Overview of the Snowflake Breach: Threat Actor Offers Data of Cloud Company’s Customers
This blog actively documents significant updates related to the Snowflake Breach.
Latest update: “DOJ Indictment Reveals Details of Massive Snowflake Data Breach and Ransom Operation”
In recent weeks, Snowflake, a leading cloud-based data storage and analytics provider, has found itself at the center of a cybersecurity controversy. Reports of the Snowflake breach have emerged suggesting unauthorized access to its systems, which may have compromised sensitive data belonging to multiple high-profile clients, including Santander Bank and Ticketmaster.
This blog post will detail the Snowflake breach, based on disclosures from Snowflake, news reports, and additional information from cybersecurity researchers, covering the full timeline of the breach with updates.
The Background of the Snowflake Breach and Initial Disclosure
Snowflake noticed unusual activity within its systems around mid-April 2024 and officially acknowledged potential unauthorized access on May 23, 2024. Since then, the company has been actively investigating the situation and has communicated with affected customers, providing them with Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) and recommended actions to secure their accounts.
Despite allegations of a widespread breach, Snowflake maintains that the incidents resulted from compromised user credentials rather than any inherent vulnerabilities or flaws within Snowflake’s product itself.
The company emphasized in a disclosure on Snowflake Forums, published a month ago, that the breach was not due to any misconfiguration or malicious activities within Snowflake’s products, and that customers are recommended to review their security configurations.
How Did the Snowflake Breach Occur?
Investigations reveal that the breach was likely facilitated by a compromised machine used by a Snowflake sales engineer. Or, just as a speculation, it might even be the work of an insider threat. However, if an account of this level is involved, the breach could potentially affect prospect and sales-related environments and production accounts.
The machine was reportedly infected with Lumma Stealer, a type of malware that logs keystrokes and other activities, which could have been the attackers’ initial access point.
Who Is Behind the Snowflake Breach?
An emerging figure in this incident is a threat actor known by the alias “Whitewarlock.” This threat actor first appeared on a Russian dark web forum, Exploit.in, on May 23, 2024, the same day they posted data allegedly obtained from the breach.
Whitewarlock’s activities and reputation within the cybersecurity community remain unclear, with no prior known history. Their sudden appearance and the specific demands suggest a potentially opportunistic attack rather than a coordinated campaign.
With SOCRadar’s Dark Web News, you can stay updated with the latest events and developments in the dark web landscape. The module allows viewing the latest posts through Deep and Dark Web forums, and various other hacker channels.
Dark Web News – Visit SOCRadar LABS to try its complementary version, DarkMirror
The First Victims of the Snowflake Breach: Santander Bank and Ticketmaster
The threat actor responsible for the breach claimed to have extracted sensitive data from major entities like Santander Bank and Ticketmaster.
Santander Bank disclosed on May 14 that attackers accessed a database hosted by a third-party provider. While they did not explicitly name Snowflake, subsequent revelations linked the breach to Snowflake’s compromised environments.
Similarly, Ticketmaster’s parent company, Live Nation Entertainment, confirmed unauthorized activity in a third-party cloud database environment containing data primarily from Ticketmaster. This breach was also later attributed to Snowflake’s platform. The company filed a report to the SEC (Securities and Exchange Commission), which is dated May 20.
How Many Individuals Are Affected by the Snowflake Breach?
The alleged breach of Santander Bank through the Snowflake incident reportedly affects 30 million customers. Meanwhile, the Ticketmaster breach is said to potentially impact 560 million customers.
Following the breach, several cybersecurity firms conducted detailed analyses to understand the scope and impact. Reports indicated that over 500 demo environment instances were detected in the stealer logs linked to the compromised Snowflake account.
Also importantly, security researcher Kevin Beaumont noted on Mastodon that six major organizations have experienced cybersecurity issues related to their use of Snowflake, indicating a broader impact.
Detailed Timeline of Events Surrounding the Snowflake Breach
Below is a detailed timeline of events regarding the Snowflake breach, in reverse chronological order.
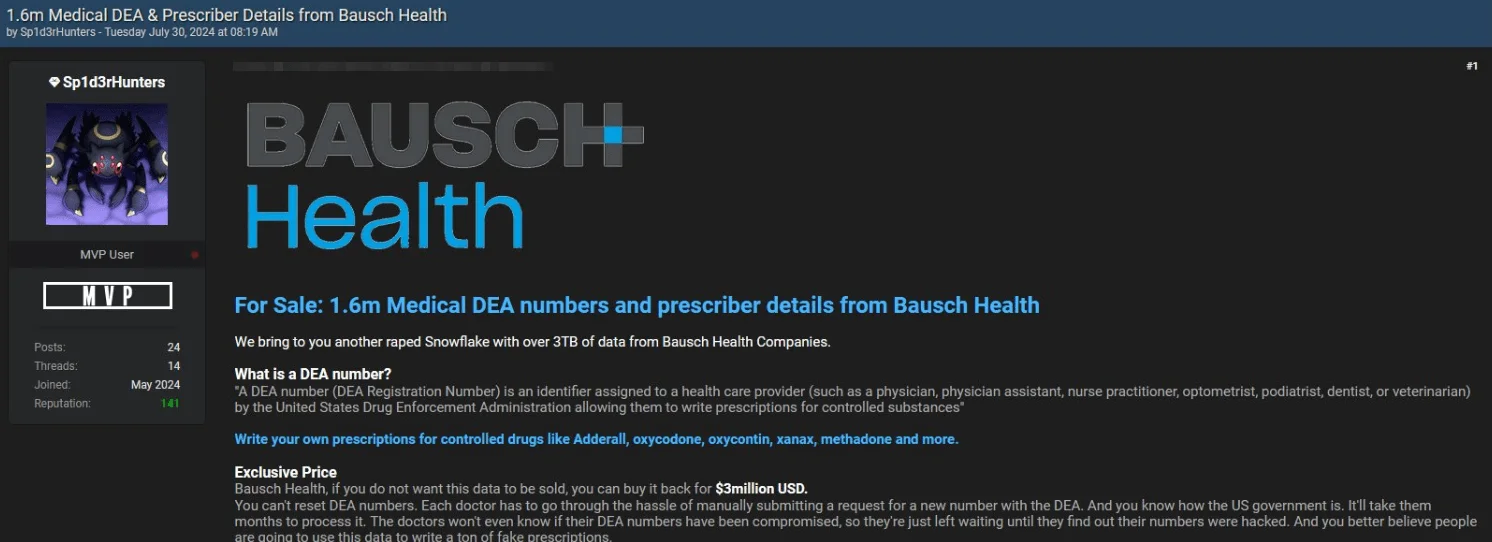
Alleged Bausch Health Breach Involves 1.6 Million DEA Numbers – July 30, 2024
On July 30, 2024, another breach post by Sp1d3rHunters surfaced, claimed to be related to Snowflake.
The post features 1.6 million DEA numbers (assigned to healthcare providers to write prescriptions) and prescriber details from Bausch Health companies, with the alleged data totaling 3TB.
Bausch Health data breach post
The threat actor provided samples of prescriber numbers with partially redacted DEA numbers as proof of the breach. Piling on the pressure, Bausch Health, a pharmaceutical company with operations in over 90 countries, is facing a $3 million ransom demand to prevent the data from being sold.
According to the threat actor’s statement, the appeal lies in the fact that the company cannot reset DEA numbers; each healthcare practitioner has to manually submit a request for it. Further complicating the matter, it might take a while before healthcare providers realize their DEA numbers have been compromised, and their work might be disrupted during the process of resetting them. Additionally, threat actors could use such information to write fake prescriptions.
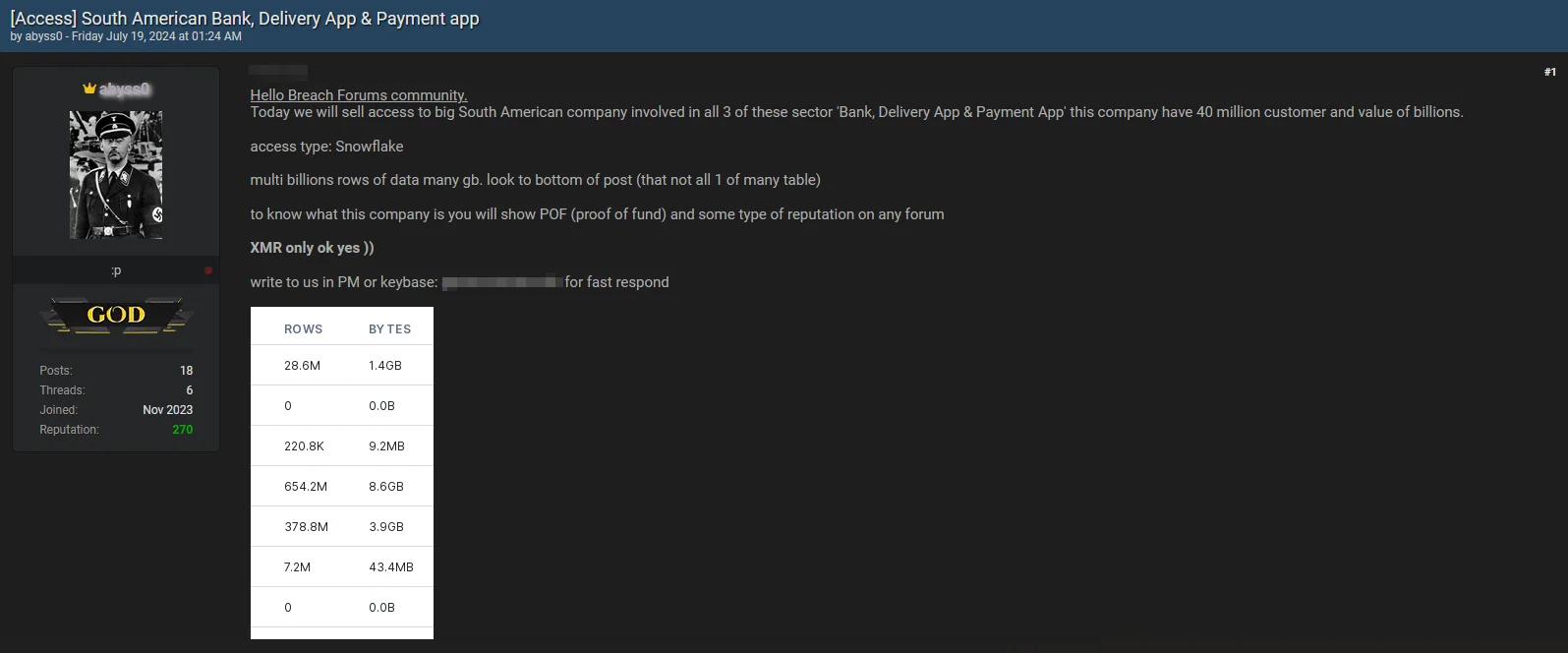
Threat Actor Sells Snowflake Access for a ‘Big South American Company’ – July 19, 2024
A new threat actor has emerged, claiming to sell Snowflake access to a large South American company. The development adds another layer of complexity to the ongoing concerns surrounding the Snowflake security breach.
The company, unnamed, operates in the sectors of banking, delivery apps, and payment apps, serving 40 million customers, and is valued in billions.
Access sale for a ‘big South American company’
The threat actor claims that the access type is Snowflake and says they can provide proof such as reputation on any forum and Proof of Fund (POF) for the company. They are willing to sell the access for payment in Monero (XMR) cryptocurrency.
While this access may not be directly connected to the recent major Snowflake breach, there is a possibility that it could be related to the activities of SpiderHunters. The threat actor’s intent in selling this access might be to reduce traceability and avoid direct involvement in exploiting the access themselves.
AT&T Data Breach Attributed to a US Hacker in Turkey – July 14, 2024
The recent AT&T data breach was attributed to a US-based hacker, John Erin Binns, operating from Turkey. Binns claimed AT&T paid a $370,000 ransom (5.7 in Bitcoin) in May to ensure the stolen data was deleted. This was verified by Wired through blockchain tracking tools, and the threat actor, linked to the ShinyHunters group, provided proof of the transaction.
Binns was arrested in Turkey in May for the 2021 T-Mobile breach, for allegedly stealing several billion records. Due to Binns’ arrest, a member of the ShinyHunters group received the ransom payment.
The AT&T breach was first reported by security researcher Reddington, who acted as an intermediary for the company in ransom negotiations with the threat actor. Although the hacker initially demanded $1 million, he settled for $370,000.
Reddington believes the deleted AT&T data was the only complete dataset taken, and the hacker provided a video as proof of data deletion. Reportedly, AT&T was among over 150 companies whose data was stolen from unsecured Snowflake accounts in April and May.
AT&T Data Breach Exposes Phone Records of Millions of Customers – July 12, 2024
In a recent SEC filing, U.S. telecommunications giant AT&T disclosed that a significant data breach occurred in April, compromising the phone records of nearly all its customers. An internal investigation revealed that hackers accessed and copied AT&T call logs stored on a third-party cloud platform, resulting in the theft of millions of customer phone numbers, calling and text records, and location-related data.
AT&T confirmed that the stolen data spans a six-month period from May 1, 2022, to October 31, 2022, and includes some records as recent as January 2, 2023, for a smaller group of customers. The data breach also impacts customers of other cell carriers utilizing AT&T’s network. However, the stolen information does not include the content of calls or texts. Instead, it comprises metadata such as the phone numbers involved in communications, the total count of calls and texts, and call durations. Notably, the breach does not cover the time or date of these communications.
This breach will necessitate AT&T notifying approximately 110 million customers, as stated by company spokesperson Andrea Huguely to TechCrunch. Huguely mentioned that the compromise occurred during a series of data thefts targeting Snowflake’s customers.
Given the sensitivity of the stolen information, AT&T customers should take several cybersecurity measures:
- Switch to Secure MFA: Use authenticator apps or hardware tokens instead of SMS-based MFA.
