
Key Threat Intelligence Sources to Access Current Threat Insights
Using various threat intelligence sources can make the difference between preventing an attack and falling victim to one.

An AI illustration on Threat Intelligence Sources & Insights (DALL-E)
In the cyber threat landscape of 2024, threat actors are becoming more sophisticated, leveraging AI and automation to enhance their attacks, shifting from ransomware to data theft, and increasingly targeting cloud environments and supply chains. In response, effectively utilizing the main intelligence sources and combining them with a trusted CTI solution can significantly improve your security posture, allowing you to better anticipate, detect, and respond to potential threats.
In this blog post, we explore different types of threat intelligence sources, including open source feeds, internal data analysis, and dark web intelligence, aiming to provide a guide to discover how leveraging threat intelligence can transform your security approach. We also provide quick tips on how to build or enhance your threat intelligence strategy.
What is Threat Intelligence? Why Do You Need It?
Threat intelligence is the process of collecting, analyzing, and acting on information about current and potential threats to your organization’s security. This intelligence provides insights into the Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs) used by threat actors, helping you to understand and anticipate their moves. But why is threat intelligence so crucial?
First, it enhances your threat detection capabilities. By staying informed about the latest threats, you can recognize potential attacks before they cause damage. Second, it improves incident response. When you know how attackers operate, you can develop more effective strategies to mitigate their impact. Lastly, threat intelligence supports proactive defense measures, allowing your organization to strengthen its security posture against future threats.
