2023, threat actors exploited a zero-day in MOVEit Transfer, a managed file transfer software developed by Progress. Exploited by the notorious CL0P Ransomware group, the vulnerability (CVE-2023-34362) allowed remote code execution and data theft via SQL injection, posing a significant threat to organizations’ data security. Notably, the incident impacted more than 2,500 organizations worldwide.
Organizations that do not closely monitor breached data and supply chain activities risk exacerbating the consequences of such incidents, resulting in increased financial losses, operational disruptions, and reputational damage from cyber threats.
Concerningly, while software supply chain attacks cost businesses nearly $46 billion in 2023, researchers predict that the total global cost of these attacks will be around $138 billion by 2031.
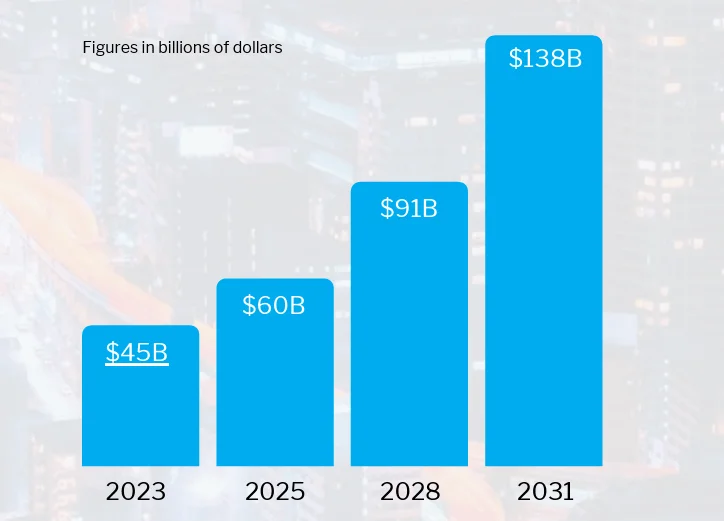
Predicted damage costs of supply chain attacks (Cybersecurity Ventures)
To explore the top supply chain attacks, you can visit our blog post: Guarding the Gates: An Exploration of the Top Supply Chain Attacks.
How Can Organizations Safeguard Against Dark Web Supply Chain Threats?
Organizations encounter unique challenges in identifying and responding to dark web risks, given the interconnected nature of modern supply chains. The extensive network of suppliers, vendors, and partners introduces complexities in monitoring and securing each link against dark web threats.
Moreover, the lack of visibility into third-party environments and digital activities poses a formidable barrier to proactively mitigating supply chain risks emanating from the dark web.
In the face of rising cyber threats, especially those from the dark web, organizations must develop strong best practices to protect their supply chains and limit the potential impacts.
- Enhancing visibility throughout the supply chain is critical. This includes gaining broad insight into suppliers’ and vendors’ digital activities, as well as monitoring their online presence for potential vulnerabilities and threats.
- Organizations should conduct continuous risk assessments to identify and prioritize potential supply chain threats. This includes assessing the security posture of third-party environments and determining their vulnerability to dark web activities such as data breaches, credentials theft, and malware distribution.
- Organizations should establish clear monitoring of their suppliers’ and vendors’ cybersecurity postures, keeping up with any emerging vulnerabilities or breaches.
- Maintaining an edge over constantly changing cyber threats requires integrating threat intelligence solutions. Organizations can proactively identify and respond to potential threats to their digital assets by leveraging real-time intelligence on dark web activity.
Monitoring Supply Chain Dark Web Activities with SOCRadar’s Supply Chain Intelligence
SOCRadar’s refurbished Supply Chain Intelligence module can help organizations effectively monitor their supply chain’s dark web activities and implement the best practices mentioned in the previous section.
The module offers advanced detection and mitigation capabilities specifically designed to address supply chain threats, enabling organizations to adequately safeguard their assets from third-party security breaches.
By automating the detection and mapping of third-party organizations and their security events, SOCRadar allows organizations to actively monitor and assess potential risks, including those originating from the dark web, such as data breaches and ransomware attacks; it also provides critical alerts about supply chain, aiding organizations in proactively defending against and mitigating the impact of cyber threats.