- Monitor Account Activity: Regularly check for suspicious transactions or changes.
- Update Passwords: Use strong, unique passwords and a reputable password manager.
- Secure Recovery Options: Avoid SMS-based account recovery methods.
- Stay Informed: Be aware of phishing tactics and avoid suspicious links or messages.
These steps can help protect personal data and accounts from potential misuse.
Is Sp1derHunt3rs ShinyHunters? – July 12, 2024
Aegis threat actor’s skeptical approach
Although it was confident that SpiderHunters (also known as Sp1d3r) and ShinyHunters were collaborating, it remained unclear whether they were the same threat actors. The former administrator of BreachForums, Aegis, who is associated with the Shiny Hunters, implied that SpiderHunters might indeed be ShinyHunters.
Over 10 Million Ticketmaster Mail & Print Event Tickets Leaked – July 12, 2024
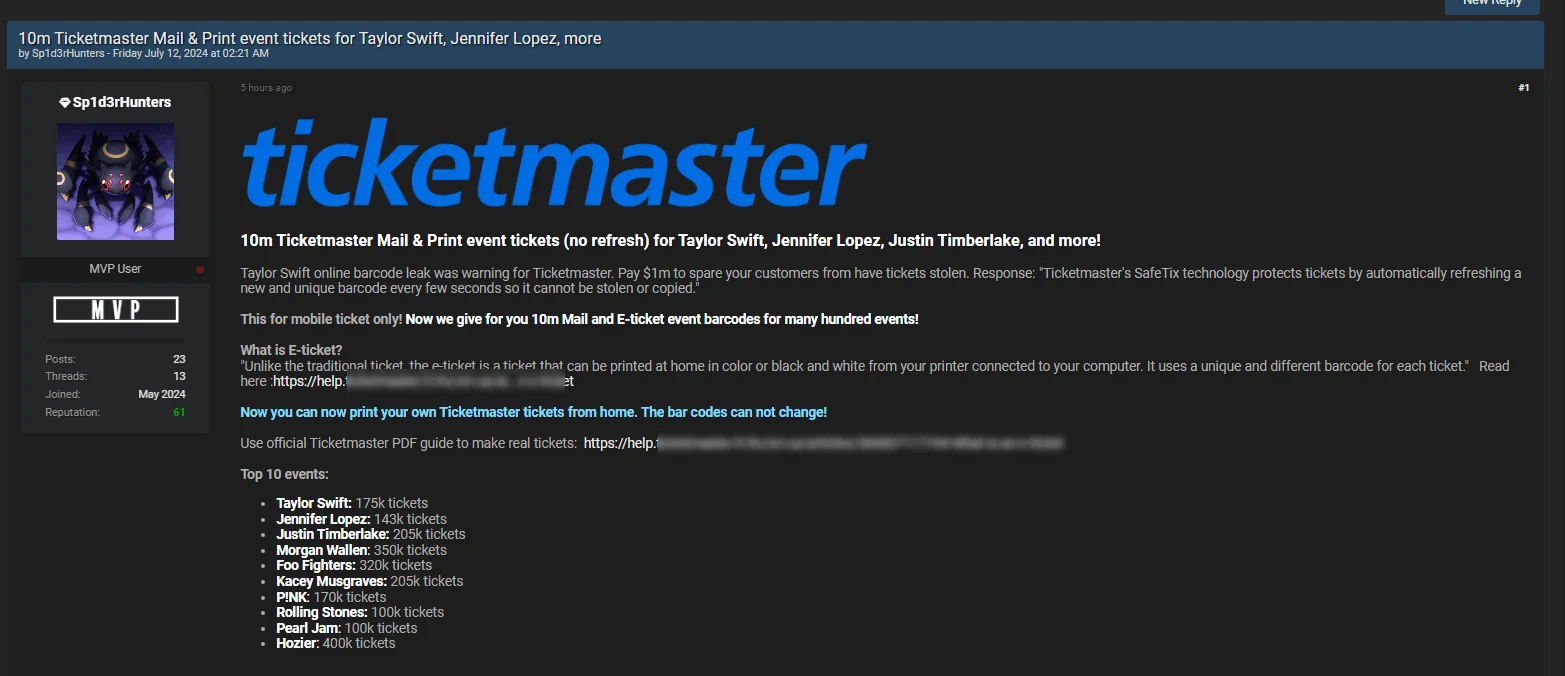
Ticketmaster event tickets leak post
The Sp1derHunt3rs threat actor claims to have leaked 10 million Ticketmaster Mail & Print event tickets for major artists like Taylor Swift, Jennifer Lopez, and Justin Timberlake. This alleged leak is part of ongoing pressure on Ticketmaster by the threat actor. The threat actor stated that the recent Taylor Swift online barcode leak was a warning for Ticketmaster and demanded $1 million to spare customers from having their tickets stolen.
Celebrity Leak Week 2 Exposes High-Profile Names from the Neiman Marcus Breach – July 10, 2024
“Celebrity Leak Week 2” post by Sp1d3rHunters has brought Neiman Marcus into the spotlight, following their previous mention in the company’s Snowflake breach.
The latest leak post purportedly includes VIP data featuring high-profile individuals; names such as Biden, Trump, Christine Pelosi, Kylie Jenner, the Kardashians, Kanye West, and Elon Musk are featured in the sample data.
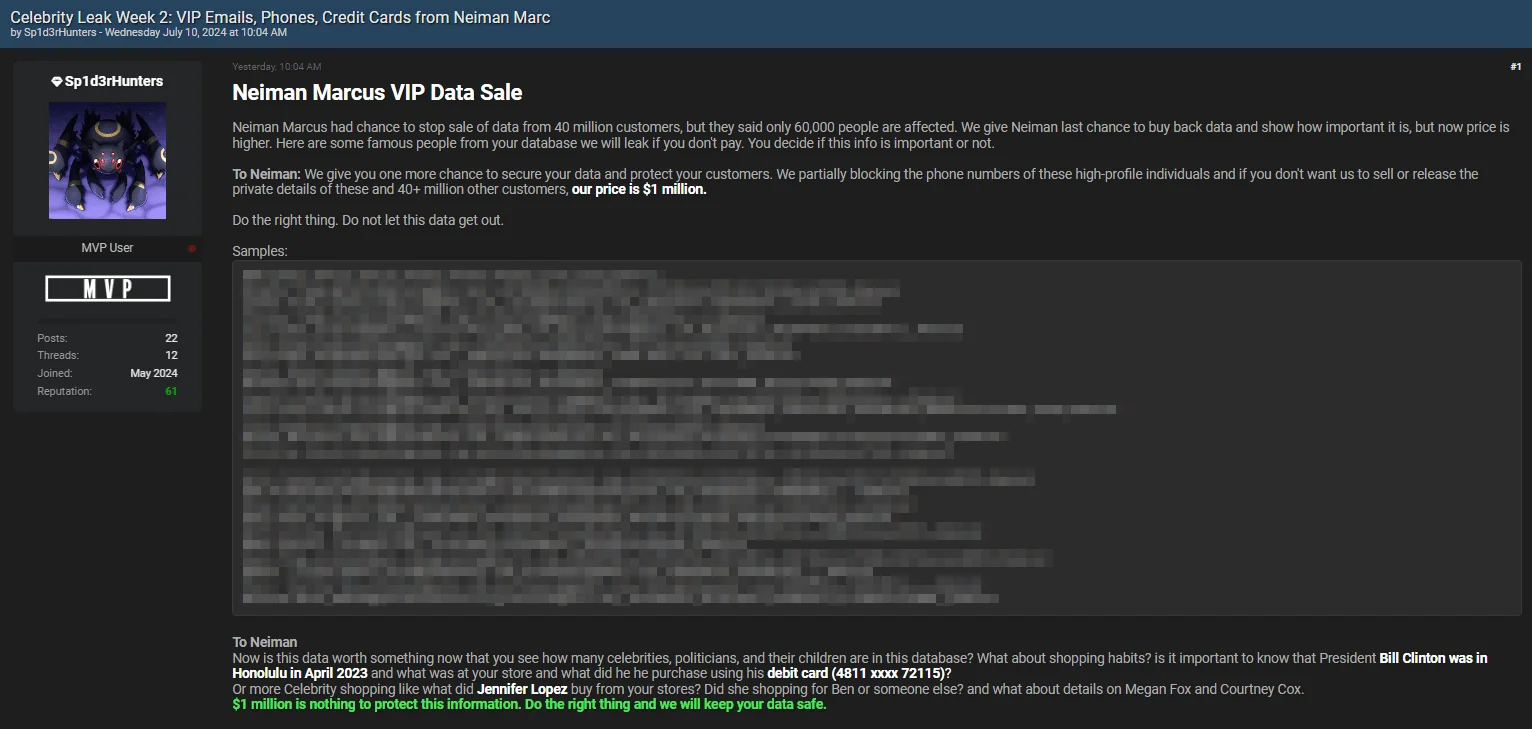
Neiman Marcus VIP Data Sale post by Sp1d3rHunters
The post, designed to create urgency, threatens a massive data leak unless Neiman Marcus pays $1 million. The threat actor stresses that the stolen data contains sensitive details about numerous celebrities, politicians, and their relatives.
Over 30,000 TicketMaster TicketFast Event Barcodes Leaked – July 8, 2024
Sp1d3rHunters quickly followed up with a second leak of event barcodes, still under the banner of Week 1. The threat actor shared over 30,000 tickets, claiming they were stolen from TicketMaster.
In their post, Sp1d3rHunters referenced TicketMaster’s use of SafeTix technology, which frequently refreshes ticket barcodes to prevent theft or duplication. They countered this by stating that the leaked database includes both online and physical tickets, physical ticket types being TicketFast, e-ticket, and mail tickets that can be printed and do not auto-refresh.
The leaked barcodes allegedly cover events for artists such as P!nk, Aerosmith, Chris Brown, Neil Young, Alanis Morissette, Red Hot Chili Peppers, Bruce Springsteen, Usher, Pearl Jam, Sammy Hagar, Stevie Nicks, Steve Miller Band, and Cirque du Soleil, across multiple dates and cities.
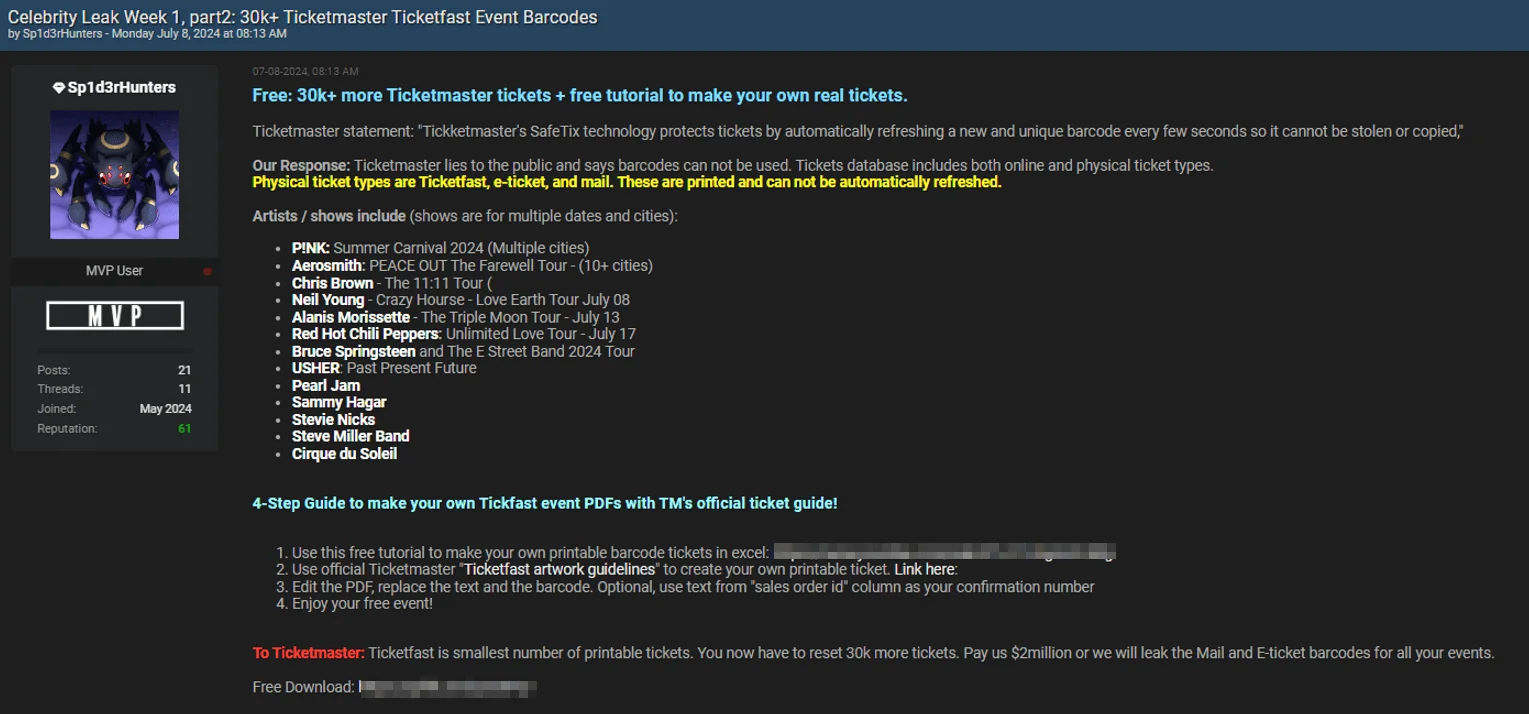
TicketMaster TicketFast event barcodes leak post
ShinyHunters and Sp1d3rHunters Escalate the Ticketmaster Breach – July 5, 2024
On July 4, 2024, the ShinyHunters threat group escalated their conflict with Ticketmaster by posting about a further breach. The hackers claimed they initially accepted a hasty $1 million offer from LiveNation, however, upon realizing the data’s true value, they raised their demand to $8 million.