All in all, organizations that leverage threat intelligence sources can stay one step ahead of cybercriminals, protecting their assets and reputation. In this pursuit, SOCRadar serves advanced threat intelligence and threat hunting capabilities, which can transform data into actionable insights, and empower security teams to proactively search for threats within their environment. This extends the capabilities of SOC teams, keeping them ahead of potential threats and ensuring effective responses.
SOCRadar’s CTI module offers threat actor profiles detailing the TTPs used by various adversaries, enabling your organization to understand the behavior and motivations of potential attackers. Additionally, our platform allows for searching Indicators of Compromise (IOCs), which are essential for detecting and responding to threats, ensuring you can effectively identify and mitigate risks.
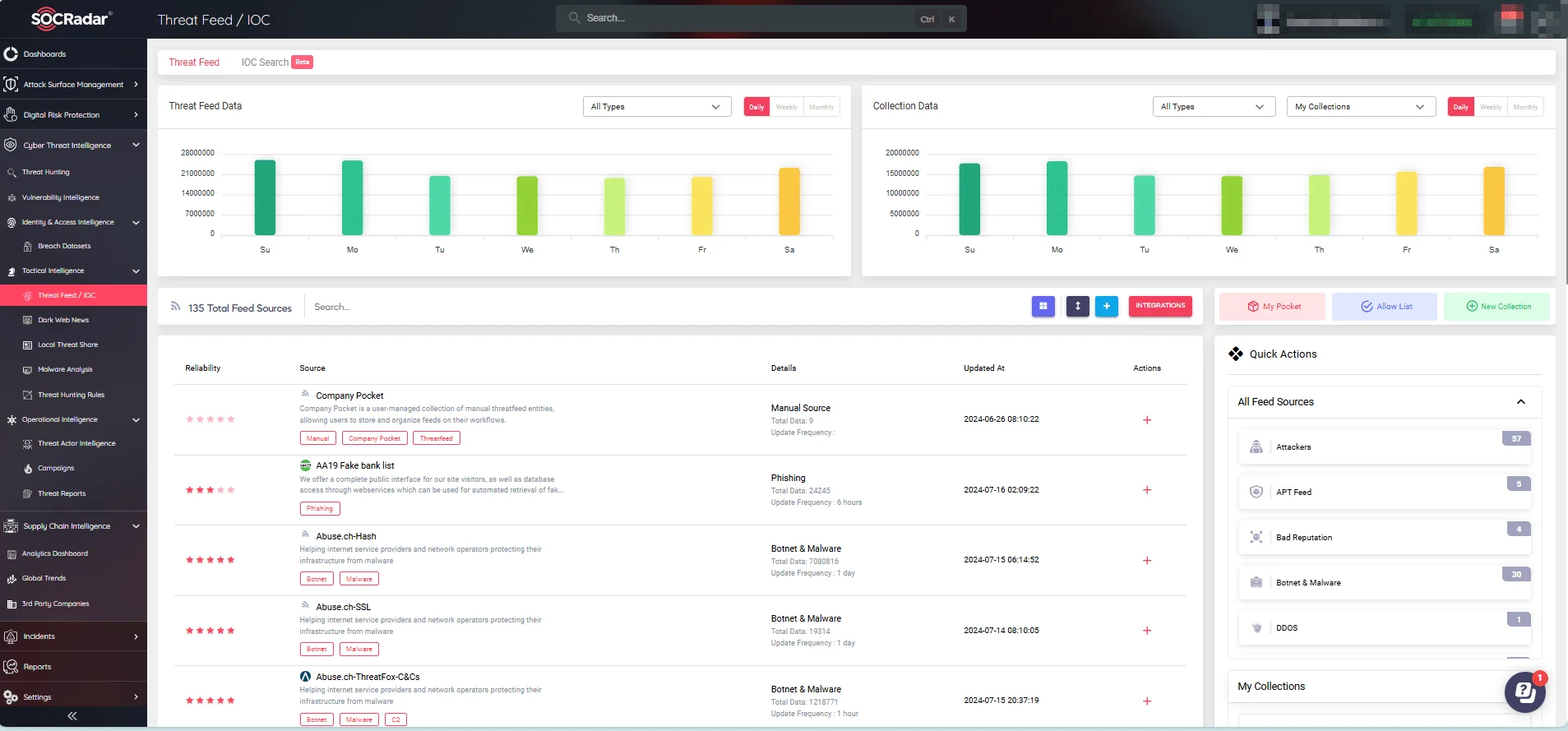
SOCRadar’s Threat Feed / IOC Search module
To test the module’s IOC search capabilities, see the IOC Radar feature on SOCRadar LABS.
What Are the Key Threat Intelligence Sources?
Leveraging various threat intelligence sources can significantly enhance your security posture, allowing you to anticipate, detect, and respond to potential threats more effectively. In this regard, let’s first examine the types of threat intelligence data, which can be collected from overlapping sources.
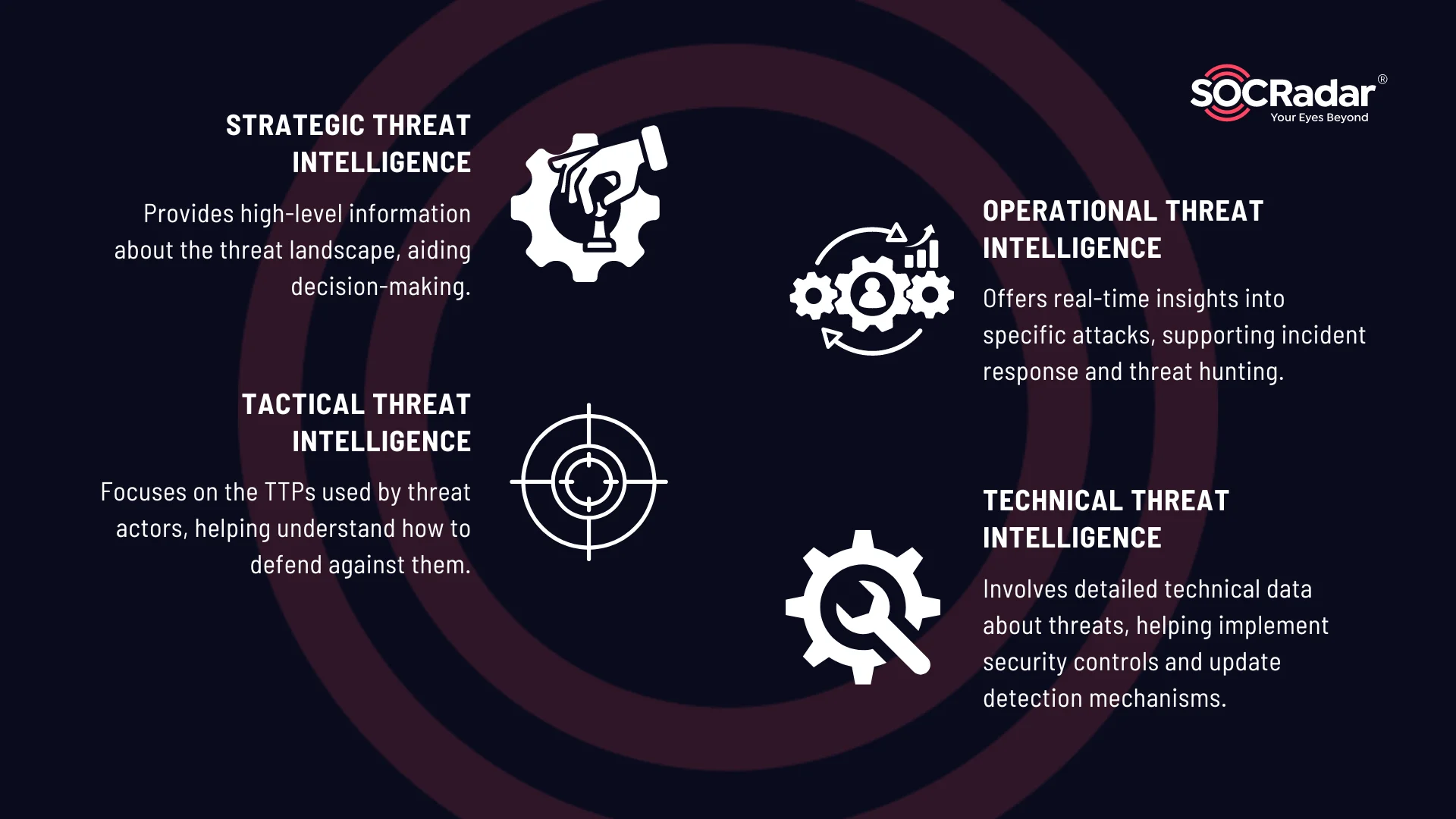
What are the types of threat intelligence?
- Strategic Threat Intelligence: Provides high-level information about the cyber threat landscape, aiding decision-making for executives and board members.
- Example sources: White papers, threat reports, expert opinions, industry analysis reports, and comprehensive threat intelligence platforms.
- Tactical Threat Intelligence: Focuses on the TTPs used by threat actors, helping organizations understand how attacks are carried out and how to defend against them.
- Example sources: Threat actor profiles, attack playbooks, MITRE ATT&CK framework, security research blogs, and shared intelligence from professional networks.
- Operational Threat Intelligence: Offers real-time insights into specific attacks or campaigns, supporting incident response and threat hunting activities.
