
The Future of Passwordless Authentication in Cybersecurity
Passwordless authentication is a validation method that eliminates the use of traditional passwords. Instead, it leverages alternative methods such as biometric characteristics (like fingerprints or facial recognition), possession elements (such as hardware tokens or smartphones), or specific actions such as clicking on a specially crafted link sent via email or entering a One-Time Password (OTP) delivered through SMS or an using a Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA).
These techniques rest on the concept of using something the user possesses or an inherent trait of the user, which is usually more secure than relying on something the user knows.
Why Passwordless Authentication?
Passwordless authentication is increasingly recognized as a more secure alternative to traditional password-based systems. Given that passwords are implicated in a significant portion of cyberattacks, the shift towards passwordless methods, such as biometrics, hardware tokens, and magic links, is gaining momentum.

Bing AI illustration of passwordless authentication
Passwordless authentication not only bolsters security but also enhances user experience by eliminating the need to remember complex passwords. This can lead to increased productivity, as users save time during the login process.
These methods are inherently more resistant to common cyber threats, including phishing, malware, social engineering, and brute force attacks. By eliminating the password element, the attack surface for cybercriminals is significantly reduced.
Types and Mechanisms of Passwordless Authentication
Possession Factors: Possession factors are authentication methods that rely on something the user physically possesses. This could be a mobile device that generates or receives authentication tokens, an authenticator app that generates Time-based One-Time Passwords (TOTPs) or push notifications, hardware tokens like USB tokens or FIDO2-compliant keys, or smart cards that contain user credentials.
Biometric Factors: Biometric factors use unique physical or behavioral traits of the user for authentication. These can include fingerprint scans, facial recognition, retinal and iris scans, voiceprints, and even the electrical activity of the user’s heart (EKG).
Knowledge Factors: While not a direct method of passwordless authentication, knowledge factors like PINs or answers to secret questions can be used in combination with other methods in a Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) setup.
Magic Links: Magic links are unique, one-time-use URLs sent to a user’s email or phone. When the user clicks on the link, they are authenticated without needing to enter a password.
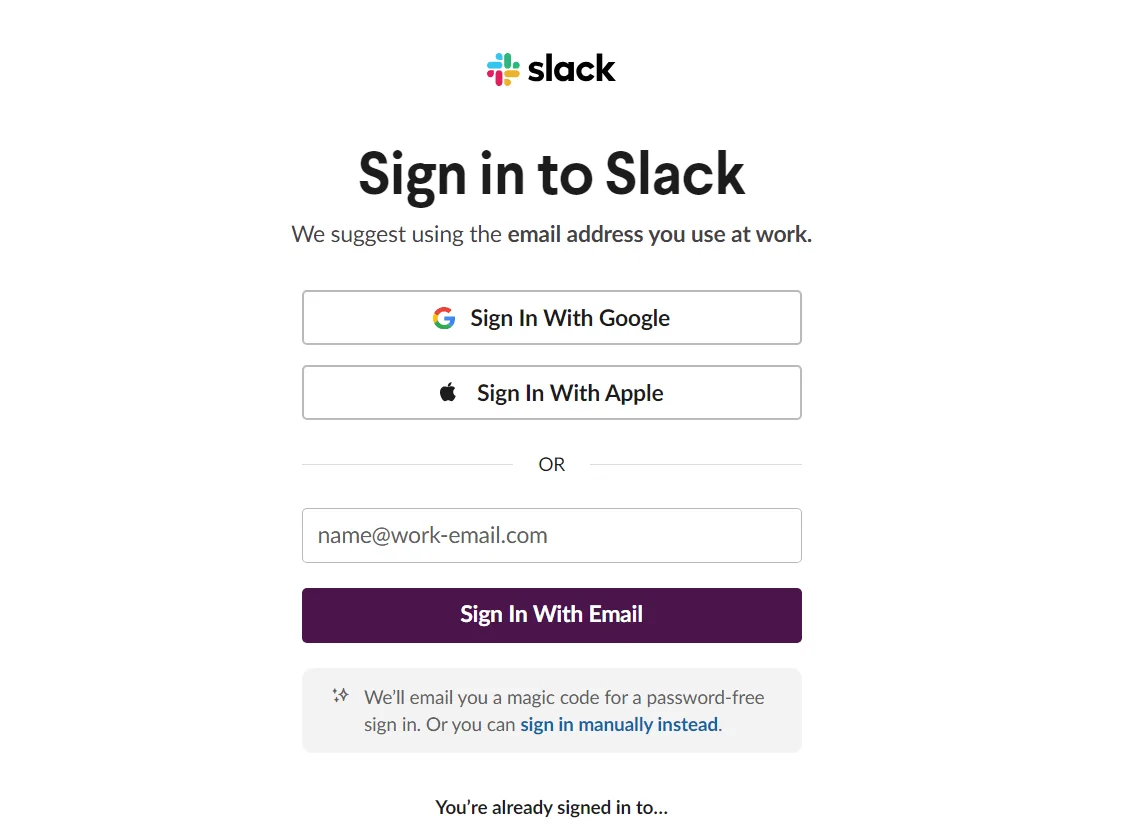
An example of magic link use in Slack under sign in
Other Methods: Other methods of passwordless authentication include push notifications, QR codes, mobile authenticator apps, and OTP and email authentication.