Notably, ShinyHunters’ post has since been removed from the forum, but here are the details:
In the post, they claimed to have stolen 193 million barcodes, including 440,000 Taylor Swift tickets, valued at nearly $23 billion. The demand in exchange for the data was set at $8 million. Their post, titled “Ticketmaster event barcodes ‘Taylor Swift’ pt 1/65000,” hinted at more alarming news: 30 million tickets for 65,000 events, valued at $4 billion.
They asserted this breach is the “largest publicly disclosed non-scrape breach of customer Personally Identifiable Information (PII) ever.”
Following ShinyHunters’ actions, the Sp1d3r threat actor, now renamed ‘Sp1d3rHunters,’ shared a related breach post on July 5, 2024, allegedly offering 170,000 event barcodes for upcoming Taylor Swift shows. They called it “Celebrity Leak Week 1” and even provided a YouTube tutorial to create printable barcode tickets.
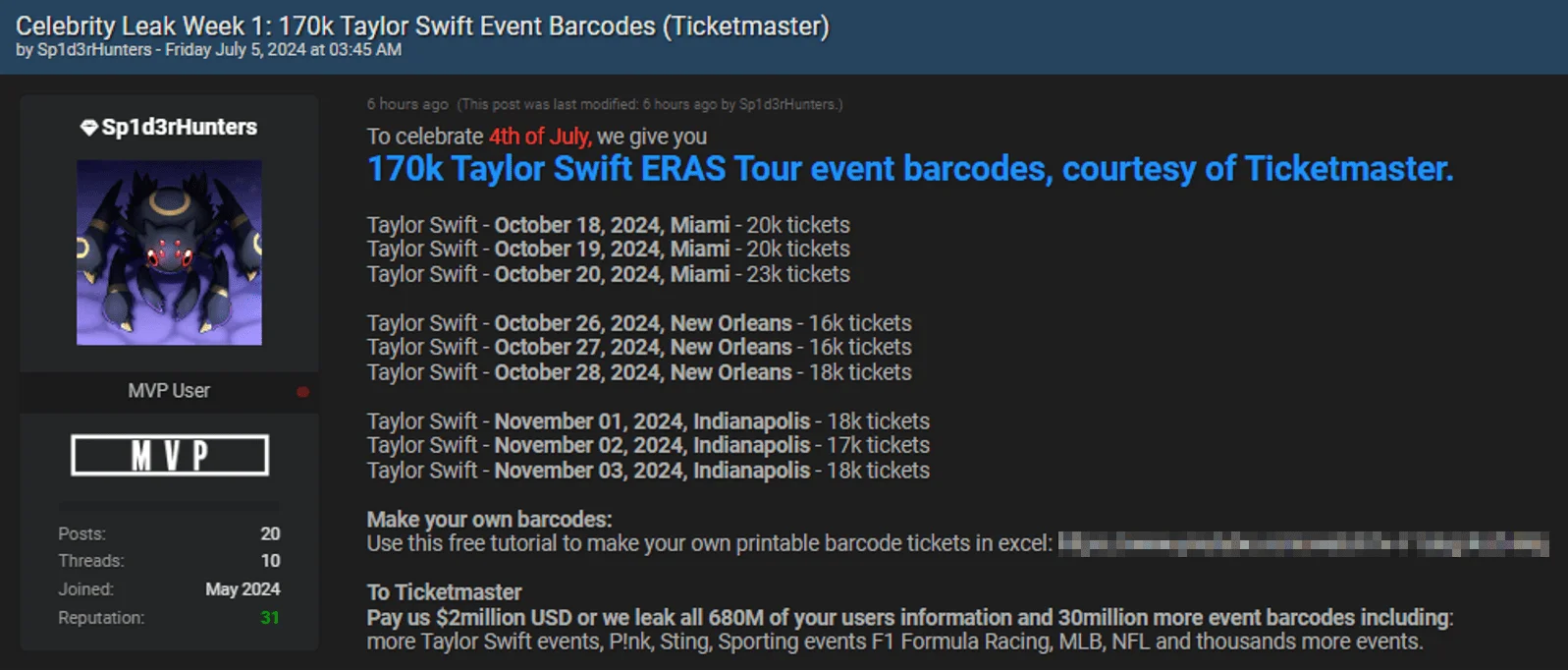
The leak post by ‘Sp1d3rHunters’ includes 170K Taylor Swift event barcodes
Sp1d3rHunters also threatened Ticketmaster, demanding $2 million to prevent the leak of purportedly stolen information on all 680 million users and more than 30 million event barcodes, including those for Taylor Swift, P!nk, Sting, F1 racing, MLB, and NFL events.
This breach poses severe implications for Ticketmaster, including financial loss, reputational damage, regulatory risks, and competitive disadvantage, while millions of users are potentially at risk of identity theft and fraud. The information can be used to create counterfeit tickets, exploit user accounts, and craft phishing emails.
Ticketmaster Notifies Customers of Data Breach – June 30, 2024
Live Nation, Ticketmaster’s parent company, disclosed the Ticketmaster breach to the SEC on May 31. Now, a month later, Ticketmaster is informing its customers that personal information was stolen in the incident.
The notification, accessible on The Office of the Maine Attorney General’s data breach notification page, reveals that attackers accessed a third-party cloud environment between April 2 and May 18, 2024.
Although the exact number of affected customers is still unknown, the Attorney General’s site indicates that over 1,000 individuals were impacted.
The notification does not specify which information was compromised, while Ticketmaster assures customers that their accounts were not directly affected. The company advises to stay vigilant against phishing attempts. Customers should be cautious of emails from unknown senders, suspicious links, attachments, and requests for personal information over the phone.
ShinyHunters Leak Databases from Neiman Marcus and Truist Bank – June 27, 2024
ShinyHunters, who previously re-shared the Santander and Ticketmaster breaches, has now leaked databases from the Neiman Marcus and Truist Bank breaches.
In the Neiman Marcus data leak post, ShinyHunters stated that the company didn’t pay “the small fee for deletion, hiding behind the legal terms they invented…” As a result, ShinyHunters posted the alleged database for free, saying, “…we decided Neiman Marcus can pay $200 million in fines instead.”
The leaked data includes email addresses, balances, credit cards, and other personal details. While Sp1d3r claimed there were 180 million records, ShinyHunters’ leak contains data for 40 million customers.
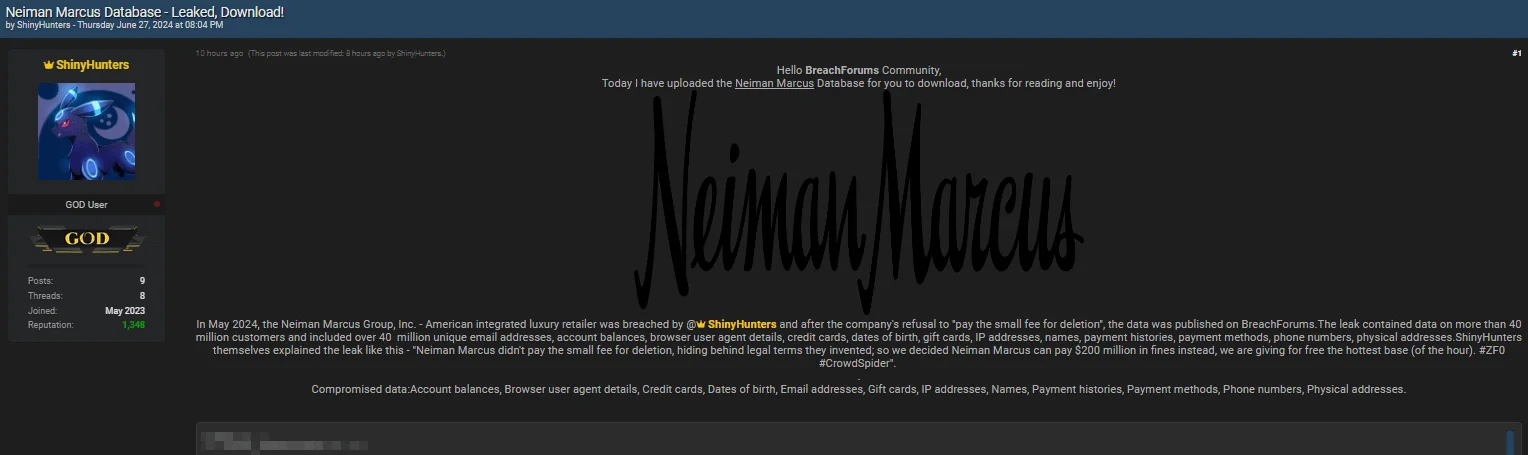
Neiman Marcus data leak post by ShinyHunters
The Truist breach was recently confirmed to be unrelated to a Snowflake breach; the threat actor’s alleged leak post for the company includes personal and partial financial information.
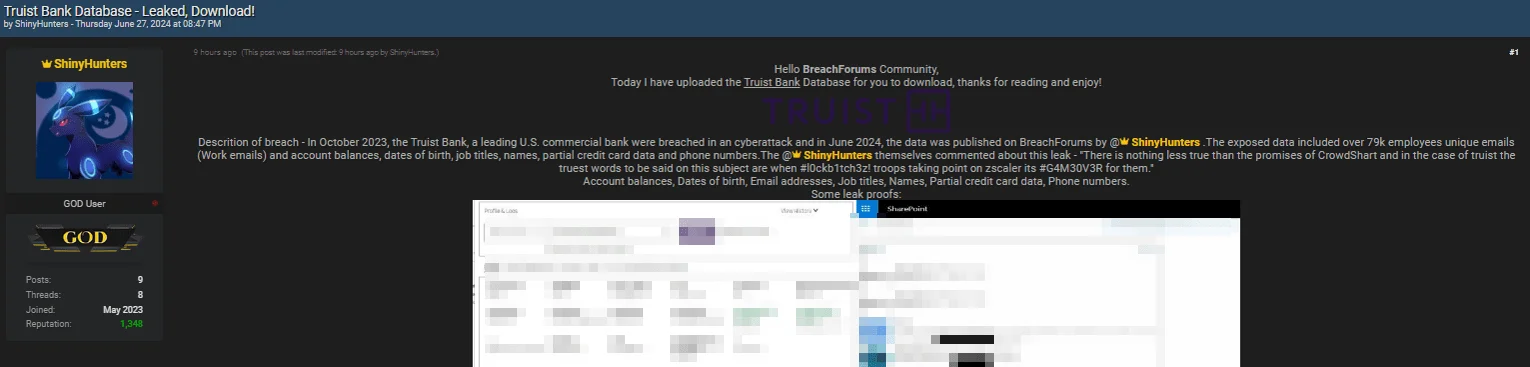
Truist Bank data leak post by ShinyHunters
Here’s a micro-timeline, showing the events of Truist and Neiman Marcus breaches:
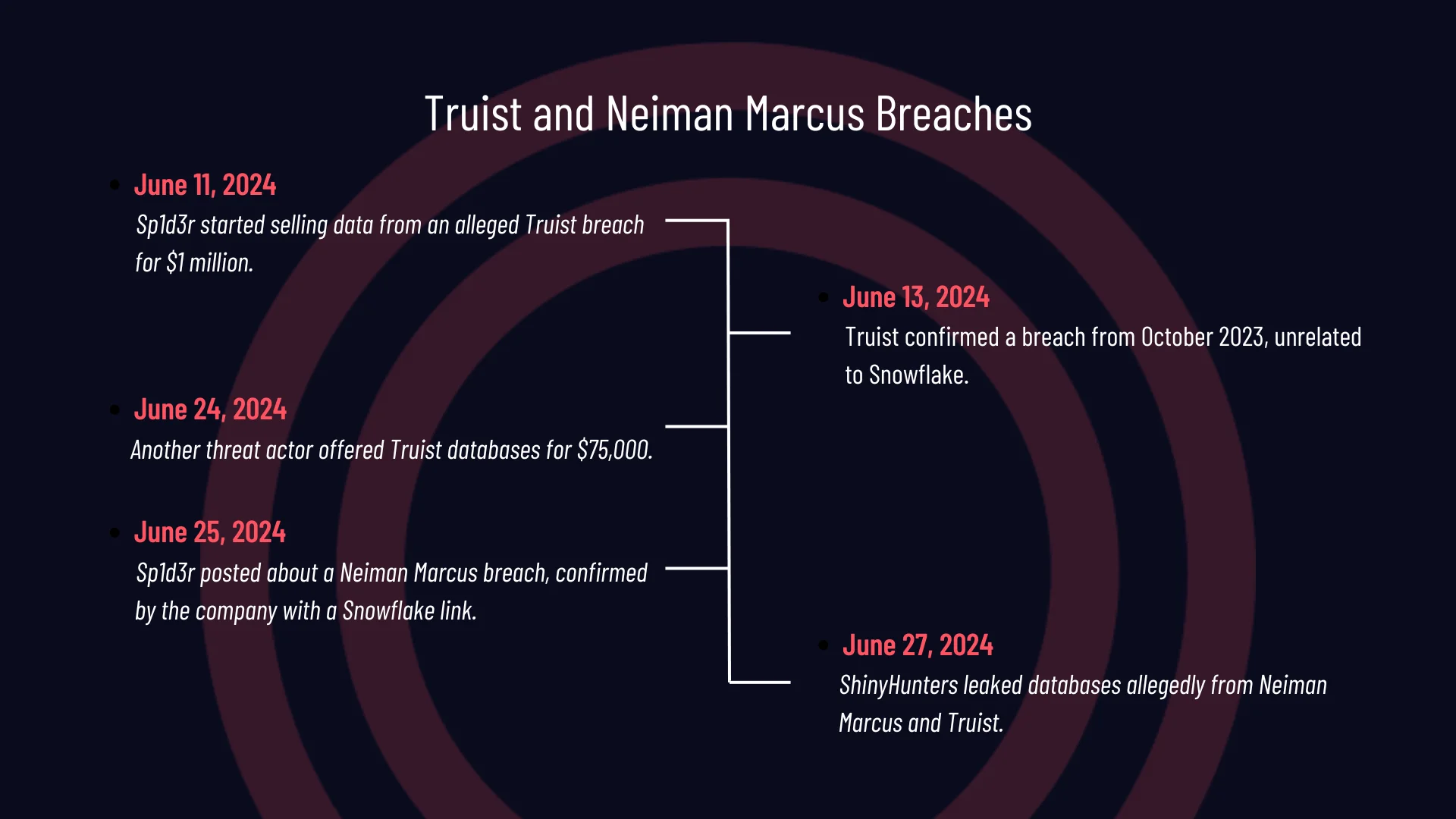
Details of the Truist and Neiman Marcus Breaches
- June 11, 2024: The Sp1d3r threat actor posted about a significant breach allegedly involving Truist Bank. The data was being sold for $1 million.