- Example sources: Malware analysis reports, threat advisories, security bulletins, shared intelligence from industry peers, and real-time feeds from threat intelligence platforms.
- Technical Threat Intelligence: Involves detailed technical data about threats, such as IP addresses, domain names, and malware hashes. This intelligence helps implement security controls and update detection mechanisms.
- Example sources: Indicators of Compromise (IOCs), vulnerability databases, OSINT feeds, threat intelligence platforms, and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems.
Now, let’s explore some of the key threat intelligence sources:
Open Source Threat Intelligence (OSINT)
Open Source Threat Intelligence (OSINT) involves collecting data from publicly accessible resources, such as news and public databases. OSINT provides a broad perspective on emerging threats and vulnerabilities, helping organizations stay updated on the latest security trends and threat landscapes.
Example OSINT sources include:
- Community-driven threat intelligence platforms, like MISP (Malware Information Sharing Platform), enable organizations to exchange threat data and improve collective defense mechanisms.
- Collaborative projects and research initiatives that pool insights from various cybersecurity professionals.
- Public databases that list known vulnerabilities, malware samples, and other relevant threat information.
- News articles and blogs can offer up-to-date information on the latest cyber threats and incidents.
- Discussions on social media and forums about new threats shared by security researchers and professionals.
Dark Web Intelligence Sources
Monitoring the dark web can provide insights into stolen or leaked data, threat actor activities, and other emerging threats like malware and phishing kits.
However, gathering intelligence from the dark web requires specialized tools and expertise. SOCRadar’s Dark Web Monitoring simplifies this process, enabling you to identify and mitigate threats on hacker channels before they can inflict damage to your assets and reputation.