Zero Trust Methodology
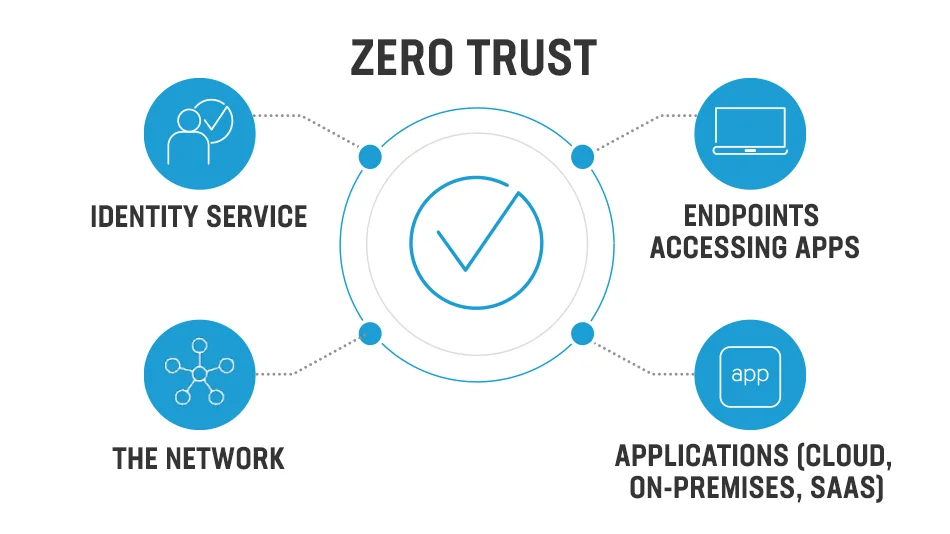
Zero Trust Methodology Diagram (Source: Linkedin)
Passwordless authentication also supports the Zero Trust security model, which operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” This approach is particularly suitable for environments with limited resources. If you wanna explore more about it check our blog post Key to Achieving a Stronger Cybersecurity Posture: Zero Trust Policy.
Passwordless Authentication Current Industries
Passwordless authentication is being adopted across various industries for its improved security and user experience. Financial services, healthcare organizations, and government agencies are using it for enhanced customer protection, privacy, and compliance with regulations such as the EU’s PSD2 and GDPR. Meanwhile, retail and hospitality sectors are modernizing user experiences and boosting productivity with this technology.
For secure access to sensitive data, the critical infrastructure and energy sectors require passwordless authentication. Call centers are using this technology to improve security and customer satisfaction. Cryptocurrency exchanges and wallets use passwordless platforms to increase user security while meeting legal standards.
Tech giants like Google, Apple, and Microsoft are leading the charge in adopting passwordless authentication, a trend projected to drive significant market growth. Large enterprises like Accenture and the Department of Veterans Affairs have reported a decrease in phishing attacks after eliminating passwords from their systems.