- June 13, 2024: Truist Bank confirmed the breach from October 2023 but clarified that it was not connected to Snowflake and found no evidence of a Snowflake-related incident.
- June 24, 2024: A hacker forum post claimed all databases in the Truist breach would be sold. This threat actor, neither ShinyHunters nor Sp1d3r, was selling the data for $75,000.
- June 25, 2024: Sp1d3r shared a data breach post involving Neiman Marcus as the company confirmed a Snowflake-related breach.
- June 27, 2024: ShinyHunters leaked databases allegedly belonging to Neiman Marcus and Truist.
Neiman Marcus Group Confirms Snowflake Data Breach – June 25, 2024
Following the post on the hacker forum, the luxury retailer Neiman Marcus confirmed it experienced a data breach due to attackers accessing its account on the Snowflake platform.
In the now-removed post, the threat actor claimed to possess data from 180 million users, including details of 70 million transactions. They also referenced ‘Raped Flake’, a utility used for initial access to Snowflake accounts via SnowSight and SnowSQL interfaces. This attacker utility is also known as ‘FROSTBITE’.
Neiman Marcus reported that the breach began on April 14 and was detected on May 24. Since their intrusion, attackers accessed customer data, including names, contact details, birthdates, and gift card numbers without PINs.
In a data breach notification, Neiman Marcus stated that nearly 65,000 customers had their personal information stolen by an unauthorized party.
The reason for the breach post’s removal is unclear, but it could point to negotiations between Neiman Marcus and the threat actors. Affected customers are advised to stay vigilant for any suspicious activity and follow any further instructions provided by Neiman Marcus.
A Breach of Neiman Marcus, Linked to Snowflake – June 25, 2024
SOCRadar observed that the Sp1d3r threat actor has come forward with a new breach, allegedly involving Neiman Marcus, an American integrated luxury retailer.
The threat actor claims that this breach is related to the Snowflake incident and mentioned they gave Neiman Marcus an opportunity to secure their data by paying a ransom. However, since the company declined their offer, the threat actor has put the data up for sale on a hacker forum.
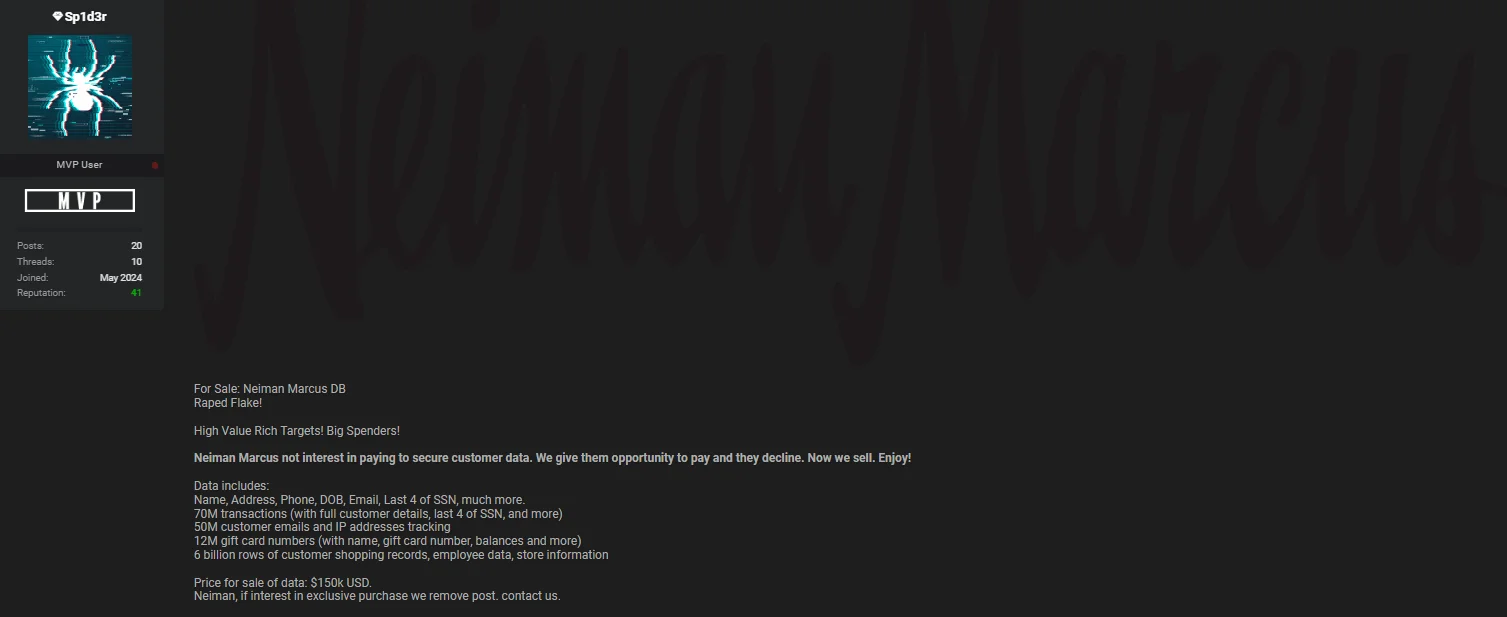
Neiman Marcus Group data breach post by Sp1d3r
The data includes 70 million transactions with full customer details, such as names, addresses, phone numbers, dates of birth, and the last four digits of Social Security numbers (SSNs). Additionally, it comprises 50 million customer emails and IP addresses, 12 million gift card numbers with names and balances, 6 billion rows of customer shopping records, employee data, and store information.
The threat actor is threatening to sell this data for $150,000 if Neiman Marcus does not contact them to take down the post.
Another Breach Post for Truist After the Company’s Latest Announcement – June 24, 2024
In a hacker forum monitored by SOCRadar, a threat actor is now claiming to sell the entire databases from the Truist breach, which was initially thought to be related to the Snowflake incident but was later clarified as unrelated.
The threat actor is offering the data for a significantly reduced price of $75,000, down from the alleged current market value of $1 million. They stated they are open to negotiation and provided samples to prove authenticity.
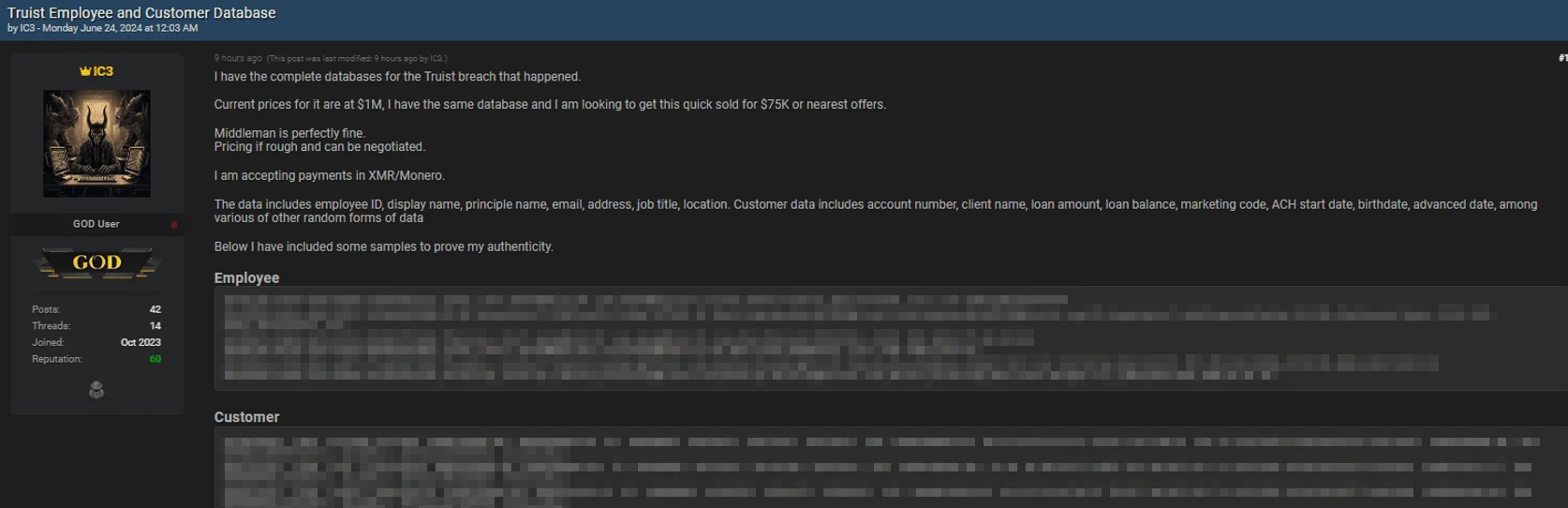
Threat actor leaks alleged databases containing Truist employee and customer information
The compromised data allegedly includes employee ID, display name, principal name, email, address, job title, and location. Customer data in the breach reportedly contains account numbers, client names, loan amounts, loan balances, marketing codes, ACH start dates, birthdates, advance dates, and various other random data forms.
Despite the breach not being connected to Snowflake, it remains significant to monitor this situation. As noted in a previous update, Truist Bank continues its investigation into the incident, which dates back to October 2023. The firm has notified clients and reported finding no indication of fraud arising from the breach. However, given the sensitive information potentially exposed in this new leak, the risk of fraud remains heightened.
1 Million Ticketmaster Users Exposed, Jollibee and TEG Also Breached – June 20, 2024
In an alarming post on a hacker forum, on June 20, the Sp1d3r threat actor leaked the information of 1 million Ticketmaster users for free as a sample.
The threat actor noted that the company did not respond to their attempts to sell the data, concluding that Ticketmaster does not care about the privacy of the 680 million users mentioned to be affected by the breach.
The leaked data includes personal information such as names, birth dates, emails, addresses, IP addresses, and financial information such as credit card type, last four digits, and expiration dates.

Threat actor leaked the information of 1 million Ticketmaster users
On the same day, the threat actor also posted about data breaches involving Jollibee, a Filipino fast food restaurant chain, and TEG, an Australian ticket vendor.
The Jollibee breach allegedly includes 32 million customer records with names, addresses, phone numbers, email addresses, and hashed passwords. Additionally, it involves 650 million rows of data covering food delivery details, sales orders, transactions, customer information, and service-related data. The data is being sold for $40,000.
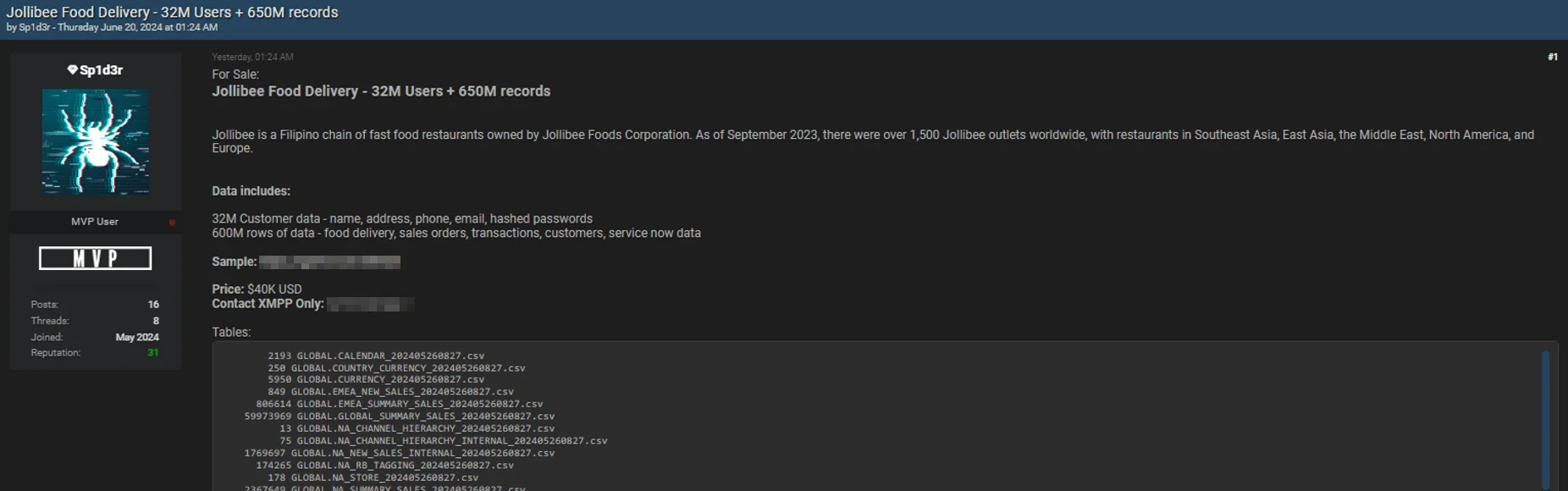
Jollibee Food Delivery data breach post
For TEG, the breached data supposedly contains information on 30 million users, including names, genders, birth dates, businesses, usernames, and hashed passwords, among other details.