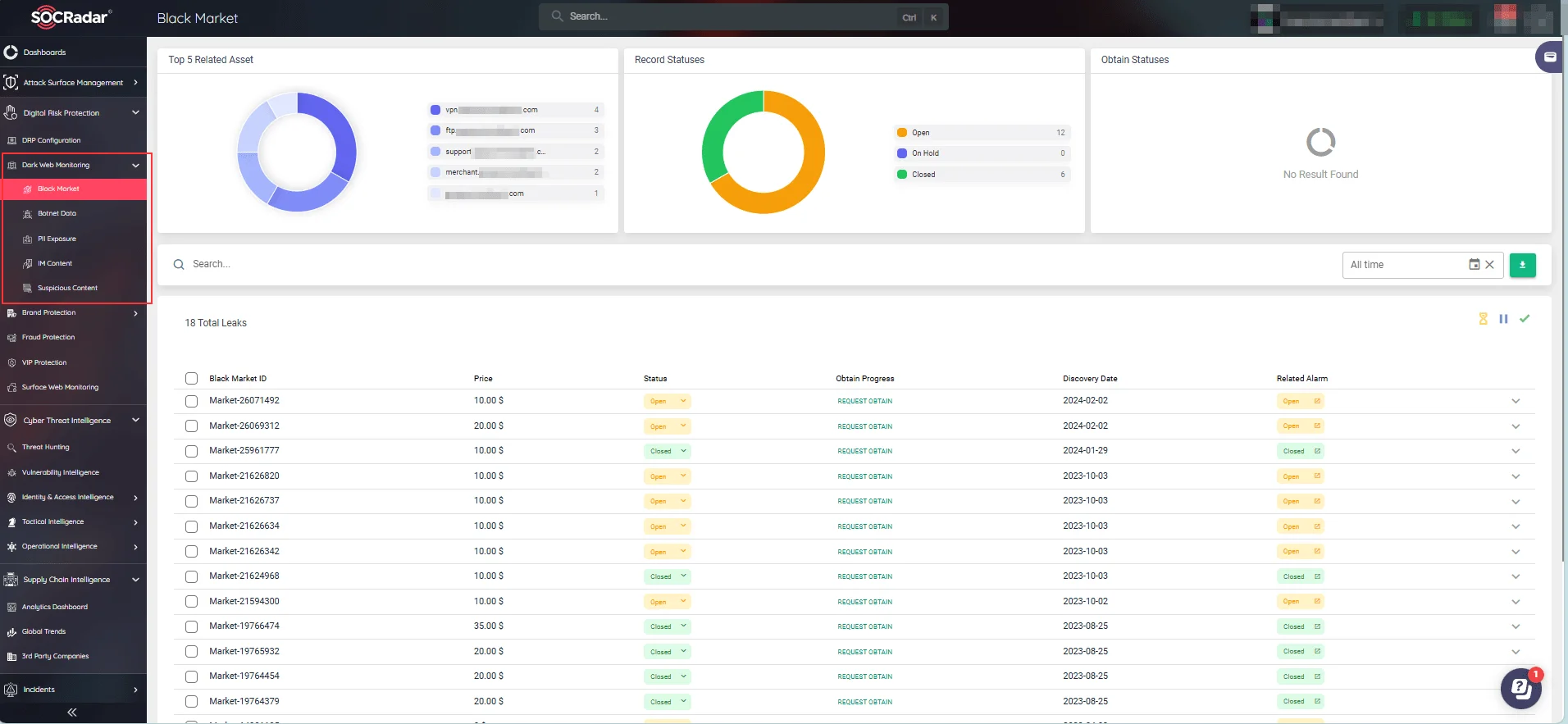
SOCRadar’s Dark Web Monitoring module
By gaining insights into dark web activities, security teams can better anticipate potential attacks and fortify their defenses.
Leading Industry Resources
In addition to the threat intelligence sources mentioned above, there are numerous leading industry resources that provide valuable threat intelligence. These include government-related sources like the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) and the FBI, as well as major companies like Microsoft. These organizations offer comprehensive threat reports and updates that are crucial for staying informed about the latest security developments.
For a curated list of top threat intelligence resources, you can visit SOCRadar’sTop 10 Threat Intelligence Resources to Follow. This list includes well-known cybersecurity companies that provide insightful research and analysis.