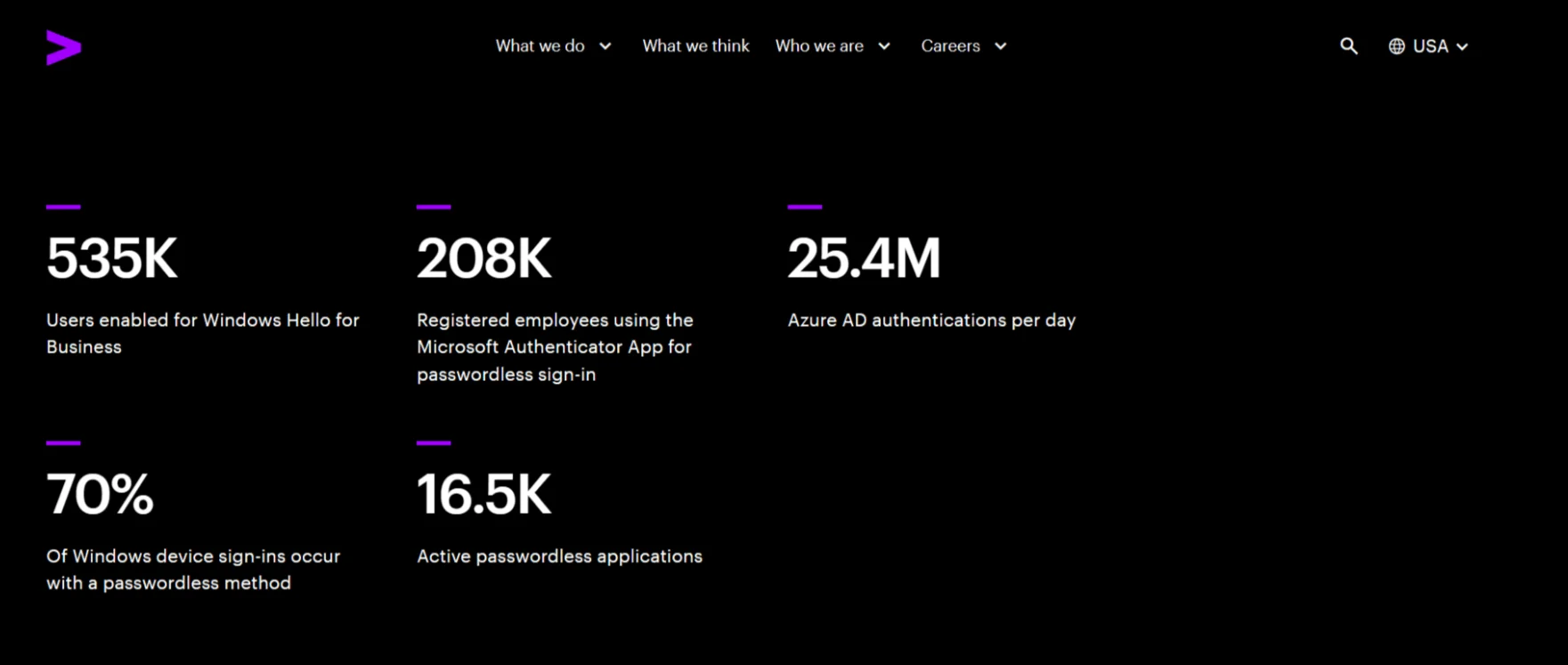
Accenture statistics for passwordless related authentications (Source: Accenture)
Emerging Trends and Innovations in Passwordless Authentication
Passwordless authentication is experiencing a rise in innovative methods to improve its systems. Emerging trends include continuous authentication and the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) to analyze user behavior. These advancements enhance fraud detection and prevention in passwordless systems.
The industry is also seeing an increase in passwordless technology providers obtaining certifications to validate their effectiveness and reliability. This trend is expected to continue, with passwordless authentication becoming the standard for authentication as more organizations transition to these methods.
It is also increasingly viewed as a strategic direction for companies aiming to improve both security and user experience. It is part of a broader shift towards Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Single Sign-On (SSO) systems that provide a more seamless and secure way of accessing multiple services.
Mitigating Deepfake Risks in Passwordless Authentication Systems
AI-driven cybersecurity attacks, particularly deepfakes, are on the rise. These attacks are becoming more convincing thanks to generative AI, which can create extremely realistic emails, websites, and even synthetic identities. Deepfake technology, which manipulates video, photo, or audio recordings, presents a significant challenge to biometric systems that were not intended to withstand such complex impersonation techniques.
Passwordless authentication is emerging as an important defense against these AI-powered threats. Passwordless methods, such as passkeys and biometrics, reduce the risk of credential theft and the bypass of legacy Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). Passkeys, which are supported by industry leaders and built on open standards, provide a phishing-resistant alternative that is both secure and user-friendly. Biometric authentication, especially when combined with liveness detection, makes it difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access using deepfakes or other synthetic biometric data.
Deepfakes are a direct threat to identity verification processes, particularly during the digital customer onboarding. Fraudsters can use deepfake technology to bypass facial recognition and other biometric systems, necessitating more stringent verification methods. A phone-centric approach, in which the mobile device serves as a key verification factor, can help to mitigate these risks.
To counter AI-powered identity attacks, organizations should adopt a multilayered cybersecurity approach, including adaptive risk identification and context-based authentication. Open standards like FIDO and OPA can help bridge the gap between attackers and defenders. A unified identity security approach can decrease the success rates of generative AI attacks by closing gaps in fragmented identity security processes.
SOCRadar’s Fraud Protection module provides a powerful response to this growing concern. It constantly searches the internet for any malicious activities directed at your brand. It uses cutting-edge technology to detect and notify you of any fraud attempts across multiple platforms, including social media and phishing websites, as well as black markets and communication channels.