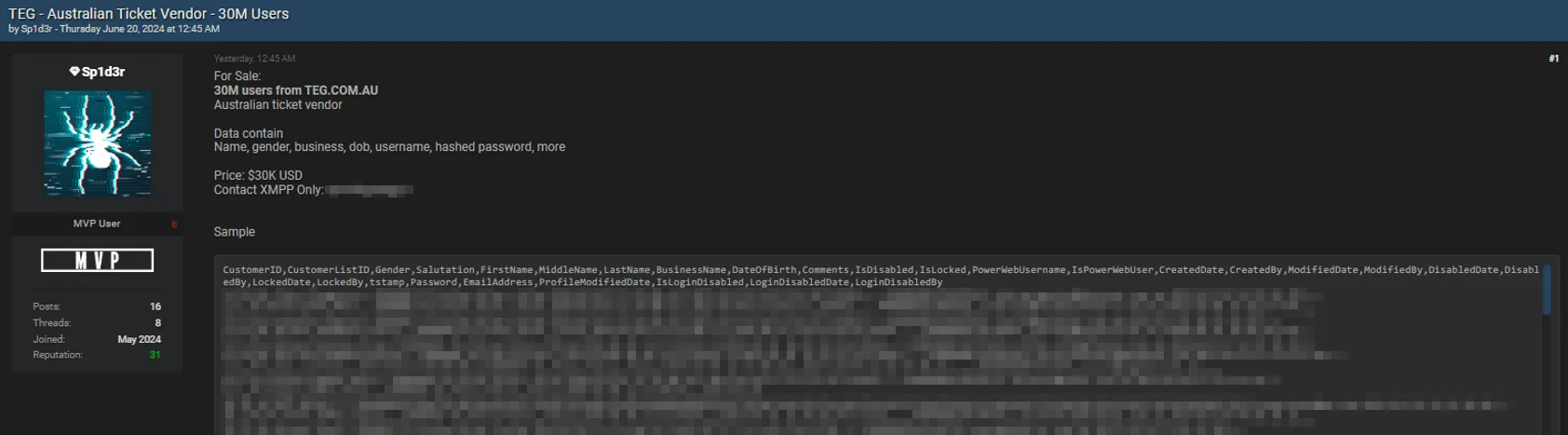
TEG.COM.AU data breach post
While it is unclear if the Jollibee or TEG data breaches are related to Snowflake, the pattern of Sp1d3r’s activity suggests a significant threat. Given their involvement in several notable breaches related to Snowflake, it is advisable to follow these and future breach posts by the threat actor.
Additionally, the threat actor’s allegations appear credible, as Advance Auto Parts (AAP) recently confirmed a breach claimed by Sp1d3r. The company acknowledged that a third-party cloud database was compromised, aligning with the threat actor’s assertions of it being a Snowflake breach.
LAUSD.net, Edgenuity and K12360.com Breached – June 18
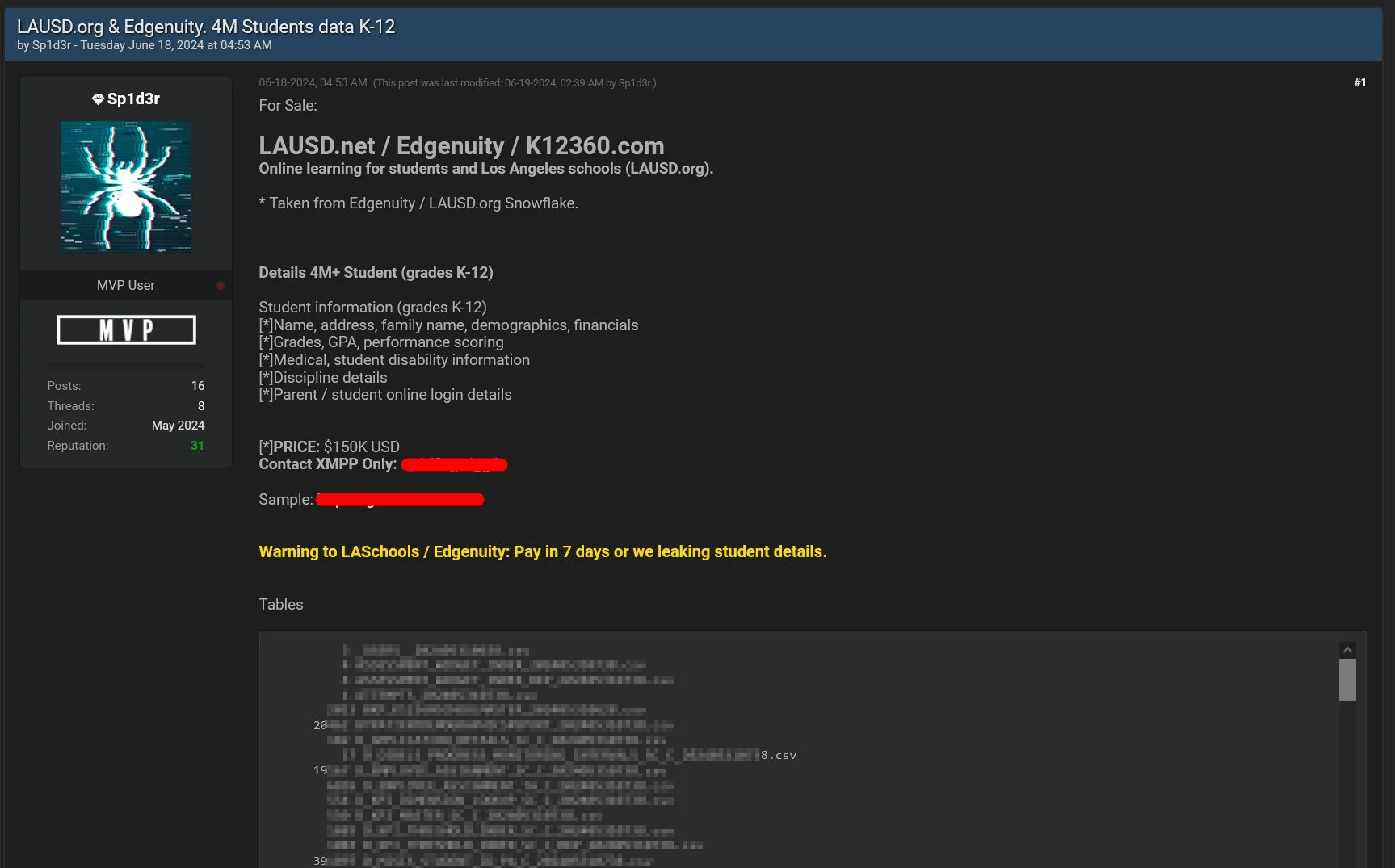
LAUSD.net, Edgenuity, K12360.com breach by @1ZRR4H
The threat actor’s post indicates that 4m+ students’ data is breached, and if LASchools or Edgenuity doesn’t pay the requested amount in 7 days, student details will be leaked.
Advance Auto Parts Confirms Breach – June 14, 2024
Advance Auto Parts has confirmed the data breach previously claimed by the Sp1d3r threat actor. In a Form 8-K filing with the SEC, the company stated that the data was stolen from a third-party cloud database environment, adding credibility to the speculation that Snowflake was involved.
Advance Auto Parts disclosed $3 million in expenses resulting from the breach, which compromised personal information, including Social Security numbers (SSNs) and other government-issued IDs, of current and former employees as well as job applicants.

SEC filing by AAP, released on June 14, 2024
This confirmation further validates the connection to the recent Snowflake breach, underscoring the severity and widespread impact of the incident.
Update on Truist Bank Data Breach – June 13, 2024
There has been a confirmation following the Truist Bank data breach we mentioned on June 11, 2024. The company revealed that its systems were breached in an October 2023 cyberattack, which was swiftly contained.
However, Truist Bank clarified that this breach was not connected to Snowflake, and they have not found any evidence pointing to a Snowflake-related incident within their systems.
Based on new information from the ongoing investigation of the October 2023 incident, Truist Bank has notified additional clients. They also report finding no indication of fraud arising from this breach.
Since the Sp1d3r threat actor’s breach of Truist Bank was confirmed to be unrelated to a Snowflake incident, this clarification calls into question any purported links to Snowflake in other previous or future breach claims by the threat actor.
Pure Storage Confirms Snowflake Breach – June 11, 2024
Pure Storage reported a security incident involving unauthorized access to a Snowflake data analytics workspace.
Pure Storage is a cloud storage systems provider; its platform serves many well-known brands, including Comcast, Equinix, Meta, Ford, JP Morgan, Johnson Controls, and NASA.
This workspace contained telemetry data for customer support, including company names, LDAP usernames, email addresses, and Purity software release versions.
According to the company’s security bulletin, although customer names, usernames, and email addresses were exposed in the Pure Storage breach, credentials for array access or other customer-stored data were not affected.
Truist Bank Data Listed Following a Snowflake Breach – June 11, 2024
The Sp1d3r threat actor has recently posted about a significant data breach involving Truist Bank. This breach, linked to the earlier Snowflake incident, has resulted in the theft of a substantial amount of sensitive data, being sold for a staggering $1 million.
The compromised information includes detailed records of 65,000 employees, covering both personal and professional details. Additionally, the breach involves sensitive bank transaction data and the source code for Truist Bank’s IVR funds transfer system.
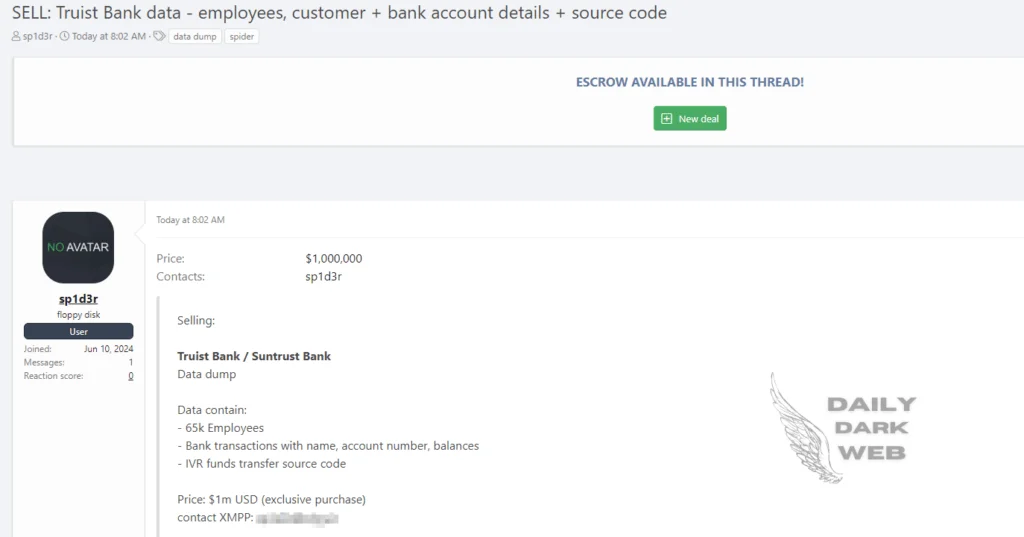
Truist Bank data breach post (Daily Dark Web)
Attribution to ‘UNC5537’ and More Details – June 10, 2024
Google Mandiant is tracking the activity targeting Snowflake customers as UNC5537, attributing it to be a financially motivated threat actor.
Researchers described UNC5537 as a threat actor who systematically compromises Snowflake customer instances, using stolen credentials from stealer logs for access. They advertise the exfiltrated victim data for sale on hacker forums and attempt to extort the victims.
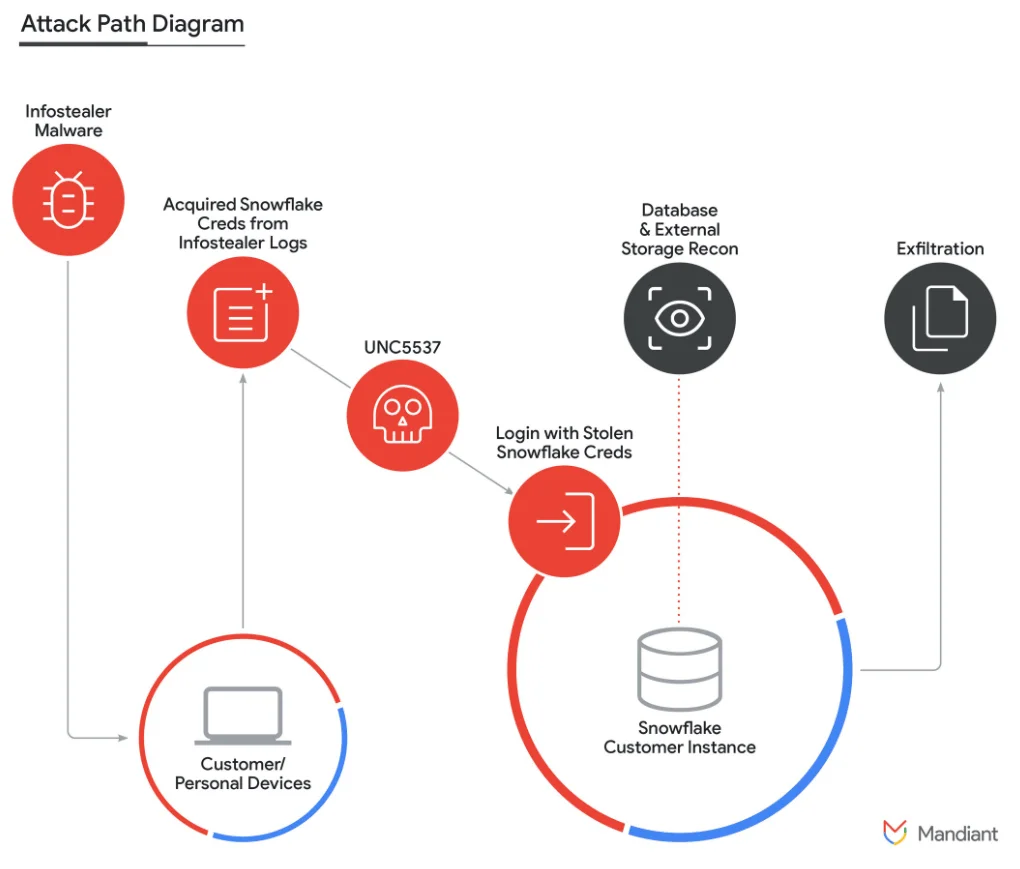
A diagram for Snowflake incidents (Google Cloud Blog)
According to reports, there is no evidence that unauthorized access to Snowflake customer accounts resulted from a breach of Snowflake’s enterprise environment. Instead, every incident responded to in this campaign was traced back to compromised customer credentials.