Internal Threat Data Analysis
Internal Threat Data Analysis involves producing threat intelligence internally by incident response teams and analysts. By examining internal data, organizations can tailor threat intelligence to their specific needs, ensuring that the insights are directly relevant to their security posture.
Key sources for this type of intelligence include:
- Network traffic analysis
- Endpoint security software logs
- User activity and access logs
- Logs from firewalls
- Alerts from Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
- Vulnerability scan results
- Email security gateways
- Incident response reports
This approach enables more precise identification of threats, as it is based on actual activity within the organization’s network. Internal analysis not only helps in detecting ongoing attacks but also in understanding the methods and tactics used by attackers in previous breaches, which can inform future security strategies.
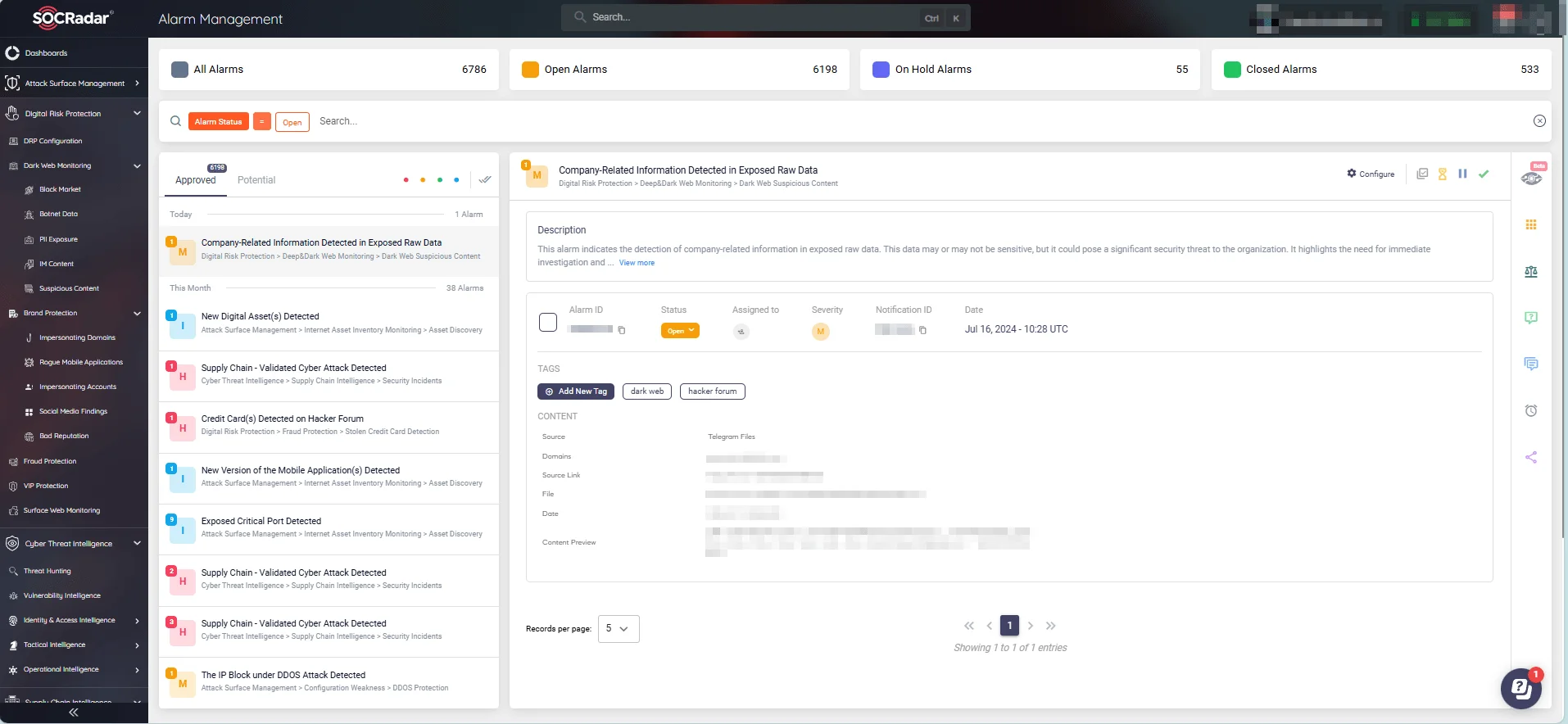
SOCRadar’s alarm management
SOCRadar delivers real-time alerts on security incidents and asset statuses, ensuring you are promptly informed of potential threats. This enables your security teams to respond swiftly and effectively, streamlining internal efforts with actionable insights.