By leveraging the module, users can effortlessly monitor the digital activities of their collaborators, spanning over 50 million organizations across 373 sectors.
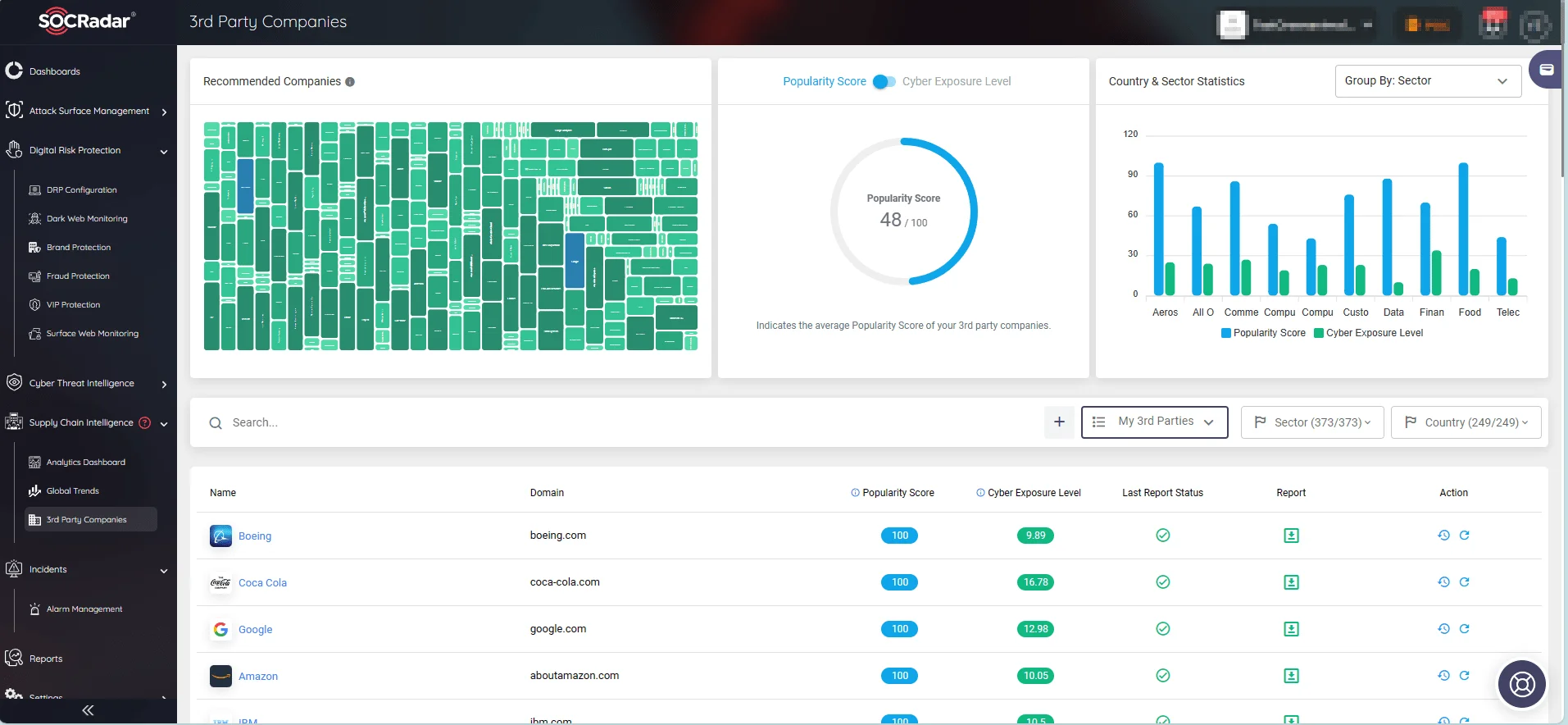
SOCRadar’s Supply Chain Intelligence automates the detection and mapping of third-party environments, enabling organizations to gain comprehensive visibility into their supply chain’s activity.



