Alleged Data Breach Post, Targeting LAUSD.org – June 7, 2024
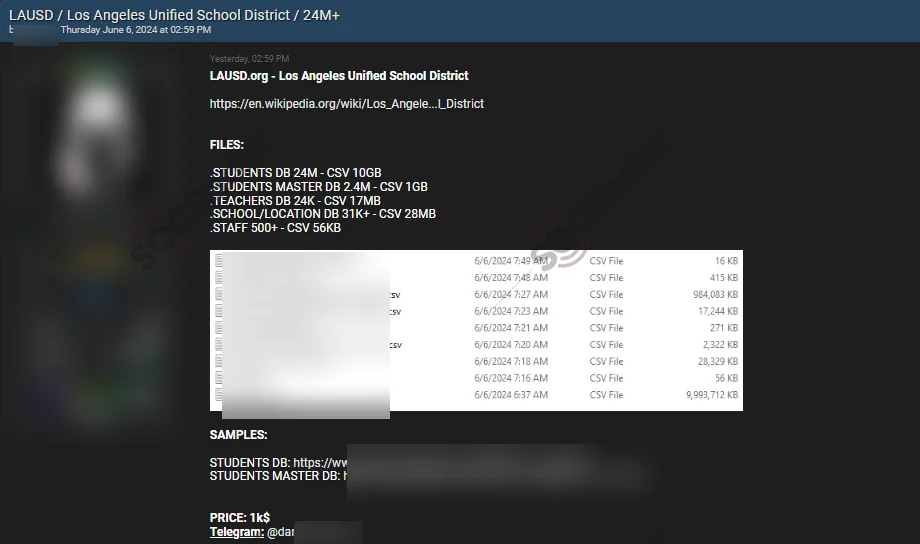
Alleged Data Breach of LAUSD from June 7
According to a post from a dark web forum monitored by SOCRadar, LAUSD was breached. The alleged breach consists of over 24 million records. The stolen data includes student, teacher, school and staff databases and sample data is published.
New Data Breach Post by Sp1d3r, Targeting Cylance – June 7, 2024
The Sp1d3r threat actor, known for claiming the Snowflake breaches, is now selling stolen data from Cylance, a cybersecurity company and Snowflake customer.
The data allegedly includes 34 million customer and employee emails and PII, along with product details, sales prospects, partners, and user lists, and is put up for $750,000.
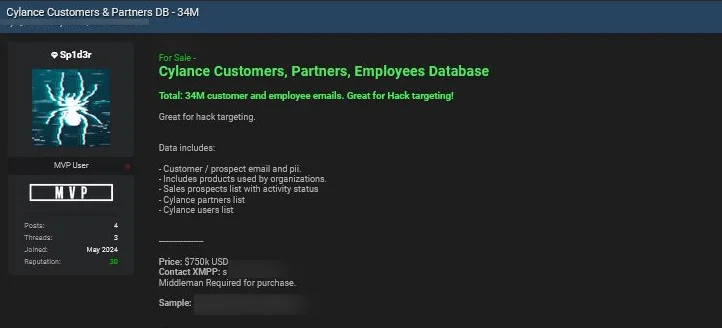
Cylance data breach post by Sp1d3r
Cylance has confirmed the legitimacy of the data breach post while clarifying that it is old data accessed from a third-party platform between 2015 and 2018, predating BlackBerry’s acquisition of Cylance. The company assured that no current customers are affected by this breach.
ShinyHunters Removes the Post for Santander – June 6, 2024
On June 6, 2024, SOCRadar noticed that ShinyHunters removed its breach post for Santander Bank. There is no trace of it in the threat group’s recent postings on their forum profile.
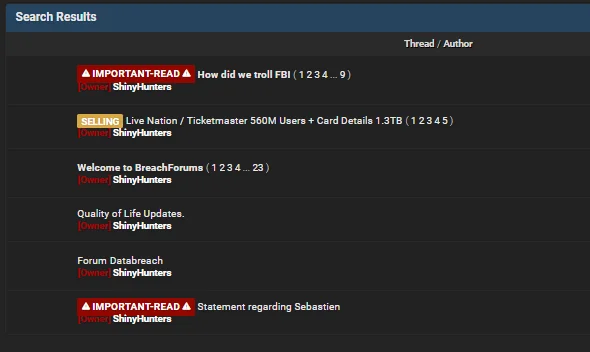
Recent forum posts by ShinyHunters
The data of Santander was initially put on sale for $2 million by the “whitewarlock” threat actor. The post was mirrored by the ShinyHunters group on BreachForums.
The removal of the breach post by ShinyHunters could suggest that the data was quickly sold by the threat actors, although there are no announcements by them.
Advance Auto Parts Data Breach Post – June 5, 2024
The Sp1d3r threat actor, previously mentioned in other breach posts, claims to be selling 3TB of data from Advance Auto Parts on a hacking forum. This breach is allegedly linked to the Snowflake incident, with data purportedly stolen after breaching the company’s Snowflake account.
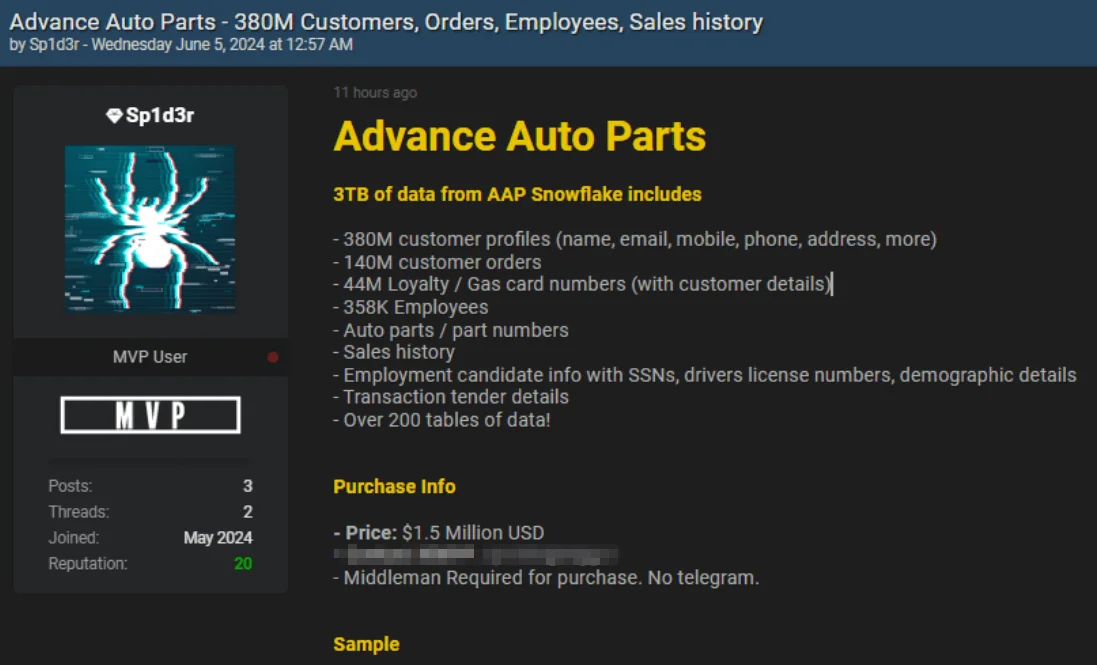
Advance Auto Parts data breach post by Sp1d3r
The threat actor lists the stolen data as including 380 million customer profiles, 140 million customer order records, 44 million loyalty card numbers with related customer details, auto parts information, sales history, and employment candidate details such as Social Security numbers, driver’s license numbers, and demographic details. It also includes transaction details, and critically, information on 358,000 employees.
In actuality, Advance Auto Parts currently employs around 68,000 people. If the breach is authentic, it could mean that the remaining data belongs to former employees.
The threat actor is offering this data for $1.5 million. The only partial confirmation of this breach is that the leaked data contains numerous references to Snowflake, supporting the claim that it is linked to the recent Snowflake breach.

References to SNOWFLAKE in the stolen data (@H4ckManac on X)
Another Breach Post, Possibly Related to the Snowflake Incident: QuoteWizard & LendingTree – June 1, 2024
On June 1, a claim posted on BreachForums caught the attention of SOCRadar researchers. The post, made by a user with a nickname resembling the “SpidermanData” threat actor from the Exploit forum, was identified as belonging to a threat actor named Sp1d3r. This threat actor claimed to have obtained a significant amount of data from two leading companies in the insurance and financial services sectors, QuoteWizard and LendingTree.
The data, which allegedly reached 2TB when compressed, was said to include highly sensitive personal information of 190 million individuals and 3 billion tracking pixel data records.
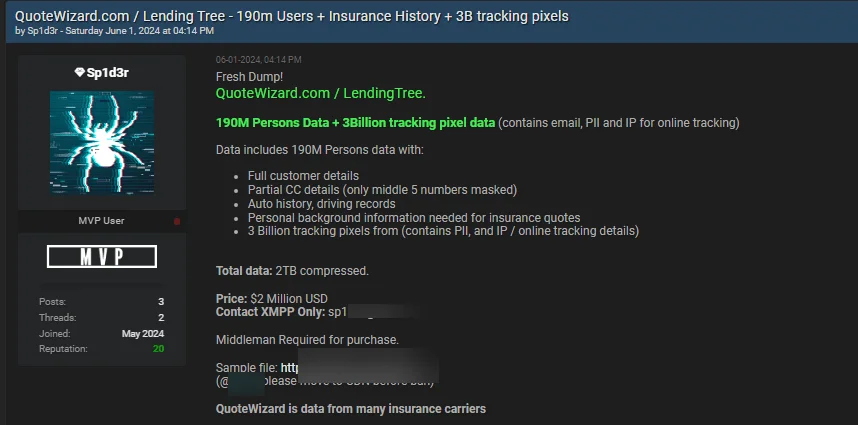
QuoteWizard & LendingTree data breach post by Sp1d3r
When asked in the comments how he obtained the data, the threat actor hinted at stealing it from SnowFlake by stating, “I *** the flake.”
Threat actor’s comment, hinting at a breach of Snowflake
Snowflake’s Disclosure About the Breach – May 31, 2024
On May 31, Snowflake began updating a thread about an investigation into a targeted threat campaign against some customer accounts. In their latest statement, Snowflake, along with third-party cybersecurity experts, reported no evidence of vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, or breaches within Snowflake’s platform. They also confirmed that no current or former employee credentials were compromised.
The thread was later updated, on June 2, to state that there was evidence that a threat actor obtained personal credentials and accessed demo accounts belonging to a former Snowflake employee.
Live Nation Confirms the Ticketmaster Data Breach – May 31, 2024
On May 31, Live Nation, Ticketmaster’s parent company, confirmed the data breach. In their SEC filing, Live Nation stated, “On May 20, 2024, Live Nation Entertainment, Inc. (the “Company” or “we”) identified unauthorized activity within a third-party cloud database environment containing Company data (primarily from its Ticketmaster L.L.C. subsidiary) and launched an investigation with industry-leading forensic investigators to understand what happened. On May 27, 2024, a criminal threat actor offered what it alleged to be Company user data for sale via the dark web. We are working to mitigate risk to our users and the Company, and have notified and are cooperating with law enforcement. As appropriate, we are also notifying regulatory authorities and users with respect to unauthorized access to personal information.”
ShinyHunters Mirrors the Santander Breach Post – May 30, 2024
On May 30, the threat actor ShinyHunters reposted the previously reported Santander breach on BreachForums, mirroring an earlier post originally published by the threat actor known as “whitewarlock”. ShinyHunters, known for acting as a data broker for various threat actors, brought significant attention to this incident.
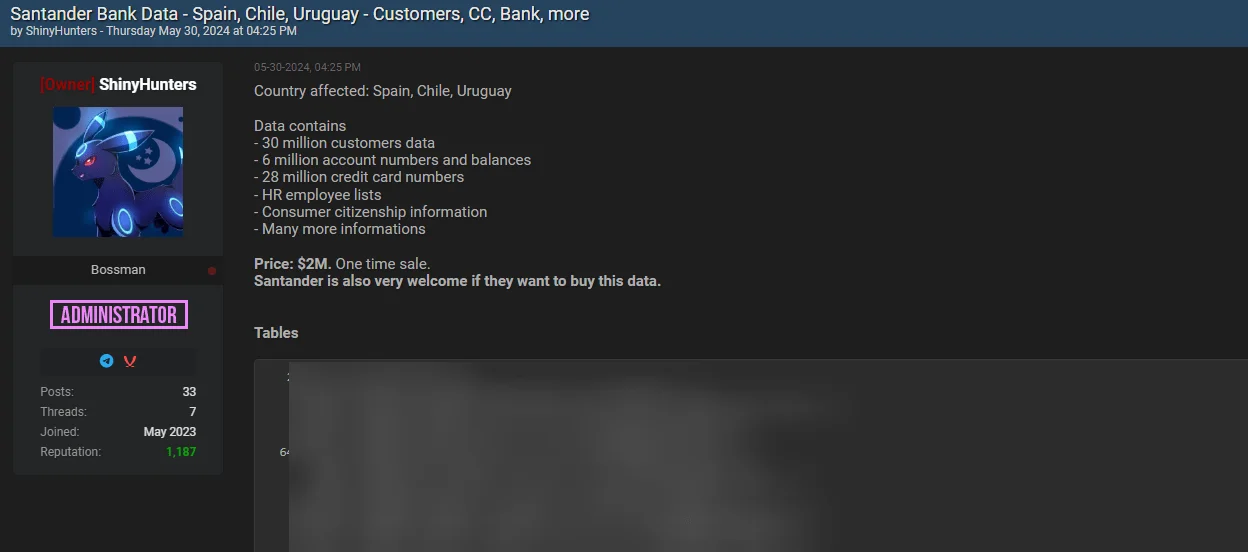
Santander Bank data breach post by ShinyHunters
ShinyHunters Mirrors the Ticketmaster Breach Post – May 28, 2024
On May 28, ShinyHunters, a notorious hacking group, shared a Ticketmaster post mirrored from Exploit on BreachForums.