CTI Platforms
Cyber threat intelligence platforms, such as SOCRadar, provide up-to-date information on emerging threats by collecting and filtering data from diverse sources. These platforms vary from free solutions used for threat intelligence and IOC enrichment to commercial services with more advanced features.
The more sophisticated platforms can provide actionable insights, often including automated alerts and specialized intelligence tools, enhancing the effectiveness of threat detection and response for your organization.
One notable solution is SOCRadar’s CTI4SOC, an advanced threat intelligence solution crafted to support SOC analysts. 4SOC merges big data with 12 functional modules, delivering all necessary data in a structured and contextual format. It filters information through the analyst’s lens, providing actionable intelligence.
For more information on valuable free cyber threat intelligence sources and tools, check out SOCRadar’s Top 10 Best Free Cyber Threat Intelligence Sources and Tools in 2023.
How to Implement Threat Intelligence in Your Organization
Implementing threat intelligence effectively within your organization involves several key steps and considerations to ensure comprehensive coverage and actionable insights. This section will guide you through the critical aspects of a threat intelligence strategy, pointing out how you can better utilize available sources.
First of all, selecting an effective Threat Intelligence Platform is essential.
- Look for a platform that integrates various threat feeds, offers a user-friendly interface, scales with your needs, and provides robust automated analysis capabilities.
- A good Threat Intelligence Platform streamlines data collection, analysis, and dissemination, delivering actionable insights to enhance your security posture. Automated tools can handle vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and generate timely alerts, allowing security teams to focus on strategic decisions and incident responses.
Keep threat intelligence sources up-to-date, and collaborate.
- Regular updates ensure that your threat data reflects the current landscape, enabling timely detection and response. Methods include subscribing to real-time feeds, participating in industry forums, and using automated update mechanisms within your intelligence platform.
- Collaborate with industry peers to enhance your defensive capabilities. Sharing threat intelligence with other organizations helps build a network of trusted partners for critical data exchange and unified defense strategies. This collaboration leads to better identification of common threats and collective security improvements.
Incorporate frameworks and models.
- Incorporating established frameworks like MITRE ATT&CK into your threat intelligence strategy provides a structured approach to understanding and mitigating threats. The ATT&CK framework details adversaries’ actions within a network, offering a common reference for post-access techniques. This helps organizations understand threat actor behavior and improve defensive strategies.
- Threat Intelligence playbooks are also good resources that outline how to detect and respond to specific threats based on real-world attack scenarios and industry best practices. These playbooks enable organizations to develop standardized response procedures and enhance their incident handling capabilities.