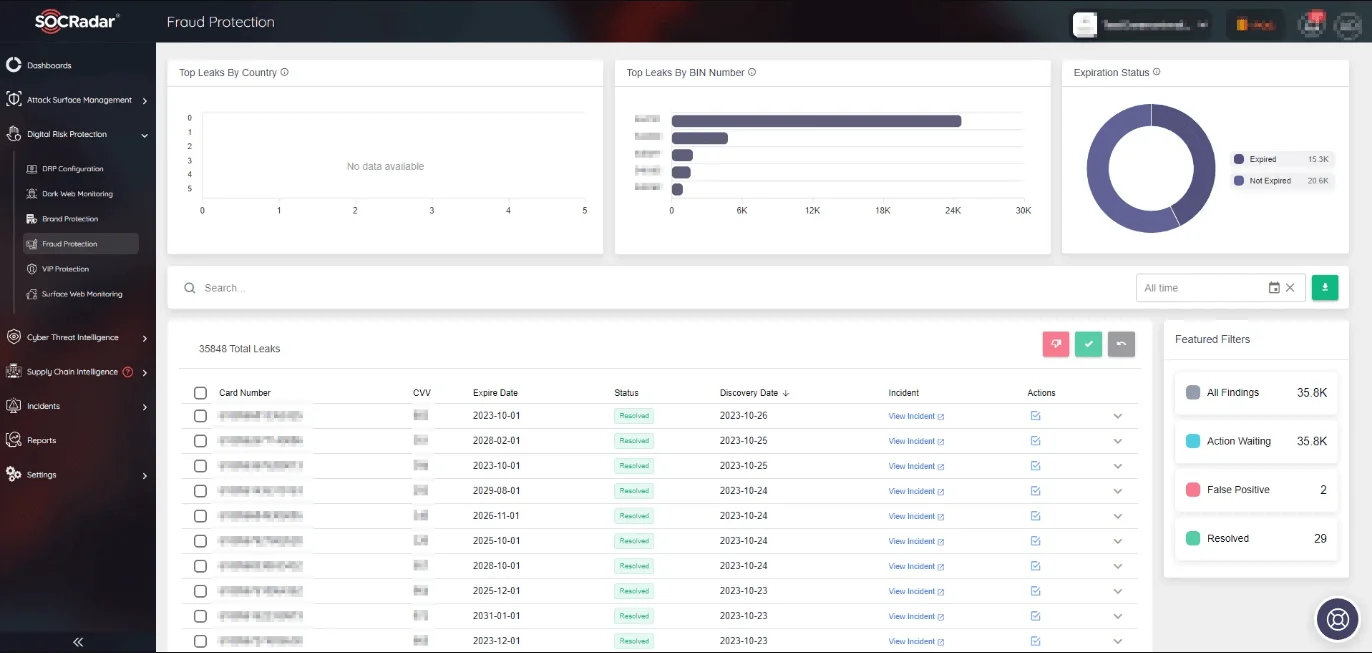
SOCRadar’s Fraud Protection module
By doing so, it protects your digital identity from advanced threats, adding an extra layer of security in the era of passwordless authentication. Stay one step ahead of cybercriminals with SOCRadar’s Fraud Protection module.
Passwordless Authentication Limitations
As Simon Carlson, a cybersecurity expert, in one of his LinkedIn posts, While passwordless authentication technologies like FIDO2 passkeys offer significant security improvements, they do not address the fundamental question of the person’s identity behind the device. Deepfake scams, such as the one that led to a Hong Kong bank losing £20m in a deepfake video call scam, highlight the limitations of passwordless authentication in verifying true identity.
Organizations must include strategies to prevent deep fake attacks in their security planning. Deep fake detectors can look for biometric signs that indicate authenticity, such as a person’s heartbeat or natural voice patterns.
The limitations of passwordless authentication emphasize the importance of a modified cybersecurity strategy that includes advanced risk identification, context-based authentication, and unified identity security approaches. As AI technology advances, the fight against deepfake and generative AI attacks will necessitate ongoing vigilance and innovation in cybersecurity measures.
Conclusion
Passwordless authentication is increasingly emerging as a user-friendly solution to a wide range of digital threats, including AI-enhanced phishing and deep fake attacks. By eliminating the need for traditional, knowledge-based credentials, passwordless authentication methods such as passkeys and biometrics pave the way for a more secure digital ecosystem.
Advancements in continuous authentication, combined with the incorporation of AI and ML into passwordless systems, are accelerating the shift to these methods. These advancements not only improve fraud detection and prevention but also lay the groundwork for a more secure user experience.
Passwordless authentication has a promising future in cybersecurity, as it becomes increasingly adopted across various sectors. Passwordless authentication is expected to play an increasingly important role in creating a safer digital future as organizations recognize its benefits and comply with regulatory requirements.



