This was significant because it coincided with the reactivation of BreachForums’ clear net domain, which had been seized by law enforcement in mid-May 2024. ShinyHunters announced via a Telegram post that they had regained control of the domain, signaling a major event in the cybercriminal community.
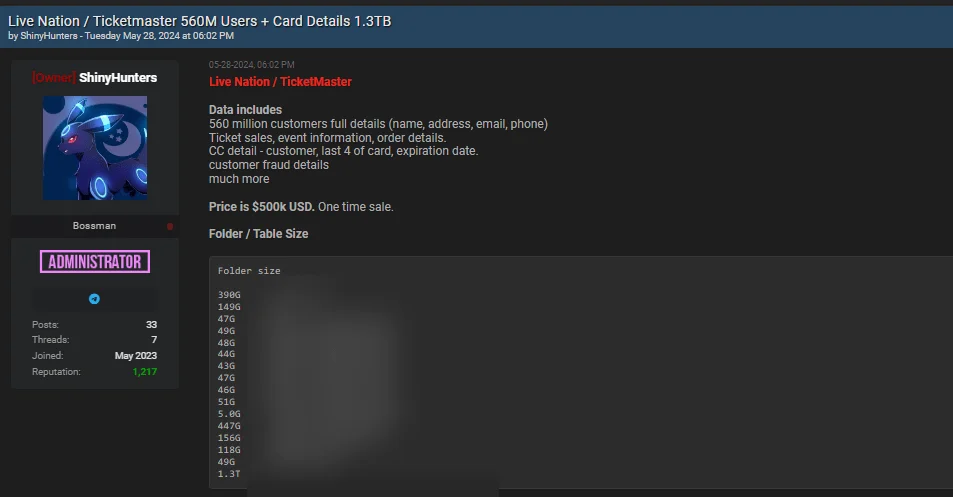
Ticketmaster Data Breach Post on Hacker Forum – May 27, 2024
On May 27, a threat actor using the alias SpidermanData registered on the Exploit hacking forum. On the same day, they claimed to have access to Ticketmaster’s systems and claimed possession of 560 million user and financial records. SpidermanData demanded $500,000 for the data.
The extensive information offered included full names, addresses, email addresses, phone numbers, order details, ticket sale information, event details, and even credit card information, including expiration dates.
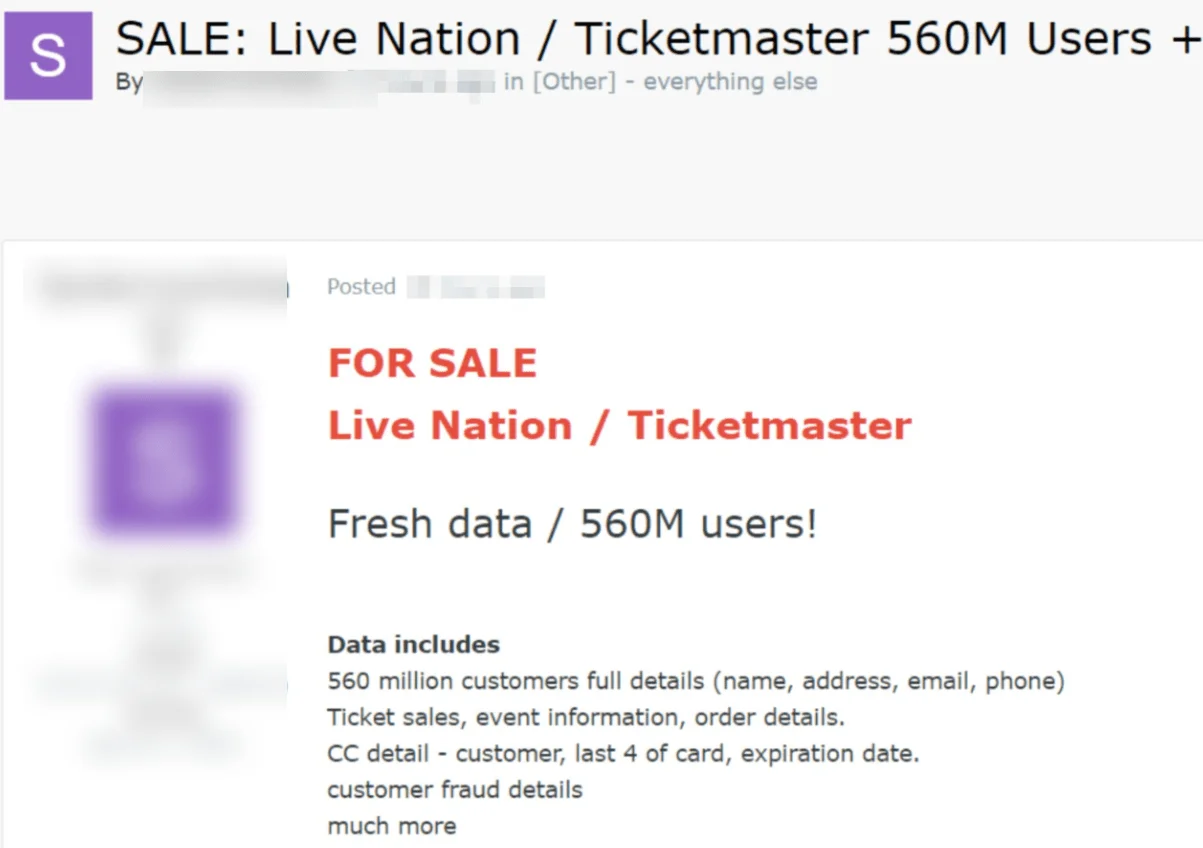
Ticketmaster data breach post
Santander Data Breach Post on Hacker Forum – May 24, 2024
On May 24, a threat actor named “whitewarlock,” who registered on the same day, claimed on the Russian-speaking hacker forum Exploit that they had hacked Santander Group.
The attacker stated that they had obtained the bank account details of 30 million people, 6 million account numbers and balances, 28 million credit card numbers, and HR information for staff. The hacker demanded 30 BTC (approximately $2 million) for the data.
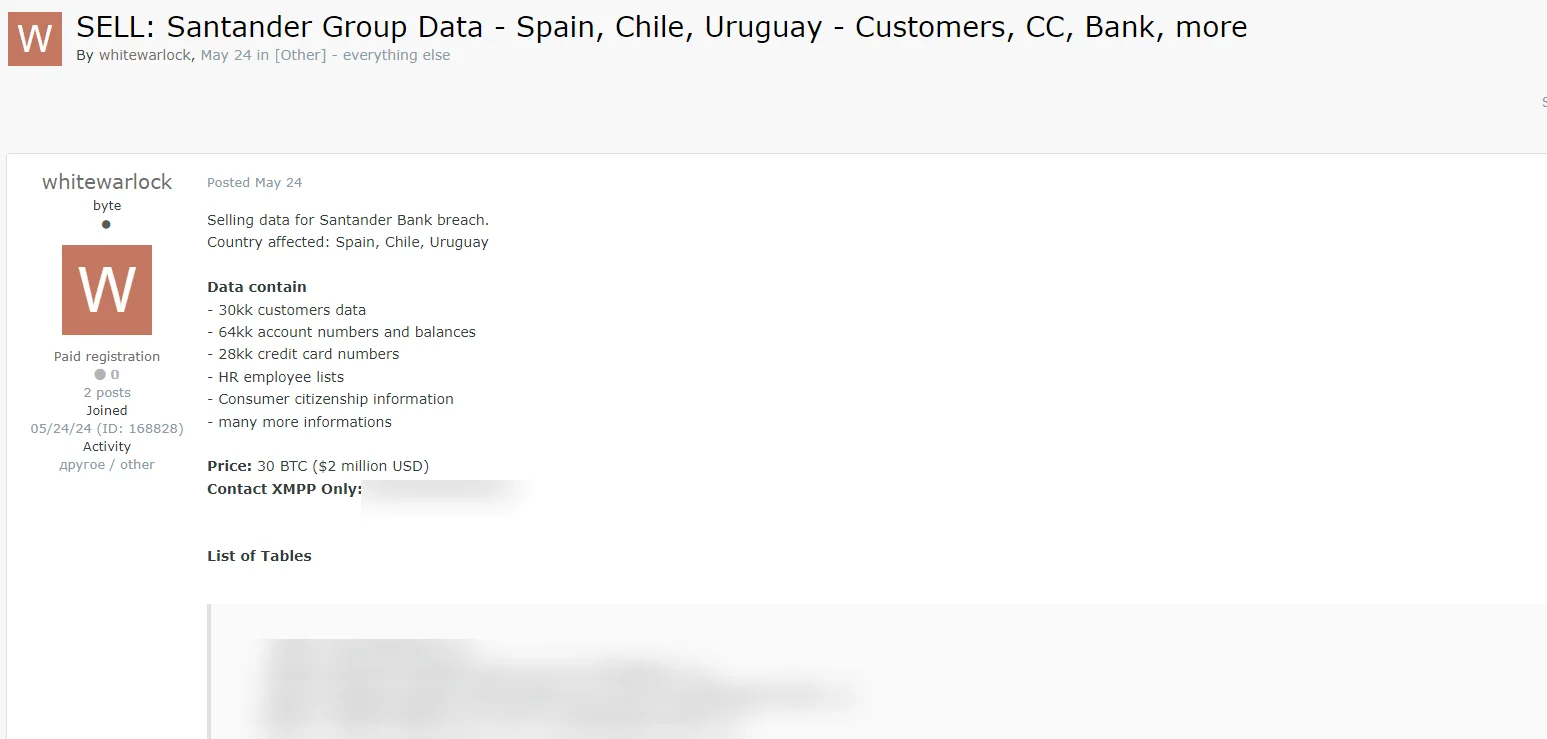
Santander Group data breach post by the Whitewarlock threat actor
Santander Bank’s Announcement – May 14, 2024
On May 14, Santander announced, “We recently became aware of an unauthorized access to a Santander database hosted by a third-party provider. We immediately implemented measures to contain the incident, including blocking the compromised access to the database and establishing additional fraud prevention controls to protect affected customers.” This initial response highlighted the bank’s quick action to secure the compromised data and mitigate potential fraud risks.
By utilizing the SOCRadar XTI platform, organizations can stay ahead of cyber threats, protecting their data and reputation. With its extensive monitoring capabilities across all internet surfaces, including the often elusive dark web, SOCRadar offers Dark Web Monitoring and Dark Web News services, among its other capabilities.
Dark Web Monitoring acts as a digital periscope, delving into the dark web to detect and track the unauthorized distribution of sensitive data. With the Dark Web Monitoring module, organizations can receive immediate notifications about potential threats, enabling swift actions to mitigate risks.
By monitoring the dark web, you can maintain a vigilant watch on discussions and activities related to your organization among threat actors, ensuring you are always informed of potential vulnerabilities.
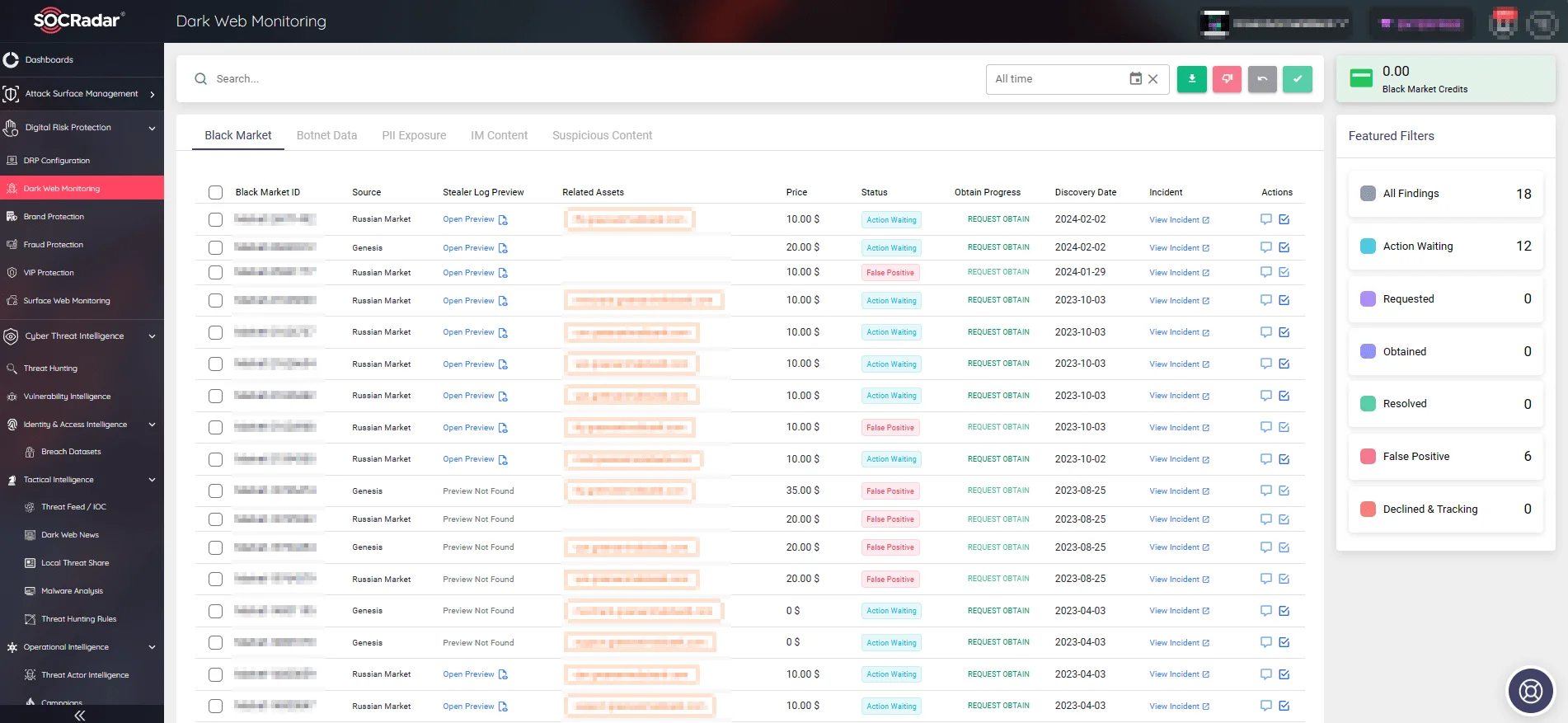
Dark Web Monitoring feature under the Digital Risk Protection module
Recommended Actions for Snowflake Users in the Aftermath of the Breach
In response to the recent security breach, Snowflake has issued several recommendations to help customers secure their accounts and prevent future incidents. The recommendations included enabling Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), reviewing IoCs, and following security best practices, along with several steps.