To effectively implement these elements, follow through a Threat Intelligence Lifecycle:
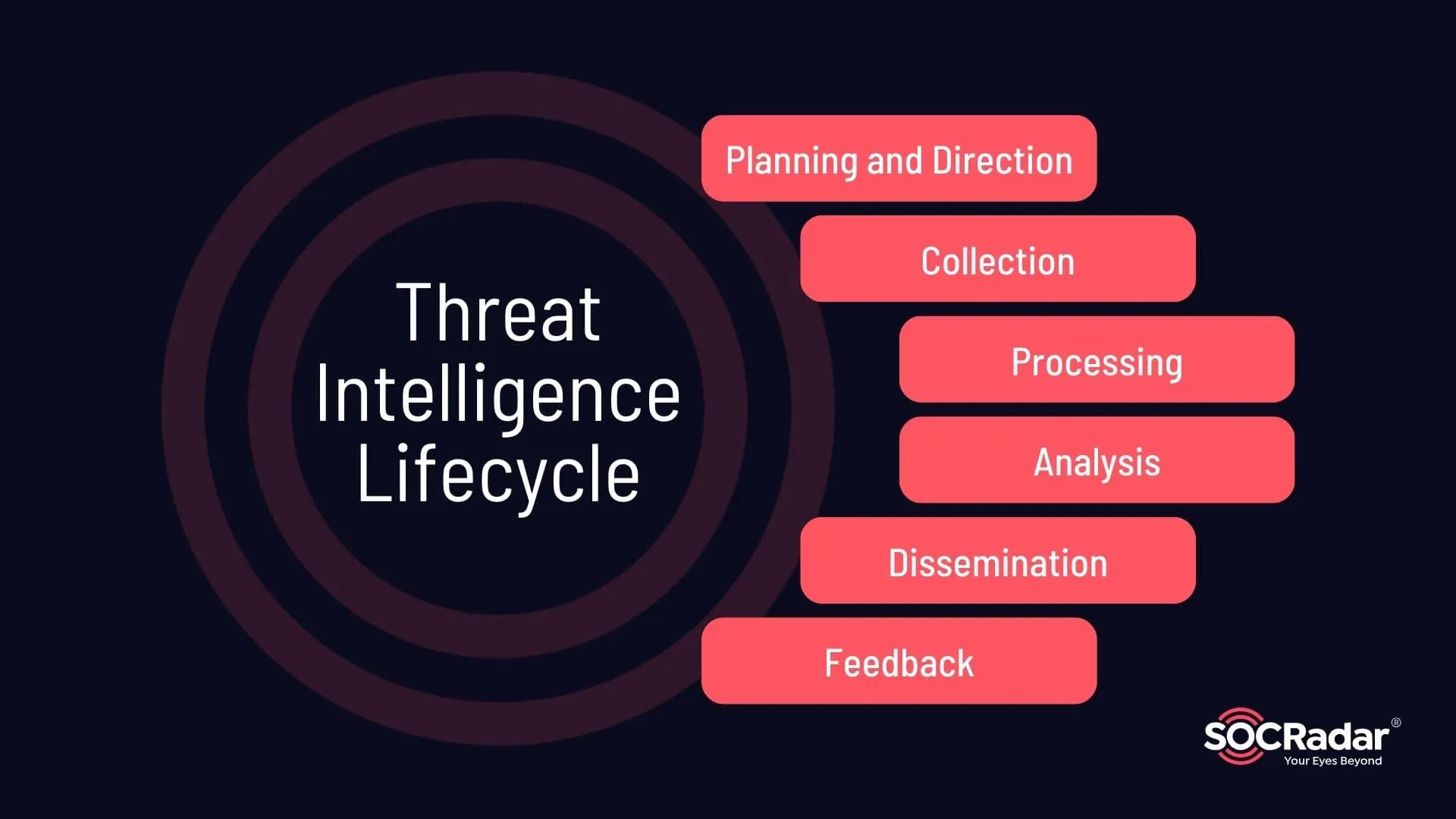
Threat Intelligence Lifecycle
- Planning and Direction: Define the objectives and requirements for threat intelligence. Identify key questions and determine the scope needed.
- Collection: Gather raw data from various sources, including internal logs, open sources, commercial feeds, and dark web monitoring. Use both automated tools and manual processes to collect relevant information.
- Processing: Clean and organize the collected data to make it usable. Convert raw data into a standardized format, removing duplicates and irrelevant information.
- Analysis: Identify patterns, trends, and potential threats through analytical tools and techniques, generating actionable insights.
- Dissemination: Share the analyzed intelligence with relevant stakeholders, ensuring clear and actionable communication.
- Feedback: Collect feedback from stakeholders on the effectiveness of the threat intelligence. Adjust the process to improve future efforts.
By integrating your efforts through a Threat Intelligence Lifecycle, your organization can create a comprehensive and effective strategy.
Conclusion
Effectively utilizing key threat intelligence sources can make all the difference in your cybersecurity efforts.
By having easy access to Indicators of Compromise (IOCs), understanding threat actor Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs), and leveraging detailed threat insights, you can significantly enhance your security posture.
Staying ahead in the cyber threat landscape of 2024 requires a proactive approach, combining these intelligence sources with robust CTI solutions like those offered by SOCRadar. This strategy enables you to anticipate, detect, and respond to threats more effectively, ensuring the protection and resilience of your organization.






