As the issue became more concerning, the company updated its initial breach disclosure from May 2024 on June 1, adding a guide for identifying non-MFA users and enabling MFA; another update came on June 3 with detection and prevention guidelines.
Here’s a detailed action plan in the context of the Snowflake security breach, based on the company’s guidelines:
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implementing MFA adds an additional layer of security, making unauthorized access more challenging.
- Review Indicators of Compromise (IoCs): Check for any signs of compromise provided by Snowflake and investigate any suspicious activity linked to these indicators. This includes identifying access from suspected IP addresses and clients.
- Disable Suspicious Users: Immediately disable any users who show unusual activity or are suspected of being compromised.
- Reset Credentials: For any users or accounts that might have been exposed, reset their credentials to prevent further unauthorized access.
- Monitor Executed Queries: Regularly review the logs for executed queries, especially those that involve external data access or could potentially expose sensitive information. Doing this for identified suspects is especially important.
- Analyze Sessions for Unusual Applications: Examine active sessions to identify any non-standard applications or tools that might indicate a breach.
There are also a few preventative measures recommended by the company:
- Set Up Network Policies: Establish network policies at both the account and user levels, particularly for users or service accounts with extensive permissions.
- Review Account Parameters: Ensure that account settings are configured to limit data exportation and align with best security practices.
- Monitor Configuration Changes: Keep an eye on your account configurations for any unauthorized changes that could suggest privilege escalation.
- Authenticate Service Accounts Securely: For machine-to-machine communications, utilize more secure methods like key pair authentication or OAuth instead of static credentials.
Snowflake’s guidance for detecting and preventing unauthorized access includes numerous IP addresses under investigation for suspicious activity, potentially related to the breach, as well as complete guides and queries to implement these measures.
CISA Issues Alert on Snowflake Breach, Urges Immediate Action
Following the security breach targeting the cloud data platform, the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) issued a new alert as a complimentary action plan to Snowflake’s guidance.
The agency noted for context that Snowflake has observed a significant increase in cyber threat activity targeting customer accounts and issued recommendations to prevent unauthorized access. CISA advises users and administrators to hunt for malicious activity, report any positive findings to CISA, and review Snowflake’s recommendations.
TTPs
- Credential Theft: Threat actors used information-stealing malware to obtain employee credentials. Specifically, a Snowflake employee’s credentials were stolen using the Lumma infostealer.
- Credential Stuffing: The attackers utilized these stolen credentials to log into Snowflake accounts, bypassing multi-factor authentication (MFA) in some cases.
- Session Token Generation: Once logged in, attackers generated session tokens, which allowed them to maintain persistent access and exfiltrate large amounts of data.
- Exploitation of Single-Factor Authentication: Many compromised accounts were not protected by MFA, making them more susceptible to unauthorized access.
- Custom Tools: The attackers used a custom tool named ‘RapeFlake’ for data exfiltration from Snowflake databases.
Threat Hunting & Real-Time Security Monitoring with SOCRadar
SOCRadar’s cybersecurity solutions can strengthen your organization’s security posture against similar breaches. The Cyber Threat Intelligence and Attack Surface Management modules from SOCRadar provide essential tools designed to proactively manage such security threats.
By using the Threat Hunting service under the CTI module, defenders can actively monitor and evaluate the security of assets, track potentially harmful IPs and domains, find exposed data on hacker forums and other channels, and examine stealer logs for compromised data.
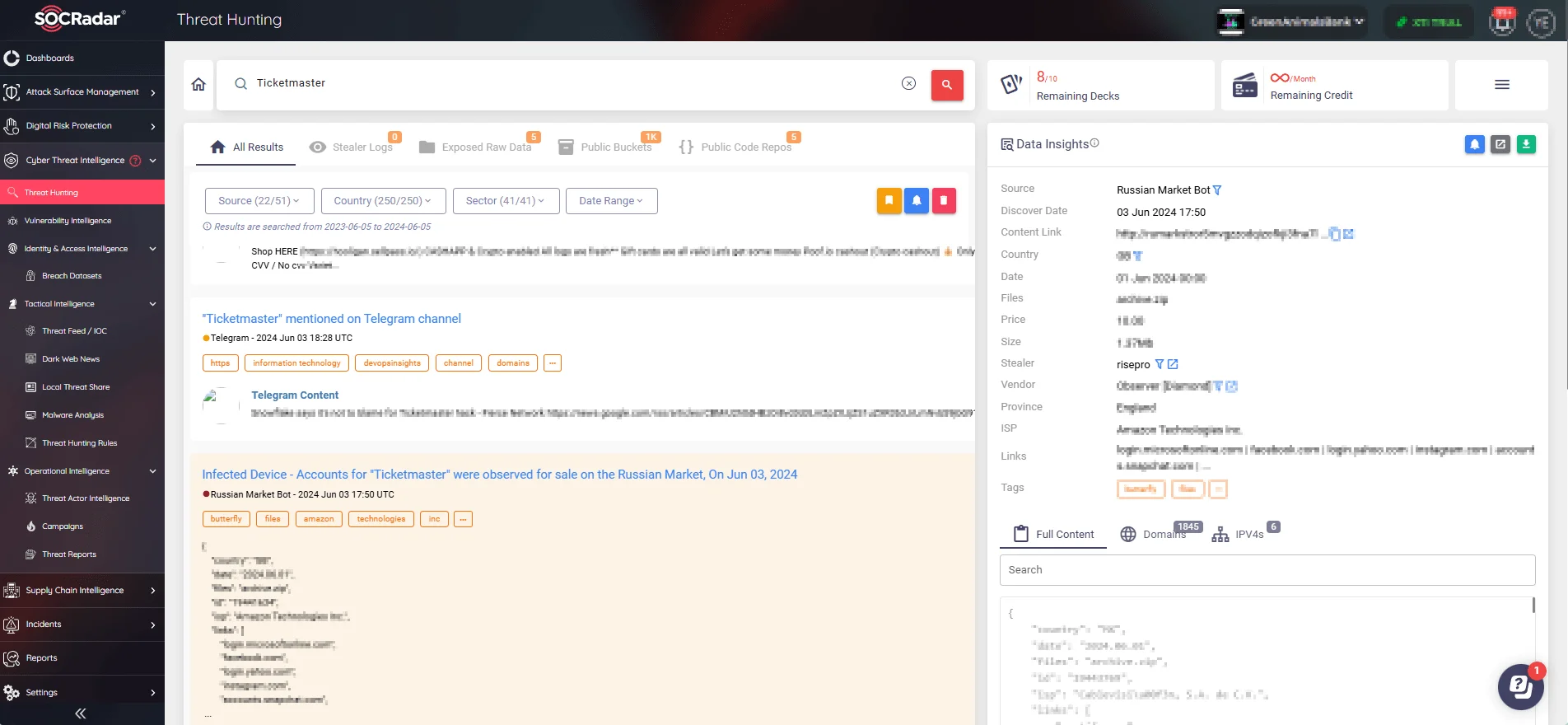
SOCRadar’s Threat Hunting
The Threat Actor Intelligence feature, also offered under our CTI module, offers insights into malicious entities and delivers actionable IoCs, enhancing your ability to respond to threats swiftly.
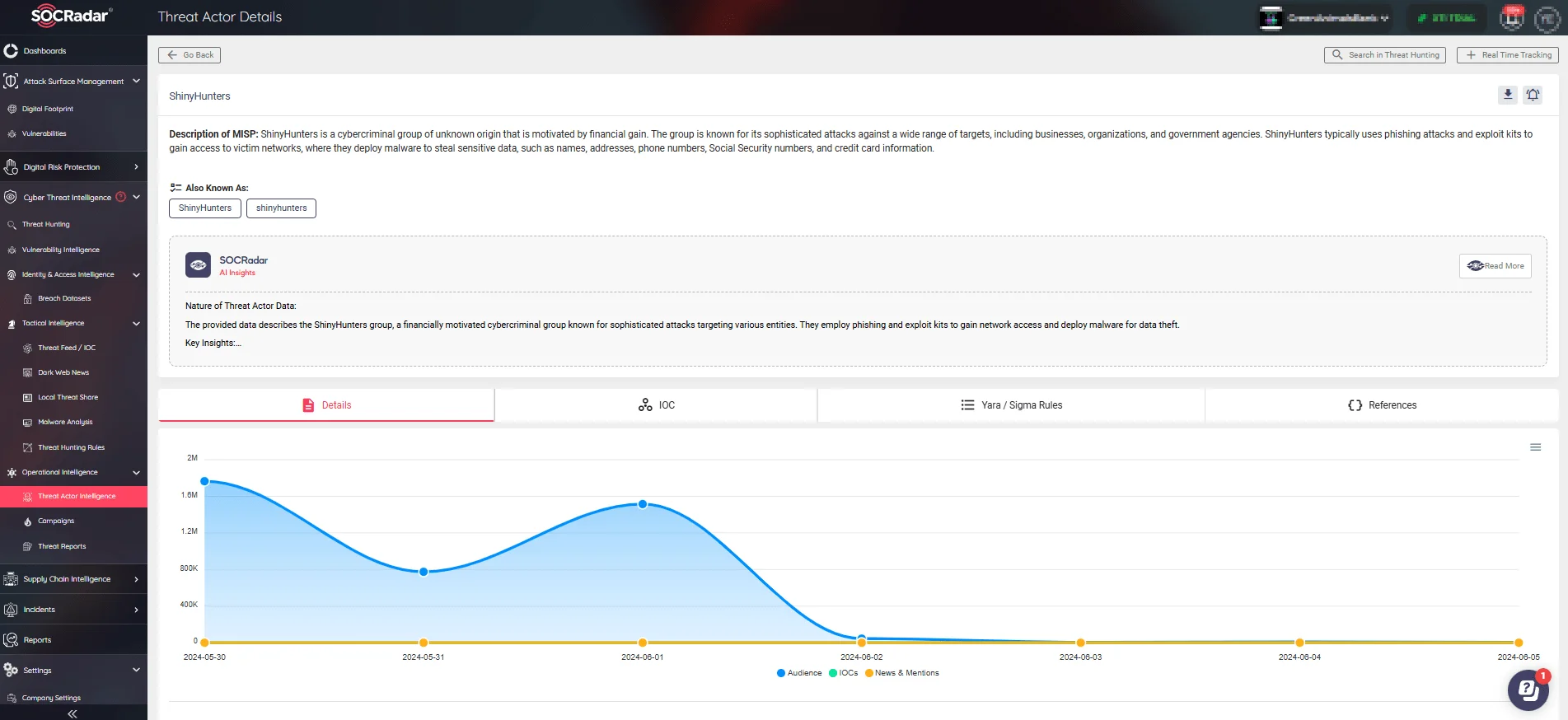
Threat actor details page of ShinyHunters (SOCRadar Threat Actor Intelligence)
Additionally, SOCRadar’s Attack Surface Management module enables real-time monitoring of your digital environment, detecting and reporting unusual activities that could indicate unauthorized access or other security breaches. This continuous monitoring helps to ensure that any anomalies are quickly identified and addressed, maintaining the integrity and security of your valuable data.
SOCRadar’s Alarm Management tab
DOJ Indictment Reveals Details of Massive Snowflake Data Breach and Ransom Operation
The U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) has released an indictment detailing allegations against hackers Connor Riley Moucka and John Erin Binns, accused of breaching over 165 organizations through compromised Snowflake cloud accounts.
The threat actor’s haul included approximately 50 billion call and text records from a prominent U.S. telecommunications firm, likely AT&T, which disclosed in July 2024 that the records of 109 million customers were accessed.
After obtaining the data, Moucka and Binns allegedly demanded ransom payments from various victims, including AT&T, which reportedly paid in cryptocurrency in May. To conceal the transaction trail, they used multiple cryptocurrency exchanges, ultimately converting the funds into Monero (XMR). Some organizations were even pressured for additional ransom after initial payments were made.
Moucka, apprehended in Canada, and Binns, detained in Turkey, face numerous charges and could be sentenced to a combined total of up to 60 years in prison if convicted. The DOJ is also seeking to seize their assets tied to these cybercrime activities.